The urinary system is narrowly defined to include
kidneys, ureters, the bladder and the urethra. In a broader
context, it encompasses the cervix, vulva, adnexa, ovaries and
fallopian tubes in women, and the prostate, vas deferens, testes
and epididymis in men. Diseases can affect each of these organs and
impact the entire system. Common urinary system diseases mainly
include infections, tumours, stones and inflammation, congenital
malformation and trauma. Among these, tumours are the most fatal
and have been a major focus of academic research. In 2022, there
were 434,419 new cases of kidney cancer and 155,702 kidney
cancer-associated mortalities worldwide (1); studies have reflected the rising
incidence of urological tumours in recent years (2-4).
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) has a recurrence rate of
≥70% requiring repeated, costly and invasive testing, making
bladder cancer (BCa) the most expensive cancer to treat per capita
(5). Urological tumours,
therefore, pose a threat to the quality of human life and incur
substantial economic costs.
The pathogenesis of urinary system diseases is
complex and remains to be actively explored. Epigenetics is an
emerging theme in disease pathogenesis, with a major focus on DNA
methylation and histone acetylation (6). Previous studies have highlighted
that DNA methylation plays an essential role in urinary system
diseases recently (5,7,8).
DNA methylation is a stable epigenetic marker in humans and has
been recognized, along with other regulatory factors, as a major
factor influencing gene activity. The DNA methyltransferase (DNMT)
family comprises a conserved set of DNA-modifying enzymes central
to epigenetic gene regulation (9). A total of three DNMTs, DNMT1,
DNMT3A and DNMT3B, catalyze the transfer of a methyl group from
S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to the C5 position of cytosine
(10), a process known as
methylation. Methylation predominantly occurs at
cytosine-phospho-guanine (CpG) islands; which are CpG-rich regions
(≥50% of cytosines and guanines) in the genome with a size >200
bp (11,12).
Methylation occurs not only in specific regions of
the X chromosome, such as retrotransposon elements and centromere
regions, and the result of methylation in these regions usually
leads to genes inactivation (13). Studies have shown a significant
association between the DNA methylation process in genes and
urinary system diseases, with this chemical modification
contributing to the development of urinary system disease and
holding potential for diagnostic and prognostic applications
(14-17). Therefore, the present study
systematically explored the pathogenic mechanism and clinical
application of DNMTs in urinary system diseases, opening a window
of opportunity for improved clinical management.
Urinary system diseases can occur in all organs of
the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra) and
spread throughout the system. It manifests itself in a variety of
symptoms, including difficulty urinating, abnormal urine (such as
changes in colour, clarity or smell), stone formation and a sense
of pain. At the same time, it may indirectly cause other health
problems, such as high blood pressure, oedema and anemia (18).
Common non-neoplastic urinary system diseases
include autonomic-induced urinary dysfunction, urinary tract
infections (UTIs) and urinary stones. Autonomic nerves are
essential in urinary tract development, growth factors production
and homeostasis control (19-21). The function of the lower urinary
tract (storage and periodic elimination of urine) highly depends on
the complex neural control system in the brain, spinal cord and
peripheral ganglia. Additionally, injury or disease of the
corresponding nerve may trigger neurogenic bladder or lower urinary
tract dysfunction (22-24).
UTIs are an inflammatory response of the urinary
tract epithelium caused by bacterial invasion. It is one of the
most common community and hospital-acquired infections (25). Infectious microorganisms,
including Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and certain
fungi, can cause UTIs via the hematogenous route and ascending
routes (26). As one of the most
common pathogens, Escherichia coli (E. coli) has
multiple virulence factors, including pili, capsule, siderophore
receptor, flagella, toxins and lipopolysaccharides, and they work
together to cause a UTI (25,27). The conventional UTI treatment is
mainly based on the use of antibiotics such as β-lactams,
trimethoprim, nitrofurantoin and quinolones; however, antibiotic
misuse has led to increased E. coli resistance, driven by
genetic variation and horizontal gene transfer (28,29). Consequently, researchers are
exploring alternative therapeutic strategies for UTI. The widely
conserved respiratory quinoline oxidase cytochrome bd is essential
for urothelial intracellular infection; hence, developing drugs
targeting this enzyme may be a good research direction (30).
Urolithiasis is a common disease with a growing
prevalence and high recurrence rate worldwide (31,32). Urinary stones are classified into
two main categories: Metabolic and infected stones. Infectious
urinary calculi account for 15% of urinary calculi, often caused by
urease positive pathogens (33).
The main treatment options include extracorporeal shock wave
lithotripsy (ESWL), surgery and drug therapy. ESWL is typically
used for renal and upper ureteral stones with diameter ≤2 cm in
diameter. In rare diseases such as congenital anatomical anomalies
where surgeons have difficulty in accomplishing the treatment of
kidney stone disease through ESWL, percutaneous nephrolithotomy,
ureteroscopy and minimally invasive surgery. Often they can only
accomplish stone removal through open surgery (34).
Epidemiological studies have shown that the
incidence of urinary system tumours is increasing globally,
significantly impacting the health and quality of life of patients
(35,36). According to the global cancer
statistics in 2020, there were >2.4 million new cases of urinary
tract tumours reported worldwide, accounting for 12.5% of cancer
diagnoses and 7.7% of new cancer-associated mortalities (37). Tumours of the urinary system are
divided into three categories: i) Urothelial carcinoma of the renal
pelvis, ureter and bladder; ii) renal malignant tumours, such as
renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and Wilms tumour; and iii) non-urethral
epithelial tumours of various organs. The relative rarity of upper
tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) complicates the establishment of
diagnostic and management strategies (38,39). Although advances in optical
diagnostic technology should reduce invasive testing for UTUC,
urinary cytology remains a primary methods for screening and
monitoring urothelial carcinoma (40,41). The mechanisms underlying urinary
system tumours remain a significant focus of academic research.
Epigenetic alterations, such as histone methylation, acetylation
and DNA methylation, are ubiquitous in urological tumours, and have
garnered considerable scholarly attention (42).
The enzymes that build, recognize and eliminate DNA
methylation are divided into three categories: i) Writing; ii)
erasing; and iii) reading enzymes. DNMTs are known as writing
enzymes. The DNMTs are a conserved family of cytosine methylases
with a critical role in epigenetic regulation, catalysing DNA
methylation by transferring a methyl group from SAM to the fifth
carbon of a cytosine residue, forming 5mC (43). DNA methylation occurs mainly at
the CpG dinucleotide site, and it occurs less frequently at
cytosine-phosphothymine, cytosine-phosphoadenine and
cytosine-phosphocytosine sites, which are collectively referred to
as non-CpG sites (44).
The human genome encodes five DNMTs: DNMT1, DNMT2,
DNMT3A, DNMT3B and DNMT3L. DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B are canonical
cytosine-5 DNMTs that catalyse the addition of methyl groups to
genomic DNA. By contrast, DNMT2 and DNMT3L are considered
non-canonical family members because they lack catalytic DNMT
activity (9). De novo
methylation and maintenance methylation are important physiological
processes in epigenetics. De novo methylation refers to the
methylation of cytosine C5 at a new site on the DNA chain.
Maintenance methylation is the process of DNA replication that
leaves the methylation of the original site unchanged; that is, the
process of methylation modification at the corresponding position
of the nascent strand results from the semi-conserved replication
of methylated DNA (45).
DNMT3A/3B is designated as a de novo DNMT and DNMT1 is
designated as a maintenance DNMT. However, DNMT3A/3B participates
in DNA maintenance methylation and DNMT1 in de novo
methylation (46).
DNMTs typically comprise an N-terminal regulatory
structural domain and a C-terminal catalytic structural domain.
DNMT3A has two isoforms while DNMT3B has >30 isoforms. Despite
this variation, both share similar domain structures: i) A Pro-T
rp-T rp-Pro (pWWP) domain; ii) an ATRX-DNMT3L-DNMT3A (ADD) domain;
and iii) a C-terminal catalytic domain. The pWWP domain recognizes
H3K36me3 and the ADD domain binds the free N-terminal tail of
histone H3 (27121154) (47).
Among the three typical cytosine-5 DNMTs, DNMT1 is the most
abundant DNMT and is considered to be the critical
methyltransferase in mammals (48).
DNMT1 prioritizes the methylation of hemi-methylated
DNA, thereby maintaining the epigenetic stability of genetic
information. The unique N-terminal regulatory region of DNMT1
contains several structural domains, including the DNA replication
foci structural domain (RFD) and the CXXC structural domain,
playing the role of the corresponding structural domains. For
example, the RFD directs DNMT1 to replicate DNA, while the CXXC
domain recognizes and binds DNA containing unmethylated CpG
sites.
The induction of epigenetic alterations,
particularly aberrant DNA methylation, is strongly associated with
chronic inflammation and various human diseases, including cancer,
neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders. Takeshima et
al (49) demonstrated that
the DNMT activation, triggered by nitrogen oxide (NO) production,
is responsible for abnormal methylation in human tissues,
indicating that DNMT activity plays a key role in the development
and progression of multiple human diseases.
DNMT1 activity is modulated by a number of molecular
interactions. Lymphoid-specific helicase (LSH), a DNA decoupling
enzyme belonging to the SNF2 family, has long been recognized to
enhance DNMT activity (50,51). Ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and
RING finger domains 1 (UHRF1), an E3-ubiquitin protein ligase that
interacts with DNMT1, is essential for maintaining DNA methylation
when it binds to DNA (9). A
previous study has shown that LSH interacts with UHRF1 in an ATPase
activity-dependent manner, facilitating DNMT1 recruitment to
replication forks and DNA methylation processes. In particular,
UHRF1 enhances the binding of LSH to replication forks. This
interaction enhances UHRF1 binding to chromatin and promotes
UHRF1-catalyzed histone H3 ubiquitination, activating DNMT1 and
facilitating its recruitment during the S phase of the cell cycle
(52).
DNMT1 activity is affected by its microenvironment.
Atrazine, a non-competitive inhibitor of the DNMT reaction,
significantly reduces DNMT1 activity. Atrazine exposure at the
embryonic stage may, therefore, have toxic effects on various
organs by modulating genes (53-56). Duraisamy et al (57) reported that DNMT1 activity in
retinal endothelial cells incubated in high glucose initially
decreases after 6 h but increases after 24 h.
Studies have shown that DNMT1 fidelity is related to
gene complexity and regional differences (58-60). High-complexity repeats and active
gene promoter regions exhibit relatively high fidelity, while
low-complexity repeats and methylated sequences in intermediate
regions show relatively lower fidelity (58-60). However, DNMT1 can correct its
inaccuracies through neighbour-guided correction, where changes in
local DNA methylation alter the de novo and maintenance
activity of DNMT1; at this point, DNMT1 becomes a key 'tuner',
effectively improving fidelity (61). Thus, the inaccuracies and
neighbour-guided correction of DNMT1 constitute essential
mechanisms for maintaining DNA methylation (61).
The activity of DNMT3A and DNMT3B is significant in
pathological processes. Studies have shown that eicosatetraenoic
acid inhibits histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and DNMT transcription
and activity by acting as a natural proliferator-activated receptor
γ (PPARγ) ligand and activator (62). Activated peroxisome PPARγ
primarily decreases HDAC1 activity, followed by decreases in
expression and activity of DNMT 3A and 3B. This process eventually
leads to the up-regulation of tumour-suppressor genes (TSGs)
(63).
A recent study reported how genetically encoded
photicaged amino acid controls DNMT activity. The technique enables
the production of DNMTs, which is otherwise inactive. and can be
rapidly activated by light irradiation. The results of this study
contribute to a deeper understanding of how cancer-associated DNMT
mutations affect their activity in organisms, providing an
important foundation for future research and ad.vancements in
cancer treatment (66).
Epigenetic modifications, particularly covalent
modifications of DNA itself by DNA methylation, are recognized as
critical in determining T cell fate (67,68). Throughout the development of T
lymphocytes in the thymus and their subsequent migration to the
periphery for differentiation, they are influenced by a series of
precisely regulated molecular mechanisms. DNMT3A plays a pivotal
role as an epigenetic mechanism component in maintaining the
stability of T cell responses (69-71). In mice with DNMT3A knocked out,
acute graft-vs.-host disease was observed, accompanied by a
significant increase in inflammatory cytokine levels and higher
pathological scores in organ tissues. T cells from DNMT3A knockout
mice migrated and proliferated earlier in secondary lymphoid organs
and showed a tendency to migrate to the small intestine. These
findings underscore the vital role for DNMT3A in regulating T cell
allogeneic responsiveness (69).
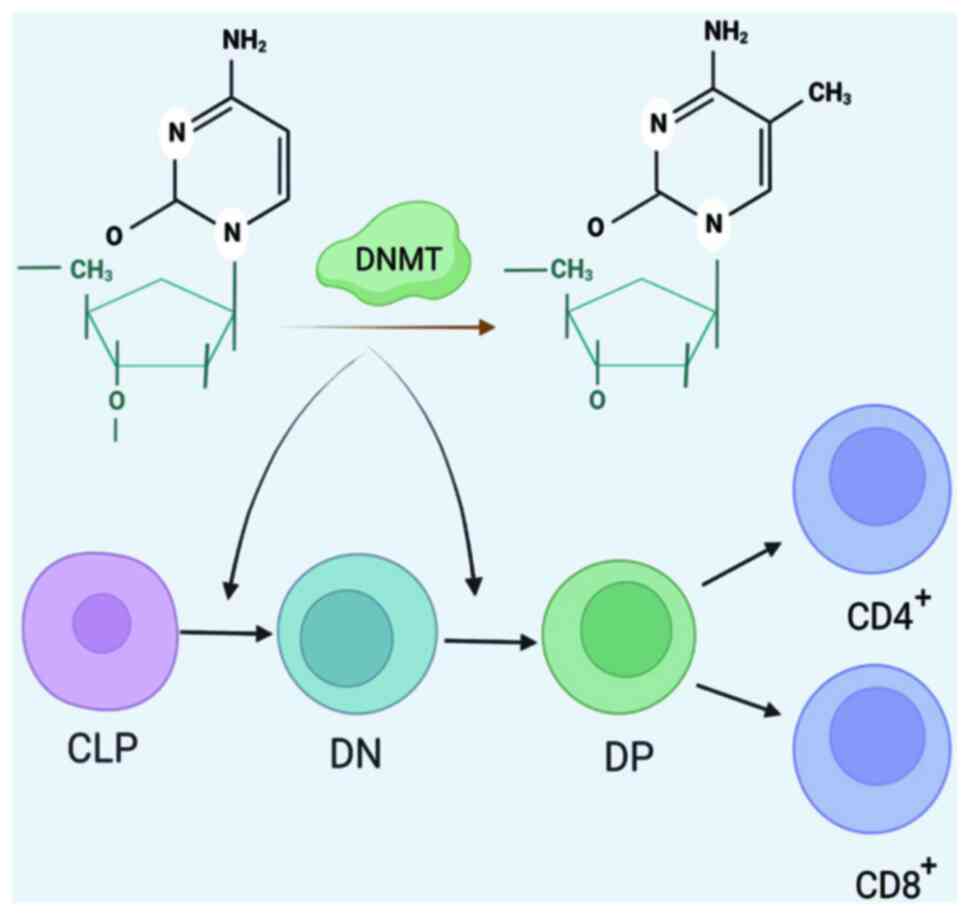
Additionally, DNMT1 plays an important regulatory role in Foxp3
expression. In regulatory T (Treg) cells, the Foxp3 promoter region
remains hypomethylated (70). Lv
et al (71) further
explored the important role of DNMT1-promoted Treg differentiation.
The results showed that pcDNA3.1(+)-mDNMT-1 blocked polymer
protein-promoted IL-10 and Foxp3 expression and Treg
differentiation (Fig. 1).
DNA methylation levels undergo tissue- and
organ-specific changes, contributing to various diseases including
neurological disorders, cancers, atherosclerosis and osteoporosis.
A distinctive feature of cancer is widespread DNA repeat
hypomethylation, a phenomenon that affects a large DNA region and
is accompanied by frequent local DNA hypermethylation events
(72). The degree of
hypermethylation has been shown to correlate with cancer
aggressiveness (73-75). DNMTs are abnormally expressed in
various malignancies, including BCa (76,77), prostate cancer (PCa) (78), colorectal cancer (79) and osteosarcoma (OSA) (80). Genes affected by hypermethylation
in cancer cells mainly include TSGs and DNA mismatch repair (MMR)
genes. The low expression of TSGs and the silencing of DNA MMR
genes are important mechanisms for cancer development (81,82). For instance, DNMT1 mediates
hypermethylation of CpG islands in the microRNA (miR)-34a promoter
region, leading to miR-34a deficiency and overexpression of Notch
proteins, ultimately promoting metastasis and progression of OSA
(83). The DNMT-1 inhibitor
enhances miR-34a expression in OSA cells, leading to an antitumour
effect and may be a promising therapeutic strategy for OSA
(83). Studies have shown that
hypermethylation of oncogenes and MMR genes due to aberrant DMNT
function may activate the MAPK (84), PI3K/ACT (85) and Wnt/b-catenin (75) signalling pathways, which
contribute to tumourigenesis (86).
In summary, DNMTs plays a crucial role in the
pathogenesis of various diseases and can serve as a potential
therapeutic targets for the corresponding diseases. With the rapid
development of epigenetics, the role and clinical application of
DNMT in urinary system diseases have received widespread
attention.
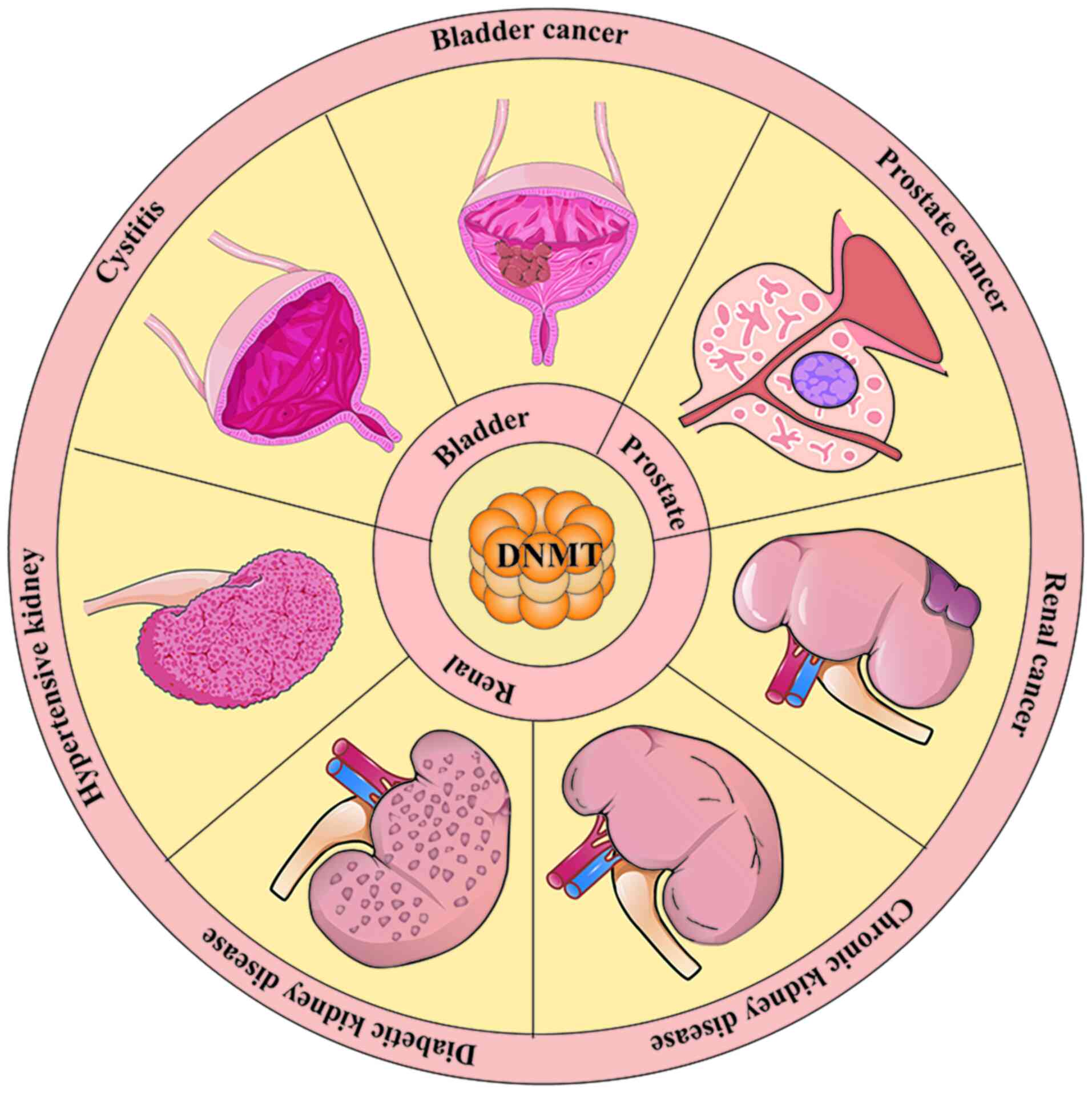
Growing evidence shows that DNMTs play a significant
role in the development of urinary system diseases. Overexpression
of DNMTs exacerbates renal fibrosis (87), tubular degeneration (88), polycystic kidney disease
(89,90), chronic bladder obstruction
(91), as well as the
progression of urinary system tumours (5,77,92,93). The aforementioned studies suggest
that DNMT is involved in the mechanisms of multiple urinary system
diseases development. The present review examines the role and
specific mechanisms of DNMTs in seven urological disorders. In
conclusion, abnormal expression of DNMTs plays an important role in
these diseases (Fig. 2).
Cystitis is a physiological process that
characterizes a number of bladder diseases such as UTIs and
haemorrhagic cystitis. Cystitis involves aberrant epigenetic
alterations through DNA methylation and histone deacetylation.
These histone modifications recruit DNMTs, mediate DNA methylation
and regulate the expression of genes implicated in pathology
(94).
A study used urine specimens from women with
interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome (IC/BPS) to assess
DNA methylation, and the findings suggest that genes within or
downstream of the MAPK pathway exhibit altered methylation in
IC/BPS (95). Infection of
mammalian tissues with bacteria, viruses and other pathogens
results in DNA methylation. In vitro studies have shown that
infection of bladder uroepithelial cells with uropathogenic E.
coli results in hypermethylation of the TSG CDKN2A (96-98). This hypermethylation may be
triggered by lipopolysaccharides (96,99), which activate NF-κB signal
transduction via Toll-like receptors, enables mimicking of the
inflammation process, and produces certain oxidants such as
superoxide and NO (100).
Damaged cytosine products resulting from
inflammation, particularly halogenated cytosine residues, are
likely to facilitate binding with methyl-binding proteins and
enzymatic methylation (101).
Uropathogenic E. coli infection modulates the host cell
epigenome (96). Systemic
chemotherapeutic agents, particularly cyclophosphamide (CPX) and
other nitrogen mustard alkylating agents, cause severe clinical
manifestations such as cystitis (102). Haldar et al (103) showed that exposure of mouse
bladders to CPX results in the DNA methylation of the Ogg1
promoter, which down-regulates gene expression. Furthermore, Choi
et al (104)
demonstrated that DNA methylation changes are observed in the
Calca, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (Timp3), matrix
metallopeptidase 2 (Mmp2) and insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor
(Igf2r) genes in a mouse model of chronic bladder inflammation
induced by CYP (104).
Hypertensive nephropathy is the second leading cause
of end-stage renal disease, following diabetes. At present,
hypertension has attracted the attention of the medical community
due to its high prevalence (105). Data shows that individuals with
hypertension account for ~33% of the global population (106,107). Long-term persistent
hypertension often leads to chronic renal failure, and in malignant
hypertension, renal failure can occur in the short term (108). Studies have shown that the
activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase and glutathione
peroxidase are lower in patients with hypertension compared with
healthy individuals (109-112). Concurrently, the expression of
key enzymes producing reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as NADPH
oxidase, increase. Since NADPH oxidase isoforms are highly
expressed in the kidneys, oxidative stress is one of the important
mechanisms of hypertensive nephropathy (113).
The mechanism of methylation also plays an important
role in this process. In an animal study involving Ang-II-induced
hypertension, the researchers reported that in addition to the
increase in blood pressure, the Ang-II-treated group also had
increased expression of DNMT1 and DNMT3A, which act as an
antioxidant defence systems to eliminate ROS (113). However, SOD and Sirtuin 1 genes
are hypermethylated and inhibited in transcription, which impairs
antioxidant function (113,114). Moreover, animal studies have
shown that a maternal low-protein diet induces hypermethylation and
increased expression of prostaglandin E receptor 1 in the kidneys
of young rats, which is associated with subsequent salt-sensitive
hypertension in adult rats (115,116). Understanding the methylation
mechanism in hypertensive nephropathy will help clarify the
specific pathogenesis and potentially lead to novel therapeutic
strategies in the future.
DN is a major global public health issue. The number
of individuals with diabetes may reach 578 million by 2030 and 700
million by 2045 (117).
Approximately 35% of individuals with diabetes develop DN (118), making it the long-term
complication of diabetes with the most significant social and
family burden (119).
Therefore, the study of DN has always been a focal point in the
academic community. In recent years, a number of studies have shown
that epigenetic changes play a role in the pathogenesis of kidney
disease (87,120-122). For example, DNMT1 expression
has been observed to be increased in damaged glomerular podocytes
of diabetic mice. The actin α4 (ACTN4) gene is hypermethylated in
podocytes, but this can be down-regulated using DNA methylation
inhibitors such as 5-Aza or epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG).
These interventions ensure the integrity of podocytes, effectively
reduce the level of urinary protein in diabetic mice, reduce
glomerular damage and basement membrane thickening, and protect the
kidneys (123,124).
In previous years, studies have reported that the
hypermethylation and low expression of the let-7a-3 gene can
influence the occurrence and development of DN by targeting
UHRF1/DNMT1. Therefore, the let-7a-3 gene is used as the target to
inhibit its hypermethylation. Moreover, it may be one of the
treatment directions for DN in the future (125,126). Additionally, depletion of the
calmodulin regulatory factor 1 (RCAN1) aggravates podocyte injury,
impairs the glomerular filtration barrier and increases
proteinuria, suggesting that RCAN1 is a protective factor for
podocytes (127). However,
under high glucose conditions, RCAN1 hypermethylation and decreased
expression aggravates kidney injuries, which is one of the
mechanisms of DN (128).
Hypermethylation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1
(129),
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (130) and KLOTHO (131) promoters have been associated
with DN. EGCG alleviates high glucose-induced kidney injury by
reversing KLOTHO promoter methylation (131). Therefore, exploring the
relationship between gene methylation and DN helps advance DN
pathogenesis research and design new therapeutic strategies.
CKD refers to the structural or functional
impairment of the kidneys by various causes (history of renal
impairment >3 months) (132). The disease burden of CKD
remains substantial and continues to grow globally. Globally,
incident cases and DALYs of CKD was 18.99 million and 41.54 million
in 2019, respectively (133),
imposing a significant societal and individual burden. The clinical
manifestations of CKD in different stages are different, but it's
typical feature is renal fibrosis. One of the important factors
promoting renal fibrosis is epigenetic changes (134-138). Research has confirmed that the
methylation of specific genes can promote CKD progression. For
example, HOXA5 promoter hypermethylation can enhance the expression
of Jagged 1 (JAG1) gene expression, activate the JAG1-Notch
signalling pathway and promote renal fibrosis (138). Similarly, the expression of the
anti-fibrotic KLOTHO gene in the kidney is decreased due to
hypermethylation in the early stage of renal injury. DNMT1/3A
inhibition can reduce the loss of the KLOTHO gene, attenuating
renal fibrosis and structural damage (137,139). Long-term cadmium exposure
induces a compensatory increase in DNMT (140) and promotes hypermethylation of
RASAL1, which is associated with a decreased estimated glomerular
filtration rate (141). RASAL1
hypermethylation has been confirmed as an important mechanism in
CKD in vitro (87,142).
The study of epigenetics in CKD offers new diagnostic and
therapeutic targets, and provides a new direction for the study of
pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative
disorder characterized by the abnormal deposition of α-synuclein
(α-Syn), with the main clinical manifestation being movement
disorders. With further research, non-motor symptoms of PD are
gradually being recognized, with urinary dysfunction being one of
the most common autonomic dysfunctions in patients with PD,
affecting 27-85% of individuals with the disease (143). Although no studies have
directly linked DNMT with urinary symptoms in PD, research has
shown that mutations in DNMT1 can lead to defects in DNA
methylation activity, resulting in neurodegenerative diseases
(144). In addition, the
abnormal accumulation of α-Syn in neurons of patients with PD can
cause a vicious cycle of α-Syn accumulation by withholding DNMT1,
leading to a decrease in the methylation level of the SNCA intron
in the α-Syn gene. These findings suggest that DNMT may contribute
to urinary dysfunction in PD by interacting with neurodegenerative
processes (145).
It is estimated that by 2024 kidney cancer will be
the sixth most common cancer among men, with an incidence number of
52,380, and the ninth most common cancer among women, with an
incidence number of 29,230 (2).
The National Cancer Database, which conducted an epidemiological
analysis of 262,597 patients diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma
(2004-2015) across more than facilities, found that the metastatic
rate of renal cell carcinoma was ~11 percent (146), leading to poor prognosis. For
example, the 5-year survival rate for the most common clear cell
RCC after metastasis is <10% (147). Therefore, early diagnosis and
treatment are crucial for improving prognosis. As a malignant
tumour, the role of epigenetics in RCC is significant.
Overexpression of DNMTs often increases gene promoter
hypermethylation, indicating gene inactivation or decreased
expression ability (148). TSGs
such as von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) (149), p16/CDKN2a, p14ARF, adenomatous
polyposis coli (APC), RAS association domain family protein 1A
(RASSF1A), B-cell translocation gene 3 (BTG3) and Timp-3 are
hypermethylated in patients with RCC (150). The hypermethylation rate of the
apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 promoter that induces
apoptosis in RCC is ~100%, and the pro-apoptotic gene
hypermethylation rate of ASC/TMS1 is ~41.1% (151,152). Promoter methylation of the HIG1
domain family member 1A and death-associated protein kinase 1
(DAPK-1) genes, which inhibit tumour metastasis, are strongly
associated with RCC (153).
Additionally, promoter methylation of secreted
frizzled-related protein 1 (sFRPs) (154,155), SCUBE3 (156) and GATA-5 (157,158) is associated with poor prognosis
in RCC. However, surface hypomethylating agents have shown the
potential to effectively reduce kidney damage and improve prognosis
(159,160). Screening for specific gene
methylation in the blood or urine of patients and applying
demethylation drugs to the corresponding targets may become a
future research directions for early non-invasive RCC
diagnosis.
PCa is the fifth most common cancer in men,
following lung cancer. In 2020, ~1,414,000 new cases were
diagnosed, and 375,304 PCa-associated mortalities occurred
worldwide (161), placing a
significant burden on society. Although the prognosis of PCa is
generally favourable, ~15% of the patients with high-risk forms of
PCa may die within a few years (162). In the past few years, the rate
of early diagnosis of PCa has increased due to the discovery of
prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, reducing the mortality
rate (163). However, due to
concerns about the overdiagnosis and treatment of PCa and the
complications of screening, the controversy about PSA continues,
reducing the willingness to screen in certain countries and slowing
the decline of PCa mortality (164,165). Therefore, identifying new
targets to replace or supplement PSA screening is one of the hot
spots in PCa research (166).
Epigenetic changes are one of the important
characteristics of PCa, offering potential new therapeutic
directions by using them as a target (167). The androgen receptor (AR) gene
is hypermethylated in advanced PCa, and may be related to
metastasis (168,169), providing a new prognostic
biomarker for PCa. Genes such as ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal
hydrolase 1 (170), APC
(171), E-Cadherin (172), ASC (173), cyclin d2, glutathione
S-transferase pi-1 (GSTP1), retinoic acid receptor β (RARB), CD44
and RASSF1A, which are hypermethylated and suppressed in PCa, have
high specificity and sensitivity, and are associated with poor
pathological classification of PCa (174,175). Prostate cells are observed in
urine, which may serve as important markers for early non-invasive
diagnosis and prognosis of PCa in the future (176). The recurrence of PCa after
treatment and the time to recurrence are the concerns of patients.
Studies have reported that the methylation of CD44 and
prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) genes are associated
with a shorter recurrence time, offering a valuable detection
target for predicting the prognosis of PCa after surgery (177). The existing research results of
epigenetics are significant for PCa diagnosis and treatment. For
example, antitumour drugs such as methylation inhibitors
5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine can specifically inhibit
the methylation of certain genes that suppress tumour growth and
metastasis and regulate cell cycle, playing a corresponding role in
curbing tumour proliferation with fewer side effects; these drugs
are likely to be significant in cancer treatment in the future
(170,178-181). Therefore, epigenetic
modification represents promising directions in PCa research.
BCa is the most lethal malignant tumour in the
urinary system, with 549,393 diagnoses and 199,922 mortalities
globally in 2018 (182). The
incidence and mortality of BCa continue to rise (183), significantly affecting quality
of life. NMIBC has a poor prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence rate
of up to 78% (184). Unlike
PCa, there is currently no universally accepted screening method
for BCa, and patients with NMIBC often endure repeated cystoscopy,
imaging and subsequent surgery, which are physically and
psychologically stressful (185). Therefore, identifying feasible
targets for early non-invasive diagnosis is crucial. The
pathogenesis of BCa is complex, and epigenetic changes are one of
its important characteristics. The methylation of certain specific
genes has been proven to be a good biomarker (186). Promoter methylation of APC is
significantly increased in BCa tissue and is associated with
disease occurrence and progression, making it a key biomarker for
the non-invasive detection of BCa.
The kidneys are closely related to the urinary
system. In clinical practice, if renal function is impaired, it
often leads to abnormal urinary drainage function of the urinary
system. Studies have shown that epigenetic repair, especially DNA
methylation, can severely affect kidney function. Oxidative stress
is a major pathological factor contributing to aging-related
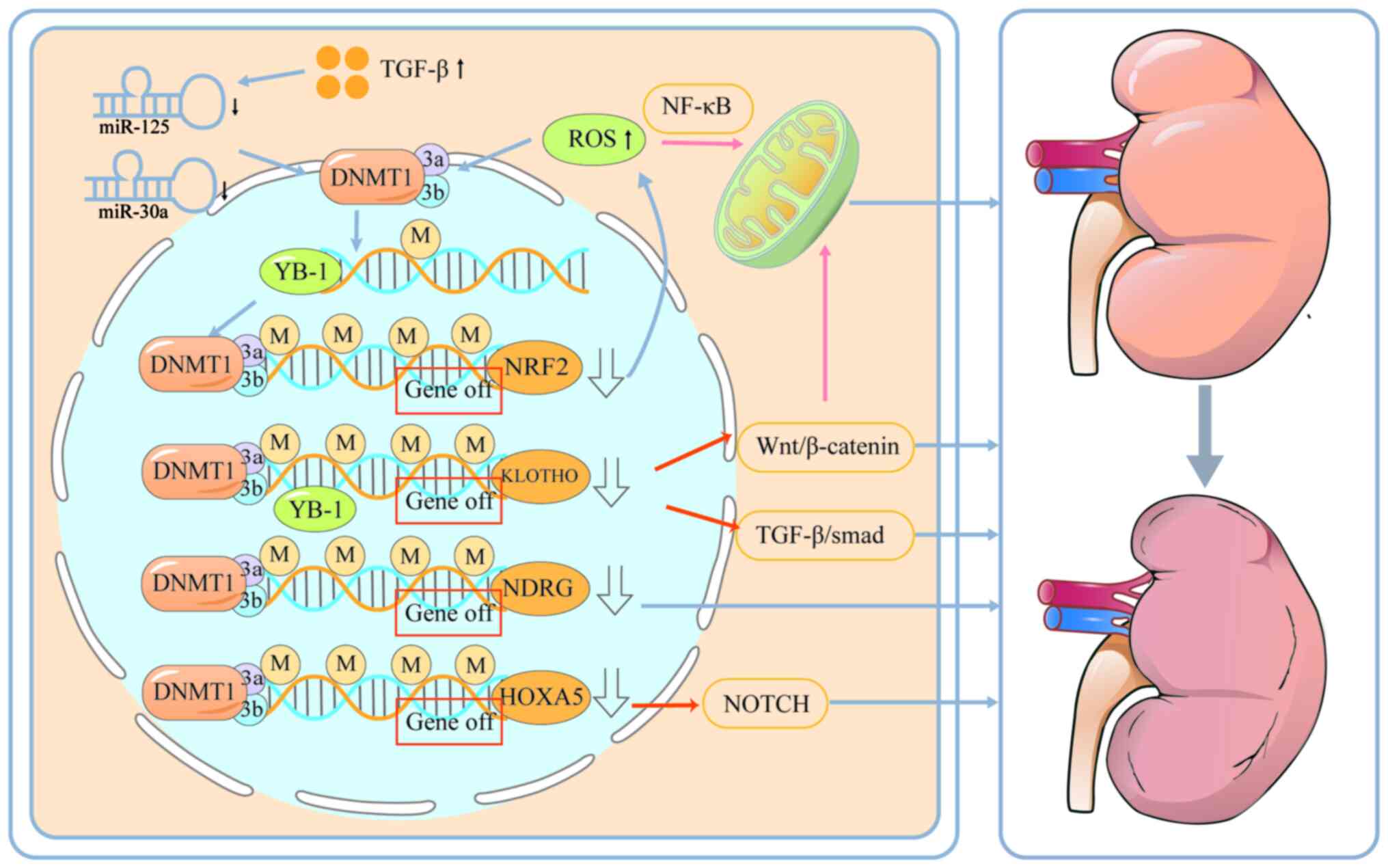
diseases. Nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (NRF2) and
KLOTHO, two major antiaging factors with antioxidant capacities,
are suppressed with aging, which is associated with increased
incidence of aging-related kidney disorders. A recent study has
shown that upregulation of DNMT1/3a/3b expression results in
promoter hypermethylation of NRF2 and KLOTHO and decreased
expression of NRF2 and KLOTHO, resulting in structural and
functional alterations in renal senescence (198). NRF2 inhibition significantly
promotes ROS production while suppressing the antioxidant capacity
of renal TEC under Ang II conditions (199). Zhao et al (200) showed that ROS production in
turn promotes the up-regulation of DNMT1/3a/3b expression, leading
to hypermethylation of the NDRG promoter and promoting renal
fibrosis. Moreover, ROS activate the NF-κB signalling pathway to
induce mitochondrial dysfunction, enhance autophagy and promote
apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells (201). The Y-box binding protein-1
(YB-1) regulates fibrosis-related genes (for example, Col1a1, Mmp2
and Tgfβ1) and contributes significantly to disease progression.
YB-1 binds to specific structural motifs in DNA, thereby recruiting
DNMT to the promoter of KLOTHO, resulting in a decrease in KLOTHO
expression, which subsequently leads to activation of the
Wnt/β-catenin and TGFβ/Smad signalling pathways (202,203). Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin
signalling pathway inhibits the mitochondrial biogenesis regulator
Pparg coactivator 1α in renal tubular cells and reduces the
mitochondrial membrane potential, oxygen consumption and ATP
production, which is closely related to renal fibrosis (204). Whereas TGF-β increases DNMT1
and DNMT3a expression by inhibiting miR-152 and miR-30a in fibrotic
kidneys thereby inhibiting KLOTHO expression (137). In addition, a recent study by
Xiao et al found that the expression of DNMT1, DNMT3a and
DNMT3b are significantly increased in CKD, which leads to the
hypermethylation of the promoter of HOXA4 and decreases its
expression (138). A decrease
in the expression of HOXA5 increases the expression of JAG1, which
activates the NOTCH signalling pathway, resulting in fibrosis in
the kidney (Fig. 3) (138,205).
Aberrant DNA methylation (genome-wide
hypomethylation and site-specific hypermethylation) are observed in
numerous types of cancer (206-208). Abnormal DNA methylation has
been shown to be strongly associated with numerous types of
cancers, particularly with tumour suppressor genes, which play an
important role in tumourigenesis and development (209). The active methyl group is
transferred to the covalent bond at the 5′ carbon position of
cytosine of tumour suppressor genes mediated by the DNMT family,
using S-adenosylmethylsulfonine as the methyl carrier. Silencing of
gene expression due to hypermethylation of TSGs promoter regions is
an important driver of tumourigenesis and progression (210). It remains less well understood
how DNMTs are targeted to specific loci in the context of aberrant
hypermethylation in cancer cells (211,212). Two possible molecular
mechanisms have been proposed (213), one being that during genotoxic
stress-induced DNA deletion, the aggregation of DNMT, histone
deacetylase complexes and multi-comb complexes at CpG-rich
promoters throughout the genome inhibits transcription (214). Alternatively, loss of
ten-eleven translocation (TET) activity in cancer cells results in
shortening of CpG islands and decreased gene expression through
histone H3 lysine 4 mono-methylation (H3K4me1)-induced de
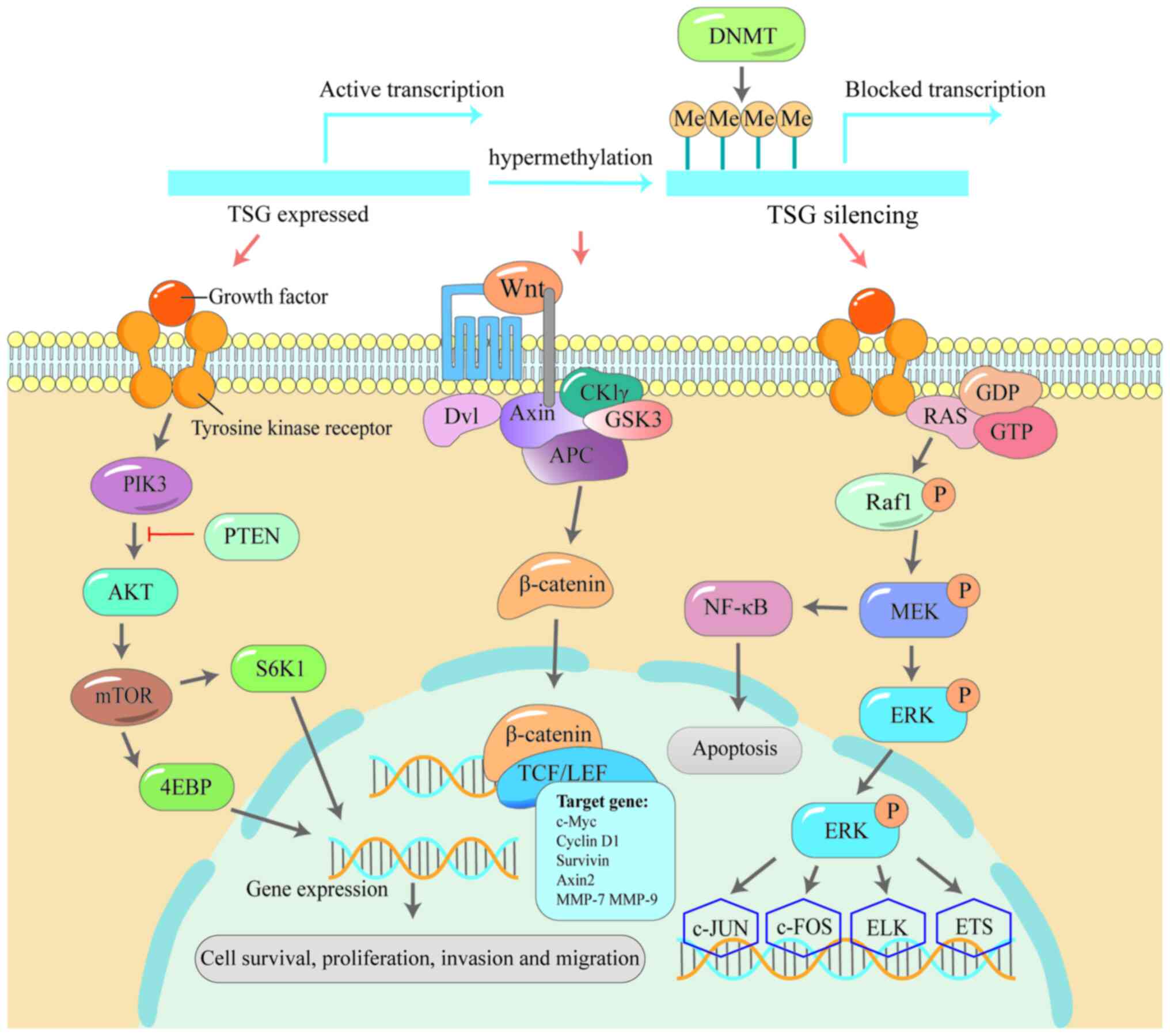
novo DNMT invasion of DNA methylation (213). Early findings suggested that
DNMT-mediated focal hypermethylation of TSGs directly triggers
transcriptional silencing of TSGs and activation of signalling
pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin (215), PI3K/AKT (216) and MAPK (217), which promotes cancerous
aggravation. These three pathways play important roles in the
occurrence and development of cancer.
Multiple studies have shown that Wnt plays a role
in maintaining stem cells, assisting their self-renewal and cell
generation capacity (218,219), and its abnormal changes are
associated with the occurrence and development of a variety of
cancers (220,221). For example, APC inactivation
leads to the abnormal activation of β-catenin, thereby affecting
the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway (222), leading to the progression of
familial adenomatosis (FAP) to colorectal cancer (223). The phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase (PI3K/Akt) signalling pathway functions in regulating cell
cycle, differentiation and metabolism (224), so the abnormality of this
signalling pathway is common in cancer. The channel PI3K3A gene
mutations or phosphate and tensin homolog (PTEN) gene promoter
methylation leading to the decrease of the expression level is
often associated with the development of breast cancer (225-227). The serine/threonine protein
kinase MAPK, also known as ERK, is a key component of the
Raf/MEK/ERK signalling pathway (228). Alterations in this pathway are
the most common in human cancers and promote malignant
proliferation of cancer cells (229). These three pathways are closely
related to DNMT, suggesting that the methylation machinery is
involved in the mutation and activation of the pathway (Fig. 4).
Promoter hypermethylation of TSGs is often the main
mechanism of their loss of function in prostate cancer. Overall,
>30 genes have been reported to be abnormally hypermethylated in
prostate cancer, including genes involved in hormonal response,
cell cycle regulation, cell invasion and DNA damage repair.
Inappropriate silencing of these genes can lead to the occurrence,
progression, invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer. The
present review found that miR-148a, miR-152 and miR-200b increase
DNMT1 expression, which results in the reduction of PTEN
expression, which leads to the activation of the PIK3/AKT
signalling pathway. In addition, loss of PTEN may lead to decreased
expression of NK3 homeobox 1, thereby up-regulating AR-related
signalling (230). Dickkopf Wnt
signalling pathway inhibitor 3 (DKK3) inhibits the transmission of
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway, and studies have shown that its
expression is decreased in prostate cancer (231-233). Bhattacharyya et al
(234) showed that increased
DNMT activity and expression lead to methylation of the DKK3
promoter, which leads to the activation of Wnt/β-catenin
signalling.
In renal cancers, the p16 and Thrombospondin 1
(THBS-1) genes seem to be hot spots of regional DNA
hypermethylation during multistage renal tumourigenesis (235). Inhibition of THBS-1 expression
can activate the PI3K/AKT pathway (236). In addition, KLOTHO, a tumour
suppressor gene, normally binds to Wnt ligands to block the Wnt
pathway (237-240). When DNMT activity is increased,
KLOTHO methylation expression is decreased, and Wnt can be
over-activated synergistically with TGF-β to induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (241) and promote the differentiation
of cancer stem cells (242),
which can promote the occurrence and development of renal cell
carcinoma. In conclusion, DNMT may down-regulate THBS-1 through the
methylation of THSB-1 promoter and KLOTHO promoter to activate the
PI3K/AKT and Wnt signalling pathways to promote cell proliferation
in renal cell carcinoma.
In the detection of methylation of bladder cancer
protective genes that are also Wnt antagonist genes such as
secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1), WNT inhibitory
factor-1 (WIF1), APC and CDH1, it was found that in all the
samples, at least one gene was found to be methylated and then
down-regulated, leading to excessive activation of Wnt pathway and
uncontrolled proliferation of bladder cells, which promote the
occurrence and development of bladder cancer (243,244). In addition to antagonising the
Wnt pathway, the SFRP1 gene also inhibits the MAPK pathway
(233,245). Therefore, when the activity of
DNMT is increased, SFRP1 in the methylated state tends to promote
the proliferation of bladder tumour cells. Decreased expression of
a tumour suppressor gene may promote cancer cell proliferation
through multiple mechanisms, so the importance of methylation is
self-evident.
Epigenetic changes are the common mechanism of a
variety of diseases in the urinary system. Methylation may lead to
specific gene expression decrease or even inactivation, affecting
the function of the gene, and eventually leading to lesions
(246). Fortunately, there are
a variety of studies exploring how to use this feature for clinical
use. DNA methylation plays an important role in early diagnosis,
accurate treatment and prognosis evaluation. Firstly, some
malignant tumours have been found to be associated with the
methylation of tumour suppressor genes (247), and the present review found
that there are some methylated genes in urinary system diseases
such as kidney cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer and other
malignant tumours that are specific due to the different
methylation patterns of different cancers (194). As methylation variation can
exist in the whole genome (248), Epigenetic Cancer of the
Prostate Test in Urine (epiCaPture), as a detection method for
high-risk PCA urine DNA methylation, measures the DNA
hypermethylation in the 5′ regulatory region of six genes (GSTP1,
SFRP2, IGFBP3, IGFBP7, APC and PTGS2), all of which had previously
been reported in PCa combined with PSA, the sensitivity and
specificity of PCA assay are >70% (249). DNA methylation is stable and
can be detected in almost any body fluid or tissue of the human
body (250). Therefore, it is
also non-invasive and effective in alleviating the pain of
patients. In addition, methylated genes can also be combined with
other examination methods such as DAPK combined with B ultrasound
examination, which has been confirmed to be as accurate as
cystoscopy (193).
At present, a variety of methylated genes have been
found to have application value in the diagnosis of diseases. As an
epigenetic marker in prostate cancer, GSTP1 has been shown to be
hypermethylated in cancer tissues and various body fluid (251). Detection of GSTP1 in urine is
even more relevant to the disease status than analysis of Gleason
score in biopsy (252).
ConfirmMDx, developed by MDxHealth Laboratories, has a negative
predictive value of >90% for hypermethylated GSTP1, RASSF1 and
APC (253). Therefore, the
present study hypothesises that methylated genes can be used as one
of the detection markers for early diagnosis in the future.
Restoring the function of genes inactivated by methylation is the
key to study the treatment strategy. Studies have revealed that
reactivating tumour suppressor genes inactivated by methylation
through targeted therapy may help treat specific types of cancer
(254,255).
In addition to this, the use of specific drugs or
techniques to intervene in the DNA methylation process has received
widespread attention. For example, the expression of genes silenced
by methylation is restored by inhibiting the activity of DNA
methyltransferases or facilitating the action of DNA demethylases.
At present, a variety of studies have found that DNMT inhibitors or
demethylases play an important role in the cure of diseases,
including diabetic nephropathy, chronic kidney disease, renal cell
carcinoma, prostate cancer and bladder cancer (Table I) (160,198,256-260). For example, RG108, a
non-nucleoside inhibitor of DNMT, exerts an antitumour effect by
reversing the silencing of antitumour genes such as GSTP1 and APC
in prostate cancer (258). In
addition to its effect on malignant tumours, DNMT inhibitor
SGI-1072 can also reduce renal aging changes by reversing the
methylation of anti-aging factor KLOTHO and enhancing its
expression (198), and this
mechanism is related to the inhibition of oxidative stress,
fibrosis and apoptosis (261).
OLP, a DNMT inhibitor similar to SGI-1072, has been found to have a
demethylation ability in D-galactose-induced senescent renal cells,
effectively reducing DNMT1/3a/3b expression, decreasing the loss of
antioxidant senescence factors KLOTHO and NRF2, and then
ameliorating renal cellular senescence (198). Thus, they may also have a role
in chronic kidney disease.
In addition, DNMT inhibitors can also be combined
with other drugs, such as synergism with the HDAC inhibitor TSC, to
effectively inhibit the proliferation of bladder cancer (259). As a pan-DNMT inhibitor,
decitabine exerts important antitumour effects in highly
DNMT-expressing neuroendocrine prostate cancer, inhibiting tumour
progression mainly by suppressing the expression of neuroendocrine
profile markers (77). Further
study has shown that decitabine can also increase the expression of
the drug target B7-h3, and an experiment has demonstrated that
decitabine combined with the B7-h3-targeting agent DS-7300a (i-DXd)
can effectively enhance the anti-tumour effect (262). As early as 2009, the
combination of 5-Azacytidine with cisplatin has been reported to
improve antitumour effects and reduce nephrotoxicity (263). 5-Azacytidine inhibits the
expression of genes related to oxidative stress and reduces
metallothionein gene expression, which reduces nephrotoxicity
(263,264). 5-Azacytidine is also known to
inhibit the expression of genes related to oxidative stress and
reduce metallothionein gene expression, which reduces
nephrotoxicity (263,264). The The combination of
5-Azacytidine with cisplatin has been reported to increase
sensitivity and resistance (265,266). The reversal of methylation is
relatively mild, and the side effects of DNMT inhibitors are
relatively small (267), which
can also effectively improve the quality of life of patients.
In addition, epigenetic changes, especially gene
methylation, can respond to a variety of mechanisms, so it is also
beneficial to explore the aetiology and pathogenesis of diseases.
For example, if a certain gene methylation degree is found to be
higher in hypertensive nephropathy and diabetic nephropathy than in
healthy individuals, it can be verified by designed experiments
when the causal relationship is not clear, which is helpful to find
new treatment ideas. Finally, the prognosis of the disease can also
be determined according to the degree of gene methylation. Several
studies have confirmed that the hypermethylation of the BNC1
(268), GATA5 (157) and SCUBE3 (156) promoters often predicts poor
prognosis of patients with renal cell carcinoma. The methylation
levels of LAD1 (154,269) and NEFH (270) can also reflect the outcome of
drug treatment of renal cell carcinoma to a certain extent, helping
physicians to adjust the treatment plan in time. The promoters of
p16INK4a and p14ARF are hypermethylated in bladder cancer, and the
degree of methylation is related to the malignant degree of bladder
cancer. For example, the methylation of invasive bladder cancer is
higher than that of superficial bladder cancer (188). The recurrence of prostate
cancer after treatment and the time to recurrence are the concerns
of patients. Studies have found that the methylation of CD44 is
correlated with progression and metastasis in prostate cancer
(271,272) and Yegnasubramanian et al
(273) indicated that the
hypermethylation of PTGS2 CpG islands predicted an increased risk
of prostate cancer recurrence in 2004. Moreover, the methylation of
CD44 and PTGS2 genes are associated with a shorter recurrence time,
which provides a good detection target for predicting the prognosis
of prostate cancer after surgery (177).
Rapid advances in the field of epigenetics not only
reveal complex genetic phenomena at the molecular level, but also
offer new hope for the treatment of diseases, especially cancer
(274). Epigenetic changes have
reversible properties, meaning that biological traits can be
affected by reversing these changes under certain conditions. DNA
methylation, histone modification and regulation of non-coding RNA
have become the focus of epigenetic therapy. Currently, several
epigenetic-based treatments have been developed, such as DNMTi.
However, the main disadvantage of these methods is their lack of
specificity, which can lead to off-target effects and other side
effects (275-277). The CRISPR/Cas9 technology is a
powerful tool that is currently widely used for genome editing. Its
modular design is not only suitable for direct modification of DNA,
but can also be used to introduce specific epigenetic
modifications, such as methylation or demethylation (278). dCas9 fuses with the catalytic
domain of DNMT or TET proteins, and the CRISPR/DCas9-DNMT or
DCas9-TET system enables precise editing of DNA methylation. Liang
et al (279)
demonstrated that this fusion protein enables site-specific DNA
methylation editing in zebrafish.
Because zebrafish embryos are transparent, grow
rapidly and are highly homologous to human genes, they are an ideal
model for studying vertebrates. Therefore, DNMTs fusion technology
combined with CRISPR/Cas9 system has the potential to be used to
specifically edit human DNA methylation in the future.
In the field of urinary tumours, some key
epigenetic changes have also been found in prostate cancer. For
example, GSTP1 and HOX family member genes are inhibited by
hypermethylation in the promoter region. Kardooni et al
(232) reported that
downregulation of the DKK3 gene is associated with the growth of
prostate tumours. The Dkk-3 protein encoded by the DKK3 gene
maintains the stable state of normal prostate epithelial cells by
regulating the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway (261). Going forward, using
CRISPR/dCas9-DNMT technology, it will be possible to regulate the
expression of these genes through methylation or demethylation,
thereby controlling tumour growth.
In conclusion, with the deepening understanding of
epigenetics, more and more studies have demonstrated that
DNMT-mediated aberrant methylation of genes plays an important role
in the development of urinary system diseases. The present review
systematically reviewed the mechanism and clinical value of DNMT in
a variety of urinary system diseases. We found that targeting DNMT
to find corresponding therapeutic approaches is of great
significance in the treatment of urinary system diseases. It is
hypothesised that DNMT will provide novel therapeutic ideas for
urinary system diseases.
Not applicable.
AW, YY and HW conceived the study. YY, YW, XF and
XX wrote and edited the manuscript. XW, TS, YG, SL, AW and JT
revised the manuscript. AW put forward constructive opinions on the
topic selection of the article. All authors have read and approved
the final manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the Weifang Municipal Health
Commission Project (grant no. WFWSJK-2021-140) and Shandong
Province Medicine and Health Science and Technology Development
Programme Project (grant no. 2021BJ000026).
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zi H, Liu MY, Luo LS, Huang Q, Luo PC,
Luan HH, Huang J, Wang DQ, Wang YB, Zhang YY, et al: Global burden
of benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinary tract infections,
urolithiasis, bladder cancer, kidney cancer, and prostate cancer
from 1990 to 2021. Mil Med Res. 11:642024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tian YQ, Yang JC, Hu JJ, Ding R, Ye DW and
Shang JW: Trends and risk factors of global incidence, mortality,
and disability of genitourinary cancers from 1990 to 2019:
Systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019.
Front Public Health. 11:11193742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen JQ, Salas LA, Wiencke JK, Koestler
DC, Molinaro AM, Andrew AS, Seigne JD, Karagas MR, Kelsey KT and
Christensen BC: Immune profiles and DNA methylation alterations
related with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer outcomes. Clin
Epigenetics. 14:142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Unnikrishnan A, Freeman WM, Jackson J,
Wren JD, Porter H and Richardson A: The role of DNA methylation in
epigenetics of aging. Pharmacol Ther. 195:172–185. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Singh NP and Vinod PK: Integrative
analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression in papillary renal
cell carcinoma. Mol Genet Genomics. 295:807–824. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deng Q, Du Y, Wang Z, Chen Y, Wang J,
Liang H and Zhang D: Identification and validation of a DNA
methylation-driven gene-based prognostic model for clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. BMC Genomics. 24:3072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lyko F: The DNA methyltransferase family:
A versatile toolkit for epigenetic regulation. Nat Rev Genet.
19:81–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Castillo-Aguilera O, Depreux P, Halby L,
Arimondo PB and Goossens L: DNA methylation targeting: The DNMT/HMT
crosstalk challenge. Biomolecules. 7:32017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferreira HJ and Esteller M: CpG islands in
cancer: Heads, tails, and sides. Methods Mol Biol. 1766:49–80.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu H, Caffo B, Jaffee HA, Irizarry RA and
Feinberg AP: Redefining CpG islands using hidden Markov models.
Biostatistics. 11:499–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rodriguez-Paredes M and Esteller M: Cancer
epigenetics reaches mainstream oncology. Nat Med. 17:330–339. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Liang Y, Fan J, Xu C, Guan B, Zhang
J, Guo B, Shi Y, Wang P, Tan Y, et al: DNA methylation subtypes
guiding prognostic assessment and linking to responses the DNA
methyltransferase inhibitor SGI-110 in urothelial carcinoma. BMC
Med. 20:2222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu JT, Hu XW, Chen HY, Yang Q, Li HD, Dong
YH, Zhang Y, Wang JN, Jin J, Wu YG, et al: DNA methylation of FTO
promotes renal inflammation by enhancing m6A of PPAR-α
in alcohol-induced kidney injury. Pharmacol Res. 163:1052862021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gu Y, Niu S, Wang Y, Duan L, Pan Y, Tong
Z, Zhang X, Yang Z, Peng B, Wang X, et al: DMDRMR-mediated
regulation of m6A-Modified CDK4 by m6A reader
IGF2BP3 drives ccRCC progression. Cancer Res. 81:923–934. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sandholm N, Cole JB, Nair V, Sheng X, Liu
H, Ahlqvist E, van Zuydam N, Dahlström EH, Fermin D, Smyth LJ, et
al: Genome-wide meta-analysis and omics integration identifies
novel genes associated with diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia.
65:1495–1509. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnston WWS: Diseases of the kidneys and
urinary system. Med J Aust. 2:57–59. 1947.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Correa-Forero V, Pinilla-Monsalve GD,
Valderrama-Chaparro JA and Amaya-Gonzalez P: Cryptococcal
meningitis presenting as acute flaccid paralysis: A case report. J
Infect Public Health. 13:143–148. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sampaolo S, Esposito T, Gianfrancesco F,
Napolitano F, Lombardi L, Lucà R, Roperto F and Di Iorio G: A novel
GBE1 mutation and features of polyglucosan bodies autophagy in
adult polyglucosan body disease. Neuromuscul Disord. 25:247–252.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Roberts NA, Hilton EN, Lopes FM, Singh S,
Randles MJ, Gardiner NJ, Chopra K, Coletta R, Bajwa Z, Hall RJ, et
al: Lrig2 and Hpse2, mutated in urofacial syndrome, pattern nerves
in the urinary bladder. Kidney Int. 95:1138–1152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liao L: Evaluation and management of
neurogenic bladder: What is new in China? Int J Mol Sci.
16:18580–18600. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoshimura N, Ogawa T, Miyazato M, Kitta T,
Furuta A, Chancellor MB and Tyagi P: Neural mechanisms underlying
lower urinary tract dysfunction. Korean J Urol. 55:81–90. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Archer M, Dogra N, Dovey Z, Ganta T, Jang
HS, Khusid JA, Lantz A, Mihalopoulos M, Stockert JA, Zahalka A, et
al: Role of α- and β-adrenergic signaling in phenotypic targeting:
Significance in benign and malignant urologic disease. Cell Commun
Signal. 19:782021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen N, Li G, Si Y, Ye Y, Zhang T, Chi D,
Zhang W, Pan L, Qu G, Lu Y, et al: Development and evaluation of a
centrifugal disk system for the rapid detection of multiple
pathogens and their antibiotic resistance genes in urinary tract
infection. Front Microbiol. 14:11574032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Simões E Silva AC, Oliveira EA and Mak RH:
Urinary tract infection in pediatrics: An overview. J Pediatr (Rio
J). 96(Suppl 1): S65–S79. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zulfiqar M, Ubilla CV, Nicola R and Menias
CO: Imaging of renal infections and inflammatory disease. Radiol
Clin North Am. 58:909–923. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bachar A, Itzhaki E, Gleizer S, Shamshoom
M, Milo R and Antonovsky N: Point mutations in topoisomerase I
alter the mutation spectrum in E. coli and impact the emergence of
drug resistance genotypes. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:761–769. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Price LB, Johnson JR, Aziz M, Clabots C,
Johnston B, Tchesnokova V, Nordstrom L, Billig M, Chattopadhyay S,
Stegger M, et al: The epidemic of extended-spectrum-β-lactama
se-producing Escherichia coli ST131 is driven by a single highly
pathogenic subclone, H30-Rx. mBio. 4:e00377–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Beebout CJ, Robertson GL, Reinfeld BI,
Blee AM, Morales GH, Brannon JR, Chazin WJ, Rathmell WK, Rathmell
JC, Gama V and Hadjifrangiskou M: Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
subverts mitochondrial metabolism to enable intracellular bacterial
pathogenesis in urinary tract infection. Nat Microbiol.
7:1348–1360. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Spradling K, Ganesan C and Conti S:
Medical treatment and prevention of urinary stone disease. Urol
Clin North Am. 49:335–344. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hong SY, Xia QD, Yang YY, Li C, Zhang JQ,
Xu JZ, Qin BL, Xun Y and Wang SG: The role of microbiome: A novel
insight into urolithiasis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 49:177–196. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hobbs T, Schultz LN, Lauchnor EG, Gerlach
R and Lange D: Evaluation of biofilm induced urinary infection
stone formation in a novel laboratory model system. J Urol.
199:178–185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sen H, Seckiner I, Bayrak O, Erturhan S
and Demirbağ A: Treatment alternatives for urinary system stone
disease in preschool aged children: Results of 616 cases. J Pediatr
Urol. 11:34.e1–e5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen F, Zhang Y, Bossé D, Lalani AA,
Hakimi AA, Hsieh JJ, Choueiri TK, Gibbons DL, Ittmann M and
Creighton CJ: Pan-urologic cancer genomic subtypes that transcend
tissue of origin. Nat Commun. 8:1992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Markowski MC, Boorjian SA, Burton JP, Hahn
NM, Ingersoll MA, Maleki Vareki S, Pal SK and Sfanos KS: The
microbiome and genitourinary cancer: A collaborative review. Eur
Urol. 75:637–646. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Compérat E, Zigeuner
R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, Cowan NC, Gontero P, Van Rhijn BWG,
Mostafid AH, et al: European association of urology guidelines on
upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: 2017 Update. Eur Urol.
73:111–122. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li Z, Xu H, Gong Y, Chen W, Zhan Y, Yu L,
Sun Y, Li A, He S, Guan B, et al: Patient-derived upper tract
urothelial carcinoma organoids as a platform for drug screening.
Adv Sci (Weinh). 9:e21039992022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang ML, Miki Y, Hang JF, Vohra M, Peyton
S, McIntire PJ, VandenBussche CJ and Vohra P: A review of upper
urinary tract cytology performance before and after the
implementation of The Paris system. Cancer Cytopathol. 129:264–274.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bus MTJ, de Bruin DM, Faber DJ, Kamphuis
GM, Zondervan PJ, Laguna Pes MP, de Reijke TM, Traxer O, van
Leeuwen TG and de la Rosette JJ: Optical diagnostics for upper
urinary tract urothelial cancer: Technology, thresholds, and
clinical applications. J Endourol. 29:113–123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
He Y, Xu W, Xiao YT, Huang H, Gu D and Ren
S: Targeting signaling pathways in prostate cancer: Mechanisms and
clinical trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1982022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kausar S, Abbas MN and Cui H: A review on
the DNA methyltransferase family of insects: Aspect and prospects.
Int J Biol Macromol. 186:289–302. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Uysal F and Ozturk S: DNA
methyltransferases in mammalian oocytes. Results Probl Cell Differ.
63:211–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA and Li E: DNA
methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo
methylation and mammalian development. Cell. 99:247–257. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ren W, Gao L and Song J: Structural basis
of DNMT1 and DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation. Genes (Basel).
9:6202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen Z and Zhang Y: Role of mammalian DNA
methyltransferases in development. Annu Rev Biochem. 89:135–158.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Poh WJ, Wee CP and Gao Z: DNA
methyltransferase activity assays: Advances and challenges.
Theranostics. 6:369–391. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takeshima H, Niwa T, Yamashita S,
Takamura-Enya T, Iida N, Wakabayashi M, Nanjo S, Abe M, Sugiyama T,
Kim YJ and Ushijima T: TET repression and increased DNMT activity
synergistically induce aberrant DNA methylation. J Clin Invest.
130:5370–5379. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang J, Fan T, Yan Q, Zhu H, Fox S, Issaq
HJ, Best L, Gangi L, Munroe D and Muegge K: Lsh, an epigenetic
guardian of repetitive elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:5019–5028.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tao Y, Xi S, Shan J, Maunakea A, Che A,
Briones V, Lee EY, Geiman T, Huang J, Stephens R, et al: Lsh,
chromatin remodeling family member, modulates genome-wide cytosine
methylation patterns at nonrepeat sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:5626–5631. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Han M, Li J, Cao Y, Huang Y, Li W, Zhu H,
Zhao Q, Han JJ, Wu Q, Li J, et al: A role for LSH in facilitating
DNA methylation by DNMT1 through enhancing UHRF1 chromatin
association. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:12116–12134. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xing H, Wang C, Wu H, Chen D, Li S and Xu
S: Effects of atrazine and chlorpyrifos on DNA methylation in the
brain and gonad of the common carp. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol
Pharmacol. 168:11–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang C, Zhang Z, Yao H, Zhao F, Wang L,
Wang X, Xing H and Xu S: Effects of atrazine and chlorpyrifos on
DNA methylation in the liver, kidney and gill of the common carp
(Cyprinus carpio L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 108:142–151. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wirbisky-Hershberger SE, Sanchez OF,
Horzmann KA, Thanki D, Yuan C and Freeman JL: Atrazine exposure
decreases the activity of DNMTs, global DNA methylation levels, and
dnmt expression. Food Chem Toxicol. 109:727–734. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Svedružić ŽM: Dnmt1 structure and
function. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 101:221–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Duraisamy AJ, Mishra M, Kowluru A and
Kowluru RA: Epigenetics and Regulation of oxidative stress in
diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:4831–4840.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao L, Sun MA, Li Z, Bai X, Yu M, Wang M,
Liang L, Shao X, Arnovitz S, Wang Q, et al: The dynamics of DNA
methylation fidelity during mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal
and differentiation. Genome Res. 24:1296–1307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mohan KN: DNMT1: Catalytic and
non-catalytic roles in different biological processes. Epigenomics.
14:629–643. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Arand J, Spieler D, Karius T, Branco MR,
Meilinger D, Meissner A, Jenuwein T, Xu G, Leonhardt H, Wolf V and
Walter J: In vivo control of CpG and non-CpG DNA methylation by DNA
methyltransferases. PLoS Genet. 8:e10027502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang Q, Yu G, Ming X, Xia W, Xu X, Zhang
Y, Zhang W, Li Y, Huang C, Xie H, et al: Imprecise DNMT1 activity
coupled with neighbor-guided correction enables robust yet flexible
epigenetic inheritance. Nat Genet. 52:828–839. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Echeverria F, Ortiz M, Valenzuela R and
Videla LA: Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids regulation of
PPARs, signaling: Relationship to tissue development and aging.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 114:28–34. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ceccarelli V, Ronchetti S, Marchetti MC,
Calvitti M, Riccardi C, Grignani F and Vecchini A: Molecular
mechanisms underlying eicosapentaenoic acid inhibition of HDAC1 and
DNMT expression and activity in carcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1863:1944812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhao D, Gao Y, Su Y, Zhou Y, Yang T, Li Y,
Wang Y, Sun Y, Chen L, Zhang F, et al: Oroxylin A regulates cGAS
DNA hypermethylation induced by methionine metabolism to promote
HSC senescence. Pharmacol Res. 187:1065902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
van der Wijst MG, Venkiteswaran M, Chen H,
Xu GL, Plösch T and Rots MG: Local chromatin microenvironment
determines DNMT activity: From DNA methyltransferase to DNA
demethylase or DNA dehydroxymethylase. Epigenetics. 10:671–676.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wolffgramm J, Buchmuller B, Palei S,
Muñoz-López Á, Kanne J, Janning P, Schweiger MR and Summerer D:
Light-activation of DNA-methyltransferases. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
60:13507–13512. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Correa LO, Jordan MS and Carty SA: DNA
methylation in T-cell development and differentiation. Crit Rev
Immunol. 40:135–156. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lee PP, Fitzpatrick DR, Beard C, Jessup
HK, Lehar S, Makar KW, Pérez-Melgosa M, Sweetser MT, Schlissel MS,
Nguyen S, et al: A critical role for Dnmt1 and DNA methylation in T
cell development, function, and survival. Immunity. 15:763–774.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ktena YP, Koldobskiy MA, Barbato MI, Fu
HH, Luznik L, Llosa NJ, Haile A, Klein OR, Liu C, Gamper CJ and
Cooke KR: Donor T cell DNMT3a regulates alloreactivity in mouse
models of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Clin Invest.
132:e1580472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lu CH, Wu CJ, Chan CC, Nguyen DT, Lin KR,
Lin SJ, Chen LC, Yen JJ and Kuo ML: DNA methyltransferase inhibitor
promotes human CD4+CD25hFOXP3+
regulatory T lymphocyte induction under suboptimal TCR stimulation.
Front Immunol. 7:4882016.
|
|
71
|
Lv Q, Shi C, Qiao S, Cao N, Guan C, Dai Y
and Wei Z: Alpinetin exerts anti-colitis efficacy by activating
AhR, regulating miR-302/DNMT-1/CREB signals, and therefore
promoting Treg differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 9:8902018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ehrlich M: DNA hypermethylation in
disease: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Epigenetics.
14:1141–1163. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ellinger J, El Kassem N, Heukamp LC,
Matthews S, Cubukluoz F, Kahl P, Perabo FG, Müller SC, von Ruecker
A and Bastian PJ: Hypermethylation of cell-free serum DNA indicates
worse outcome in patients with bladder cancer. J Urol. 179:346–352.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Marsit CJ, Karagas MR, Danaee H, Liu M,
Andrew A, Schned A, Nelson HH and Kelsey KT: Carcinogen exposure
and gene promoter hypermethylation in bladder cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 27:112–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Yates DR, Rehman I, Abbod MF, Meuth M,
Cross SS, Linkens DA, Hamdy FC and Catto JW: Promoter
hypermethylation identifies progression risk in bladder cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:2046–2053. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Thompson D, Lawrentschuk N and Bolton D:
New approaches to targeting epigenetic regulation in bladder
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15:18562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nunes SP, Henrique R, Jerónimo C and
Paramio JM: DNA methylation as a therapeutic target for bladder
cancer. Cells. 9:18502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wang R and Liu X: Epigenetic regulation of
prostate cancer. Genes Dis. 7:606–613. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang Z, Chu B, Tu Y, Li L, Chen D, Huang
S, Huang W, Fan W, Li Q, Zhang C, et al: Dual inhibitors of DNMT
and HDAC remodels the immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer
and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy. Pharmacol Res.
206:1072712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang JH, Zeng Z, Sun J, Chen Y and Gao X:
A novel small-molecule antagonist enhances the sensitivity of
osteosarcoma to cabozantinib in vitro and in vivo by targeting
DNMT-1 correlated with disease severity in human patients.
Pharmacol Res. 173:1058692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li KK, Li F, Li QS, Yang K and Jin B: DNA
methylation as a target of epigenetic therapeutics in cancer.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:242–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Nagaraju GP, Wu C, Merchant N, Chen Z,
Lesinski GB and El-Rayes BF: Epigenetic effects of inhibition of
heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) in human pancreatic and colon cancer.
Cancer Lett. 402:110–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Manara MC, Valente S, Cristalli C,
Nicoletti G, Landuzzi L, Zwergel C, Mazzone R, Stazi G, Arimondo
PB, Pasello M, et al: A quinoline-based DNA methyltransferase
inhibitor as a possible adjuvant in osteosarcoma therapy. Mol
Cancer Ther. 17:1881–1892. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Jin T, Hao J and Fan D: Nicotine induces
aberrant hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes in pancreatic
epithelial ductal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 499:934–940.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bazzichetto C, Conciatori F, Pallocca M,
Falcone I, Fanciulli M, Cognetti F, Milella M and Ciuffreda L: PTEN
as a prognostic/predictive biomarker in cancer: An unfulfilled
promise? Cancers (Basel). 11:4352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Carbajo-Garcia MC, Corachán A,
Segura-Benitez M, Monleón J, Escrig J, Faus A, Pellicer A, Cervelló
I and Ferrero H: 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine inhibits cell
proliferation, extracellular matrix formation and Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in human uterine leiomyomas. Reprod Biol Endocrinol.
19:1062021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Bechtel W, McGoohan S, Zeisberg EM, Müller
GA, Kalbacher H, Salant DJ, Müller CA, Kalluri R and Zeisberg M:
Methylation determines fibroblast activation and fibrogenesis in
the kidney. Nat Med. 16:544–550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kato M and Natarajan R: Epigenetics and
epigenomics in diabetic kidney disease and metabolic memory. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 15:327–345. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bowden SA, Rodger EJ, Chatterjee A, Eccles
MR and Stayner C: Recent discoveries in epigenetic modifications of
polycystic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 22:133272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Marumo T, Yagi S, Kawarazaki W, Nishimoto
M, Ayuzawa N, Watanabe A, Ueda K, Hirahashi J, Hishikawa K, Sakurai
H, et al: Diabetes induces aberrant DNA methylation in the proximal
tubules of the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:2388–2397. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sidler M, Aitken KJ, Jiang JX, Yadav P,
Lloyd E, Ibrahim M, Choufani S, Weksberg R and Bägli D: Inhibition
of DNA methylation during chronic obstructive bladder disease
(COBD) improves function, pathology and expression. Sci Rep.
11:173072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li Y, Luo Q, Li Z, Wang Y, Zhu C, Li T and
Li X: Long non-coding RNA IRAIN inhibits VEGFA expression via
enhancing its DNA methylation leading to tumor suppression in renal
carcinoma. Front Oncol. 10:10822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Huang YQ, Guan H, Liu CH, Liu DC, Xu B,
Jiang L, Lin ZX and Chen M: Association between RASSF1A promoter
methylation and renal cell cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis.
Genet Mol Res. 15:gmr.150269942016.
|
|
94
|
Bayarsaihan D: Epigenetic mechanisms in
inflammation. J Dent Res. 90:9–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Bradley MS, Burke EE, Grenier C, Amundsen
CL, Murphy SK and Siddiqui NY: A genome-scale DNA methylation study
in women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.
Neurourol Urodyn. 37:1485–1493. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Tolg C and Bägli DJ: Uropathogenic
Escherichia coli infection: Potential importance of epigenetics.
Epigenomics. 4:229–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Emam M, Cánovas A, Islas-Trejo AD, Fonseca
PAS, Medrano JF and Mallard B: Transcriptomic profiles of
monocyte-derived macrophages in response to Escherichia coli is
associated with the host genetics. Sci Rep. 10:2712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tolg C, Sabha N, Cortese R, Panchal T,
Ahsan A, Soliman A, Aitken KJ, Petronis A and Bägli DJ:
Uropathogenic E. coli infection provokes epigenetic downregulation
of CDKN2A (p16INK4A) in uroepithelial cells. Lab Invest.
91:825–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Tatemichi M, Hata H, Tazawa H and Nakadate
T: Lipopolysaccharide induces aberrant hypermethylation of Hic-1 in
mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking p53 gene. Anticancer Res.
28:2101–2108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yang RB, Mark MR, Gray A, Huang A, Xie MH,
Zhang M, Goddard A, Wood WI, Gurney AL and Godowski PJ: Toll-like
receptor-2 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular signalling.
Nature. 395:284–288. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Valinluck V and Sowers LC:
Inflammation-mediated cytosine damage: A mechanistic link between
inflammation and the epigenetic alterations in human cancers.
Cancer Res. 67:5583–5586. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ding H, Chen J, Su M, Lin Z, Zhan H, Yang
F, Li W, Xie J, Huang Y, Liu X, et al: BDNF promotes activation of
astrocytes and microglia contributing to neuroinflammation and
mechanical allodynia in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. J
Neuroinflammation. 17:192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Haldar S, Dru C, Mishra R, Tripathi M,
Duong F, Angara B, Fernandez A, Arditi M and Bhowmick NA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors mediate DNA damage repair in ameliorating
hemorrhagic cystitis. Sci Rep. 6:392572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Choi IS, Yu K, Kim J, De Guzman E,
Weisenberger DJ, Oghamian S, Kim HJ, Lee KH, Carroll C, Trinh BN,
et al: Alterations in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation
patterns of Calca, Timp3, Mmp2, and Igf2r are associated with
chronic cystitis in a cyclophosphamide-induced mouse model.
Urology. 82:253.e9–e15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Mennuni S, Rubattu S, Pierelli G, Tocci G,
Fofi C and Volpe M: Hypertension and kidneys: Unraveling complex
molecular mechanisms underlying hypertensive renal damage. J Hum
Hypertens. 28:74–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Tomaszewski M and Itoh H: ISH2022KYOTO
hypertension zero declaration. Cardiovasc Res. 119:e1362023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC):
Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in
treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201
population-representative studies with 104 million participants.
Lancet. 398:957–980. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Pinheiro LC and Oliveira-Paula GH: Sources
and effects of oxidative stress in hypertension. Curr Hypertens
Rev. 16:166–180. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Sepassi L, Quiroz Y,
Ni Z, Wallace DC and Vaziri ND: Association of mitochondrial SOD
deficiency with salt-sensitive hypertension and accelerated renal
senescence. J Appl Physiol (1985). 102:255–260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Godin N, Liu F, Lau GJ, Brezniceanu ML,
Chénier I, Filep JG, Ingelfinger JR, Zhang SL and Chan JS: Catalase
overexpression prevents hypertension and tubular apoptosis in
angiotensinogen transgenic mice. Kidney Int. 77:1086–1097. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Chen Y, Li X, Wang S, Miao R and Zhong J:
Targeting iron metabolism and ferroptosis as novel therapeutic
approaches in cardiovascular diseases. Nutrients. 15:5912023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Vaziri ND, Lin CY, Farmand F and Sindhu
RK: Superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and
NADPH oxidase in lead-induced hypertension. Kidney Int. 63:186–194.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Pushpakumar S, Ren L, Juin SK, Majumder S,
Kulkarni R and Sen U: Methylation-dependent antioxidant-redox
imbalance regulates hypertensive kidney injury in aging. Redox
Biol. 37:1017542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Cencioni C, Spallotta F, Martelli F,
Valente S, Mai A, Zeiher AM and Gaetano C: Oxidative stress and
epigenetic regulation in ageing and age-related diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:17643–17663. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Miyoshi M, Sato M, Saito K, Otani L,
Shirahige K, Miura F, Ito T, Jia H and Kato H: Maternal protein
restriction alters the renal ptger1 DNA methylation state in SHRSP
offspring. Nutrients. 10:14362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Jia H, Miyoshi M, Li X, Furukawa K, Otani
L, Shirahige K, Miura F, Ito T and Kato H: The epigenetic legacy of
maternal protein restriction: Renal ptger1 DNA methylation changes
in hypertensive rat offspring. Nutrients. 15:39572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the International diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157:1078432019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Lin E and Erickson KF: Payer mix among
patients receiving dialysis. JAMA. 324:900–901. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, Sharma
K, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Zoungas S, Rossing P, Groop PH and Cooper ME:
Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150182015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Sun G, Reddy MA, Yuan H, Lanting L, Kato M
and Natarajan R: Epigenetic histone methylation modulates fibrotic
gene expression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:2069–2080. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Schlosser P, Tin A, Matias-Garcia PR, Thio
CHL, Joehanes R, Liu H, Weihs A, Yu Z, Hoppmann A,
Grundner-Culemann F, et al: Meta-analyses identify DNA methylation
associated with kidney function and damage. Nat Commun.
12:71742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Smyth LJ, Dahlström EH, Syreeni A, Kerr K,
Kilner J, Doyle R, Brennan E, Nair V, Fermin D, Nelson RG, et al:
Epigenome-wide meta-analysis identifies DNA methylation biomarkers
associated with diabetic kidney disease. Nat Commun. 13:78912022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
He C, Wang D, Wang R, Huang Y, Huang X,
Shen S, Lv J and Wu M: Epigallocatechin gallate induces the
demethylation of actinin alpha 4 to inhibit diabetic nephropathy
renal fibrosis via the NF-KB signaling pathway in vitro. Dose
Response. 20:155932582211057042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Zhang L, Zhang Q, Liu S, Chen Y, Li R, Lin
T, Yu C, Zhang H, Huang Z, Zhao X, et al: DNA methyltransferase 1
may be a therapy target for attenuating diabetic nephropathy and
podocyte injury. Kidney Int. 92:140–153. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Peng R, Liu H, Peng H, Zhou J, Zha H, Chen
X, Zhang L, Sun Y, Yin P, Wen L, et al: Promoter hypermethylation
of let-7a-3 is relevant to its down-expression in diabetic
nephropathy by targeting UHRF1. Gene. 570:57–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhou J, Peng R, Li T, Luo X, Peng H, Zha
H, Yin P, Wen L and Zhang Z: A potentially functional polymorphism
in the regulatory region of let-7a-2 is associated with an
increased risk for diabetic nephropathy. Gene. 527:456–461. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Lane BM, Murray S, Benson K, Bierzynska A,
Chryst-Stangl M, Wang L, Wu G, Cavalleri G, Doyle B, Fennelly N, et
al: A rare autosomal dominant variant in regulator of calcineurin
type 1 (RCAN1) gene confers enhanced calcineurin activity and may
cause FSGS. J Am Soc Nephrol. 32:1682–1695. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Li H, Zhang W, Zhong F, Das GC, Xie Y, Li
Z, Cai W, Jiang G, Choi J, Sidani M, et al: Epigenetic regulation
of RCAN1 expression in kidney disease and its role in podocyte
injury. Kidney Int. 94:1160–1176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Hasan NS, Gamal El Dine H, Kamel SA, Hamed
M, Youssef RN, Mahmoud Hassan E, Abdelrahman AH, Musa NI, Ali A and
Awadallah E: Association of genetic and epigenetic changes of
insulin like growth factor binding protein-1 in Egyptian patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
200:1106772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Yang XH, Cao RF, Yu Y, Sui M, Zhang T, Xu
JY and Wang XM: A study on the correlation between MTHFR promoter
methylation and diabetic nephropathy. Am J Transl Res. 8:4960–4967.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Yang XH, Zhang BL, Zhang XM, Tong JD, Gu
YH, Guo LL and Jin HM: EGCG attenuates renal damage via reversing
Klotho hypermethylation in diabetic db/db mice and HK-2 cells. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2020:60927152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Tomson CRV, Cheung AK, Mann JFE, Chang TI,
Cushman WC, Furth SL, Hou FF, Knoll GA, Muntner P, Pecoits-Filho R,
et al: Management of blood pressure in patients with chronic kidney
disease not receiving dialysis: Synopsis of the 2021 KDIGO clinical
practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 174:1270–1281. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Ying M, Shao X, Qin H, Yin P, Lin Y, Wu J,
Ren J and Zheng Y: Disease burden and epidemiological trends of
chronic kidney disease at the global, regional, national levels
from 1990 to 2019. Nephron. 148:113–123. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Ko YA, Mohtat D, Suzuki M, Park AS,
Izquierdo MC, Han SY, Kang HM, Si H, Hostetter T, Pullman JM, et
al: Cytosine methylation changes in enhancer regions of core
pro-fibrotic genes characterize kidney fibrosis development. Genome
Biol. 14:R1082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Morgado-Pascual JL, Marchant V,
Rodrigues-Diez R, Dolade N, Suarez-Alvarez B, Kerr B, Valdivielso
JM, Ruiz-Ortega M and Rayego-Mateos S: Epigenetic modification
mechanisms involved in inflammation and fibrosis in renal
pathology. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:29310492018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Panizo S, Martinez-Arias L, Alonso-Montes
C, Cannata P, Martín-Carro B, Fernández-Martín JL, Naves-Díaz M,
Carrillo-López N and Cannata-Andía JB: Fibrosis in chronic kidney
disease: Pathogenesis and consequences. Int J Mol Sci. 22:4082021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Yin S, Zhang Q, Yang J, Lin W, Li Y, Chen
F and Cao W: TGFβ-incurred epigenetic aberrations of miRNA and DNA
methyltransferase suppress Klotho and potentiate renal fibrosis.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1864:1207–1216. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Xiao X, Wang W, Guo C, Wu J, Zhang S, Shi
H, Kwon S, Chen J and Dong Z: Hypermethylation leads to the loss of
HOXA5, resulting in JAG1 expression and NOTCH signaling
contributing to kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 106:98–114. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Li Y, Chen F, Wei A, Bi F, Zhu X, Yin S,
Lin W and Cao W: Klotho recovery by genistein via promoter histone
acetylation and DNA demethylation mitigates renal fibrosis in mice.
J Mol Med (Berl). 97:541–552. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Takiguchi M, Achanzar WE, Qu W, Li G and
Waalkes MP: Effects of cadmium on DNA-(Cytosine-5)
methyltransferase activity and DNA methylation status during
cadmium-induced cellular transformation. Exp Cell Res. 286:355–365.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zhang C, Liang Y, Lei L, Zhu G, Chen X,
Jin T and Wu Q: Hypermethylations of RASAL1 and KLOTHO is
associated with renal dysfunction in a Chinese population
environmentally exposed to cadmium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
271:78–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Azuma M, Koyama D, Kikuchi J, Yoshizawa H,
Thasinas D, Shiizaki K, Kuro-o M, Furukawa Y and Kusano E: Promoter
methylation confers kidney-specific expression of the Klotho gene.
FASEB J. 26:4264–4274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Chen Z, Li G and Liu J: Autonomic
dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: Implications for
pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurobiol Dis.
134:1047002020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Wang W, Zhao X, Shao Y, Duan X, Wang Y, Li
J, Li J, Li D, Li X and Wong J: Mutation-induced DNMT1 cleavage
drives neurodegenerative disease. Sci Adv. 7:eabe85112021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ye S, Zhong J, Huang J, Chen L, Yi L, Li
X, Lv J, Miao J, Li H, Chen D and Li C: Protective effect of
plastrum testudinis extract on dopaminergic neurons in a
Parkinson's disease model through DNMT1 nuclear translocation and
SNCA's methylation. Biomed Pharmacother. 141:1118322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Patel HD, Gupta M, Joice GA, Srivastava A,
Alam R, Allaf ME and Pierorazio PM: Clinical stage migration and
survival for renal cell carcinoma in the United States. Eur Urol
Oncol. 2:343–348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Turajlic S, Swanton C and Boshoff C:
Kidney cancer: The next decade. J Exp Med. 215:2477–2479. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Lin RK and Wang YC: Dysregulated
transcriptional and post-translational control of DNA
methyltransferases in cancer. Cell Biosci. 4:462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Arai E and Kanai Y: Genetic and epigenetic
alterations during renal carcinogenesis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
4:58–73. 2010.
|
|
150
|
Bahadoram S, Davoodi M, Hassanzadeh S,
Bahadoram M, Barahman M and Mafakher L: Renal cell carcinoma: An
overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. G Ital
Nefrol. 39:2022–vol3. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Christoph F, Kempkensteffen C, Weikert S,
Köllermann J, Krause H, Miller K, Schostak M and Schrader M:
Methylation of tumour suppressor genes APAF-1 and DAPK-1 and in
vitro effects of demethylating agents in bladder and kidney cancer.
Br J Cancer. 95:1701–1707. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Christoph F, Weikert S, Kempkensteffen C,
Krause H, Schostak M, Köllermann J, Miller K and Schrader M:
Promoter hypermethylation profile of kidney cancer with new
proapoptotic p53 target genes and clinical implications. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:5040–5046. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Liu Q, Jin J, Ying J, Cui Y, Sun M, Zhang
L, Fan Y, Xu B and Zhang Q: Epigenetic inactivation of the
candidate tumor suppressor gene ASC/TMS1 in human renal cell
carcinoma and its role as a potential therapeutic target.
Oncotarget. 6:22706–22723. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Joosten SC, Deckers IA, Aarts MJ, Hoeben
A, van Roermund JG, Smits KM, Melotte V, van Engeland M and
Tjan-Heijnen VC: Prognostic DNA methylation markers for renal cell
carcinoma: A systematic review. Epigenomics. 9:1243–1257. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Mo S, Su Z, Heng B, Chen W, Shi L, Du X
and Lai C: SFRP1 promoter methylation and renal carcinoma risk: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nippon Med Sch. 85:78–86.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Morris MR, Ricketts CJ, Gentle D, McRonald
F, Carli N, Khalili H, Brown M, Kishida T, Yao M, Banks RE, et al:
Genome-wide methylation analysis identifies epigenetically
inactivated candidate tumour suppressor genes in renal cell
carcinoma. Oncogene. 30:1390–1401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Peters I, Eggers H, Atschekzei F,
Hennenlotter J, Waalkes S, Tränkenschuh W, Grosshennig A,
Merseburger AS, Stenzl A, Kuczyk MA and Serth J: GATA5 CpG island
methylation in renal cell cancer: A potential biomarker for
metastasis and disease progression. BJU Int. 110:E144–E152. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Peters I, Gebauer K, Dubrowinskaja N,
Atschekzei F, Kramer MW, Hennenlotter J, Tezval H, Abbas M, Scherer
R, Merseburger AS, et al: GATA5 CpG island hypermethylation is an
independent predictor for poor clinical outcome in renal cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:1523–1530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Rohilla S, Singh M, Priya S, Almalki WH,
Haniffa SM, Subramaniyan V, Fuloria S, Fuloria NK, Sekar M, Singh
SK, et al: Exploring the mechanical perspective of a new anti-tumor
agent: Melatonin. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 42:1–16. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Ahmad AE, Hirata H,
Kawakami K, Shahryari V, Saini S, Tanaka Y, Dahiya AV, Khatri G and
Dahiya R: BTG3 tumor suppressor gene promoter demethylation,
histone modification and cell cycle arrest by genistein in renal
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 30:662–670. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Wang L, Lu B, He M, Wang Y, Wang Z and Du
L: Prostate cancer incidence and mortality: Global status and
temporal trends in 89 countries from 2000 to 2019. Front Public
Health. 10:8110442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Chang AJ, Autio KA, Roach M III and Scher
HI: High-risk prostate cancer-classification and therapy. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 11:308–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Jemal A, Culp MB, Ma J, Islami F and
Fedewa SA: Prostate cancer incidence 5 years after US preventive
services task force recommendations against screening. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 113:64–71. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
164
|
Zargar H, van den Bergh R, Moon D,
Lawrentschuk N, Costello A and Murphy D: The impact of the United
States preventive services task force (USPTSTF) recommendations
against prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing on PSA testing in
Australia. BJU Int. 119:110–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Curry SJ, Krist AH and Owens DK: Annual
report to the nation on the status of cancer, part II: Recent
changes in prostate cancer trends and disease characteristics.
Cancer. 125:317–318. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Hatakeyama S, Yoneyama T, Tobisawa Y and
Ohyama C: Recent progress and perspectives on prostate cancer
biomarkers. Int J Clin Oncol. 22:214–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
167
|
Jerónimo C, Bastian PJ, Bjartell A,
Carbone GM, Catto JW, Clark SJ, Henrique R, Nelson WG and Shariat
SF: Epigenetics in prostate cancer: Biologic and clinical
relevance. Eur Urol. 60:753–766. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Zhao SG, Chen WS, Li H, Foye A, Zhang M,
Sjöström M, Aggarwal R, Playdle D, Liao A, Alumkal JJ, et al: The
DNA methylation landscape of advanced prostate cancer. Nat Genet.
52:778–789. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Zhao Y, Hu X, Yu H, Liu X, Sun H and Shao
C: Alternations of gene expression in PI3K and AR pathways and DNA
methylation features contribute to metastasis of prostate cancer.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:4362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Ummanni R, Jost E, Braig M, Lohmann F,
Mundt F, Barett C, Schlomm T, Sauter G, Senff T, Bokemeyer C, et
al: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (UCHL1) is a potential
tumour suppressor in prostate cancer and is frequently silenced by
promoter methylation. Mol Cancer. 10:1292011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Chen Y, Li J, Yu X, Li S, Zhang X, Mo Z
and Hu Y: APC gene hypermethylation and prostate cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Hum Genet. 21:929–935.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Zhang SQ, Zhang GQ and Zhang L:
Correlation between methylation of the E-cadherin gene and
malignancy of prostate cancer. Genet Mol Res.
15:gmr.150280462016.
|
|
173
|
Miyauchi T, Takahashi M, Mitsuzuka K,
Saiki Y, Okubo T, Vertino PM, Goto A, Arai Y, Horii A and Fukushige
S: Aberrant hypermethylation-mediated suppression of PYCARD is
extremely frequent in prostate cancer with gleason score ≥7. Dis
Markers. 2021:88589052021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Singal R, Ferdinand L, Reis IM and
Schlesselman JJ: Methylation of multiple genes in prostate cancer
and the relationship with clinicopathological features of disease.
Oncol Rep. 12:631–637. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Zhang W, Zeng S, Gong L, Zhang D and Hu X:
Gene methylation status in focus of advanced prostate cancer
diagnostics and improved individual outcomes. Transl Androl Urol.
12:1813–1826. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
van der Pol Y, Moldovan N, Ramaker J,
Bootsma S, Lenos KJ, Vermeulen L, Sandhu S, Bahce I, Pegtel DM,
Wong SQ, et al: The landscape of cell-free mitochondrial DNA in
liquid biopsy for cancer detection. Genome Biol. 24:2292023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Woodson K, O'Reilly KJ, Ward DE, Walter J,
Hanson J, Walk EL and Tangrea JA: CD44 and PTGS2 methylation are
independent prognostic markers for biochemical recurrence among
prostate cancer patients with clinically localized disease.
Epigenetics. 1:183–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Boiron M: Genetics and cellular cellular
biology of cancer. Pathol Biol (Paris). 38:765–767. 1990.In French.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Zorn CS, Wojno KJ, McCabe MT, Kuefer R,
Gschwend JE and Day ML: 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine delays
androgen-independent disease and improves survival in the
transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate mouse model of
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2136–2143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Shang D, Liu Y, Liu Q, Zhang F, Feng L, Lv
W and Tian Y: Synergy of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (DAC) and
paclitaxel in both androgen-dependent and -independent prostate
cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 278:82–87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Thibault A, Figg WD, Bergan RC, Lush RM,
Myers CE, Tompkins A, Reed E and Samid D: A phase II study of
5-aza-2′deoxycytidine (decitabine) in hormone independent
metastatic (D2) prostate cancer. Tumori. 84:87–89. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Teoh JYC, Huang J, Ko WYK, Lok V, Choi P,
Ng CF, Sengupta S, Mostafid H, Kamat AM, Black PC, et al: Global
trends of bladder cancer incidence and mortality, and their
associations with tobacco use and gross domestic product per
capita. Eur Urol. 78:893–906. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP,
Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW and
Kurth K: Predicting recurrence and progression in individual
patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A
combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur
Urol. 49:466–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Dobruch J and Oszczudlowski M: Bladder
cancer: Current challenges and future directions. Medicina
(Kaunas). 57:7492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Scher MB, Elbaum MB, Mogilevkin Y, Hilbert
DW, Mydlo JH, Sidi AA, Adelson ME, Mordechai E and Trama JP:
Detecting DNA methylation of the BCL2, CDKN2A and NID2 genes in
urine using a nested methylation specific polymerase chain reaction
assay to predict bladder cancer. J Urol. 188:2101–2107. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Bai ZJ, Liu Q, Wang XS and Liu WY: APC
promoter methylation is correlated with development and progression
of bladder cancer, but not linked to overall survival: A
meta-analysis. Neoplasma. 66:470–480. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Kawamoto K, Enokida H, Gotanda T, Kubo H,
Nishiyama K, Kawahara M and Nakagawa M: p16INK4a and p14ARF
methylation as a potential biomarker for human bladder cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 339:790–796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Jahed M, Ebadi N, Mivehchi M, Majidizadeh
T, Shahshanipour M, Asgari M, Ghadakzadeh S and Hosseini SA: MGMT
hypermethylation and BCL-2 overexpression associated with
superficial bladder cancer and recurrence. Cancer Biomark.
16:627–632. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Bayramov B, Gunes S, Buyukalpelli R, Aydin
O and Henkel R: Promoter methylation analysis of CDH1 and p14ARF
genes in patients with urothelial bladder cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:4189–4196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Chen F, Huang T, Ren Y, Wei J, Lou Z, Wang
X, Fan X, Chen Y, Weng G and Yao X: Clinical significance of CDH13
promoter methylation as a biomarker for bladder cancer: A
meta-analysis. BMC Urol. 16:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Dai L, Ma C, Zhang Z, Zeng S, Liu A, Tang
S, Ren Q, Sun Y and Xu C: DAPK promoter methylation and bladder
cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
11:e01672282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Wang D, Qiu Z and Wu C: Diagnostic value
of the combination of DAPK methylation in urinary sediment and B
ultrasound for recurrent urinary bladder cancer. World J Surg
Oncol. 21:2672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Han SY, Iliopoulos D, Druck T, Guler G,
Grubbs CJ, Pereira M, Zhang Z, You M, Lubet RA, Fong LY and Huebner
K: CpG methylation in the Fhit regulatory region: Relation to Fhit
expression in murine tumors. Oncogene. 23:3990–3998. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Kandimalla R, van Tilborg AA and Zwarthoff
EC: DNA methylation-based biomarkers in bladder cancer. Nat Rev
Urol. 10:327–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Costa VL, Henrique R, Danielsen SA,
Duarte-Pereira S, Eknaes M, Skotheim RI, Rodrigues A, Magalhães JS,
Oliveira J, Lothe RA, et al: Three epigenetic biomarkers, GDF15,
TMEFF2, and VIM, accurately predict bladder cancer from DNA-based
analyses of urine samples. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5842–5851. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Sun J, Chen Z, Zhu T, Yu J, Ma K, Zhang H,
He Y, Luo X and Zhu J: Hypermethylated SFRP1, but none of other
nine genes 'informative' for western countries, is valuable for
bladder cancer detection in Mainland China. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 135:1717–1727. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Gao Q, Chen F, Zhang L, Wei A, Wang Y, Wu
Z and Cao W: Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase aberrations
reinstates antioxidant aging suppressors and ameliorates renal
aging. Aging Cell. 21:e135262022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
199
|
Li XT, Song JW, Zhang ZZ, Zhang MW, Liang
LR, Miao R, Liu Y, Chen YH, Liu XY and Zhong JC: Sirtuin 7
mitigates renal ferroptosis, fibrosis and injury in hypertensive
mice by facilitating the KLF15/Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med.
193:459–473. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Zhao Y, Fan X, Wang Q, Zhen J, Li X, Zhou
P, Lang Y, Sheng Q, Zhang T, Huang T, et al: ROS promote
hyper-methylation of NDRG2 promoters in a DNMTS-dependent manner:
Contributes to the progression of renal fibrosis. Redox Biol.
62:1026742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Ming S, Tian J, Ma K, Pei C, Li L, Wang Z,
Fang Z, Liu M, Dong H, Li W, et al: Oxalate-induced apoptosis
through ERS-ROS-NF-κB signalling pathway in renal tubular
epithelial cell. Mol Med. 28:882022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
202
|
Doi S, Zou Y, Togao O, Pastor JV, John GB,
Wang L, Shiizaki K, Gotschall R, Schiavi S, Yorioka N, et al:
Klotho inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1)
signaling and suppresses renal fibrosis and cancer metastasis in
mice. J Biol Chem. 286:8655–8665. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Brandt S, Bernhardt A, Häberer S, Wolters
K, Gehringer F, Reichardt C, Krause A, Geffers R, Kahlfuß S, Jeron
A, et al: Comparative analysis of acute kidney injury models and
related fibrogenic responses: Convergence on methylation patterns
regulated by cold shock protein. Cells. 13:3672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Miao J, Liu J, Niu J, Zhang Y, Shen W, Luo
C, Liu Y, Li C, Li H, Yang P, et al: Wnt/β-catenin/RAS signaling
mediates age-related renal fibrosis and is associated with
mitochondrial dysfunction. Aging Cell. 18:e130042019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Edeling M, Ragi G, Huang S, Pavenstadt H
and Susztak K: Developmental signalling pathways in renal fibrosis:
The roles of Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog. Nat Rev Nephrol. 12:426–439.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Wu J, Wei Y, Li T, Lin L, Yang Z and Ye L:
DNA methylation-mediated lowly expressed AOX1 promotes cell
migration and invasion of prostate cancer. Urol Int. 107:517–525.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Ding M, Wang Q, Zhu W, Chang J, Liao H and
Xiao G: DNA methylation-mediated low expression of ZNF582 promotes
the proliferation, migration, and invasion of clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Clin Exp Nephrol. 27:24–31. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Heichman KA and Warren JD: DNA methylation
biomarkers and their utility for solid cancer diagnostics. Clin
Chem Lab Med. 50:1707–1721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Du Y, Xu Y, Guo X, Tan C, Zhu X, Liu G,
Lyu X and Bei C: Methylation-regulated tumor suppressor gene PDE7B
promotes HCC invasion and metastasis through the PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. BMC Cancer. 24:6242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Lopez-Serra P and Esteller M: DNA
methylation-associated silencing of tumor-suppressor microRNAs in
cancer. Oncogene. 31:1609–1622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
211
|
Zhu L, Tang N, Hang H, Zhou Y, Dong J,
Yang Y, Mao L, Qiu Y, Fu X and Cao W: Loss of Claudin-1 incurred by
DNMT aberration promotes pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer
Lett. 586:2166112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Lam TW, Tong JH, To KF, Chan A, Liew CT,
Lai PB and Wong N: Correlative analysis of DNA methyltransferase
expression and promoter hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 3:271–277.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Nishiyama A and Nakanishi M: Navigating
the DNA methylation landscape of cancer. Trends Genet.
37:1012–1027. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
O'Hagan HM, Wang W, Sen S, Destefano
Shields C, Lee SS, Zhang YW, Clements EG, Cai Y, Van Neste L,
Easwaran H, et al: Oxidative damage targets complexes containing
DNA methyltransferases, SIRT1, and polycomb members to promoter CpG
Islands. Cancer Cell. 20:606–619. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Xiao X, Chen M, Sang Y, Xue J, Jiang K,
Chen Y, Zhang L, Yu S, Lv W, Li Y, et al: Methylation-mediated
silencing of ATF3 promotes thyroid cancer progression by regulating
prognostic genes in the MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways. Thyroid.
33:1441–1454. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Zhu S, Xu H, Chen R, Shen Q, Yang D, Peng
H, Tong J and Fu Q: DNA methylation and miR-92a-3p-mediated
repression of HIP1R promotes pancreatic cancer progression by
activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 27:788–802. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Jin Y, Cui D, Ren J, Wang K, Zeng T and
Gao L: CACNA2D3 is downregulated in gliomas and functions as a
tumor suppressor. Mol Carcinog. 56:945–959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
van Es JH, Haegebarth A, Kujala P,
Itzkovitz S, Koo BK, Boj SF, Korving J, van den Born M, van
Oudenaarden A, Robine S and Clevers H: A critical role for the Wnt
effector Tcf4 in adult intestinal homeostatic self-renewal. Mol
Cell Biol. 32:1918–1927. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Yao H, Ashihara E and Maekawa T: Targeting
the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 15:873–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Yang XZ, Cheng TT, He QJ, Lei ZY, Chi J,
Tang Z, Liao QX, Zhang H, Zeng LS and Cui SZ: LINC01133 as ceRNA
inhibits gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-106a-3p to
regulate APC expression and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol Cancer.
17:1262018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Korinek V, Barker N, Morin PJ, van Wichen
D, de Weger R, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Clevers H: Constitutive
transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin-Tcf complex in APC-/-
colon carcinoma. Science. 275:1784–1787. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Nishisho I, Nakamura Y, Miyoshi Y, Miki Y,
Ando H, Horii A, Koyama K, Utsunomiya J, Baba S and Hedge P:
Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer
patients. Science. 253:665–669. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Yuan TL and Cantley LC: PI3K pathway
alterations in cancer: Variations on a theme. Oncogene.
27:5497–5510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Stemke-Hale K, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch
A, Neve RM, Kuo WL, Davies M, Carey M, Hu Z, Guan Y, Sahin A, et
al: An integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of PIK3CA, PTEN,
and AKT mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6084–6091. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Jouali F, Marchoudi N, Talbi S, Bilal B,
El Khasmi M, Rhaissi H and Fekkak J: Detection of PIK3/AKT pathway
in Moroccan population with triple negative breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 18:9002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y and
Mills GB: Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug
discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:988–1004. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Park JI: MAPK-ERK pathway. Int J Mol Sci.
24:96662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Ullah R, Yin Q, Snell AH and Wan L:
RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer evolution and treatment. Semin Cancer
Biol. 85:123–154. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Gurbuz V, Sozen S, Bilen CY and Konac E:
miR-148a, miR-152 and miR-200b promote prostate cancer metastasis
by targeting DNMT1 and PTEN expression. Oncol Lett. 22:8052021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Bhattacharyya S, Feferman L and Tobacman
JK: Dihydrotestosterone inhibits arylsulfatase B and Dickkopf Wnt
signaling pathway inhibitor (DKK)-3 leading to enhanced Wnt
signaling in prostate epithelium in response to stromal Wnt3A.
Prostate. 79:689–700. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Kardooni H, Gonzalez-Gualda E, Stylianakis
E, Saffaran S, Waxman J and Kypta RM: CRISPR-mediated reactivation
of DKK3 expression attenuates TGF-β signaling in prostate cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 10:1652018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Lodygin D, Epanchintsev A, Menssen A,
Diebold J and Hermeking H: Functional epigenomics identifies genes
frequently silenced in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 65:4218–4227.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Bhattacharyya S, Feferman L and Tobacman
JK: Chondroitin sulfatases differentially regulate Wnt signaling in
prostate stem cells through effects on SHP2, phospho-ERK1/2, and
Dickkopf Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor (DKK3). Oncotarget.
8:100242–100260. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Arai E, Kanai Y, Ushijima S, Fujimoto H,
Mukai K and Hirohashi S: Regional DNA hypermethylation and DNA
methyltransferase (DNMT) 1 protein overexpression in both renal
tumors and corresponding nontumorous renal tissues. Int J Cancer.
119:288–296. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Liao F, Liao Z, Zhang T, Jiang W, Zhu P,
Zhao Z, Shi H, Zhao D, Zhou N and Huang X: ECFC-derived exosomal
THBS1 mediates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in distraction
osteogenesis via the PI3K/AKT/ERK pathway. J Orthop Translat.
37:12–22. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Rubinek T and Wolf I: The role of
alpha-Klotho as a universal tumor suppressor. Vitam Horm.
101:197–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Wang Y and Sun Z: Current understanding of
Klotho. Ageing Res Rev. 8:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
239
|
Chen B, Ma X, Liu S, Zhao W and Wu J:
Inhibition of lung cancer cells growth, motility and induction of
apoptosis by Klotho, a novel secreted Wnt antagonist, in a
dose-dependent manner. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1221–1228. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Camilli TC, Xu M, O'Connell MP, Chien B,
Frank BP, Subaran S, Indig FE, Morin PJ, Hewitt SM and Weeraratna
AT: Loss of Klotho during melanoma progression leads to increased
filamin cleavage, increased Wnt5A expression, and enhanced melanoma
cell motility. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 24:175–186. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
241
|
Li X, Lu P, Shao XF, Jiang T, Liu F and Li
G: Klotho regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in vitro
via Wnt/β-catenin pathway and attenuates chronic allograft
dysfunction in a rat renal transplant model. Ann Transplant.
26:e9300662021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
242
|
Prud'homme GJ: Cancer stem cells and novel
targets for antitumor strategies. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2838–2849.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Costa VL, Henrique R, Ribeiro FR, Carvalho
JR, Oliveira J, Lobo F, Teixeira MR and Jerónimo C: Epigenetic
regulation of Wnt signaling pathway in urological cancer.
Epigenetics. 5:343–351. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Henrique R, Ribeiro FR, Fonseca D, Hoque
MO, Carvalho AL, Costa VL, Pinto M, Oliveira J, Teixeira MR,
Sidransky D and Jerónimo C: High promoter methylation levels of APC
predict poor prognosis in sextant biopsies from prostate cancer
patients. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6122–6129. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Rogler A, Kendziorra E, Giedl J, Stoehr C,
Taubert H, Goebell PJ, Wullich B, Stöckle M, Lehmann J, Petsch S,
et al: Functional analyses and prognostic significance of SFRP1
expression in bladder cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
141:1779–1790. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Robertson KD and Jones PA: DNA
methylation: Past, present and future directions. Carcinogenesis.
21:461–467. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Myöhänen SK, Baylin SB and Herman JG:
Hypermethylation can selectively silence individual p16ink4A
alleles in neoplasia. Cancer Res. 58:591–593. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Kucuk O: Cancer biomarkers. Mol Aspects
Med. 45:1–2. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
O'Reilly E, Tuzova AV, Walsh AL, Russell
NM, O'Brien O, Kelly S, Dhomhnallain ON, DeBarra L, Dale CM,
Brugman R, et al: epiCaPture: A urine DNA methylation test for
early detection of aggressive prostate cancer. JCO Precis Oncol.
2019:PO.18.001342019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Mikeska T and Craig JM: DNA methylation
biomarkers: Cancer and beyond. Genes (Basel). 5:821–864. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Mahon KL, Qu W, Devaney J, Paul C,
Castillo L, Wykes RJ, Chatfield MD, Boyer MJ, Stockler MR, Marx G,
et al: Methylated glutathione S-transferase 1 (mGSTP1) is a
potential plasma free DNA epigenetic marker of prognosis and
response to chemotherapy in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Br
J Cancer. 111:1802–1809. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Ibrahim J, Peeters M, Van Camp G and Opde
Beeck K: Methylation biomarkers for early cancer detection and
diagnosis: Current and future perspectives. Eur J Cancer.
178:91–113. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
253
|
Waterhouse RL Jr, Van Neste L, Moses KA,
Barnswell C, Silberstein JL, Jalkut M, Tutrone R, Sylora J, Anglade
R, Murdock M, et al: Evaluation of an epigenetic assay for
predicting repeat prostate biopsy outcome in African American men.
Urology. 128:62–65. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
254
|
Yamagishi M, Kuze Y, Kobayashi S,
Nakashima M, Morishima S, Kawamata T, Makiyama J, Suzuki K, Seki M,
Abe K, et al: Mechanisms of action and resistance in histone
methylation-targeted therapy. Nature. 627:221–228. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Sgro A, Cursons J, Waryah C, Woodward EA,
Foroutan M, Lyu R, Yeoh GCT, Leedman PJ and Blancafort P:
Epigenetic reactivation of tumor suppressor genes with CRISPRa
technologies as precision therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Epigenetics. 15:732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Patra A, Deb M, Dahiya R and Patra SK:
5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine stress response and apoptosis in prostate
cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 2:339–348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
257
|
Issa JP: Decitabine. Curr Opin Oncol.
15:446–451. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Graça I, Sousa EJ, Baptista T, Almeida M,
Ramalho-Carvalho J, Palmeira C, Henrique R and Jerónimo C:
Anti-tumoral effect of the non-nucleoside DNMT inhibitor RG108 in
human prostate cancer cells. Curr Pharm Des. 20:1803–1811. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Wang C, Lei L, Xu Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Xu Y
and Si S: Trichostatin C synergistically interacts with DNMT
inhibitor to induce antineoplastic effect via inhibition of axl in
bladder and lung cancer cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 17:4252024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Laranjeira ABA, Hollingshead MG, Nguyen D,
Kinders RJ, Doroshow JH and Yang SX: DNA damage, demethylation and
anticancer activity of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitors. Sci
Rep. 13:59642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Kim SJ, Cheresh P, Eren M, Jablonski RP,
Yeldandi A, Ridge KM, Budinger GRS, Kim DH, Wolf M, Vaughan DE and
Kamp DW: Klotho, an antiaging molecule, attenuates oxidant-induced
alveolar epithelial cell mtDNA damage and apoptosis. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 313:L16–L26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Yamada Y, Venkadakrishnan VB, Mizuno K,
Bakht M, Ku SY, Garcia MM and Beltran H: Targeting DNA methylation
and B7-H3 in RB1-deficient and neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Sci
Transl Med. 15:eadf67322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Tikoo K, Ali IY, Gupta J and Gupta C:
5-Azacytidine prevents cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity and
potentiates anticancer activity of cisplatin by involving
inhibition of metallothionein, pAKT and DNMT1 expression in
chemical induced cancer rats. Toxicol Lett. 191:158–166. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Hosokawa O, Okabe M, Saito S, Saito T and
Kurasaki M: Protective role of metallothionein on DNA damage in rat
kidney caused by cis-diamminedichloroplatinum. Pharmacol Toxicol.
86:276–282. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Francia G, Green SK, Bocci G, Man S,
Emmenegger U, Ebos JM, Weinerman A, Shaked Y and Kerbel RS:
Down-regulation of DNA mismatch repair proteins in human and murine
tumor spheroids: Implications for multicellular resistance to
alkylating agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1484–1494. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Plumb JA, Strathdee G, Sludden J, Kaye SB
and Brown R: Reversal of drug resistance in human tumor xenografts
by 2′-deoxy-5-azacytidine-induced demethylation of the hMLH1 gene
promoter. Cancer Res. 60:6039–6044. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Dai X, Ren T, Zhang Y and Nan N:
Methylation multiplicity and its clinical values in cancer. Expert
Rev Mol Med. 23:e22021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Ricketts CJ, Hill VK and Linehan WM:
Tumor-specific hypermethylation of epigenetic biomarkers, including
SFRP1, predicts for poorer survival in patients from the TCGA
kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) project. PLoS One.
9:e856212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Peters I, Dubrowinskaja N, Abbas M, Seidel
C, Kogosov M, Scherer R, Gebauer K, Merseburger AS, Kuczyk MA,
Grünwald V and Serth J: DNA methylation biomarkers predict
progression-free and overall survival of metastatic renal cell
cancer (mRCC) treated with antiangiogenic therapies. PLoS One.
9:e914402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Dubrowinskaja N, Gebauer K, Peters I,
Hennenlotter J, Abbas M, Scherer R, Tezval H, Merseburger AS,
Stenzl A, Grünwald V, et al: Neurofilament heavy polypeptide CpG
island methylation associates with prognosis of renal cell
carcinoma and prediction of antivascular endothelial growth factor
therapy response. Cancer Med. 3:300–309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Lou W, Krill D, Dhir R, Becich MJ, Dong
JT, Frierson HF Jr, Isaacs WB, Isaacs JT and Gao AC: Methylation of
the CD44 metastasis suppressor gene in human prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 59:2329–2331. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Kito H, Suzuki H, Ichikawa T, Sekita N,
Kamiya N, Akakura K, Igarashi T, Nakayama T, Watanabe M, Harigaya K
and Ito H: Hypermethylation of the CD44 gene is associated with
progression and metastasis of human prostate cancer. Prostate.
49:110–115. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Yegnasubramanian S, Kowalski J, Gonzalgo
ML, Zahurak M, Piantadosi S, Walsh PC, Bova GS, De Marzo AM, Isaacs
WB and Nelson WG: Hypermethylation of CpG islands in primary and
metastatic human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 64:1975–1986. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Pan Y, Liu G, Zhou F, Su B and Li Y: DNA
methylation profiles in cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Clin Exp
Med. 18:1–14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
275
|
Altucci L and Rots MG: Epigenetic drugs:
From chemistry via biology to medicine and back. Clin Epigenetics.
8:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy.
Nature. 429:457–463. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Cossio FP, Esteller M and Berdasco M:
Towards a more precise therapy in cancer: Exploring epigenetic
complexity. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 57:41–49. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Kondrashov A and Karpova E: Notes on
functional modules in the assembly of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated
epigenetic modifiers. Methods Mol Biol. 2198:401–428. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
279
|
Liang F, Dong Z, Ye J, Hu W, Bhandari RK,
Mai K and Wang X: In vivo DNA methylation editing in zebrafish.
Epigenetics. 18:21923262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|