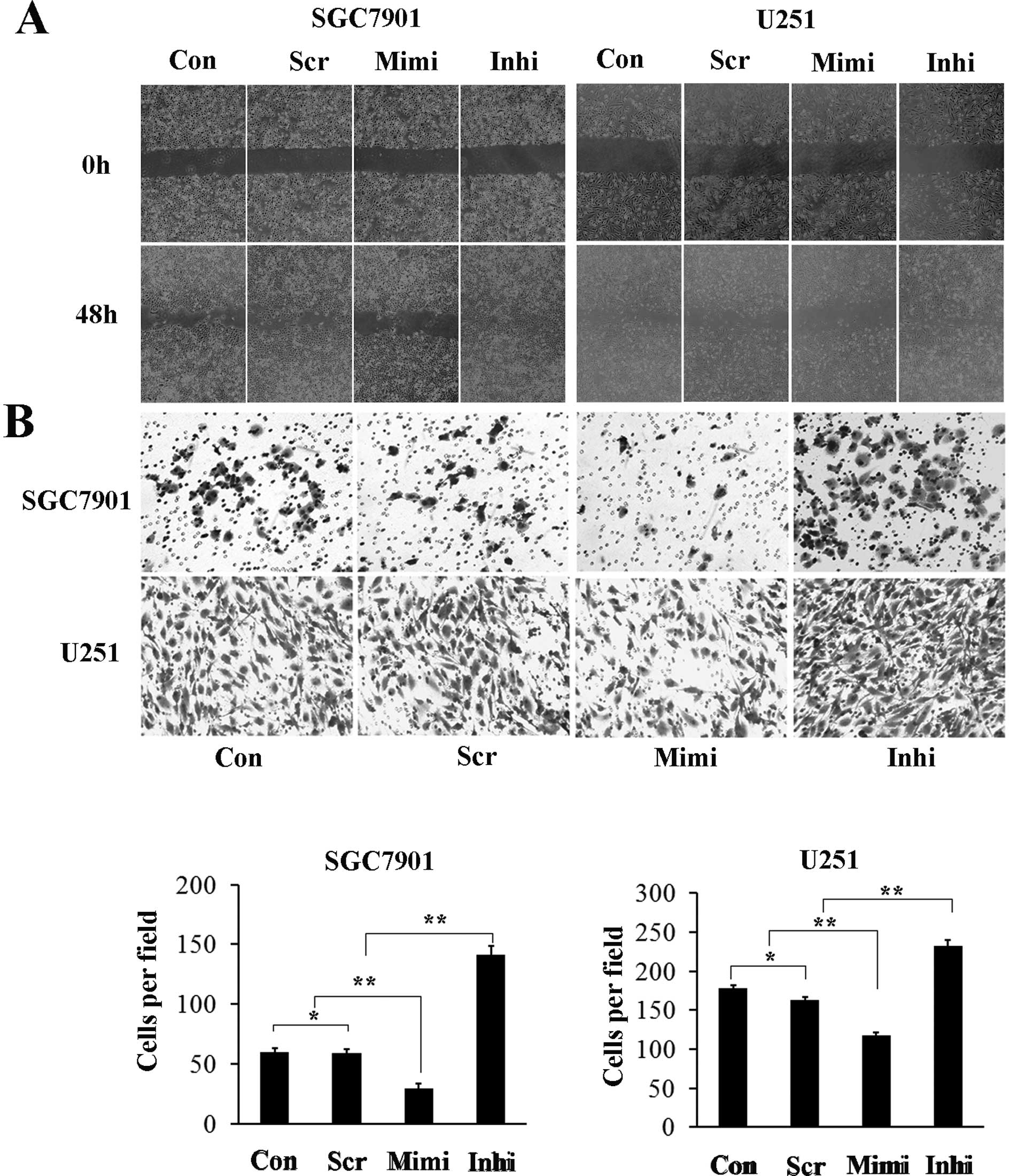
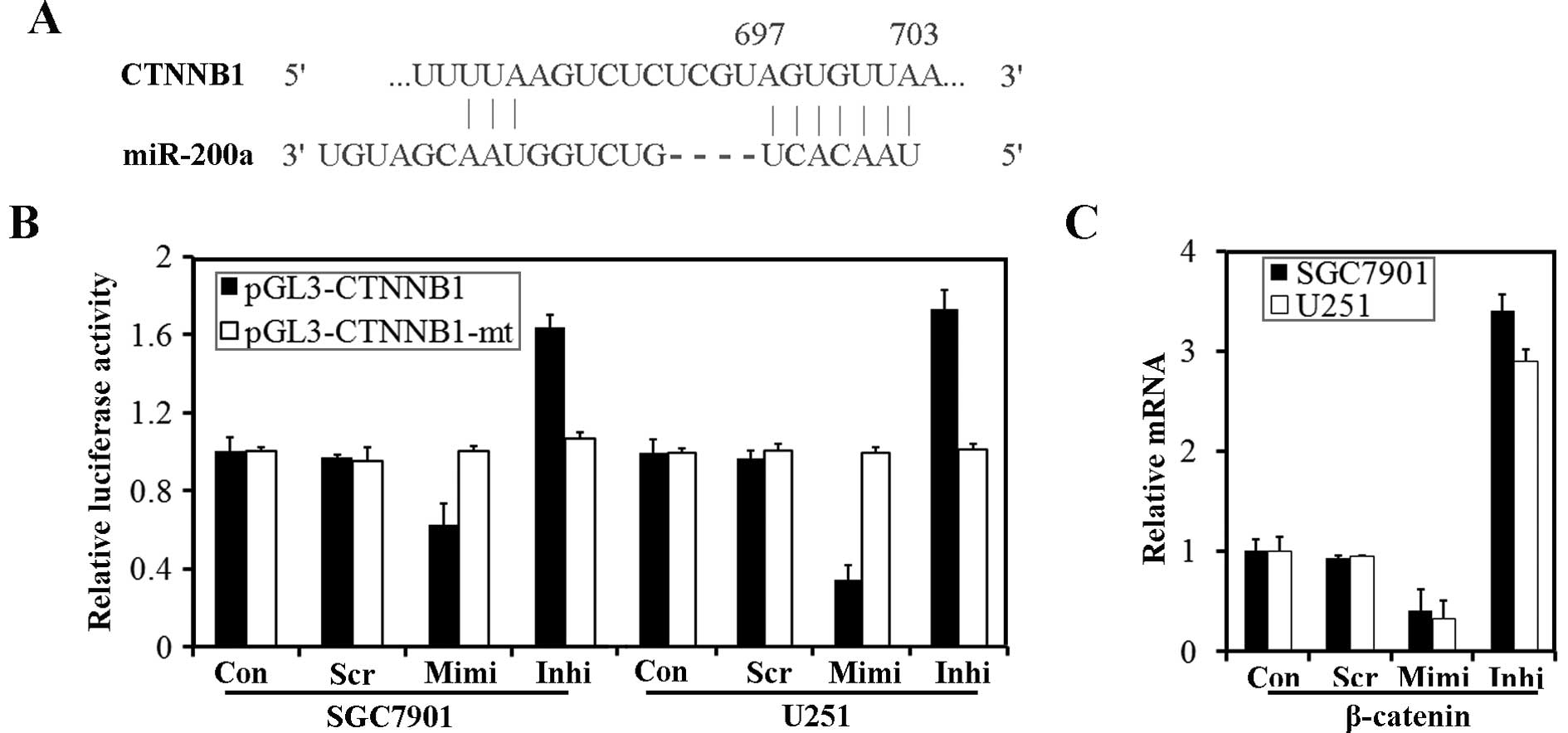
|
1
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006.
|
|
2
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Pinto D, Gregorieff A, Begthel H and
Clevers H: Canonical Wnt signals are essential for homeostasis of
the intestinal epithelium. Genes Dev. 17:1709–1713. 2003.
|
|
4
|
Yang LH, Xu HT, Han Y, et al: Axin
downregulates TCF-4 transcription via beta-catenin, but not p53,
and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells.
Mol Cancer. 9:252010.
|
|
5
|
Sansom OJ, Reed KR, Hayes AJ, et al: Loss
of Apc in vivo immediately perturbs Wnt signaling, differentiation,
and migration. Genes Dev. 18:1385–1390. 2004.
|
|
6
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, et al:
Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by
mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997.
|
|
7
|
Ying Y and Tao Q: Epigenetic disruption of
the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers.
Epigenetics. 4:307–312. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Huang K, Zhang JX, Han L, et al: MicroRNA
roles in beta-catenin pathway. Mol Cancer. 9:2522010.
|
|
10
|
Han L, Yang Y, Yue X, et al: Inactivation
of PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits glioma cell growth through
modulation of beta-catenin-mediated transcription. Brain Res.
1366:9–17. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Brabletz T, Herrmann K, Jung A, Faller G
and Kirchner T: Expression of nuclear beta-catenin and c-myc is
correlated with tumor size but not with proliferative activity of
colorectal adenomas. Am J Pathol. 156:865–870. 2000.
|
|
13
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999.
|
|
14
|
Wu B, Crampton SP and Hughes CC: Wnt
signaling induces matrix metalloproteinase expression and regulates
T cell transmigration. Immunity. 26:227–239. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Xia H, Cheung WK, Sze J, et al: miR-200a
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal to stem-like transition via ZEB2
and beta-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem. 285:36995–37004. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Adam L, Zhong M, Choi W, et al: miR-200
expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth
factor receptor therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5060–5072. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Hiroki E, Akahira J, Suzuki F, et al:
Changes in microRNA expression levels correlate with
clinicopathological features and prognoses in endometrial serous
adenocarcinomas. Cancer Sci. 101:241–249. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Saydam O, Shen Y, Wurdinger T, et al:
Downregulated microRNA-200a in meningiomas promotes tumor growth by
reducing E-cadherin and activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5923–5940. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Wang B, Koh P, Winbanks C, et al: miR-200a
prevents renal fibrogenesis through repression of TGF-beta2
expression. Diabetes. 60:280–287. 2011.
|
|
20
|
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, et al:
miR-200a-mediated downregulation of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially
inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration and
invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:535–541. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008.
|
|
22
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008.
|
|
23
|
Sareddy GR, Panigrahi M, Challa S,
Mahadevan A and Babu PP: Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf
signaling pathway in human astrocytomas. Neurochem Int. 55:307–317.
2009.
|
|
24
|
Yue X, Lan F, Yang W, et al: Interruption
of beta-catenin sup-presses the EGFR pathway by blocking multiple
oncogenic targets in human glioma cells. Brain Res. 1366:27–37.
2010.
|
|
25
|
Svedlund J, Auren M, Sundstrom M, et al:
Aberrant WNT/beta-catenin signaling in parathyroid carcinoma. Mol
Cancer. 9:2942010.
|
|
26
|
Li F, Chong ZZ and Maiese K: Winding
through the WNT pathway during cellular development and demise.
Histol Histopathol. 21:103–124. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Rosano L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, et al:
Endothelin-1 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human
ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:11649–11657. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Vandewalle C, Comijn J, De Craene B, et
al: SIP1/ZEB2 induces EMT by repressing genes of different
epithelial cell-cell junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:6566–6578.
2005.
|
|
29
|
Maeda M, Johnson KR and Wheelock MJ:
Cadherin switching: essential for behavioral but not morphological
changes during an epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition. J Cell Sci.
118:873–887. 2005.
|