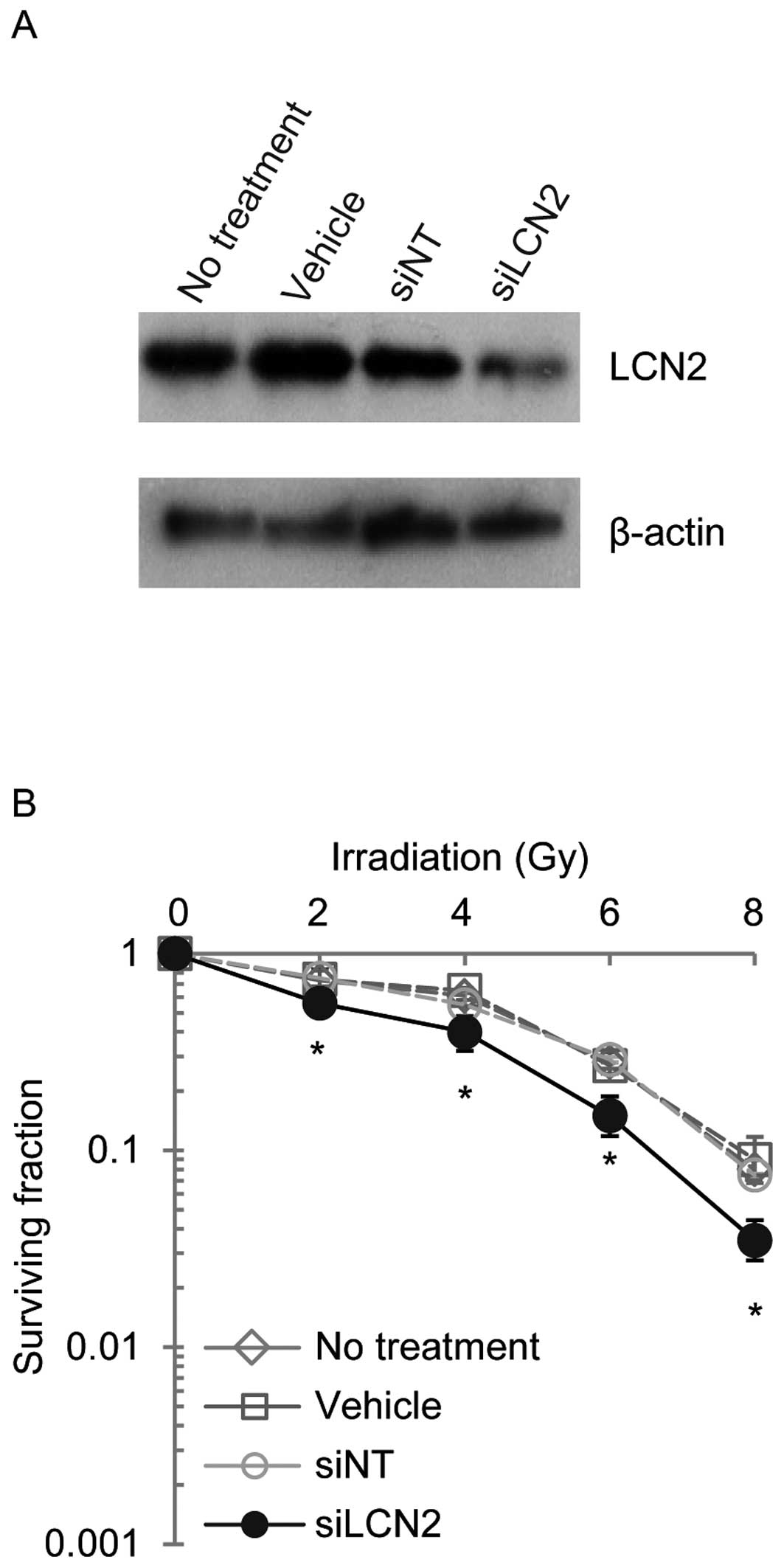
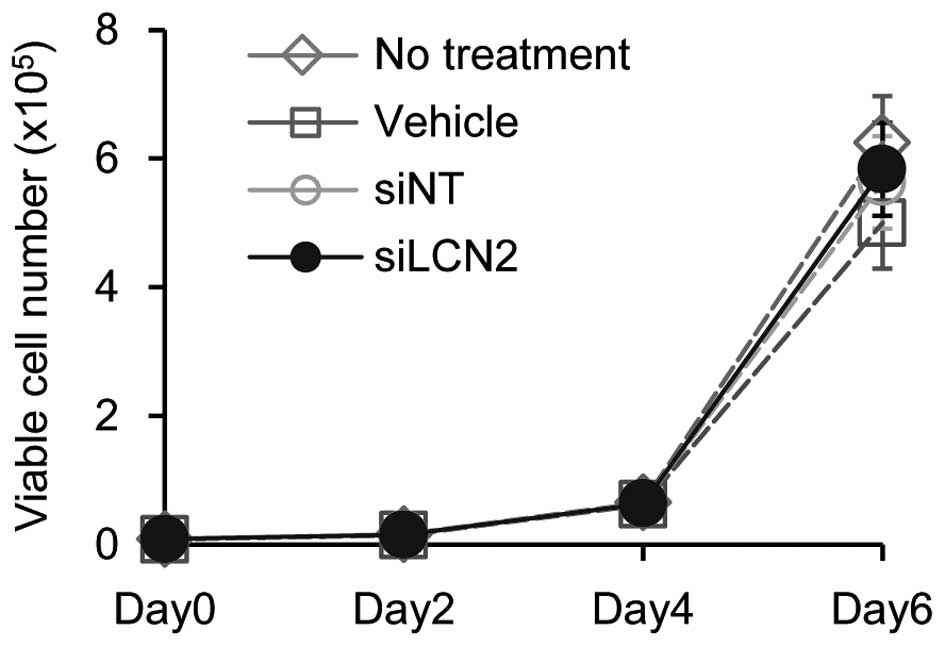
|
1
|
Lehnert S: Prediction of tumor response to
therapy: molecular markers and the microenvironment. Apoptosis and
chips: an overview of the proceedings. Radiat Res. 154:121–124.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Joki T, Carroll RS, Dunn IF, Zhang J, Abe
T and Black PM: Assessment of alterations in gene expression in
recurrent malignant glioma after radiotherapy using complementary
deoxyribonucleic acid microarrays. Neurosurgery. 48:195–202.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Keyse SM: The induction of gene expression
in mammalian cells by radiation. Semin Cancer Biol. 4:119–128.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iliakis G: Cell cycle regulation in
irradiated and nonirradiated cells. Semin Oncol. 24:602–615.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eckardt-Schupp F and Klaus C: Radiation
inducible DNA repair processes in eukaryotes. Biochimie.
81:161–171. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maity A, McKenna WG and Muschel RJ: The
molecular basis for cell cycle delays following ionizing radiation:
a review. Radiother Oncol. 31:1–13. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forrester HB, Vidair CA, Albright N, Ling
CC and Dewey WC: Using computerized video time lapse for
quantifying cell death of X-irradiated rat embryo cells transfected
with c-myc or c-Ha-ras. Cancer Res. 59:931–939. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Terakado N, Shintani S, Yano J, et al:
Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with
radioresistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
40:383–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Freier K, Pungs S, Sticht C, et al: High
survivin expression is associated with favorable outcome in
advanced primary oral squamous cell carcinoma after radiation
therapy. Int J Cancer. 120:942–946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamazaki Y, Chiba I, Hirai A, et al:
Radioresistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma with p53 DNA
contact mutation. Am J Clin Oncol. 26:e124–e129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moergel M, Abt E, Stockinger M and Kunkel
M: Overexpression of p63 is associated with radiation resistance
and prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
46:667–671. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gu Y, Fan S, Liu B, et al: TCRP1 promotes
radioresistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via Akt
signal pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 357:107–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ishigami T, Uzawa K, Fushimi K, et al:
Inhibition of ICAM2 induces radiosensitization in oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 98:1357–1365. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tong Z, Wu X, Ovcharenko D, Zhu J, Chen CS
and Kehrer JP: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a
survival factor. Biochem J. 391:441–448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flower DR: The lipocalin protein family:
structure and function. Biochem J. 318:1–14. 1996.
|
|
16
|
Triebel S, Blaser J, Reinke H and
Tschesche H: A 25 kDa alpha 2-microglobulin-related protein is a
component of the 125 kDa form of human gelatinase. FEBS Lett.
314:386–388. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nilsen-Hamilton M, Liu Q, Ryon J,
Bendickson L, Lepont P and Chang Q: Tissue involution and the acute
phase response. Ann NY Acad Sci. 995:94–108. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nielsen BS, Borregaard N, Bundgaard JR,
Timshel S, Sehested M and Kjeldsen L: Induction of NGAL synthesis
in epithelial cells of human colorectal neoplasia and inflammatory
bowel diseases. Gut. 38:414–420. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bratt T: Lipocalins and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1482:318–326. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Furutani M, Arii S, Mizumoto M, Kato M and
Imamura M: Identification of a neutrophil gelatinase-associated
lipocalin mRNA in human pancreatic cancers using a modified signal
sequence trap method. Cancer Lett. 122:209–214. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bartsch S and Tschesche H: Cloning and
expression of human neutrophil lipocalin cDNA derived from bone
marrow and ovarian cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 357:255–259. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hiromoto T, Noguchi K, Yamamura M, et al:
Upregulation of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in oral
squamous cell carcinoma: relation to cell differentiation. Oncol
Rep. 26:1415–1421. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ishigami T, Uzawa K, Higo M, et al: Genes
and molecular pathways related to radioresistance of oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 120:2262–2270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogawa K, Utsunomiya T, Mimori K, et al:
Differential gene expression profiles of radioresistant pancreatic
cancer cell lines established by fractionated irradiation. Int J
Oncol. 28:705–713. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo WF, Lin RX, Huang J, et al:
Identification of differentially expressed genes contributing to
radioresistance in lung cancer cells using microarray analysis.
Radiat Res. 164:27–35. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hellman B, Brodin D, Andersson M, et al:
Radiation-induced DNA-damage and gene expression profiles in human
lung cancer cells with different radiosensitivity. Exp Oncol.
27:102–107. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fukuda K, Sakakura C, Miyagawa K, et al:
Differential gene expression profiles of radioresistant oesophageal
cancer cell lines established by continuous fractionated
irradiation. Br J Cancer. 91:1543–1550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kitahara O, Katagiri T, Tsunoda T, Harima
Y and Nakamura Y: Classification of sensitivity or resistance of
cervical cancers to ionizing radiation according to expression
profiles of 62 genes selected by cDNA microarray analysis.
Neoplasia. 4:295–303. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Achary MP, Jaggernauth W, Gross E, Alfieri
A, Klinger HP and Vikram B: Cell lines from the same cervical
carcinoma but with different radiosensitivities exhibit different
cDNA microarray patterns of gene expression. Cytogenet Cell Genet.
91:39–43. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chu ST, Lin HJ, Huang HL and Chen YH: The
hydrophobic pocket of 24p3 protein from mouse uterine luminal
fluid: fatty acid and retinol binding activity and predicted
structural similarity to lipocalins. J Pept Res. 52:390–397.
1998.
|
|
31
|
Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, et al: An iron
delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell. 10:1045–1056.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cowland JB and Borregaard N: Molecular
characterization and pattern of tissue expression of the gene for
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin from humans. Genomics.
45:17–23. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Roudkenar MH, Kuwahara Y, Baba T, et al:
Oxidative stress induced lipocalin 2 gene expression: addressing
its expression under the harmful conditions. J Radiat Res.
48:39–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park S, Guo J, Kim D and Cheng JQ:
Identification of 24p3 as a direct target of Foxo3a regulated by
interleukin-3 through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J
Biol Chem. 284:2187–2193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rosen JM and Jordan CT: The increasing
complexity of the cancer stem cell paradigm. Science.
324:1670–1673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|