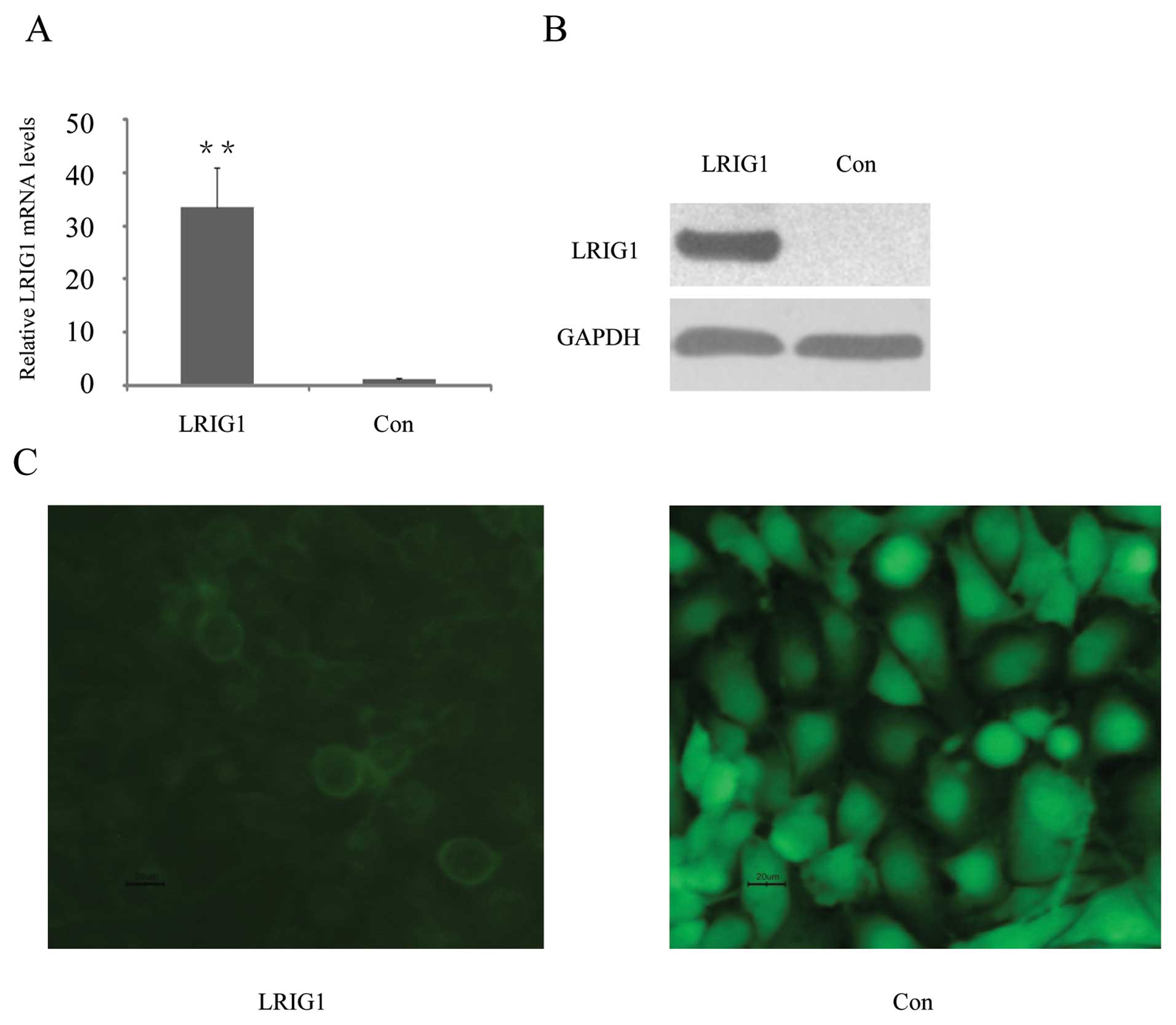
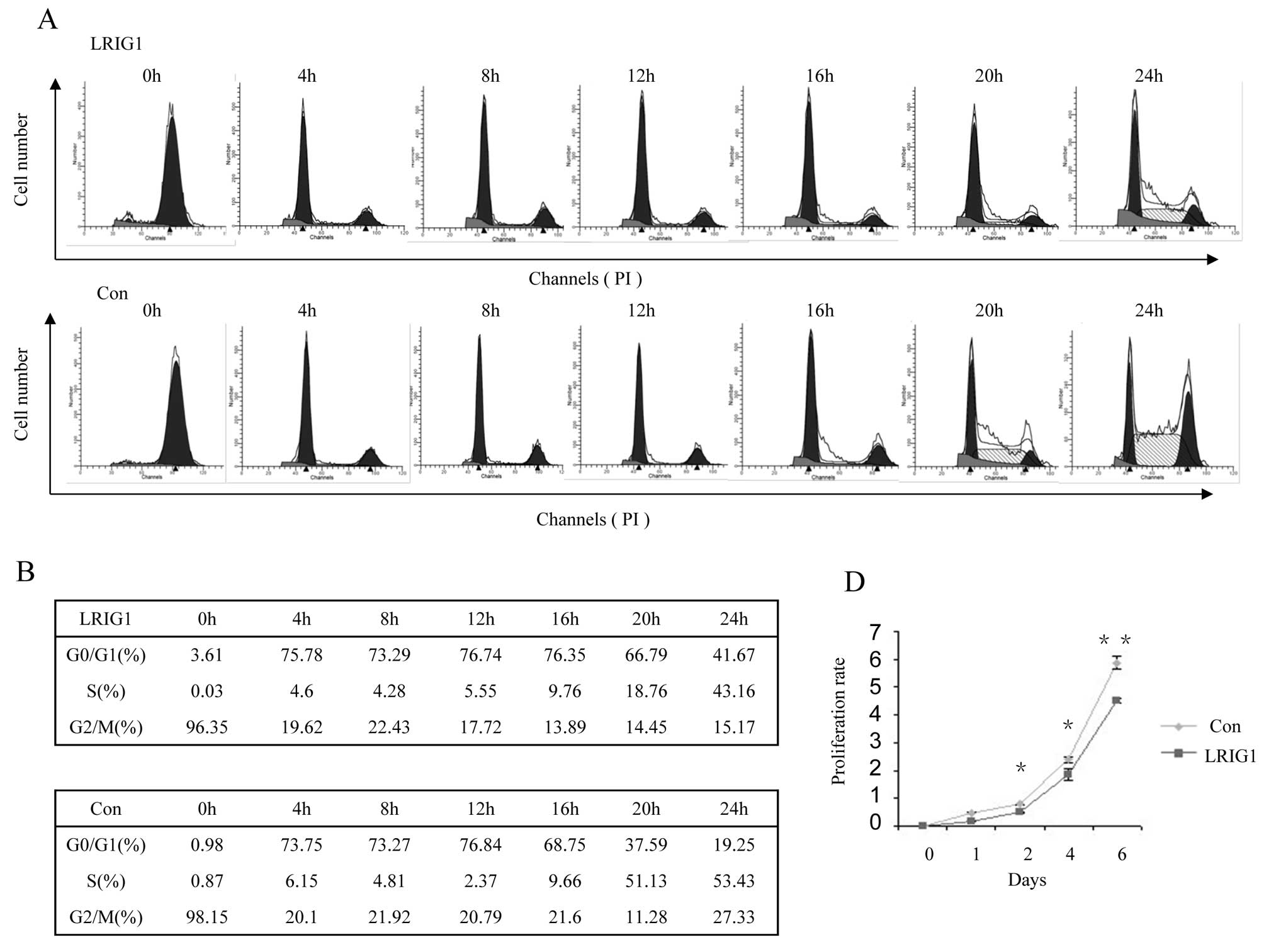
|
1
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
MacDonald TJ, Aguilera D and Kramm CM:
Treatment of high-grade glioma in children and adolescents.
Neurooncology. 13:1049–1058. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sathornsumetee S, Reardon DA, Desjardins
A, Quinn JA, Vredenburgh JJ and Rich JN: Molecularly targeted
therapy for malignant glioma. Cancer. 110:13–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith JS, Tachibana I, Passe SM, et al:
PTEN mutation, EGFR amplification and outcome in patients with
anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 93:1246–1256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reifenberger G and Collins VP: Pathology
and molecular genetics of astrocytic gliomas. J Mol Med.
82:656–670. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Frederick L, Wang XY, Eley G and James CD:
Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor
mutations in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 60:1383–1387.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heimberger AB, Hlatky R, Suki D, et al:
Prognostic effect of epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII
in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1462–1466.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nilsson J, Vallbo C, Guo D, et al:
Cloning, characterization and expression of human LIG1. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 284:1155–1161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo D, Holmlund C, Henriksson R and Hedman
H: The LRIG gene family has three vertebrate paralogs widely
expressed in human and mouse tissues and a homolog in Ascidiacea.
Genomics. 84:157–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hedman H, Nilsson J, Guo D and Henriksson
R: Is LRIG1 a tumour suppressor gene at chromosome 3p14.3? Acta
Oncol. 41:352–354. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Knuutila S, Aalto Y, Autio K, et al: DNA
copy number losses in human neoplasms. Am J Pathol. 155:683–694.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boelens MC, van den Berg A, Fehrmann RS,
et al: Current smoking-specific gene expression signature in normal
bronchial epithelium is enhanced in squamous cell lung cancer. J
Pathol. 218:182–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miller JK, Shattuck DL, Ingalla EQ, et al:
Suppression of the negative regulator LRIG1 contributes to ErbB2
overexpression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 68:8286–8294. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sheu JJ, Lee CH, Ko JY, et al: Chromosome
3p12.3–p14.2 and 3q26.2–q26.32 are genomic markers for prognosis of
advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 18:2709–2716. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Tanemura A, Nagasawa T, Inui S and Itami
S: LRIG-1 provides a novel prognostic predictor in squamous cell
carcinoma of the skin: immunohistochemical analysis for 38 cases.
Dermatol Surg. 31:423–430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thomasson M, Hedman H, Guo D, Ljungberg B
and Henriksson R: LRIG1 and epidermal growth factor receptor in
renal cell carcinoma: a quantitative RT-PCR and
immunohisto-chemical analysis. Br J Cancer. 89:1285–1289. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang WM, Yan ZJ, Ye ZQ and Guo DS: LRIG1,
a candidate tumour-suppressor gene in human bladder cancer cell
line BIU87. BJU Int. 98:898–902. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gur G, Rubin C, Katz M, et al: LRIG1
restricts growth factor signaling by enhancing receptor
ubiquitylation and degradation. EMBO J. 23:3270–3281. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Laederich MB, Funes-Duran M, Yen L, et al:
The leucine-rich repeat protein LRIG1 is a negative regulator of
ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem.
279:47050–47056. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goldoni S, Iozzo RA, Kay P, et al: A
soluble ectodomain of LRIG1 inhibits cancer cell growth by
attenuating basal and ligand-dependent EGFR activity. Oncogene.
26:368–381. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yi W, Holmlund C, Nilsson J, et al:
Paracrine regulation of growth factor signaling by shed
leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1. Exp Cell
Res. 317:504–512. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stutz MA, Shattuck DL, Laederich MB,
Carraway KL III and Sweeney C: LRIG1 negatively regulates the
oncogenic EGF receptor mutant EGFRvIII. Oncogene. 27:5741–5752.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye F, Gao Q, Xu T, et al: Upregulation of
LRIG1 suppresses malignant glioma cell growth by attenuating EGFR
activity. J Neurooncol. 94:183–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nilsson J, Starefeldt A, Henriksson R and
Hedman H: LRIG1 protein in human cells and tissues. Cell Tissue
Res. 312:65–71. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song H, Li Y, Lee J, Schwartz AL and Bu G:
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 promotes cancer
cell migration and invasion by inducing the expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Cancer Res. 69:879–886. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang B, Han L, Chen R, et al:
Downregulation of LRIG2 expression by RNA interference inhibits
glioblastoma cell (GL15) growth, causes cell cycle redistribution,
increases cell apoptosis and enhances cell adhesion and invasion in
vitro. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1018–1023. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lau YK, Murray LB, Houshmandi SS, Xu Y,
Gutmann DH and Yu Q: Merlin is a potent inhibitor of glioma growth.
Cancer Res. 68:5733–5742. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cai M, Han L, Chen R, et al: Inhibition of
LRIG3 gene expression via RNA interference modulates the
proliferation, cell cycle, cell apoptosis, adhesion and invasion of
glioblastoma cell (GL15). Cancer Lett. 278:104–112. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Galis ZS, Muszynski M, Sukhova GK, et al:
Cytokine-stimulated human vascular smooth muscle cells synthesize a
complement of enzymes required for extracellular matrix digestion.
Circ Res. 75:181–189. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Guo D, Nilsson J, Haapasalo H, et al:
Perinuclear leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domain
proteins (LRIG1-3) as prognostic indicators in astrocytic tumors.
Acta Neuropathol. 111:238–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stamenkovic I: Extracellular matrix
remodelling: the role of matrix metalloproteinases. J Pathol.
200:448–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakada M, Okada Y and Yamashita J: The
role of matrix metalloproteinases in glioma invasion. Front Biosci.
8:e261–269. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kodali R, Hajjou M, Berman AB, et al:
Chemokines induce matrix metalloproteinase-2 through activation of
epidermal growth factor receptor in arterial smooth muscle cells.
Cardiovasc Res. 69:706–715. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Alper O, Bergmann-Leitner ES, Bennett TA,
Hacker NF, Stromberg K and Stetler-Stevenson WG: Epidermal growth
factor receptor signaling and the invasive phenotype of ovarian
carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:1375–1384. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cox G, Jones JL and O’Byrne KJ: Matrix
metalloproteinase 9 and the epidermal growth factor signal pathway
in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
6:2349–2355. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang PH, Xu AM and White FM: Oncogenic
EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci Signal. 2:re62009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Knobbe CB, Trampe-Kieslich A and
Reifenberger G: Genetic alteration and expression of the
phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt pathway genes PIK3CA and PIKE in human
glioblastomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 31:486–490. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|