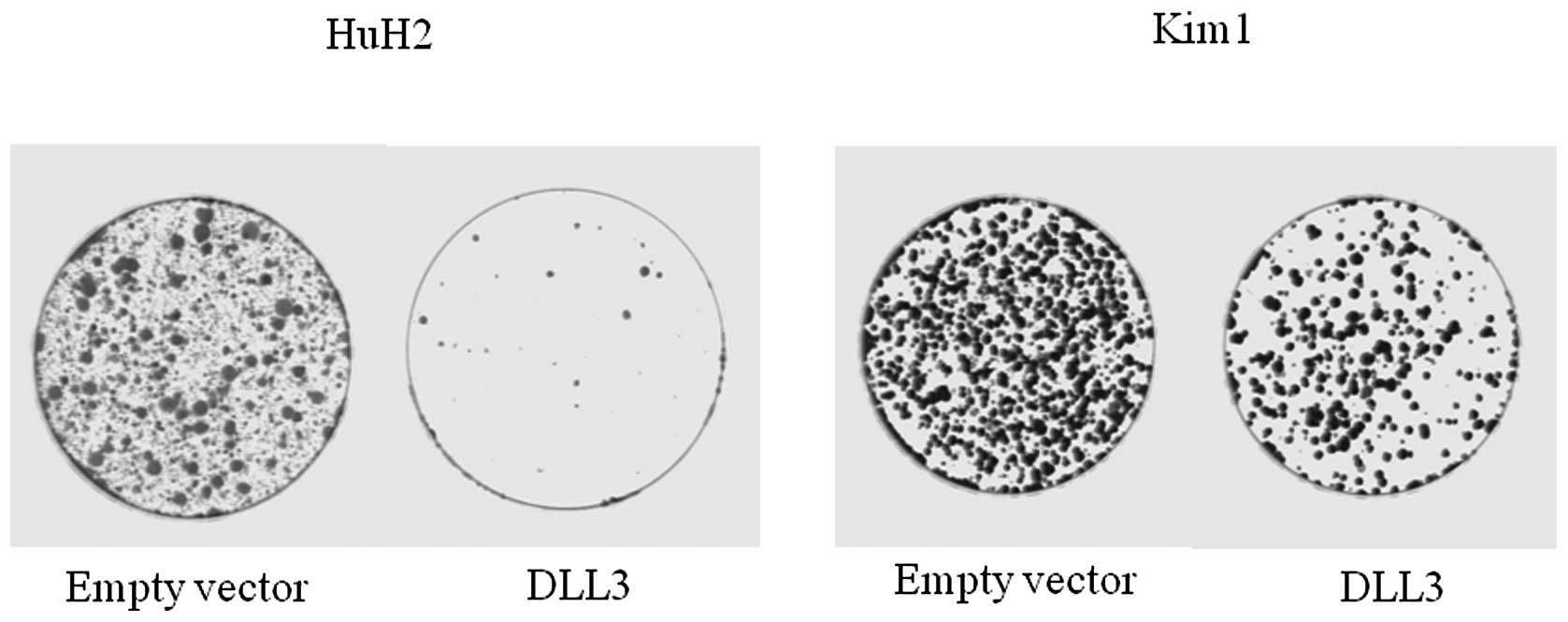
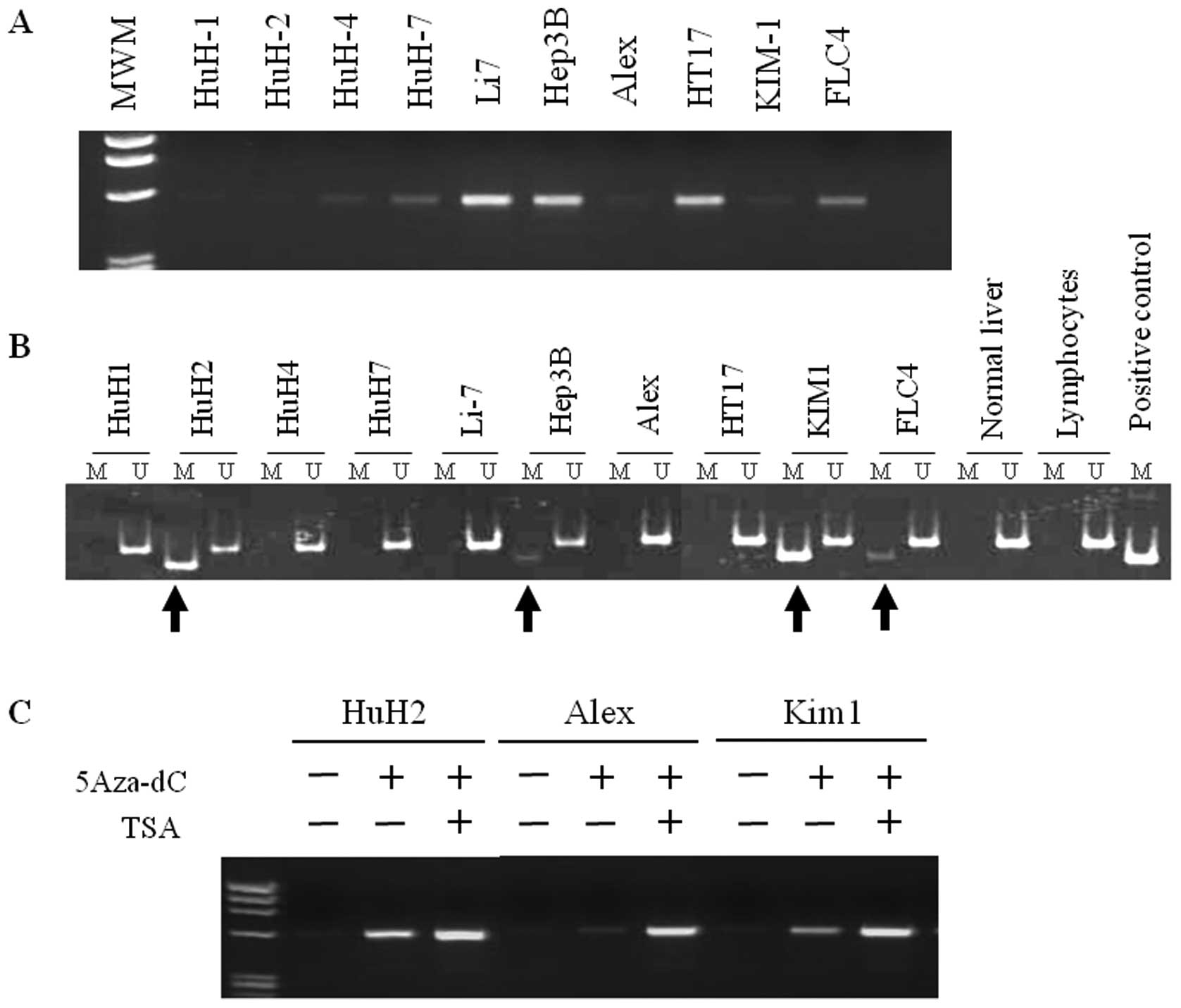
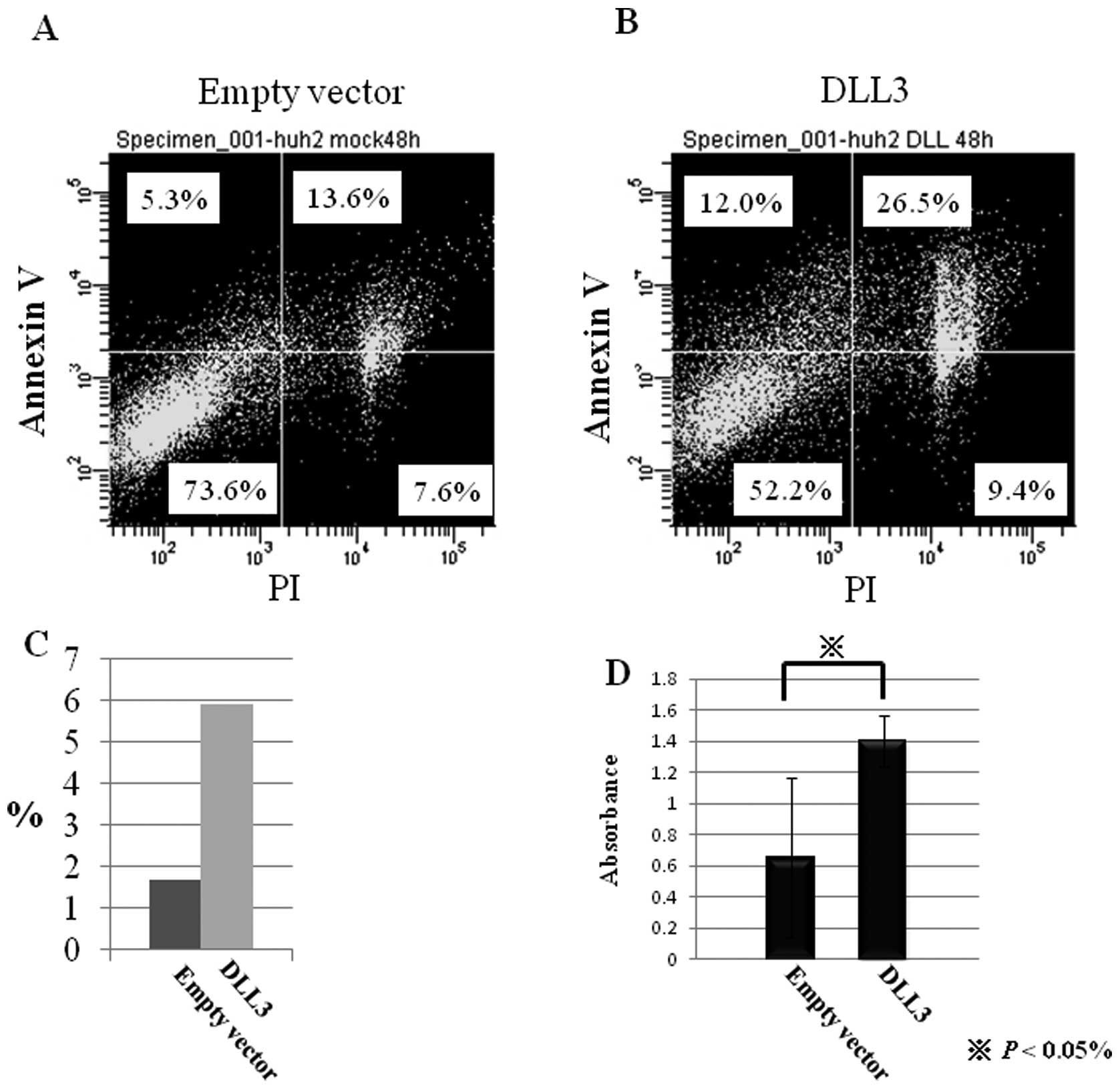
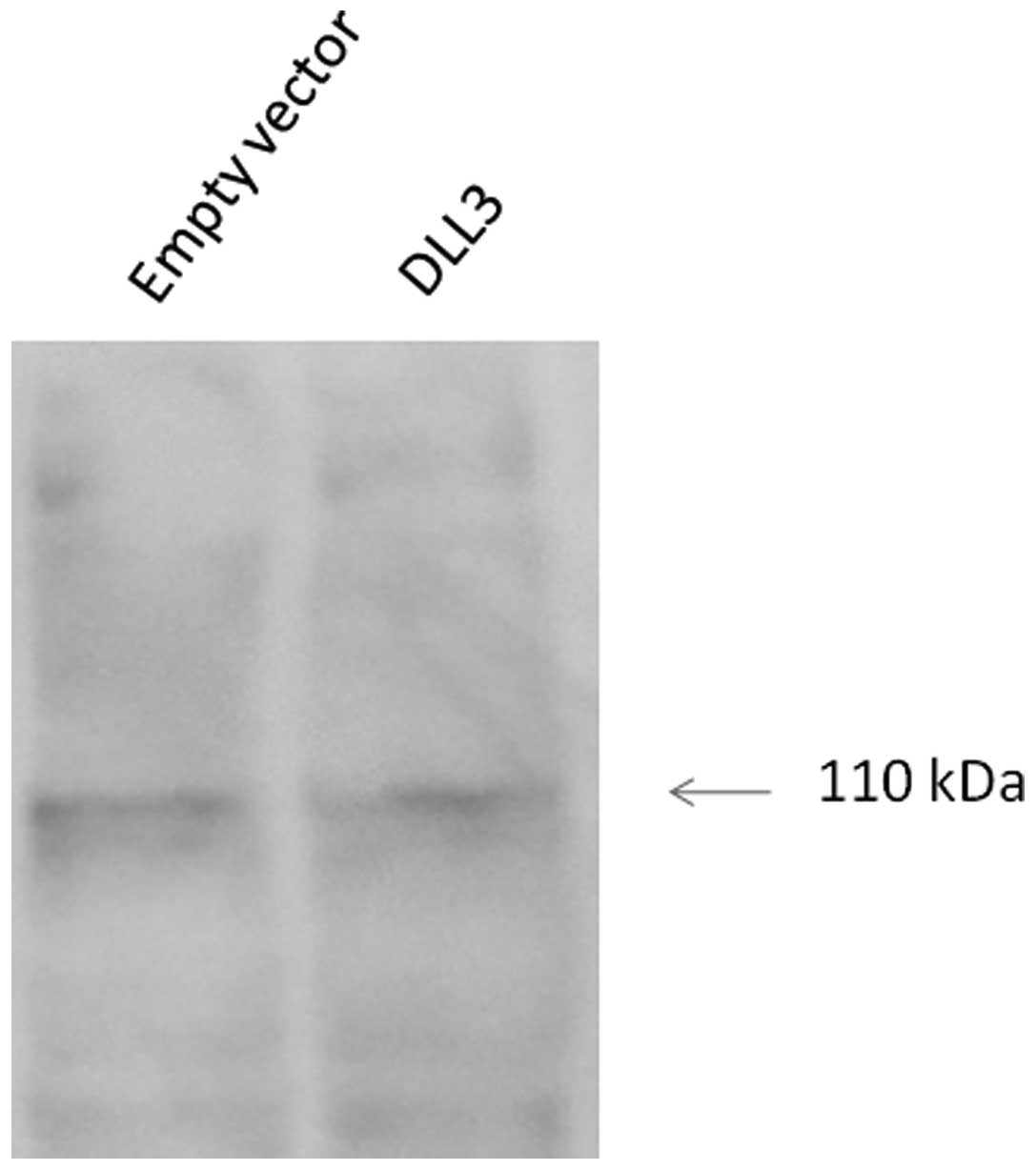
|
1
|
Herath NI, Leggett BA and MacDonald GA:
Review of genetic and epigenetic alterations in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:15–21. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang B, Guo M, Herman JG and Clark DP:
Aberrant promoter methylation profiles of tumor suppressor genes in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 163:1101–1107. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu JD: DNA methylation and hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 13:265–273. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee S, Lee HJ, Kim JH, Lee HS, Jang JJ and
Kang GH: Aberrant CpG island hypermethylation along multistep
hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 163:1371–1378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagai H, Ponglikitmongkol M, Mita E,
Ohmachi Y, Yoshikawa H, Saeki R, Yumoto Y, Nakanishi T and
Matsubara K: Aberration of genomic DNA in association with human
hepatocellular carcinomas detected by 2-dimensional gel analysis.
Cancer Res. 54:1545–1550. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoshikawa H, Monte DL, Nagai H, Wands JR,
Matsubara K and Fujiyama A: Chromosomal assignment of human genomic
NotI restriction fragments in a two-dimentional electrophoresis
profile. Genomics. 31:28–35. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshikawa H, Nagai H, Oh KS, Tamai S,
Fujiyama A, Nakanishi T, Kajiyama G and Matsubara K: Chromosomal
assignment of aberrant NotI restriction DNA fragments in primary
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene. 197:129–135. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoshikawa H, Matsubara K, Qian GS, Jackson
P, Groopman JD, Manning JE, Harris C and Herman JG: SOCS-1, a
negative regulator of the JAK/STAT pathway, is silenced by
methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and shows
growth-suppression activity. Nat Genet. 28:29–35. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura A,
Matsubara K, Kitagawa T, Yamamoto J, Kubo T and Yoshikawa H:
Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration
by enhancing JAK/STS and FAK signaling in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:6406–6417. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kubo T, Yamamoto J, Shikauchi Y, Niwa Y,
Matsubara K and Yoshikawa H: Apoptotic speck protein-like, a highly
homologous protein to apoptotic speck protein in the pyrin domain,
is silenced by DNA methylation and induces apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 64:5172–5177. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
D’Souza B, Miyamoto A and Weinmaster G:
The many facets of Notch ligands. Oncogene. 27:5148–5167. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Bray SJ: Notch signaling: a simple pathway
becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:678–689. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fiuza UM and Arias AM: Cell and molecular
biology of Notch. J Endocrinol. 194:459–474. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dunwoodie SL, Henrique D, Harrison SM and
Beddington RSP: Mouse Dll3: a novel divergent Delta gene which may
complement the function of other Delta homologues during early
pattern formation in the mouse. Development. 124:3065–3076.
1997.
|
|
15
|
Ladi E, Nichols JT, Ge W, Miyamoto A, Yao
C, Yang LT, Boulter J, Sun YE, Kintner C and Weinmaster G: The
divergent DSL ligand Dll3 does not activate Notch signaling but
cell autonomously attenuates signaling induced by other DSL
ligands. J Cell Biol. 170:983–992. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geffers I, Serth K, Chapman G, Jaekel R,
Schuster-Gossler K, Cardes R, Sparrow DB, Kremmer E, Dunwoodie S,
Klein T and Gossler A: Divergent functions and distinct
localization of the Notch ligands DLL1 and DLL3 in vivo. J Cell
Biol. 30:465–476. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Conlon RA, Reaume AG and Rossant J: Notch1
is required for the coordinate segmentation of somites.
Development. 121:1633–1645. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kusumi K, Sun ES, Kerrebrock AW, Bronson
RT, Chi DC and Bulotsky MS: The mouse pudgy mutation disrupts Delta
homologue Dll3 and initiation of early somite boundaries. Nat
Genet. 19:274–278. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dunwoodie SL, Clements M, Sparrow DB, Sa
X, Conlon RA and Beddington RS: Axial skeletal defects caused by
mutation in the spondylocostal dysplasia/pudgy gene Dll3 are
associated with disruption of the segmentation clock within the
presomitic mesoderm. Development. 129:1795–1806. 2002.
|
|
20
|
Bulman MP, Kusumi K, Frayling TM, McKeown
C, Garrette C, Lander ES, Krumlauf R, Hattersley AT, Ellard S and
Turnpenny PD: Mutations in the human delta homologues, DLL3, cause
axial skeletal defects in spondylocostal dysostosis. Nat Genet.
24:438–441. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sparrow DB, Clements M, Withington SL,
Scott AN, Novotny J, Sillence D, Kusumi K, Beddington RS and
Dunwoodie SL: Diverse requirements for N signaling in mammals. Int
J Dev Biol. 46:365–374. 2002.
|
|
22
|
Turnpenny PD, Whittock N, Duncan J,
Dunwoodie S, Kusumi K and Ellard S: Novel mutations in DLL3, a
somitogenesis gene encoding a ligand for the N signaling pathway,
cause a consistent pattern of abnormal vertebral segmentation in
spondylocostal dysostosis. J Med Genet. 40:333–339. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD
and Baylin SB: Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for
methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:9821–9826. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lunn RM, Zhang YJ, Wang LY, Chen CJ, Lee
PH, Lee CS, Tsai WY and Santella RM: p53 mutations, chronic
hepatitis B virus infection, and aflatoxin exposure in
hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. Cancer Res. 57:3471–3477.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De la Costa A, Romagnolo B, Billuart P,
Renard CA, Buendia MA, Soubrane O, Fabre M, Chelly J, Beldjord C,
Kahn A and Perret C: Somatic mutations of the beta-catenin gene are
frequent in mouse and human hepatocellular carcinomas. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:8847–8851. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Matsuda Y, Ichida T, Matsuzawa J, Sugimura
K and Asakura H: p16(INK4) is inactivated by extensive CpG
methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
116:394–400. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schagdarsurengin U, Wikens L, Steinemann
D, Flemming P, Kreipe HH, Pfeifer GP, Schlegelberger B and Dammann
R: Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the RASSF1A gene in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 22:1866–1871. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tchou JC, Lin X, Freije D, Isaacs WB,
Brooks JD, Rashid A, De Marzo AM, Kanai Y, Hirohashi S and Nelson
WG: GSTP1 CpG island DNA hypermethylation in hepatocellular
carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 16:663–676. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu J, Lian Z, Han S, Waye MMY, Wang H, Wu
MC, Wu K, Ding J, Arbuthnot P, Kew M, Fan D and Feitelson MA:
Downregulation of E-cadherin by hepatitis B virus X antigen in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 25:1008–1017. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Parks AL, Stout JR, Shepard SB, Klueg KM,
Dos Santos AA, Parody TR, Voskova M and Muskavitch AT:
Structure-function analysis of delta trafficking, receptor binding
and signaling in Drosophila. Genetics. 174:1947–1961. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shimizu K, Chiba S, Kumano K, Hosoya N,
Takahashi T, Kanda Y, Hamada Y, Yazaki Y and Hirai H: Mouse Jagged1
physically interacts with Notch2 and other Notch receptors.
Assessment by quantitative methods. J Biol Chem. 274:32961–32969.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|