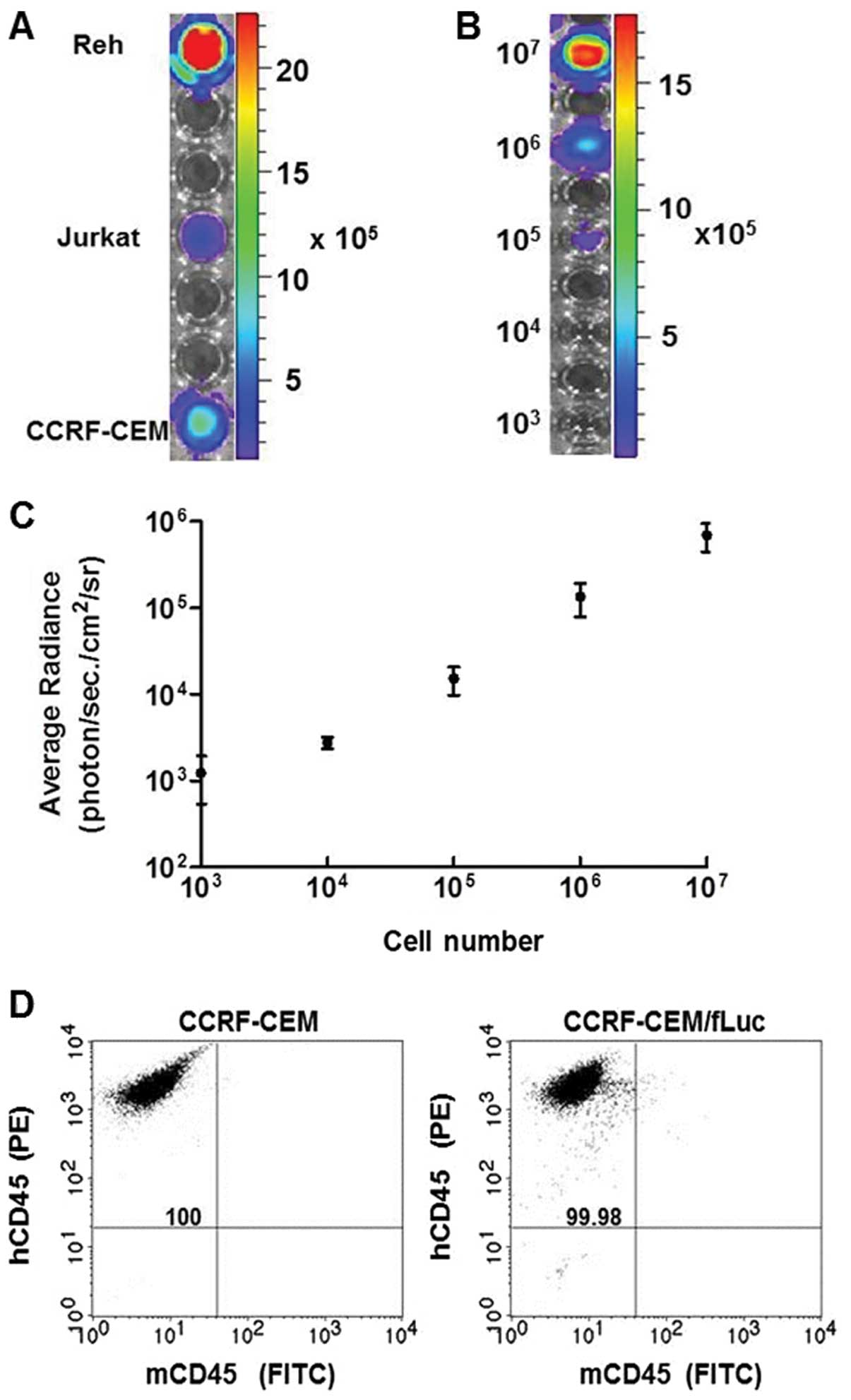
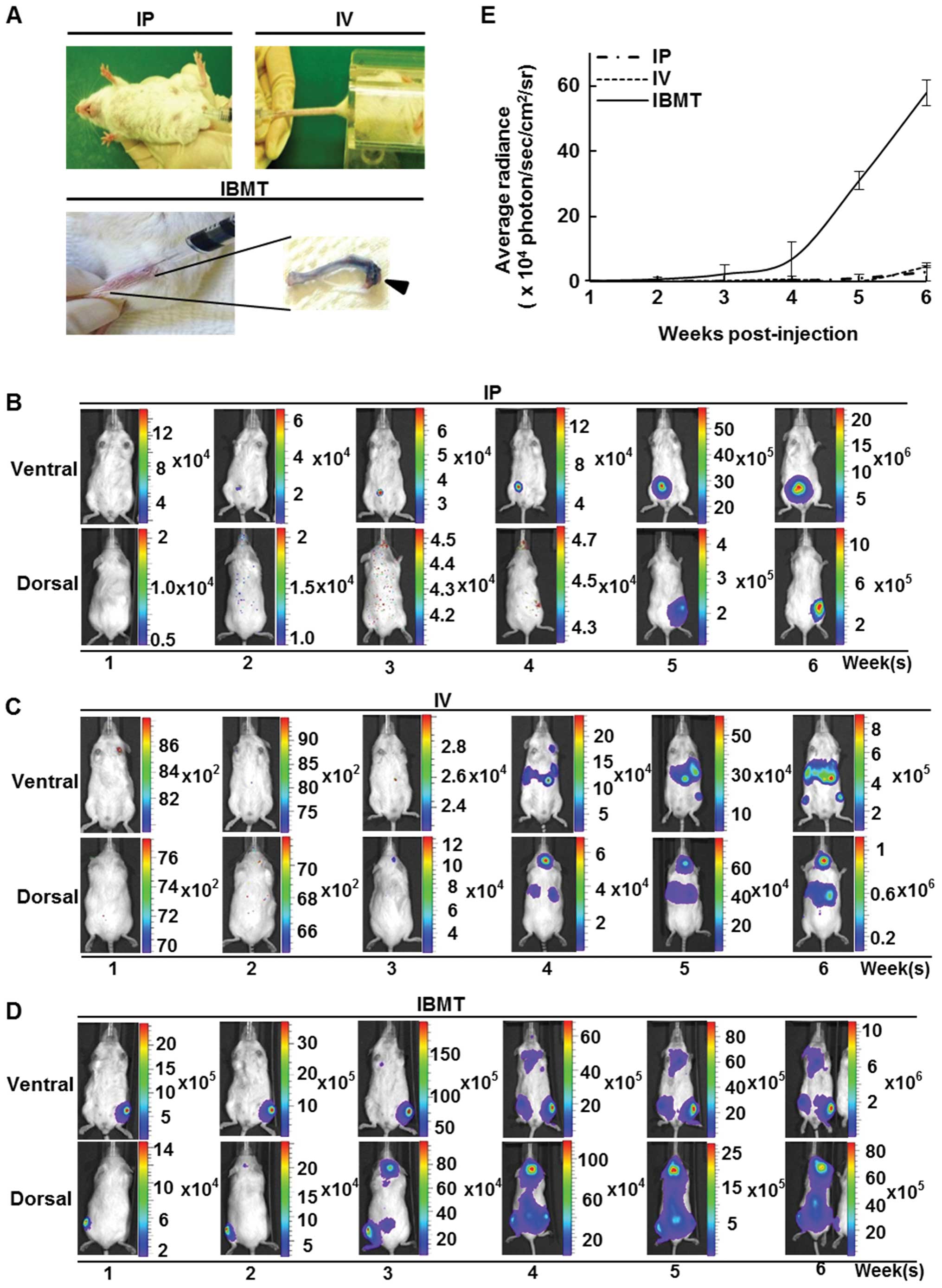
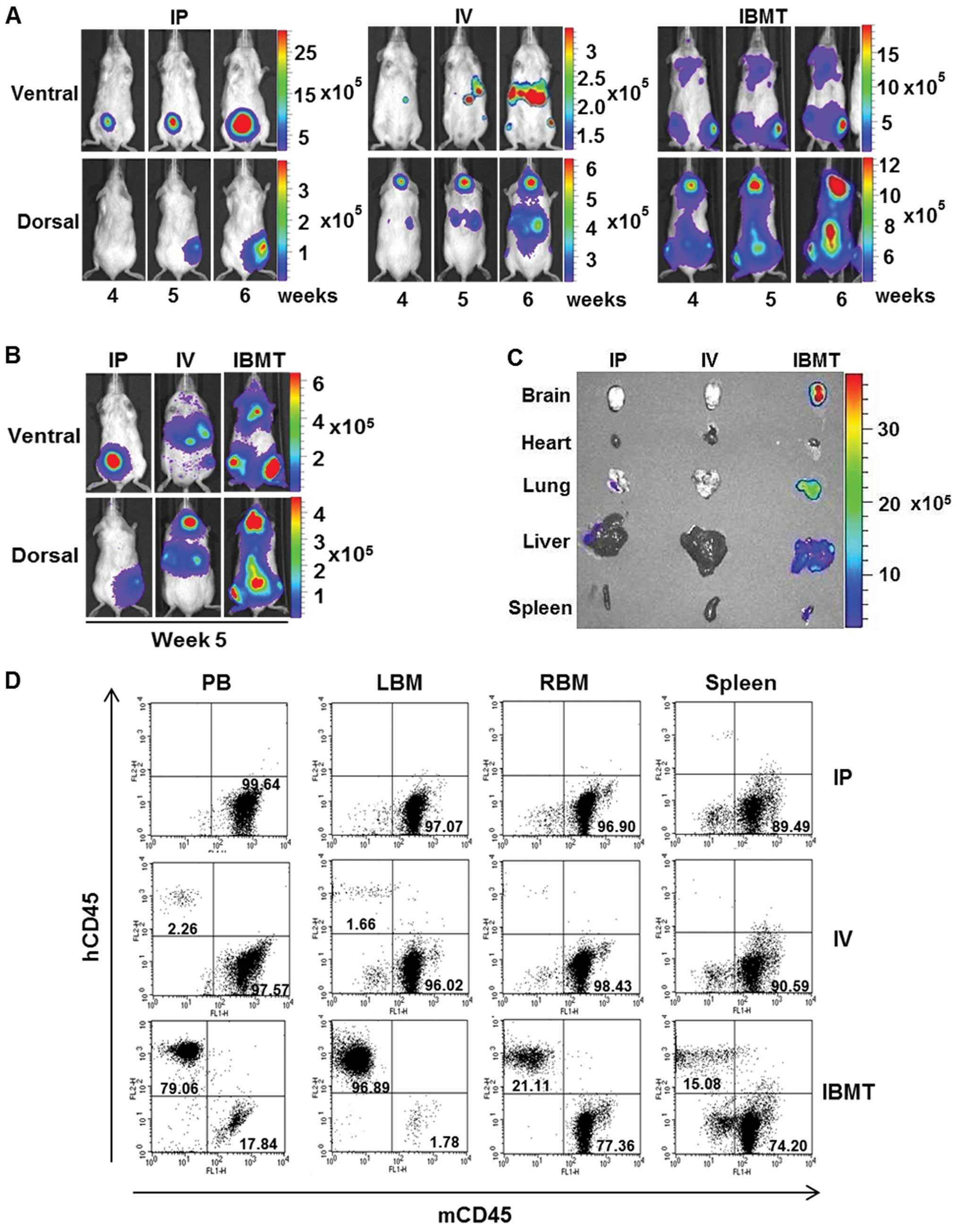
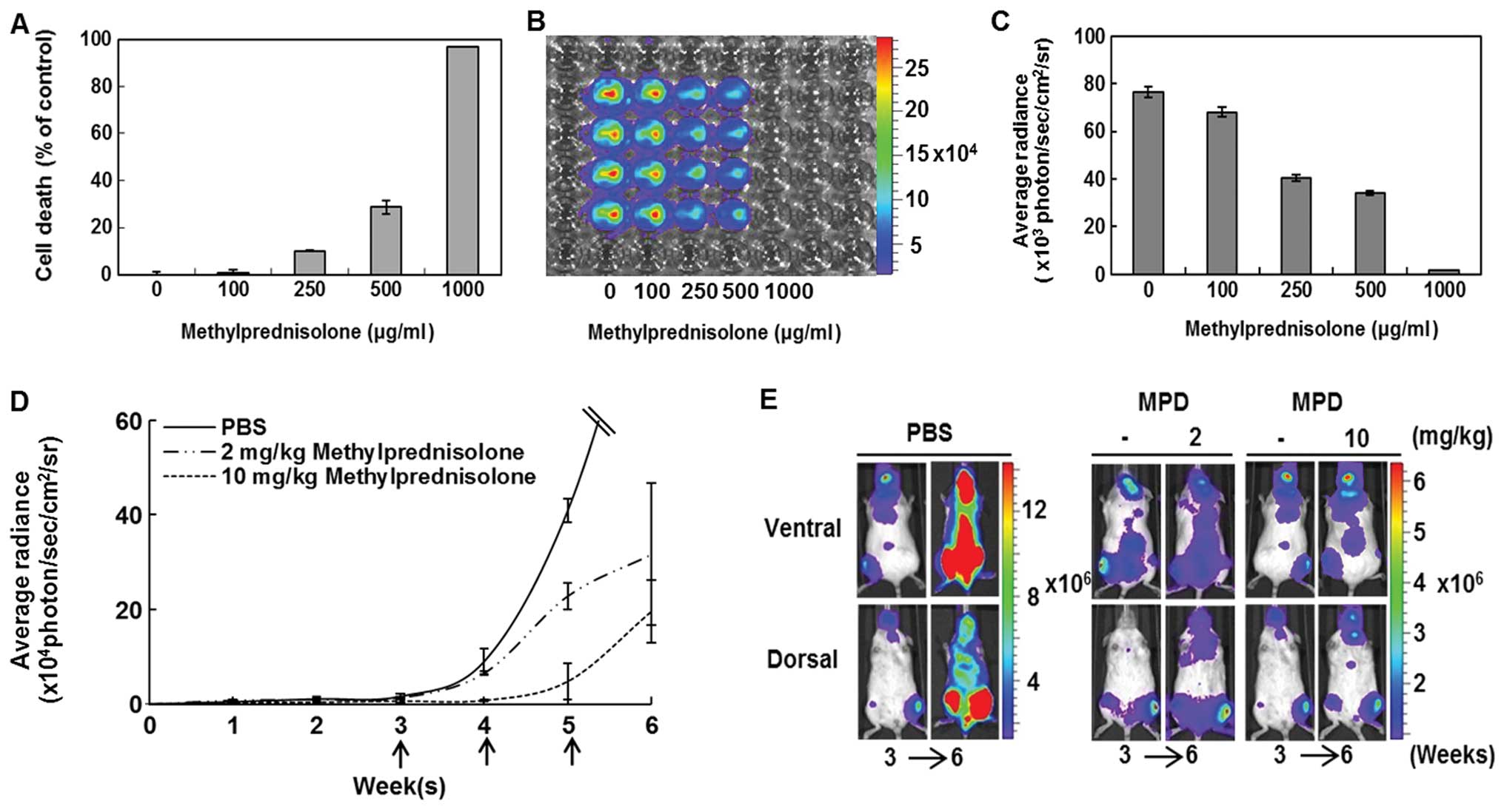
|
1.
|
Seaman ME, Contino G, Bardeesy N and Kelly
KA: Molecular imaging agents: impact on diagnosis and therapeutics
in oncology. Expert Rev Mol Med. 12:e202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Desar IM, van Herpen CM, van Laarhoven HW,
Barentsz JO, Oyen WJ and van der Graaf WT: Beyond RECIST: molecular
and functional imaging techniques for evaluation of response to
targeted therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 35:309–321. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Shu ST, Nadella MV, Dirksen WP, et al: A
novel bioluminescent mouse model and effective therapy for adult
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Res. 67:11859–11866. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Siegers GM, Felizardo TC, Mathieson AM,
Kosaka Y, Wang XH, Medin JA and Keating A: Anti-leukemia activity
of in vitro-expanded human gamma delta T cells in a xenogeneic
Ph+ leukemia model. PLoS One. 6:e167002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Inoue Y, Izawa K, Tojo A, Nomura Y, Sekine
R, Oyaizu N and Ohtomo K: Monitoring of disease progression by
bioluminescence imaging and magnetic resonance imaging in an animal
model of hematologic malignancy. Exp Hematol. 35:407–415. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Bhadri VA, Cowley MJ, Kaplan W, Trahair TN
and Lock RB: Evaluation of the NOD/SCID xenograft model for
glucocorticoid-regulated gene expression in childhood B-cell
precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Genomics. 12:5652011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Nijmeijer BA, Willemze R and Falkenburg
JH: An animal model for human cellular immunotherapy: specific
eradication of human acute lymphoblastic leukemia by cytotoxic T
lymphocytes in NOD/scid mice. Blood. 100:654–660. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Fichtner I, Becker M and Baumgart J:
Antileukaemic activity of treosulfan in xenografted human acute
lymphoblastic leukaemias (ALL). Eur J Cancer. 39:801–807. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lock RB, Liem N, Farnsworth ML, et al: The
nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse
model of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals intrinsic
differences in biologic characteristics at diagnosis and relapse.
Blood. 99:4100–4108. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Nijmeijer BA, Mollevanger P, van
Zelderen-Bhola SL, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Willemze R and Falkenburg JH:
Monitoring of engraftment and progression of acute lymphoblastic
leukemia in individual NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol. 29:322–329.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Inoue Y, Izawa K, Kiryu S, Kobayashi S,
Tojo A and Ohtomo K: Bioluminescent evaluation of the therapeutic
effects of total body irradiation in a murine hematological
malignancy model. Exp Hematol. 36:1634–1641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Jenkins DE, Oei Y, Hornig YS, et al:
Bioluminescent imaging (BLI) to improve and refine traditional
murine models of tumor growth and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis.
20:733–744. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Sipkins DA, Wei X, Wu JW, et al: In vivo
imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for
tumour engraftment. Nature. 435:969–973. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Fragoso R, Pereira T, Wu Y, Zhu Z,
Cabecadas J and Dias S: VEGFR-1 (FLT-1) activation modulates acute
lymphoblastic leukemia localization and survival within the bone
marrow, determining the onset of extramedullary disease. Blood.
107:1608–1616. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ayala F, Dewar R, Kieran M and Kalluri R:
Contribution of bone microenvironment to leukemogenesis and
leukemia progression. Leukemia. 23:2233–2241. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Zhou J, Mauerer K, Farina L and Gribben
JG: The role of the tumor microenvironment in hematological
malignancies and implication for therapy. Front Biosci.
10:1581–1596. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Veiga JP, Costa LF, Sallan SE, Nadler LM
and Cardoso AA: Leukemia-stimulated bone marrow endothelium
promotes leukemia cell survival. Exp Hematol. 34:610–621. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Schmitz M, Breithaupt P, Scheidegger N, et
al: Xenografts of highly resistant leukemia recapitulate the clonal
composition of the leukemogenic compartment. Blood. 118:1854–1864.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Silva A, Laranjeira AB, Martins LR, et al:
IL-7 contributes to the progression of human T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemias. Cancer Res. 71:4780–4789. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL, Wang S,
Jablonski E and Sipkins DA: Leukemic cells create bone marrow
niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor
cells. Science. 322:1861–1865. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Ninomiya M, Abe A, Katsumi A, et al:
Homing, proliferation and survival sites of human leukemia cells in
vivo in immunodeficient mice. Leukemia. 21:136–142. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Rauch D, Gross S, Harding J, Niewiesk S,
Lairmore M, Piwnica-Worms D and Ratner L: Imaging spontaneous
tumorigenesis: inflammation precedes development of peripheral NK
tumors. Blood. 113:1493–1500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Inoue Y, Tojo A, Sekine R, et al: In vitro
validation of biolumine-scent monitoring of disease progression and
therapeutic response in leukaemia model animals. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 33:557–565. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lassailly F, Griessinger E and Bonnet D:
‘Microenvironmental contaminations’ induced by fluorescent
lipophilic dyes used for non-invasive in vitro and in vivo cell
tracking. Blood. 115:5347–5354. 2010.
|
|
26.
|
Tsai HJ, Kobayashi S, Izawa K, et al:
Bioimaging analysis of nuclear factor-kappaB activity in
Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
reveals its synergistic upregulation by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-stimulated changes to the microenvironment. Cancer
Sci. 102:2014–2021. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Liem NL, Papa RA, Milross CG, et al:
Characterization of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
xenograft models for the preclinical evaluation of new therapies.
Blood. 103:3905–3914. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Zhou B, Ju SG, Ju SW, Xie F and Zhang XG:
Establishment of human acute monocytic leukemia model in severe
combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice and the analysis of
pathological changes. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
23:501–503. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Mezzanotte L, Fazzina R, Michelini E,
Tonelli R, Pession A, Branchini B and Roda A: In vivo
bioluminescence imaging of murine xenograft cancer models with a
red-shifted thermostable luciferase. Mol Imaging Biol. 12:406–414.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Samuels AL, Peeva VK, Papa RA, et al:
Validation of a mouse xenograft model system for gene expression
analysis of human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. BMC Genomics.
11:2562010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Komeno Y, Kitaura J, Watanabe-Okochi N, et
al: AID-induced T-lymphoma or B-leukemia/lymphoma in a mouse BMT
model. Leukemia. 24:1018–1024. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Barabe F, Kennedy JA, Hope KJ and Dick JE:
Modeling the initiation and progression of human acute leukemia in
mice. Science. 316:600–604. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Hoyos V, Savoldo B, Quintarelli C, et al:
Engineering CD19-specific T lymphocytes with interleukin-15 and a
suicide gene to enhance their anti-lymphoma/leukemia effects and
safety. Leukemia. 24:1160–1170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Messinger Y, Chelstrom L, Gunther R and
Uckun FM: Selective homing of human leukemic B-cell precursors to
specific lymphohematopoietic microenvironments in SCID mice: a role
for the beta 1 integrin family surface adhesion molecules VLA-4 and
VLA-5. Leuk Lymphoma. 23:61–69. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Cesano A, O’Connor R, Lange B, Finan J,
Rovera G and Santoli D: Homing and progression patterns of
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemias in severe combined
immunodeficiency mice. Blood. 77:2463–2474. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Biagi E, Bambacioni F, Gaipa G, Casati C,
Golay J, Biondi A and Introna M: Efficient lentiviral transduction
of primary human acute myelogenous and lymphoblastic leukemia
cells. Haematologica. 86:13–16. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Konopleva M, Konoplev S, Hu W, Zaritskey
AY, Afanasiev BV and Andreeff M: Stromal cells prevent apoptosis of
AML cells by up-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins. Leukemia.
16:1713–1724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Horisberger MA: A method for prolonged
survival of primary cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
42:143–148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Barrett DM, Seif AE, Carpenito C, et al:
Noninvasive bioluminescent imaging of primary patient acute
lymphoblastic leukemia: a strategy for preclinical modeling. Blood.
118:e112–117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|