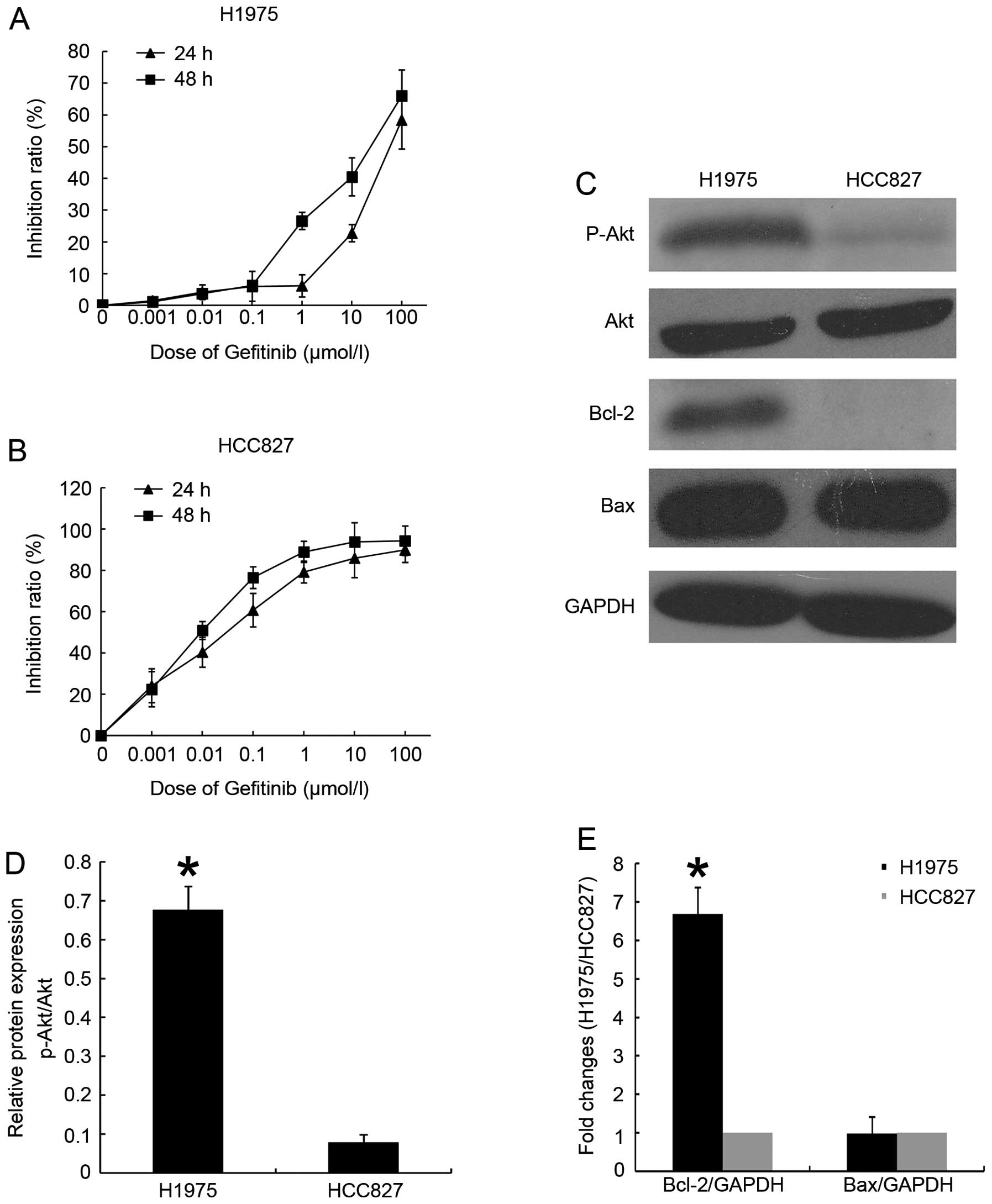
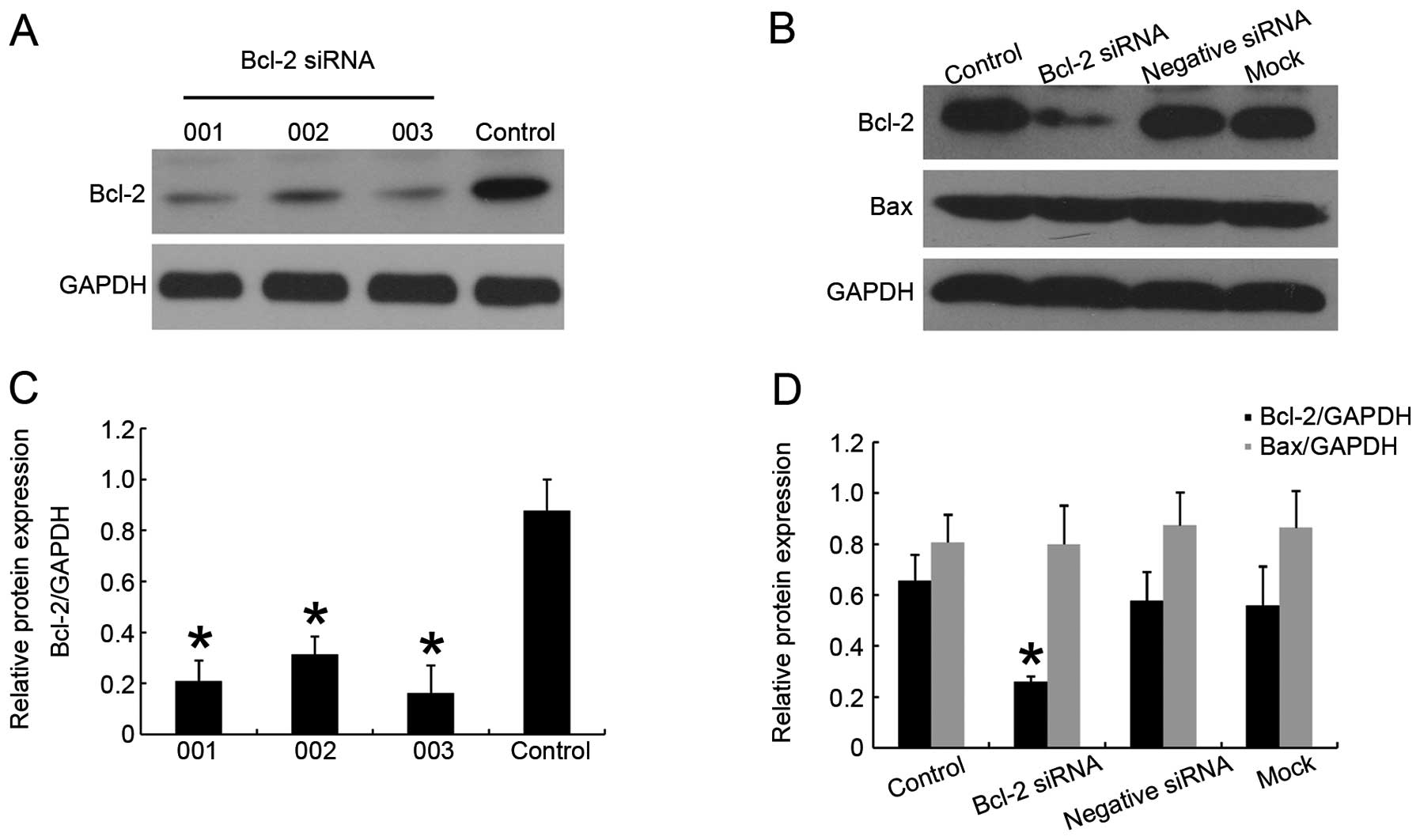
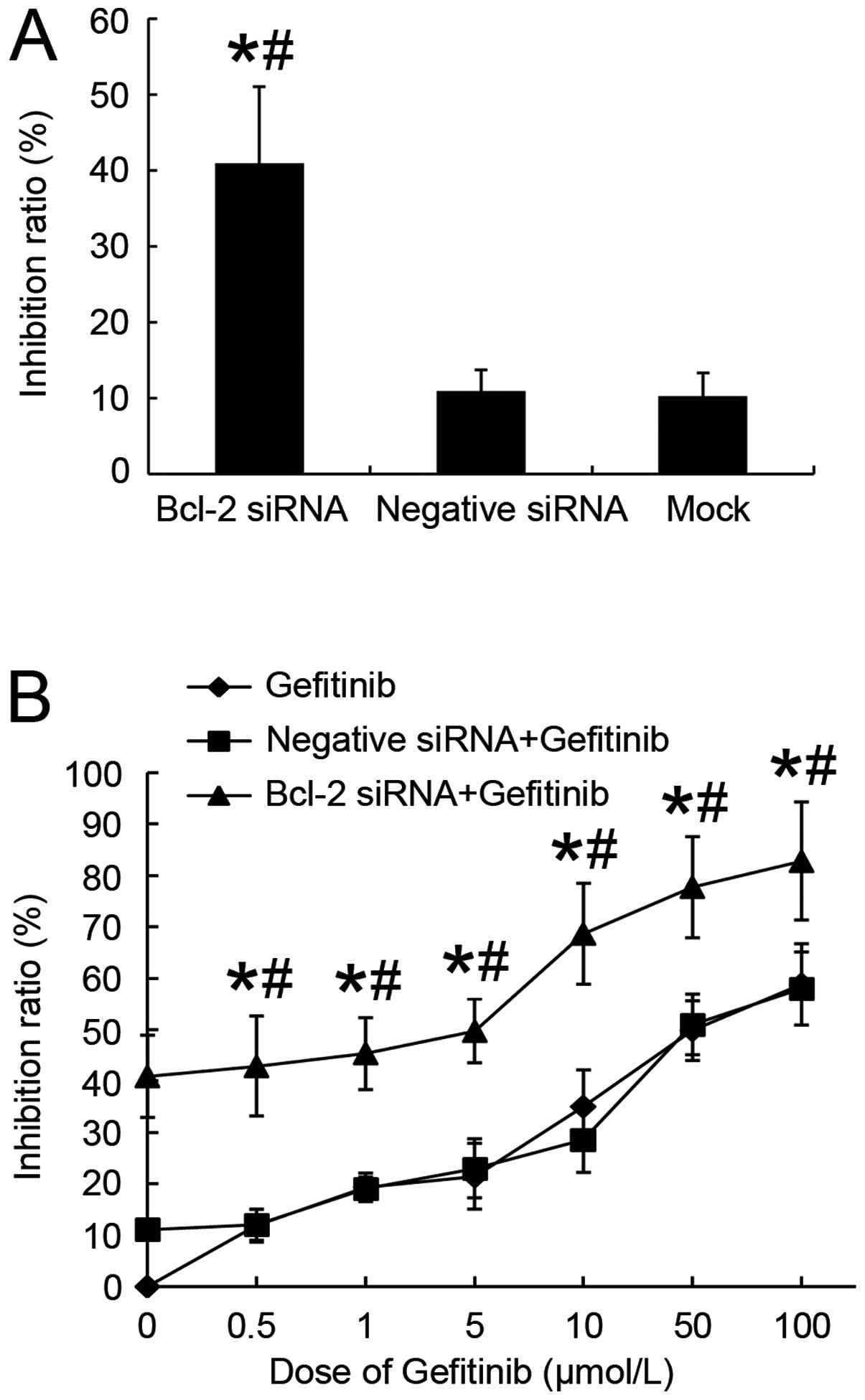
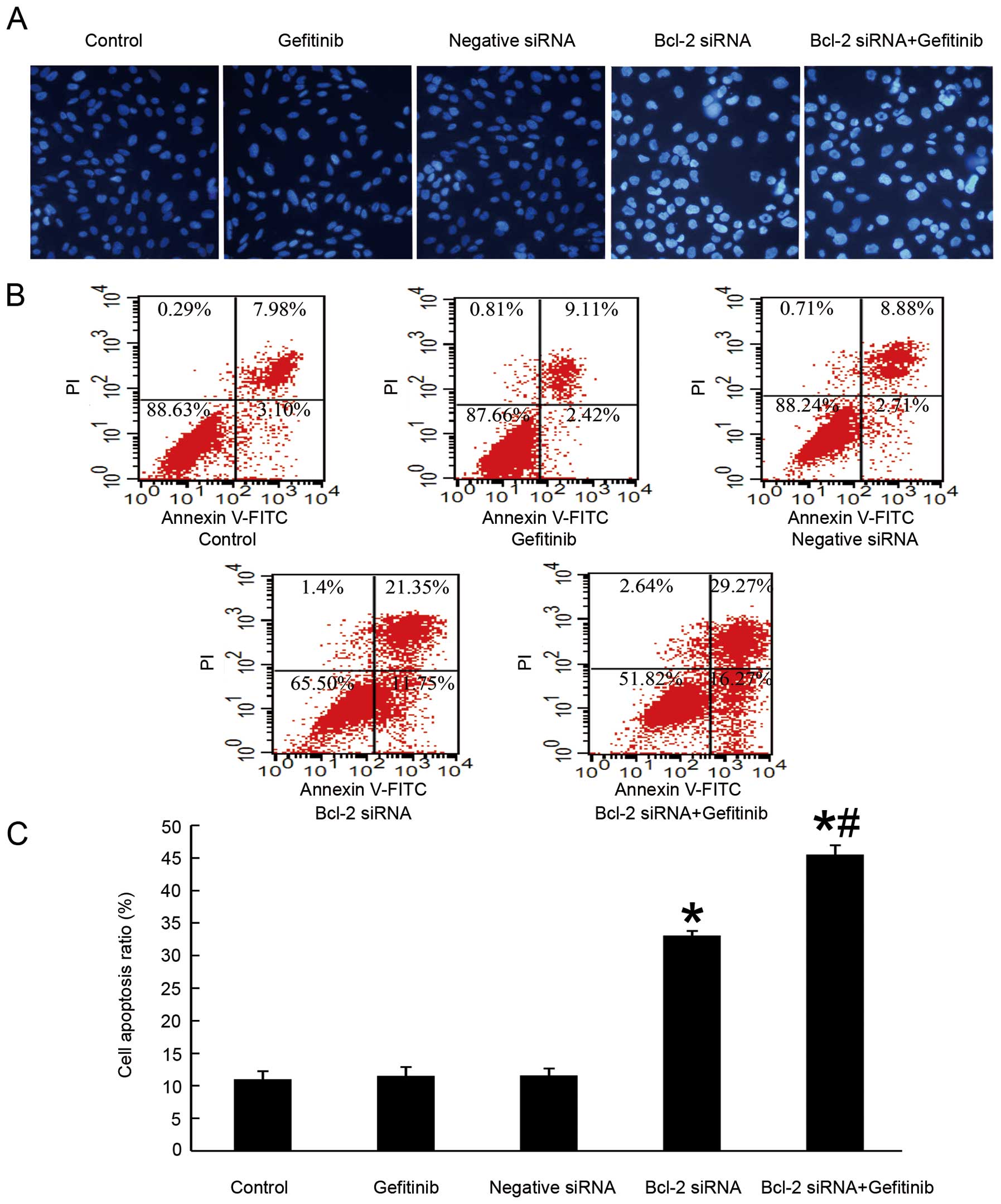
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tracy S, Mukohara T, Hansen M, Meyerson M,
Johnson BE and Janne PA: Gefitinib induces apoptosis in the
EGFRL858R non-small-cell lung cancer cell line H3255. Cancer Res.
64:7241–7244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al:
Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor
underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, et al: EGF
receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never
smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib
and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:13306–13311. 2004.
|
|
5
|
Sequist LV, Martins RG, Spigel D, et al:
First-line gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer harboring somatic EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol.
26:2442–2449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, et al:
EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352:786–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, et al:
Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or
erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase
domain. PLoS Med. 2:e732005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et
al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer
by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bianco R, Shin I, Ritter CA, et al: Loss
of PTEN/MMAC1/TEP in EGF receptor-expressing tumor cells
counteracts the antitumor action of EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. Oncogene. 22:2812–2822. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sos ML, Koker M, Weir BA, et al: PTEN loss
contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer by
activation of Akt and EGFR. Cancer Res. 69:3256–3261. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guix M, Faber AC, Wang SE, et al: Acquired
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer cells is
mediated by loss of IGF-binding proteins. J Clin Invest.
118:2609–2619. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jain A, Tindell CA, Laux I, et al:
Epithelial membrane protein-1 is a biomarker of gefitinib
resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:11858–11863. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Uchida A, Hirano S, Kitao H, et al:
Activation of downstream epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
signaling provides gefitinib-resistance in cells carrying EGFR
mutation. Cancer Sci. 98:357–363. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M, et al:
Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung
cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J Clin Oncol. 27:4247–4253. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang JM, He QY, Guo RX and Chang XJ:
Phosphorylated Akt overexpression and loss of PTEN expression in
non-small cell lung cancer confers poor prognosis. Lung Cancer J
Iaslc. 51:181–191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scrima M, De Marco C, Fabiani F, et al:
Signaling networks associated with AKT activation in non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC): new insights on the role of
phosphatydil-inositol-3 kinase. PLoS One. 7:e304272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y and Dennis PA:
Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell
lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to
chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 61:3986–3997.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Janmaat ML, Kruyt FA, Rodriguez JA and
Giaccone G: Response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
in non-small cell lung cancer cells: limited antiproliferative
effects and absence of apoptosis associated with persistent
activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase or Akt kinase
pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 9:2316–2326. 2003.
|
|
19
|
Yao M, Zhang W, Zhang Q, et al:
Overexpression of MUC1 enhances proangiogenic activity of
non-small-cell lung cancer cells through activation of Akt and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Lung. 189:453–460.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, et al:
Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a
double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial.
Lancet. 372:449–456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakachi I, Naoki K, Soejima K, et al: The
combination of multiple receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and
mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor overcomes erlotinib
resistance in lung cancer cell lines through c-Met inhibition. Mol
Cancer Res. 8:1142–1151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Price KA, Azzoli CG, Krug LM, et al: Phase
II trial of gefitinib and everolimus in advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5:1623–1629. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brown I, Shalli K, McDonald SL, et al:
Reduced expression of p27 is a novel mechanism of docetaxel
resistance in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 6:R601–R607.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Costa DB, Halmos B, Kumar A, et al: BIM
mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung
cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 4:1669–1679.
16802007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lima RT, Martins LM, Guimaraes JE, Sambade
C and Vasconcelos MH: Specific downregulation of bcl-2 and xIAP by
RNAi enhances the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 11:309–316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tumilasci VF, Oliere S, Nguyen TL, Shamy
A, Bell J and Hiscott J: Targeting the apoptotic pathway with BCL-2
inhibitors sensitizes primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to
vesicular stomatitis virus-induced oncolysis. J Virol.
82:8487–8499. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Aoki Y, Cioca DP, Oidaira H, Kamiya J and
Kiyosawa K: RNA interference may be more potent than antisense RNA
in human cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 30:96–102.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Witta SE, Gemmill RM, Hirsch FR, et al:
Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal
growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer
Res. 66:944–950. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baselga J, Rischin D, Ranson M, et al:
Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic trial of
ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, in patients with five selected solid tumor types.
J Clin Oncol. 20:4292–4302. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bursztajn S, Feng JJ, Berman SA and Nanda
A: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase induction is an early signal of
apoptosis in human neuroblastoma. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
76:363–376. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu XH, Lu Y, Fang YW and Jiang YX: The
polyamidoamine-mediated inhibition of bcl-2 by small hairpin RNA to
induce apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 18:74–80.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
George J, Banik NL and Ray SK: Combination
of taxol and Bcl-2 siRNA induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma
cells and inhibits invasion, angiogenesis and tumour growth. J Cell
Mol Med. 13:4205–4218. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, et al:
Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein
kinase Akt. Science. 275:661–665. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Janmaat ML, Rodriguez JA, Gallegos-Ruiz M,
Kruyt FA and Giaccone G: Enhanced cytotoxicity induced by gefitinib
and specific inhibitors of the Ras or phosphatidyl inositol-3
kinase pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
118:209–214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Morgillo F, D’Aiuto E, Troiani T, et al:
Antitumor activity of bortezomib in human cancer cells with
acquired resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Lung Cancer J Iaslc. 71:283–290. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zitzmann K, Ruden J, Brand S, et al:
Compensatory activation of Akt in response to mTOR and Raf
inhibitors - a rationale for dual-targeted therapy approaches in
neuroendocrine tumor disease. Cancer Lett. 295:100–109. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han SW and Roman J: Targeting apoptotic
signaling pathways in human lung cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
10:566–574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Losert D, Pratscher B, Soutschek J, et al:
Bcl-2 downregulation sensitizes nonsmall cell lung cancer cells to
cisplatin, but not to docetaxel. Anticancer Drugs. 18:755–761.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoo SH, Yoon YG, Lee JS, et al: Etoposide
induces a mixed type of programmed cell death and overcomes the
resistance conferred by Bcl-2 in Hep3B hepatoma cells. Int J Oncol.
41:1443–1454. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lawson MH, Cummings NM, Rassl DM, et al:
Bcl-2 and beta1-integrin predict survival in a tissue microarray of
small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 103:1710–1715. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Roberts AW, Seymour JF, Brown JR, et al:
Substantial susceptibility of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to BCL2
inhibition: results of a phase I study of navitoclax in patients
with relapsed or refractory disease. J Clin Oncol. 30:488–496.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schimmer AD, O’Brien S, Kantarjian H, et
al: A phase I study of the pan bcl-2 family inhibitor obatoclax
mesylate in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:8295–8301. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gandhi L, Camidge DR, Ribeiro DOM, et al:
Phase I study of Navitoclax (ABT-263), a novel Bcl-2 family
inhibitor, in patients with small-cell lung cancer and other solid
tumors. J Clin Oncol. 29:909–916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chiappori AA, Schreeder MT, Moezi MM, et
al: A phase I trial of pan-Bcl-2 antagonist obatoclax administered
as a 3-h or a 24-h infusion in combination with carboplatin and
etoposide in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Br J Cancer. 106:839–845. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen KF, Lin JP, Shiau CW, et al:
Inhibition of Bcl-2 improves effect of LCL161, a SMAC mimetic, in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:268–277.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan W, Tang Z, Yin L, et al:
MET-independent lung cancer cells evading EGFR kinase inhibitors
are therapeutically susceptible to BH3 mimetic agents. Cancer Res.
71:4494–4505. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu X, Zhang X, Dhakal IB, Beggs M,
Kadlubar S and Luo D: Induction of cell proliferation and survival
genes by estradiol-repressed microRNAs in breast cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 12:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang XF, Shi ZM, Wang XR, et al: MiR-181d
acts as a tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting K-ras and Bcl-2.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:573–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang Y, Wu J, Guan H, et al: MiR-136
promotes apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting AEG-1 and Bcl-2.
FEBS Lett. 586:3608–3612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hung JH, Teng YN, Wang LH, et al:
Induction of Bcl-2 expression by hepatitis B virus pre-S2 mutant
large surface protein resistance to 5-fluorouracil treatment in
Huh-7 cells. PLoS One. 6:e289772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|