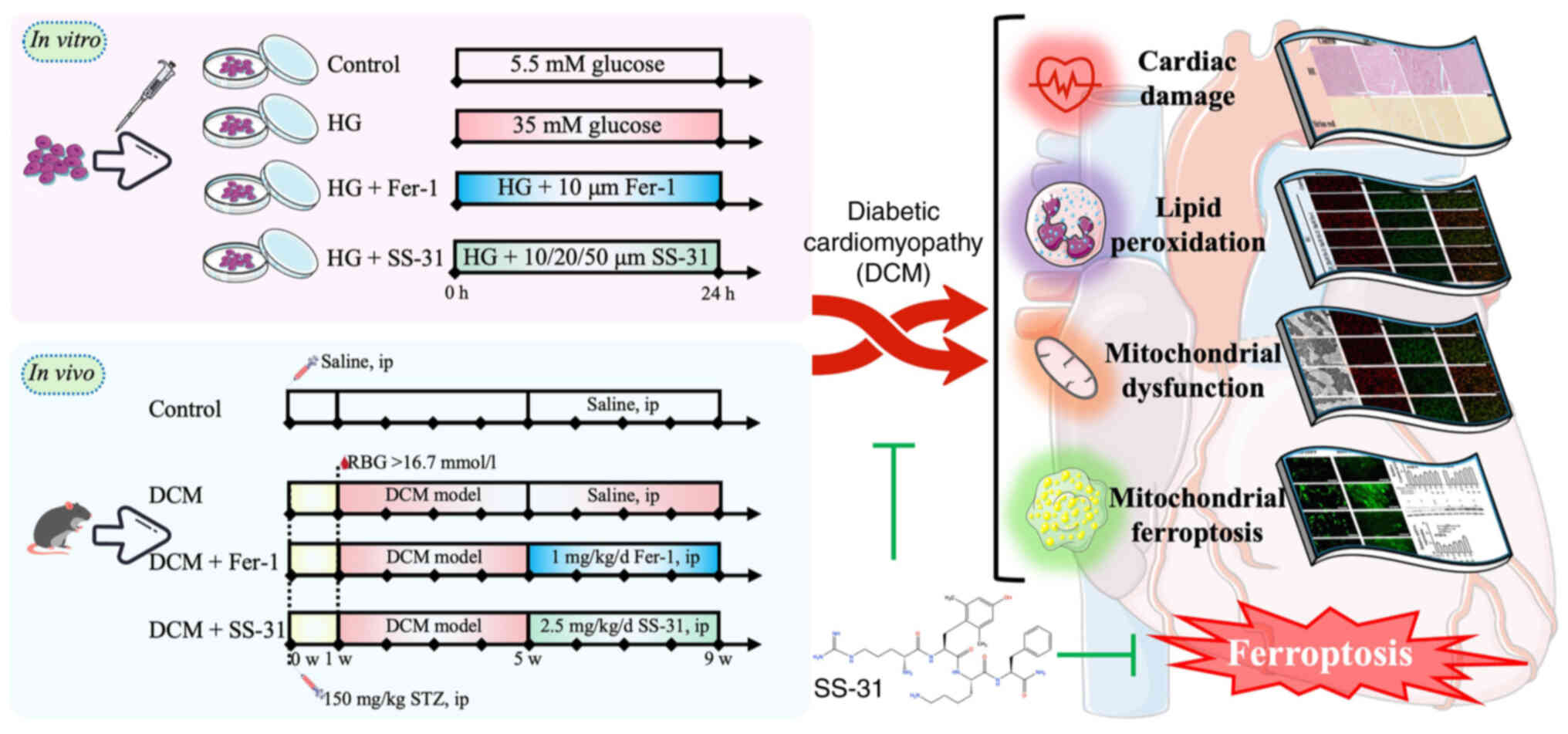
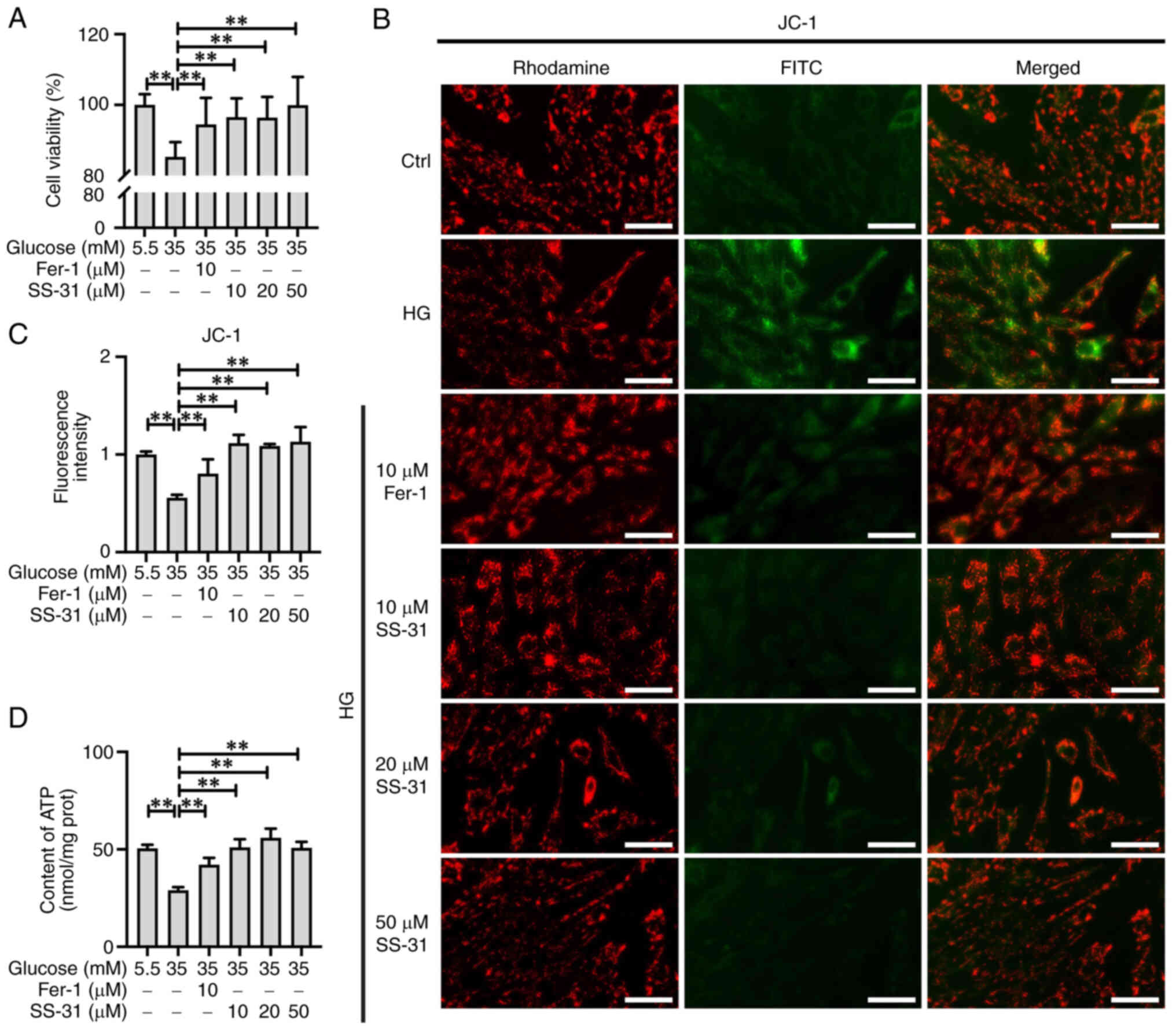
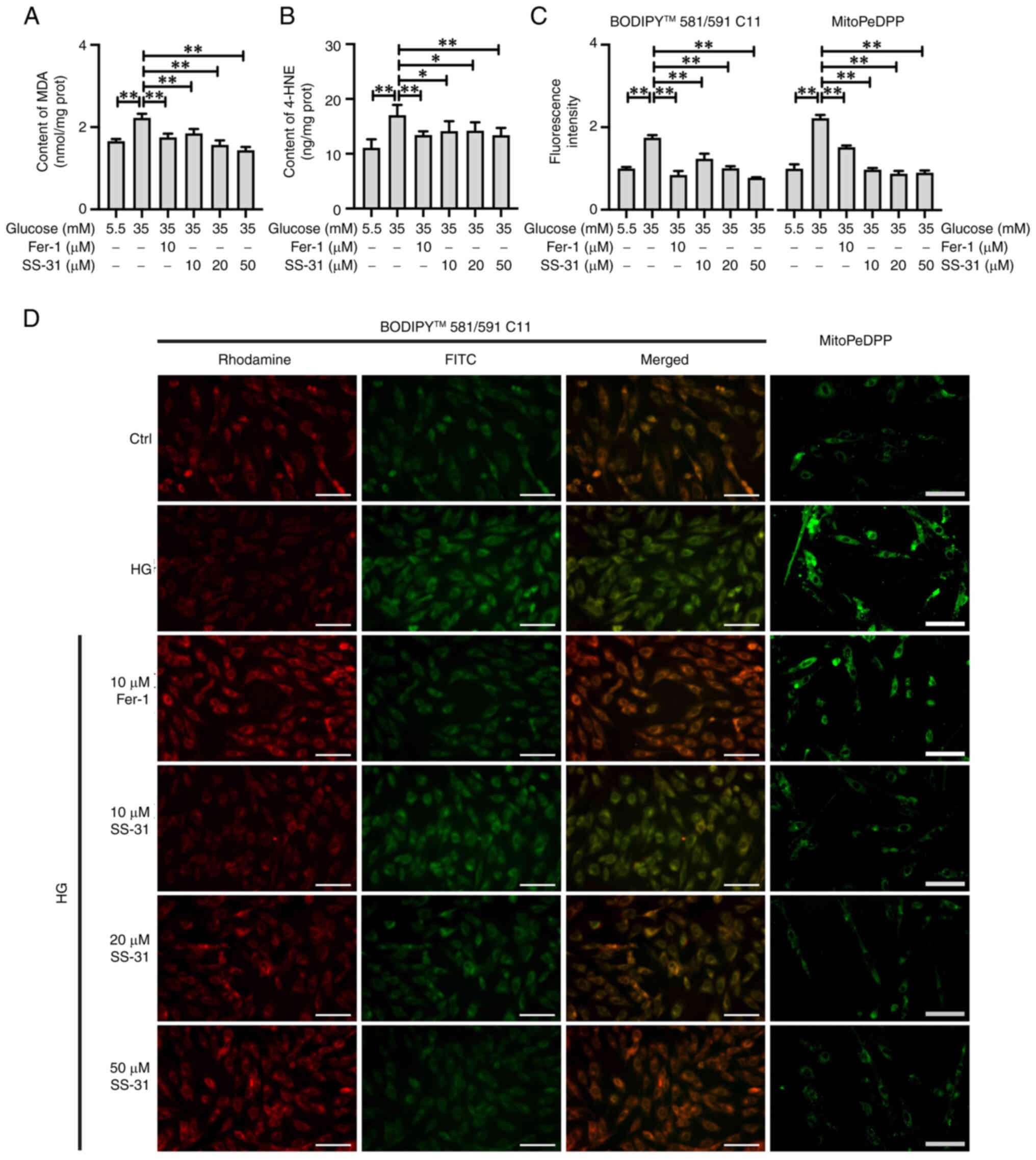
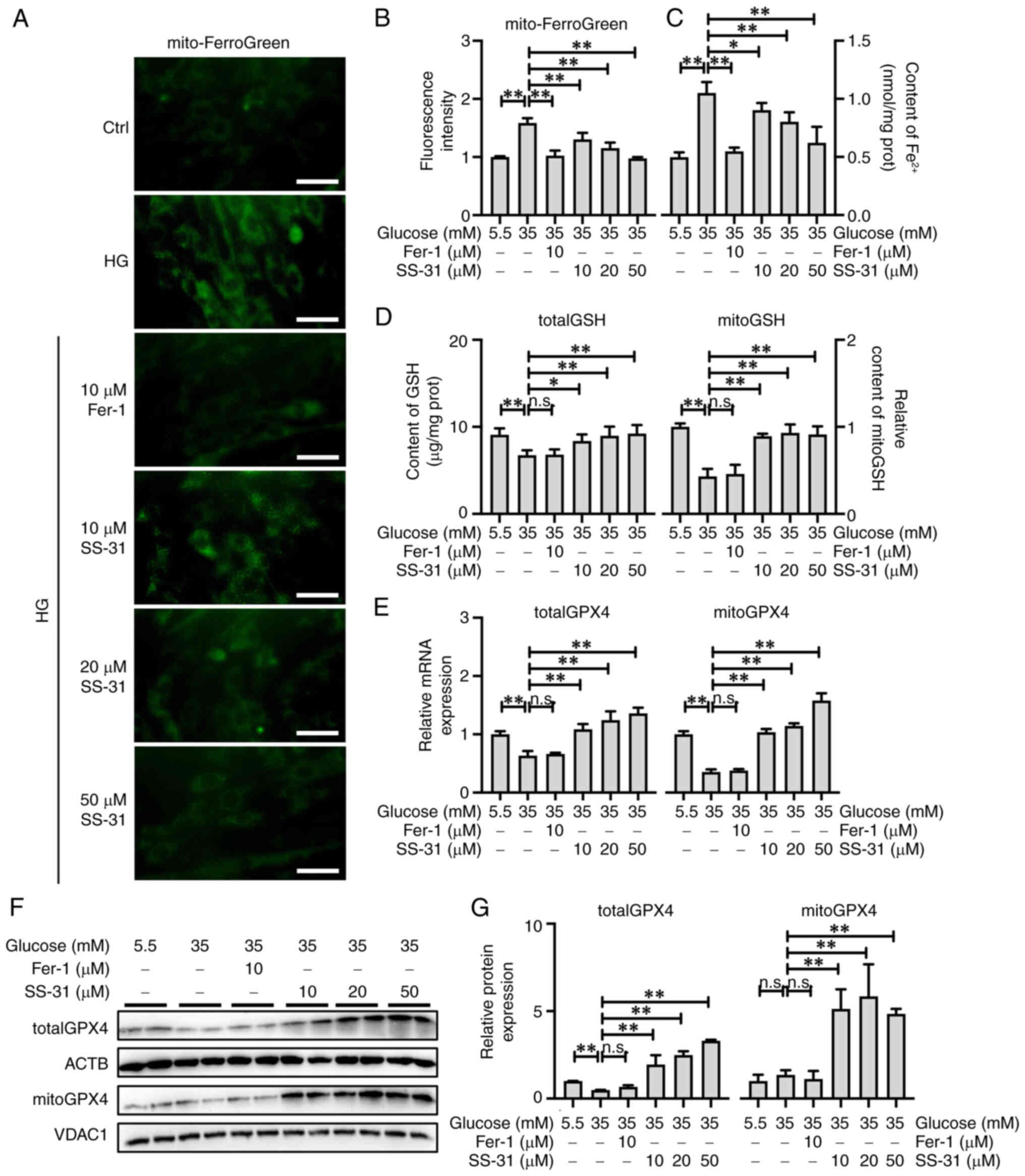
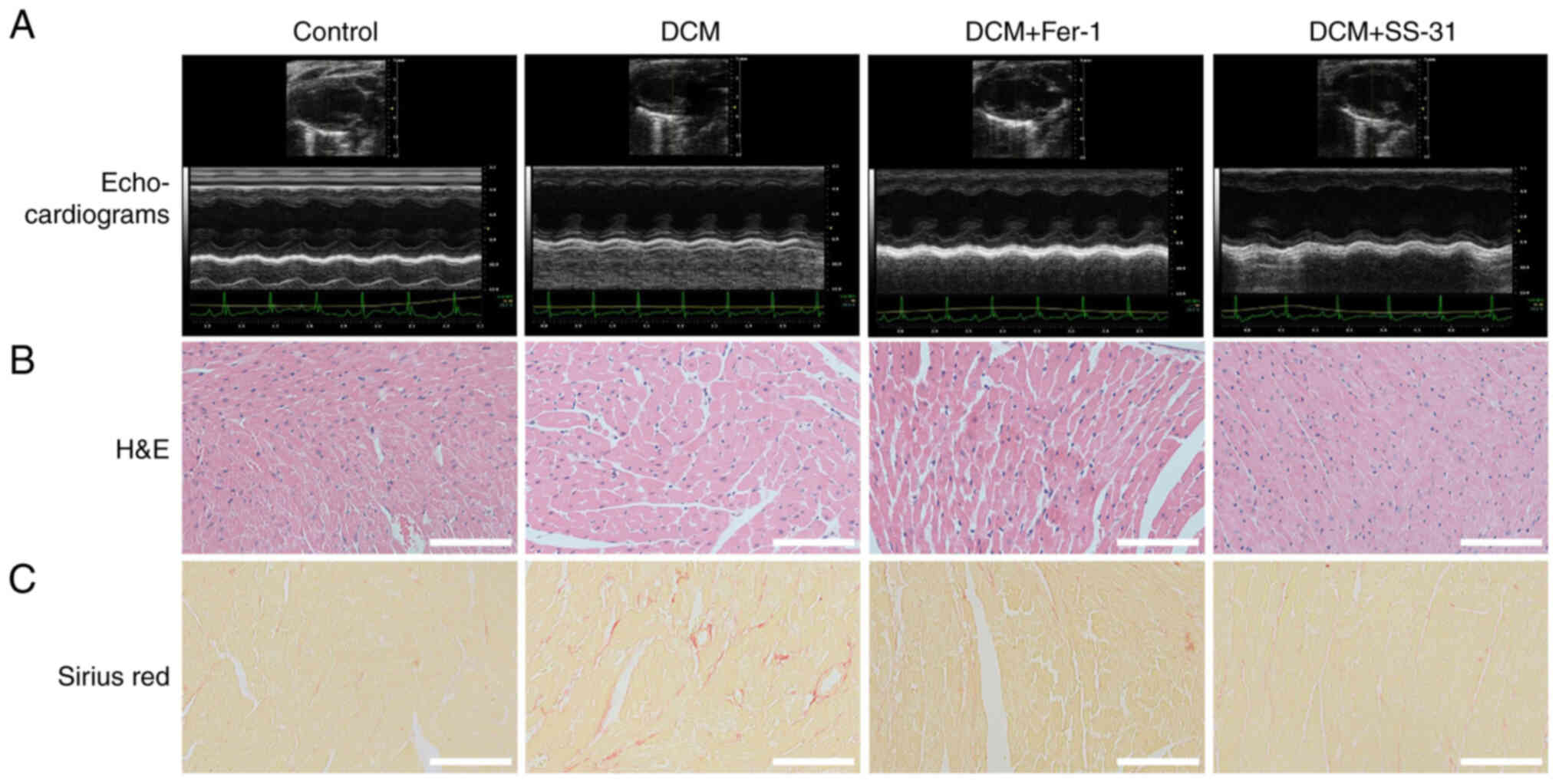
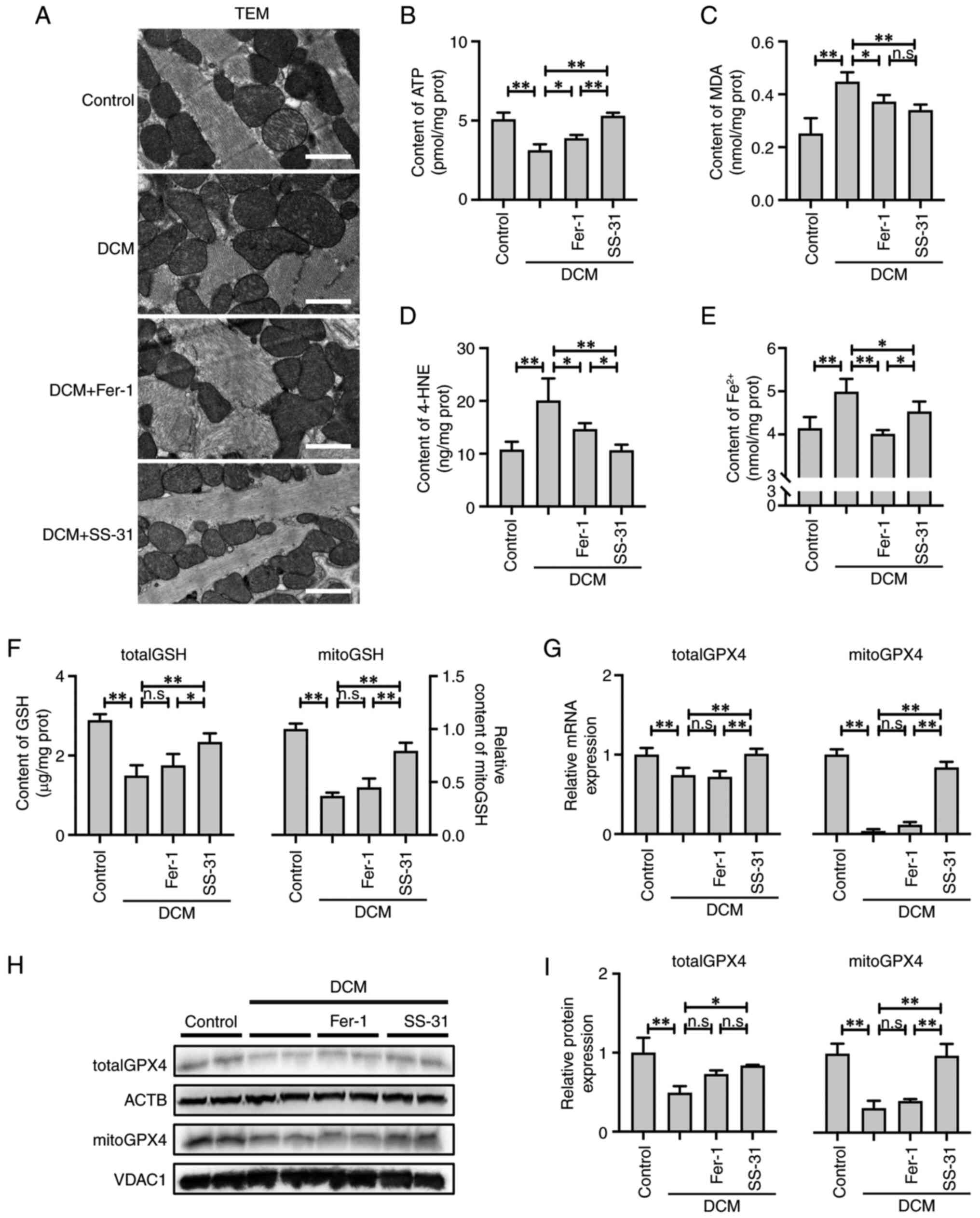
|
1
|
Bhagani H, Nasser SA, Dakroub A, El-Yazbi
AF, Eid AA, Kobeissy F, Pintus G and Eid AH: The mitochondria: A
target of polyphenols in the treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:49622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jia G, Hill MA and Sowers JR: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: An update of mechanisms contributing to this
clinical entity. Circ Res. 122:624–638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dillmann WH: Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circ
Res. 124:1160–1162. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao X, Liu S, Wang X, Chen Y, Pang P,
Yang Q, Lin J, Deng S, Wu S, Fan and Wang B: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: Clinical phenotype and practice. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:10322682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei
J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, et al: Ferroptosis as a target for
protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2672–2680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML, Orian
L, Venerando R, Roveri A, Vučković AM, Bosello Travain V, Zaccarin
M, Zennaro L, et al: Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis
inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 28:1013282020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME,
Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji
AF, Clish CB, et al: Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by
GPX4. Cell. 156(1-2): 317–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du S, Shi H, Xiong L, Wang P and Shi Y:
Canagliflozin mitigates ferroptosis and improves myocardial
oxidative stress in mice with diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10116692022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Anderson EJ, Rodriguez E, Anderson CA,
Thayne K, Chitwood WR and Kypson AP: Increased propensity for cell
death in diabetic human heart is mediated by
mitochondrial-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
300:H118–H124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Giacco F and Brownlee M: Oxidative stress
and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 107:1058–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao M, Yi J, Zhu J, Minikes AM, Monian P,
Thompson CB and Jiang X: Role of mitochondria in ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 73:354–363.e3. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, Sakamoto T
and Koumura T: Lipid peroxidation-dependent cell death regulated by
GPx4 and ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 403:143–170.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tadokoro T, Ikeda M, Ide T, Deguchi H,
Ikeda S, Okabe K, Ishikita A, Matsushima S, Koumura T, Yamada KI,
et al: Mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in
doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. JCI Insigh. 5:e1327472020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schiller PW, Nguyen TM, Berezowska I,
Dupuis S, Weltrowska G, Chung NN and Lemieux C: Synthesis and in
vitro opioid activity profiles of DALDA analogues. Eur J Med Chem.
35:895–901. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Du X, Zeng Q, Luo Y, He L, Zhao Y, Li N,
Han C, Zhang G and Liu W: Application research of novel peptide
mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant SS-31 in mitigating
mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrion. 75:1018462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dai DF, Chen T, Szeto H, Nieves-Cintrón M,
Kutyavin V, Santana LF and Rabinovitch PS: Mitochondrial targeted
antioxidant peptide ameliorates hypertensive cardiomyopathy. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 58:73–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Machiraju P, Wang X, Sabouny R, Huang J,
Zhao T, Iqbal F, King M, Prasher D, Lodha A, Jimenez-Tellez N, et
al: SS-31 peptide reverses the mitochondrial fragmentation present
in fibroblasts from patients with DCMA, a mitochondrial
cardiomyopathy. Front Cardiovasc Med. 6:1672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Feng M, Wang X, Zhang H, Ding J,
Cheng Z and Qian L: Peptide Szeto-Schiller 31 ameliorates
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting the activation of
the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 47:632021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Zhang P, Chen Y, Zhang S and Chen G:
Mitochondria-related ferroptosis drives cognitive deficits in
neonatal mice following sevoflurane administration. Front Med
(Lausanne). 9:8870622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu X, Wang FY, Chi S, Liu T, Yang HL,
Zhong RJ, Li XY and Gao J: Mitochondria-targeting peptide SS-31
attenuates ferroptosis via inhibition of the p38 MAPK signaling
pathway in the hippocampus of epileptic rats. Brain Res.
1836:1488822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zacchigna S, Paldino A, Falcão-Pires I,
Daskalopoulos EP, Dal Ferro M, Vodret S, Lesizza P, Cannatà A,
Miranda-Silva D, Lourenço AP, et al: Towards standardization of
echocardiography for the evaluation of left ventricular function in
adult rodents: A position paper of the ESC Working Group on
Myocardial Function. Cardiovasc Res. 117:43–59. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Martinez AM, Kim A and Yang WS: Detection
of ferroptosis by BODIPY™ 581/591 C11. Methods Mol Biol.
2108:125–130. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–8. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhao K, Luo G, Zhao GM, Schiller PW and
Szeto HH: Transcellular transport of a highly polar 3+ net charge
opioid tetrapeptide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 304:425–32. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao K, Zhao GM, Wu D, Soong Y, Birk AV,
Schiller PW and Szeto HH: Cell-permeable peptide antioxidants
targeted to inner mitochondrial membrane inhibit mitochondrial
swelling, oxidative cell death, and reperfusion injury. J Biol
Chem. 279:34682–34690. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Birk AV, Liu S, Soong Y, Mills W, Singh P,
Warren JD, Seshan SV, Pardee JD and Szeto HH: The
mitochondrial-targeted compound SS-31 re-energizes ischemic
mitochondria by interacting with cardiolipin. J Am Soc Nephrol.
24:1250–1261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park MW, Cha HW, Kim J, Kim JH, Yang H,
Yoon S, Boonpraman N, Yi SS, Yoo ID and Moon JS: NOX4 promotes
ferroptosis of astrocytes by oxidative stress-induced lipid
peroxidation via the impairment of mitochondrial metabolism in
Alzheimer's diseases. Redox Biol. 41:1019472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Conrad M and Sato H: The oxidative
stress-inducible cystine/glutamate antiporter, system x (c) (-):
Cystine supplier and beyond. Amino Acids. 42:231–246. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Imai H, Saito M, Kirai N, Hasegawa J,
Konishi K, Hattori H, Nishimura M, Naito S and Nakagawa Y:
Identification of the positive regulatory and distinct core regions
of promoters, and transcriptional regulation in three types of
mouse phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase. J Biochem.
140:573–590. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|