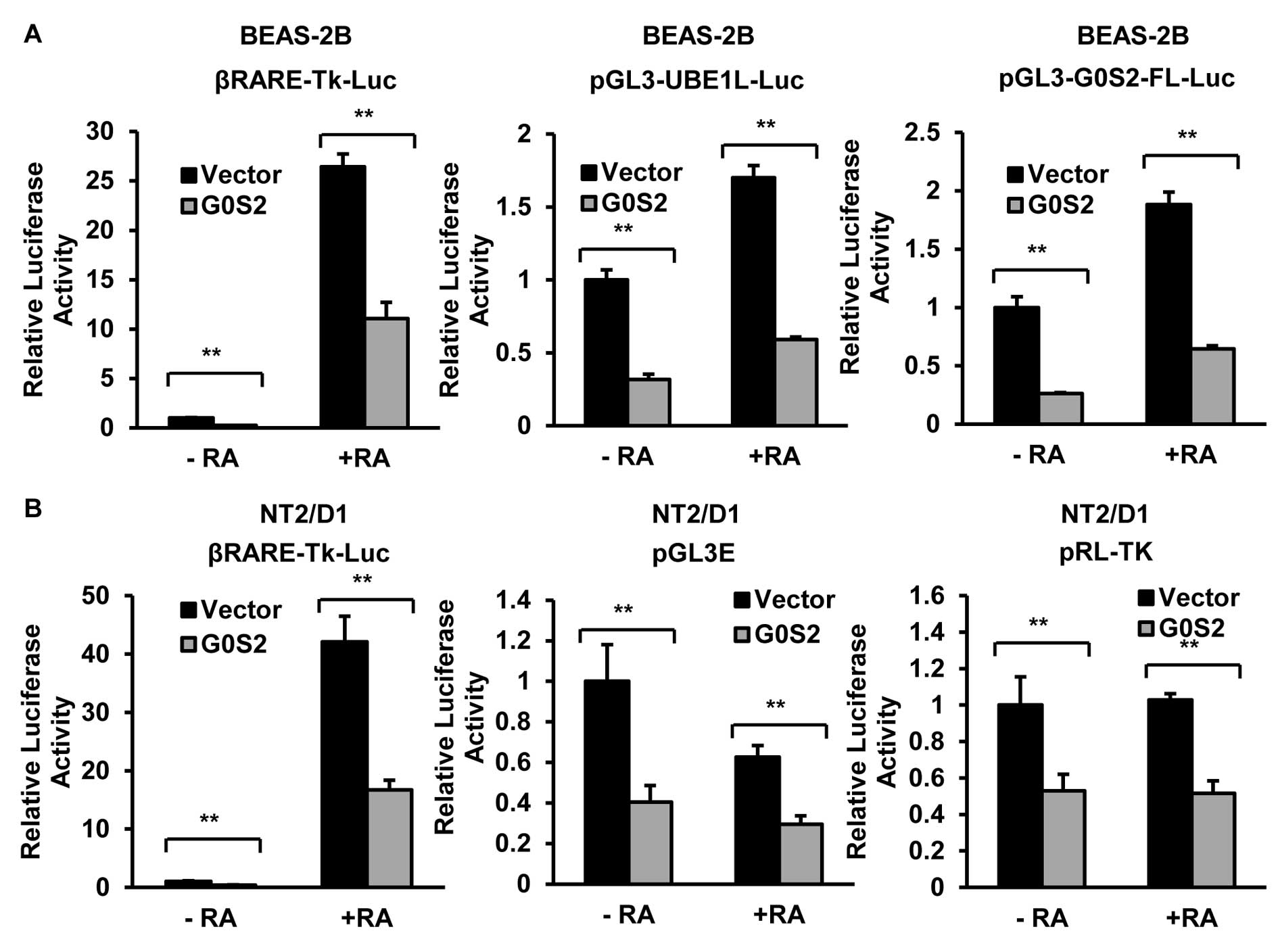
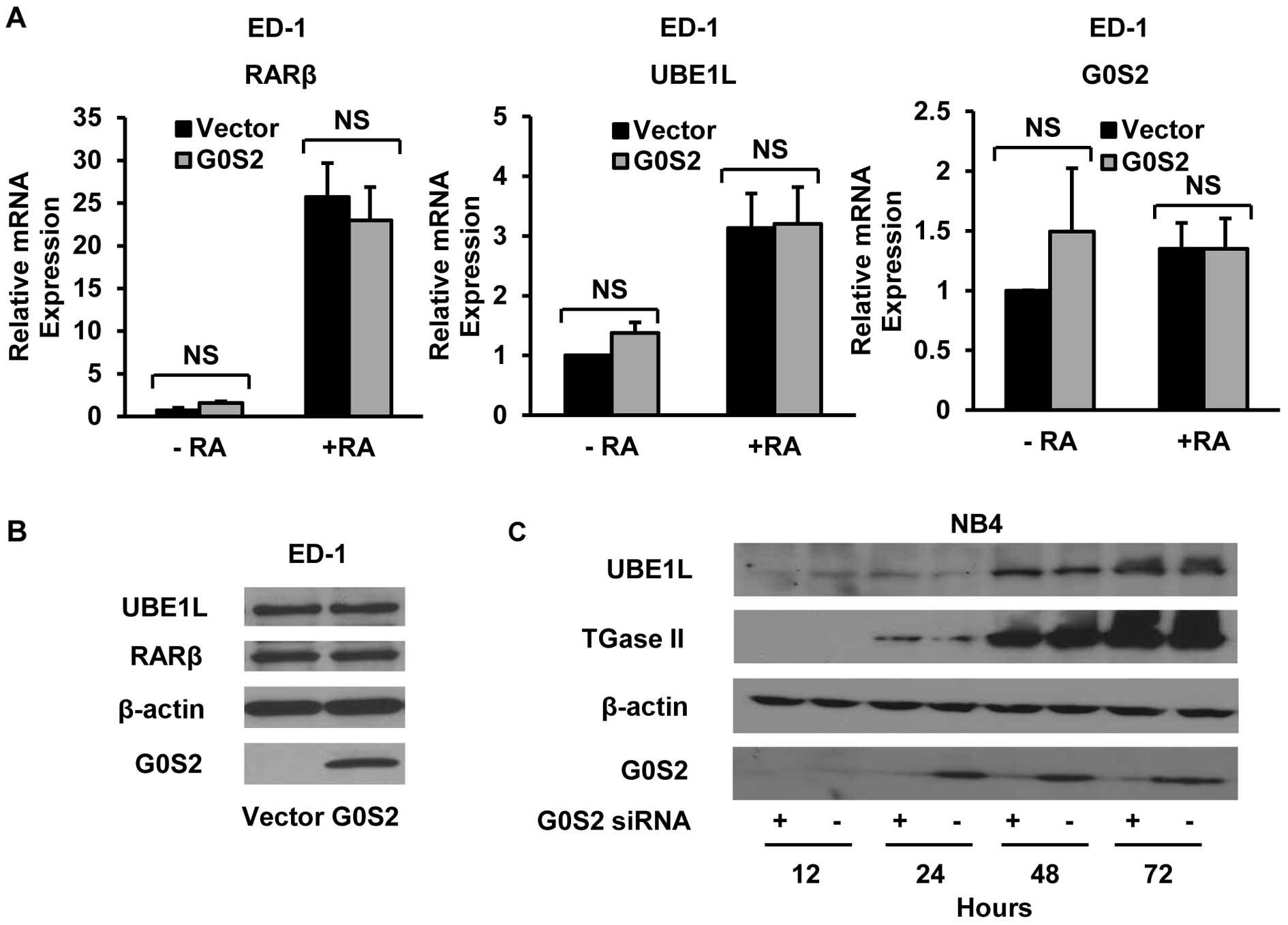
|
1.
|
Massaro D and Massaro GD: Lung
development, lung function, and retinoids. New Eng J Med.
362:1829–1831. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Palczewski K: Chemistry and biology of
vision. J Biol Chem. 287:1612–1619. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Pino-Lagos K, Benson MJ and Noelle RJ:
Retinoic acid in the immune system. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1143:170–187.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Freemantle SJ, Spinella MJ and Dmitrovsky
E: Retinoids in cancer therapy and chemoprevention: promise meets
resistance. Oncogene. 22:7305–7315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Miller WH Jr,
et al: Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with
tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). New Eng J Med. 324:1385–1393.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kakizuka A, Miller WH Jr, Umesono K, et
al: Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic
leukemia fuses RARα with a novel putative transcription factor,
PML. Cell. 66:663–674. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Melnick A and Licht JD: Deconstructing a
disease: RARalpha, its fusion partners, and their roles in the
pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 93:3167–3215.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Pitha-Rowe I, Petty WJ, Kitareewan S and
Dmitrovsky E: Retinoid target genes in acute promyelocytic
leukemia. Leukemia. 17:1723–1730. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Kitareewan S, Blumen S, Sekula D, et al:
G0S2 is an all-transretinoic acid target gene. Int J Oncol.
33:397–404. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Tamayo P, Slonim D, Mesirov J, et al:
Interpreting patterns of gene expression with self-organizing maps:
methods and application to hematopoietic differentiation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 96:2907–2912. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Russell L and Forsdyke D: A human putative
lymphocyte G0/G1 switch gene containing a CpG-rich island encodes a
small basic protein with the potential to be phosphorylated. DNA
Cell Biol. 10:581–591. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Zandbergen F, Mandard S, Escher P, et al:
The G0/G1 switch gene 2 is a novel PPAR target gene. Biochem J.
392:313–324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Yang X, Lu X, Lombès M, et al: The
G(0)/G(1) switch gene 2 regulates adipose lipolysis through
association with adipose triglyceride lipase. Cell Metab.
11:194–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Cristillo AD, Heximer SP, Russell L and
Forsdyke DR: Cyclosporin A inhibits early mRNA expression of G0/G1
switch (G0S2) in cultured human blood mononuclear cells. DNA Cell
Biol. 16:1449–1458. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Koczan D, Guthke R, Thiesen HJ, et al:
Gene expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear
leukocytes from psoriasis patients identifies new immune regulatory
molecules. Euro J Dermatol. 15:251–257. 2005.
|
|
16.
|
Nakamura N, Shimaoka Y, Tougan T, et al:
Isolation and expression profiling of genes upregulated in bone
marrow-derived mononuclear cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
DNA Res. 13:169–183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kobayashi S, Ito A, Okuzaki D, et al:
Expression profiling of PBMC-based diagnostic gene markers isolated
from vasculitis patients. DNA Res. 15:253–265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Tokumaru Y, Yamashita K, Osada M, et al:
Inverse correlation between cyclin A1 hypermethylation and p53
mutation in head and neck cancer identified by reversal of
epigenetic silencing. Cancer Res. 64:5982–5987. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Chang X, Monitto CL, Demokan S, et al:
Identification of hypermethylated genes associated with cisplatin
resistance in human cancers. Cancer Res. 70:2870–2879. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kusakabe M, Kutomi T, Watanabe K, et al:
Identification of G0S2 as a gene frequently methylated in squamous
lung cancer by combination of in silico and experimental
approaches. Int J Cancer. 126:1895–1902. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kusakabe M, Watanabe K, Emoto N, et al:
Impact of DNA demethylation of the G0S2 gene on the transcription
of G0S2 in squamous lung cancer cell lines with or without nuclear
receptor agonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 390:1283–1287. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Welch C, Santra MK, El-Assaad W, et al:
Identification of a protein, G0S2, that lacks Bcl-2 homology
domains and interacts with and antagonizes Bcl-2. Cancer Res.
69:6782–6789. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Boyle JO, Langenfeld J, Lonardo F, et al:
Cyclin D1 proteolysis: a retinoid chemoprevention signal in normal,
immortalized, and transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 91:373–379. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Spinella MJ, Freemantle SJ, Sekula D,
Chang JH, Christie AJ and Dmitrovsky E: Retinoic acid promotes
ubiquitination and proteolysis of cyclin D1 during induced tumor
cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 274:22013–22018. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Liu X, Sempere LF, Galimberti F, et al:
2009. Uncovering growth-suppressive microRNAs in lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1177–1183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
White KA, Yore MM, Deng D and Spinella MJ:
Limiting effects of RIP140 in estrogen signaling: potential
mediation of anti-estrogenic effects of retinoic acid. J Biol Chem.
280:7829–7835. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Kitareewan S, Pitha-Rowe I, Sekula D, et
al: UBE1L is a retinoid target that triggers PML/RARalpha
degradation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:3806–3811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Lee SB, Park JH, Woster PM, Casero RA Jr
and Park MH: Suppression of exogenous gene expression by
spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (SSAT1) cotransfection.
J Biol Chem. 285:15548–15556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Zaiou M: Multifunctional antimicrobial
peptides: therapeutic targets in several human diseases. J Mol Med.
85:317–329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Sandgren S, Wittrup A, Cheng F, Jönsson M,
Eklund E, Busch S and Belting M: The human antimicrobial peptide
LL-37 transfers extracellular DNA plasmid to the nuclear
compartment of mammalian cells via lipid rafts and
proteoglycan-dependent endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 279:17951–17956.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Heckmann BL, Zhang X, Xie X and Liu J: The
G0/G1 switch gene 2 (G0S2): regulating metabolism and beyond.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:276–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|