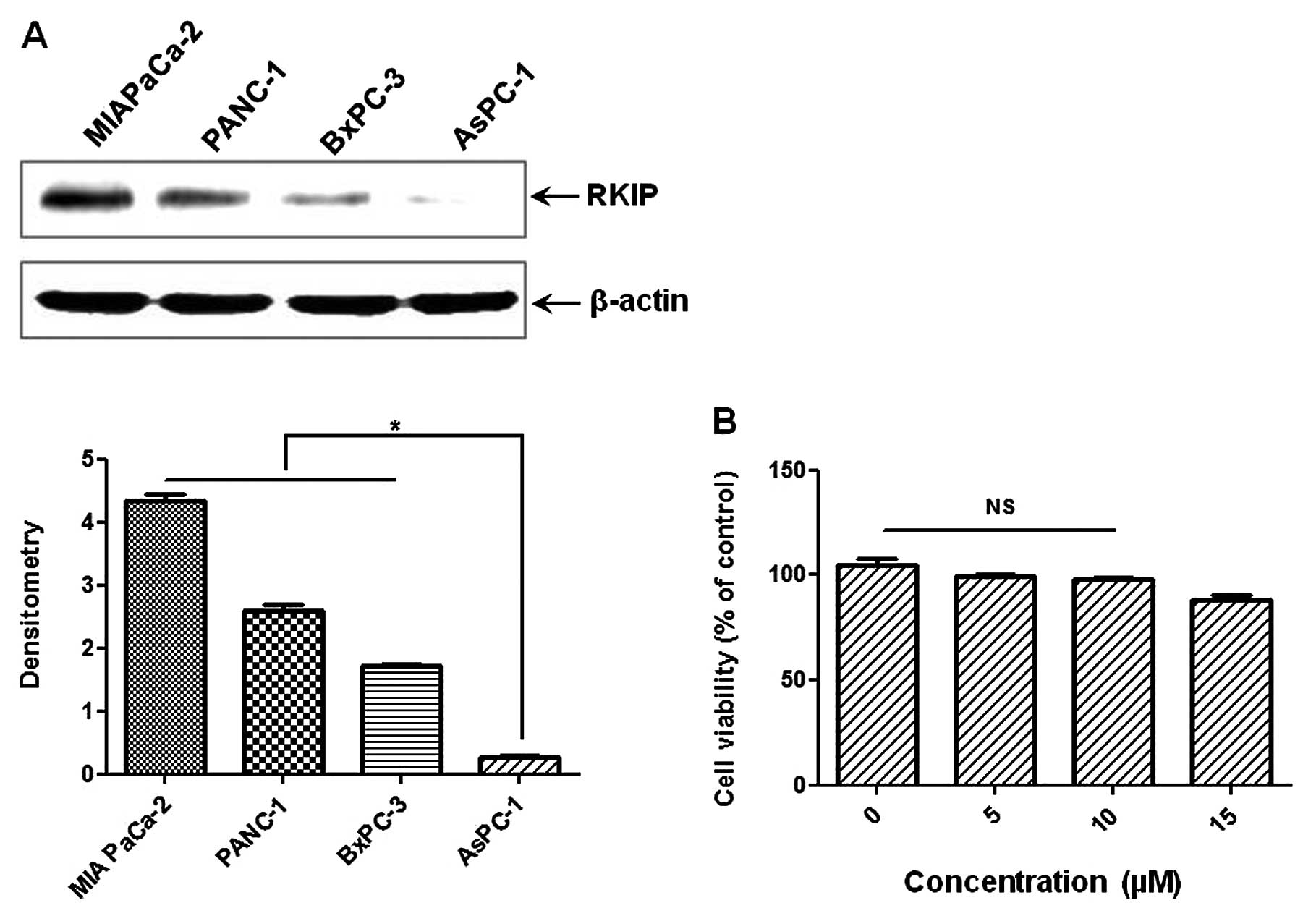
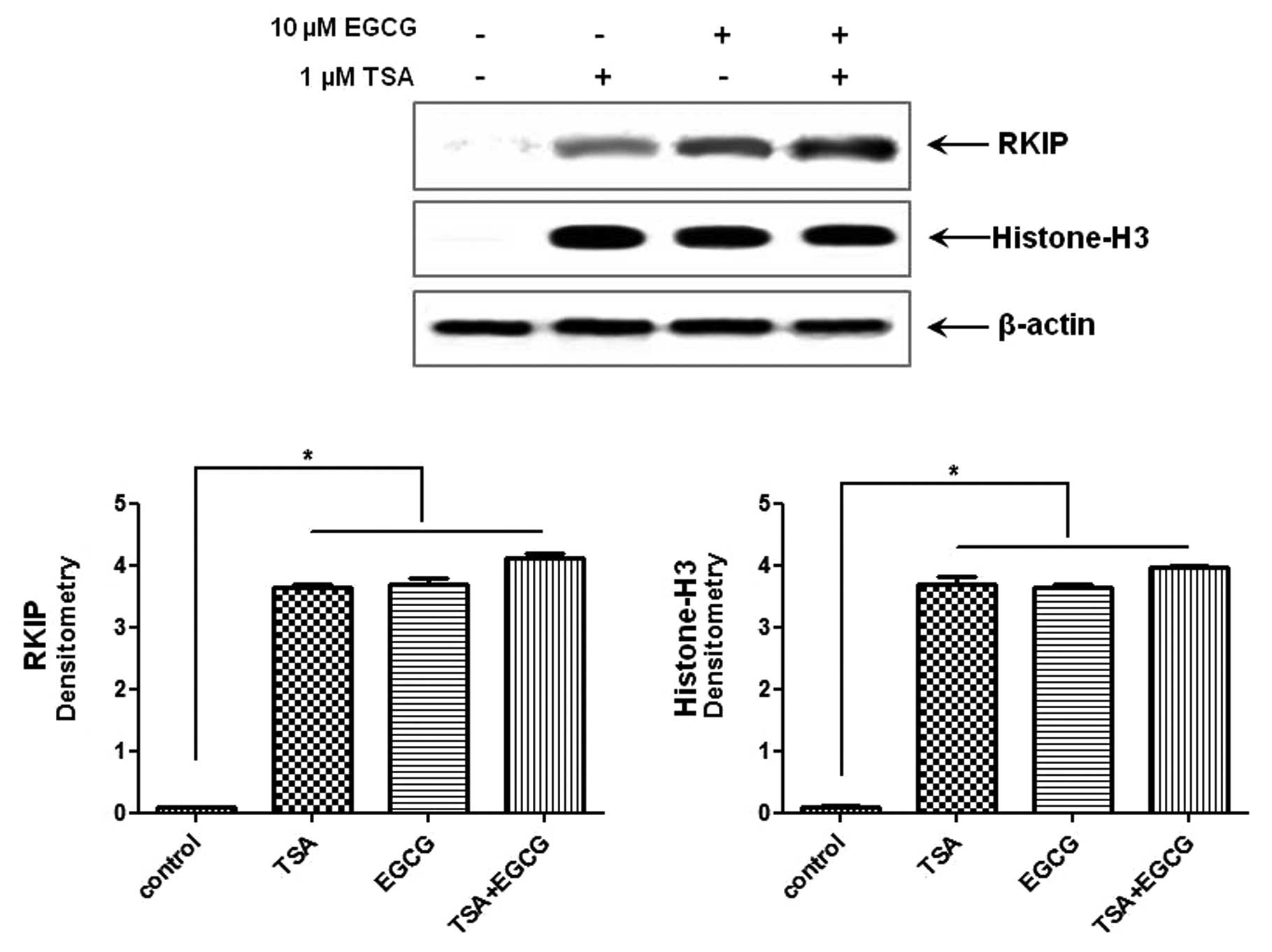
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Korea Ministry of Health and Welfare:
Annual report of cancer statistics in Korea in 2008. http://mw.go.kr.
2011
|
|
3.
|
Warshaw AL, Gu ZY, Wittenberg J and
Waltman AC: Preoperative staging and assessment of resectability of
pancreatic cancer. Arch Surg. 125:230–233. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Whitcomb DC: Inflammation and Cancer V.
Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G315–G319. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Tang H, Park S, Sun SC, Trumbly R, Ren G,
Tsung E and Yeung KC: RKIP inhibits NF-kappaB in cancer cells by
regulating upstream signaling components of the IkappaB kinase
complex. FEBS Lett. 4:662–668. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yeung K, Janosch P, McFerran B, Rose DW,
Mischak H, Sedivy JM and Kolch W: Mechanism of suppression of the
Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the raf
kinase inhibitor protein. Mol Cell Biol. 20:3079–3085. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Barbera MJ, Puig I, Dominguez D,
Julien-Grille S, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Peiró S, Baulida J, Francí C,
Dedhar S, Larue L and García de Herreros A: Regulation of Snail
transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor
cells. Oncogene. 23:7345–7354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Munshi HG and Stack MS: Reciprocal
interactions between adhesion receptor signaling and MMP
regulation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:45–56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Gregory PD, Wagner K and Horz W: Histone
acetylation and chromatin remodeling. Exp Cell Res. 265:195–202.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Struhl K: Histone acetylation and
transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev. 12:599–606. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Gray SG and Teh BT: Histone
acetylation/deacetylation and cancer: an ‘open’ and ‘shut’ case?
Curr Mol Med. 1:401–429. 2001.
|
|
12.
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to NF-κB.
Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004.
|
|
13.
|
Choi KC, Jung MG, Lee YH, Yoon JC, Kwon
SH, Kang HB, Kim MJ, Cha JH, Kim YJ, Jun WJ, Lee JM and Yoon HG:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor,
inhibits EBV-induced B lymphocyte transformation via suppression of
RelA acetylation. Cancer Res. 69:583–592. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Thakur VS, Gupta K and Gupta S: Green tea
polyphenols increase p53 transcriptional activity and acetylation
by suppressing class I histone deacetylases. Int J Oncol.
41:353–361. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Choudhury SR, Balasubramanian S, Chew YC,
Han B, Marquez VE and Eckert RL: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
DZNep reduce polycomb protein level via a proteasome-dependent
mechanism in skin cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 32:1525–1532. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Li Y, Yuan YY, Meeran SM and Tollefsbol
TO: Synergistic epigenetic reactivation of estrogen receptor-α
(ERα) by combined green tea polyphenol and histone deacetylase
inhibitor in ERα-negative breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
9:274–286. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yun JM, Jialal I and Devaraj S: Effects of
epigallocatechin gallate on regulatory T cell number and function
in obese v. lean volunteers. Br J Nutr. 103:1771–1777. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Fang M, Chen D and Yang CS: Dietary
polyphenols may affect DNA methylation. J Nutr. 137:223S–228S.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P,
McFerran B, Kaiser C, Fee F, Katsanakis KD, Rose DW, Mischak H,
Sedivy JM and Kolch W: Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP
kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature. 401:173–177. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Ren G, Baritaki S, Marathe H, Feng J, Park
S, Beach S, Bazeley PS, Beshir AB, Fenteany G, Mehra R, Daignault
S, Al-Mulla F, Keller E, Bonavida B, de la Serna I and Yeung KC:
Polycomb protein EZH2 regulates tumor invasion via the
transcriptional repression of the metastasis suppressor RKIP in
breast and prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 72:3091–3104. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Minn AJ, Bevilacqua E, Yun J and Rosner
MR: Identification of novel metastasis suppressor signaling
pathways for breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 11:2452–2457. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Karamitopoulou E, Zlobec I, Panayiotides
I, Patsouris ES, Peros G, Rallis G, Lapas C, Karakitsos P,
Terracciano LM and Lugli A: Systematic analysis of proteins from
different signaling pathways in the tumor center and the invasive
front of colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol. 42:1888–1896. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hu CJ, Zhou L, Zhang J, Huang C and Zhang
GM: Immunohistochemical detection of Raf kinase inhibitor protein
in normal cervical tissue and cervical cancer tissue. J Int Med
Res. 39:229–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Zebisch A, Wölfler A, Fried I, Wolf O,
Lind K, Bodner C, Haller M, Drasche A, Pirkebner D, Matallanas D,
Rath O, Blyth K, Delwel R, Taskesen E, Quehenberger F, Kolch W,
Troppmair J and Sill H: Frequent loss of RAF kinase inhibitor
protein expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
26:1842–1849. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Wu K and Bonavida B: The activated
NF-kappaB-Snail-RKIP circuitry in cancer regulates both the
metastatic cascade and resistance to apoptosis by cytotoxic drugs.
Crit Rev Immunol. 29:241–254. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D,
Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, McFerran B, Wyche J, Kolch W and Sedivy
JM: Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing
kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol.
21:7207–7217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Emonds E, Fitzner B and Jaster R:
Molecular determinants of the antitumor effects of trichostatin A
in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 16:1970–1978.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Farrow B, Rychahou P, O’Connor KL and
Evers BM: Butyrate inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion. J
Gastrointest Surg. 7:864–870. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Hardtner C, Multhoff G, Falk W and Radons
J: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a green tea-derived catechin,
synergizes with celecoxib to inhibit IL-1-induced tumorigenic
mediators by human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells Colo357. Eur J
Pharmacol. 684:36–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Choi KC, Lee YH, Jung MG, Kwon SH, Kim MJ,
Jun WJ, Lee J, Lee JM and Yoon HG: Gallic acid suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear factor-kappaB signaling by
preventing RelA acetylation in A549 lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 7:2011–2021. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Zucker S, Cao J and Chen WT: Critical
appraisal of the use of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in
cancer treatment. Oncogene. 19:6642–6650. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Mook OR, Frederiks WM and Van Noorden CJ:
The role of gelatinases in colorectal cancer progression and
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1705:69–89. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, McDermott E
and O’Higgins N: Metalloproteinases: role in breast carcinogenesis,
invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2:252–257. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Vihinen P, Ala-aho R and Kähäri VM: Matrix
metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets in cancer. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 5:203–220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Gibbs DF, Warner RL, Weiss SJ, Johnson KJ
and Varani J: Characterization of matrix metalloproteinases
produced by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
20:1136–1144. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Yokoyama K, Kamata N, Hayashi E, Hoteiya
T, Ueda N, Fujimoto R and Nagayama M: Reverse correlation of
E-cadherin and snail expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells in vitro. Oral Oncol. 37:65–71. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and García De Herreros A: The transcription
factor Snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumor cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Jiao W, Miyazaki K and Kitajima Y: Inverse
correlation of E-cadherin and Snail expression in hepatocellular
cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer. 86:98–101. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Poser I, Domínguez D, de Herreros AG,
Varnai A, Buettner R and Bosserhoff AK: Loss of E-cadherin
expression in melanoma cells involves up-regulation of the
transcriptional repression Snail. J Biol Chem. 276:24661–24666.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Luo J, Lubaroff DM and Hendrix MJ:
Suppression of prostate cancer invasive potential and matrix
metalloproteinase activity by E-cadherin transfection. Cancer Res.
59:3552–3556. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Oka H, Shiozaki H, Kobayashi K, Inoue M,
Tahara H, Kobayashi T, Takatsuka Y, Matsuyoshi N, Hirano S,
Takeichi M and Mori T: Expression of E-cadherin cell adhesion
molecules in human breast cancer tissues and its relationship to
metastasis. Cancer Res. 53:1696–1701. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Graff JR, Herman JG, Lapidus RG, Chopra H,
Xu R, Jarrard DF, Isaacs WB, Pitha PM, Davidson NE and Baylin SB:
E-cadherin expression is silenced by DNA hypermethylation in human
breast and prostate carcinomas. Cancer Res. 55:5195–5199.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Odabaei G, Chatterjee D, Jazirehi AR,
Goodglick L, Yeung K and Bonavida B: Raf-1 kinase inhibitor
protein: structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and
pivotal role in apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res. 91:169–200. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Eckel F, Schneider G and Schmid RM:
Pancreatic cancer: a review of recent advances. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 15:1395–1410. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Schneider G, Siveke JT, Eckel F and Schmid
RM: Pancreatic cancer: basic and clinical aspects.
Gastroenterology. 128:1606–1625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Escara-Wilke J, Yeung K and Keller ET: Raf
kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
Jun 9–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
48.
|
Klysik J, Theroux SJ, Sedivy JM, Moffit JS
and Boekelheide K: Signaling crossroads: the function of Raf kinase
inhibitory protein in cancer, the central nervous system and
reproduction. Cell Signal. 20:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Zeng L, Imamoto A and Rosner MR: Raf
kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP): a physiological regulator and
future therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:1275–1287.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Beach S, Tang H, Park S, Dhillon AS,
Keller ET, Kolch W and Yeung KC: Snail is a repressor of RKIP
transcription in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene.
27:2243–2248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Fujimori Y, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y, Kato K,
Kojima K and Sugihara K: Prognostic value of RKIP and p-ERK in
gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:30–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Hazgui S, Bonnomet A, Nawrocki-Raby B,
Milliot M, Terryn C, Cutrona J, Polette M, Birembaut P and Zahm JM:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits the migratory behavior
of tumor bronchial epithelial cells. Respir Res. 9:33–46. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Shankar S, Ganapathy S, Hingorani SR and
Srivastava RK: EGCG inhibits growth, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Front Biosci. 13:440–452. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Takada Y, Andreeff M and Aggarwal BB:
Indole-3-carbinol suppresses NF-κB and IκBα kinase activation,
causing inhibition of expression of NF-κB-regulated antiapoptotic
and metastatic gene products and enhancement of apoptosis in
myeloid and leukemia cells. Blood. 106:641–649. 2005.
|
|
55.
|
Jin H, Yu Y, Zhang T, Zhou X, Zhou J, Jia
L, Wu Y, Zhou BP and Feng Y: Snail is critical for tumor growth and
metastasis of ovarian carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:2102–2111.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Kido S, Shimonishi
T, Matsuyama S, Kitahara K and Miyazaki K: Snail accelerates cancer
invasion by upregulating MMP expression and is associated with poor
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 92:252–258.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|