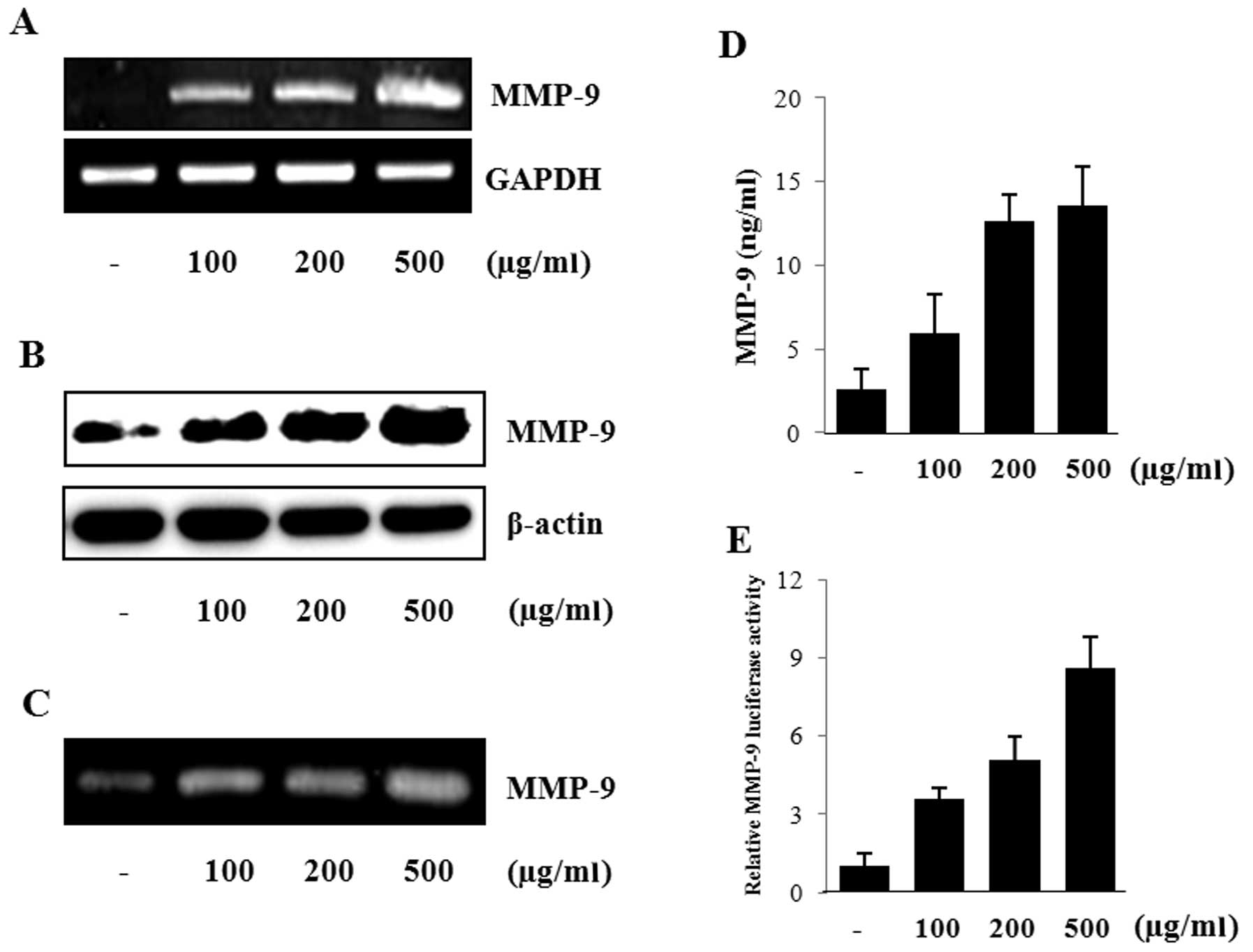
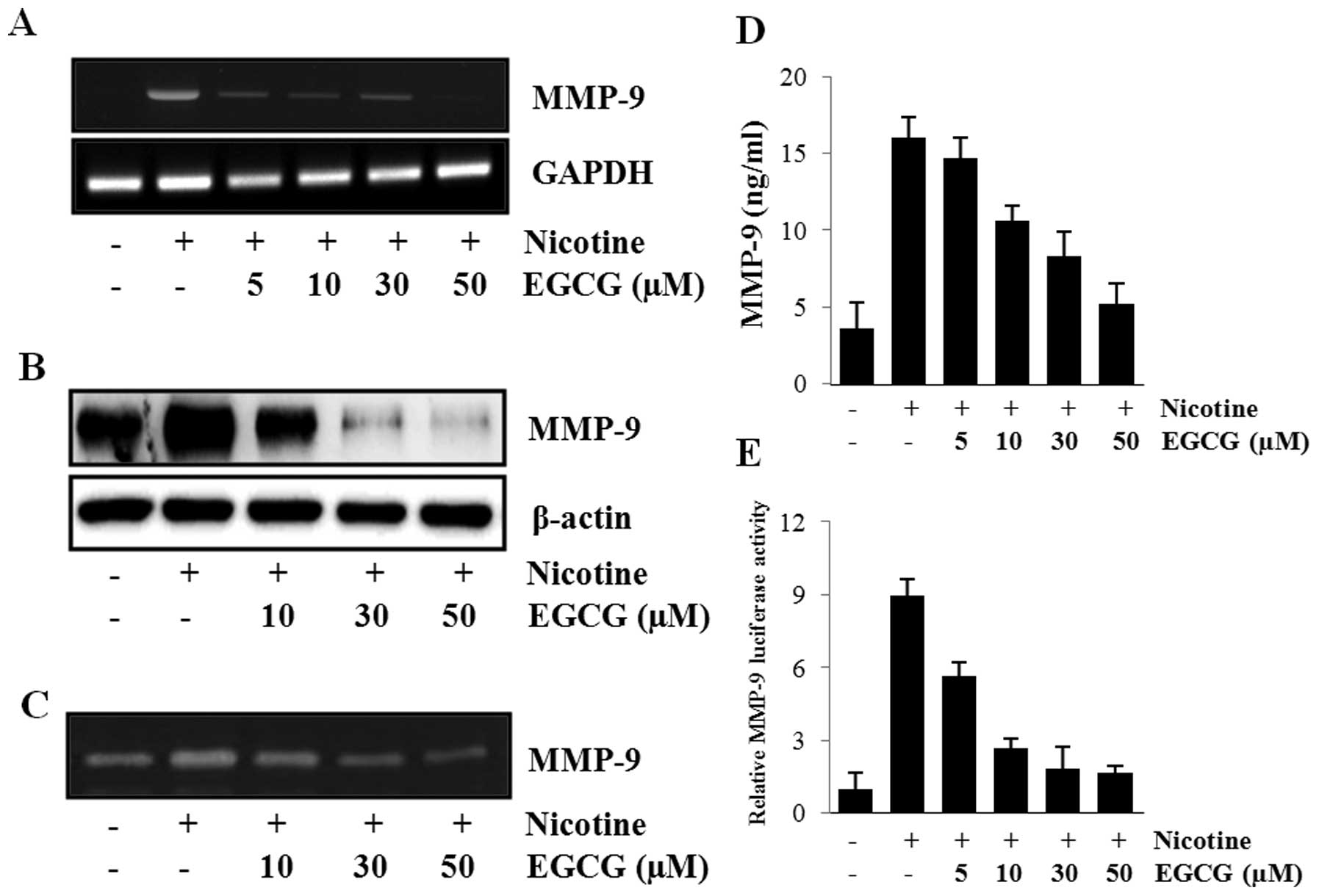
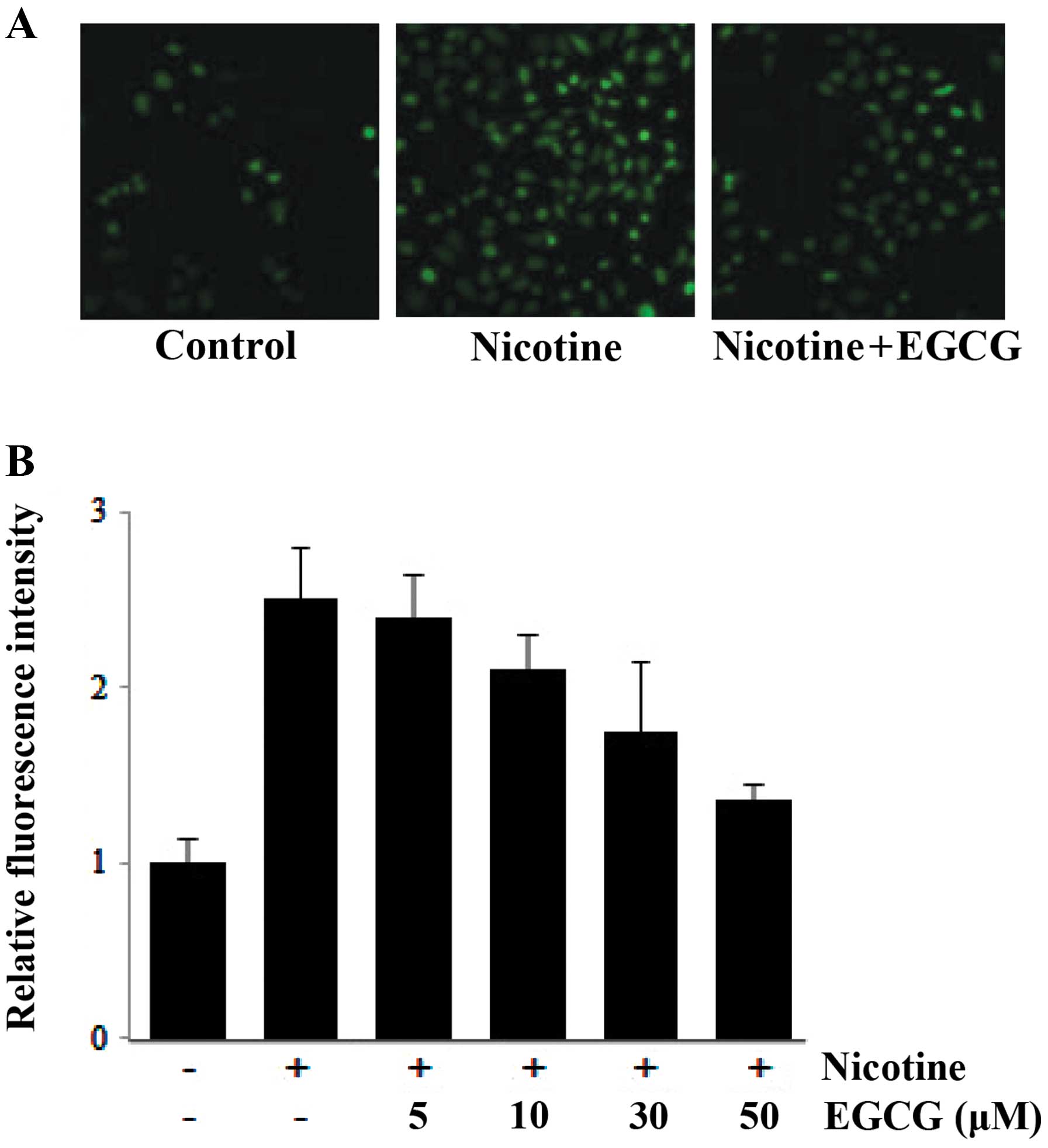
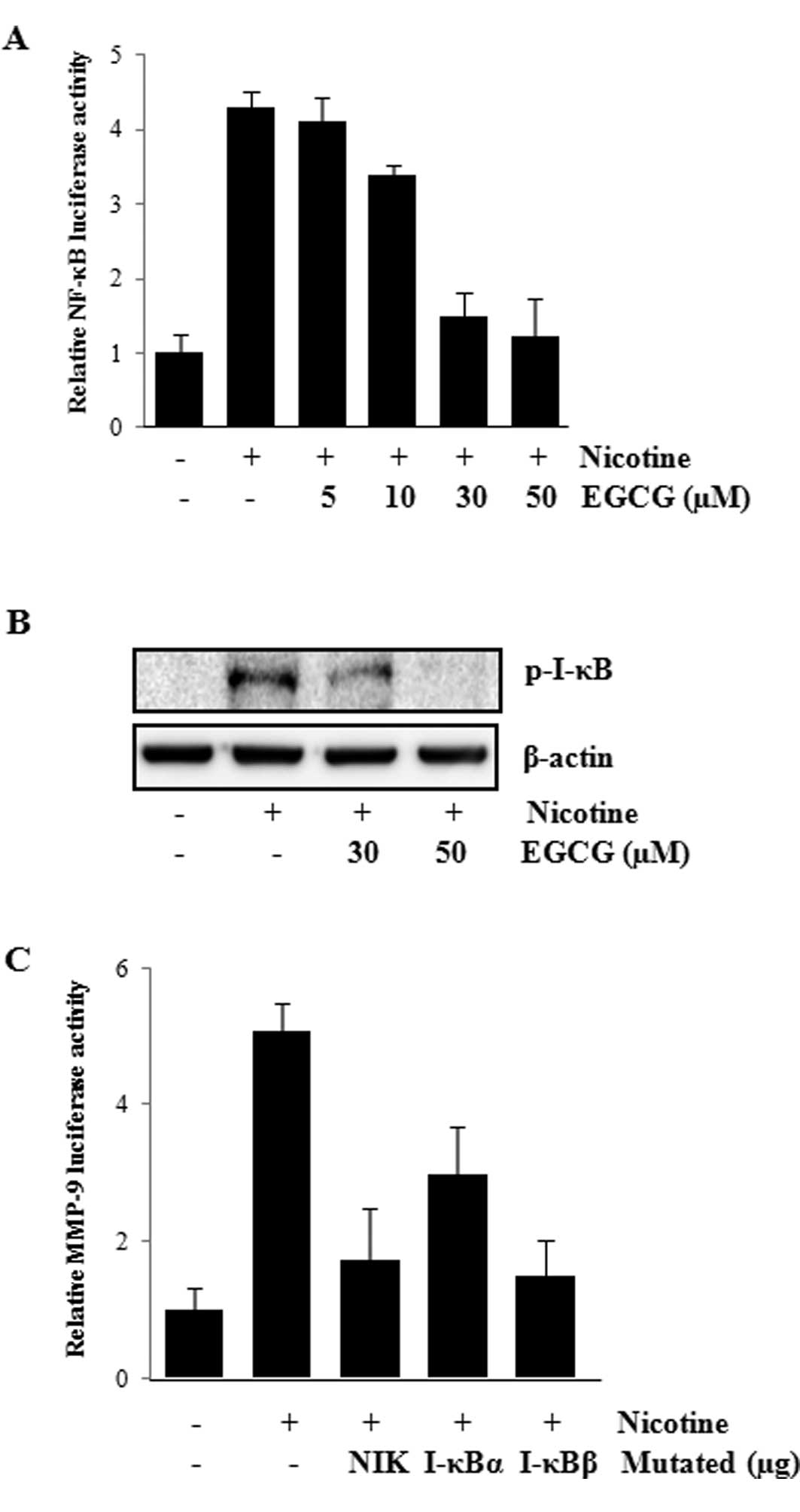
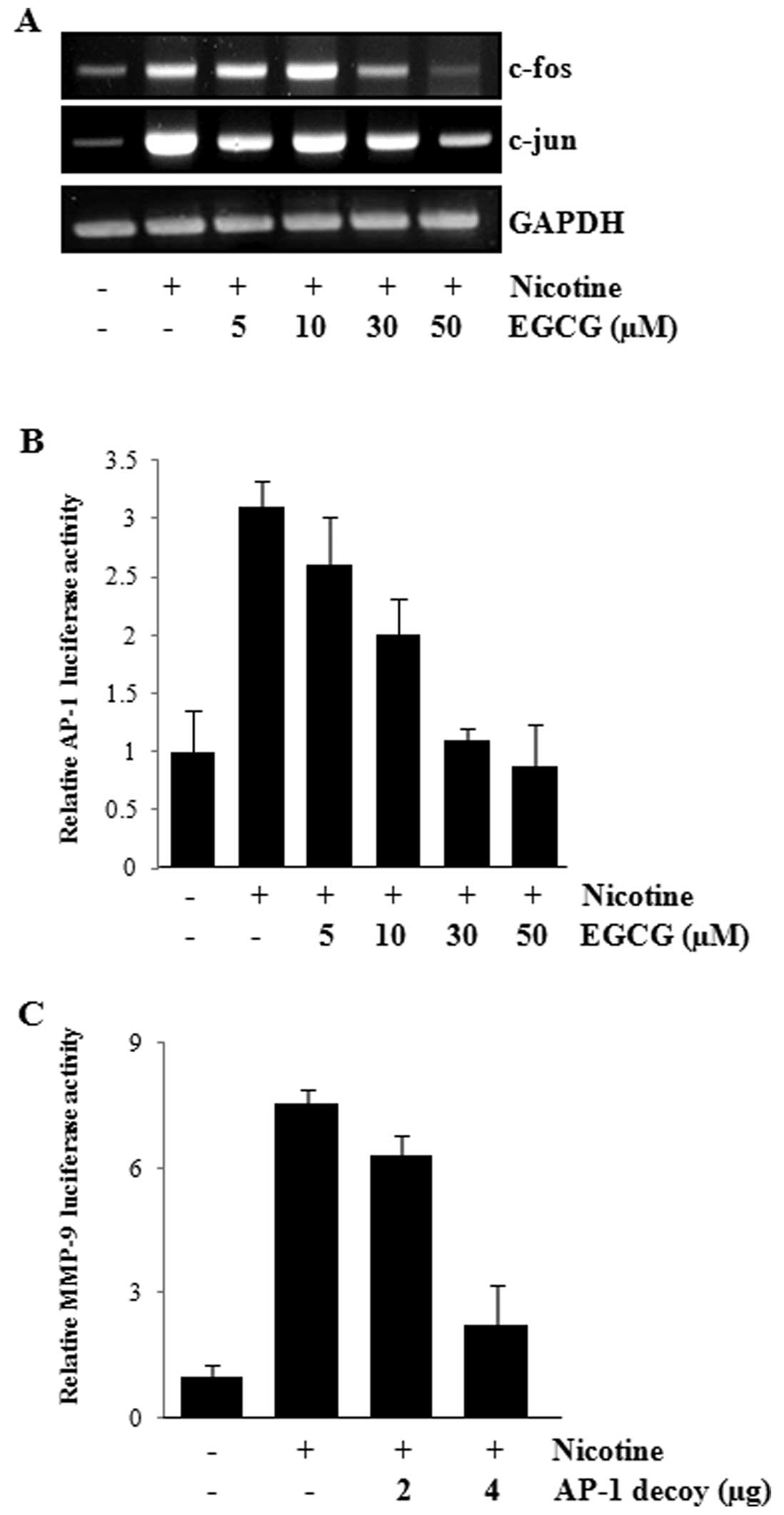
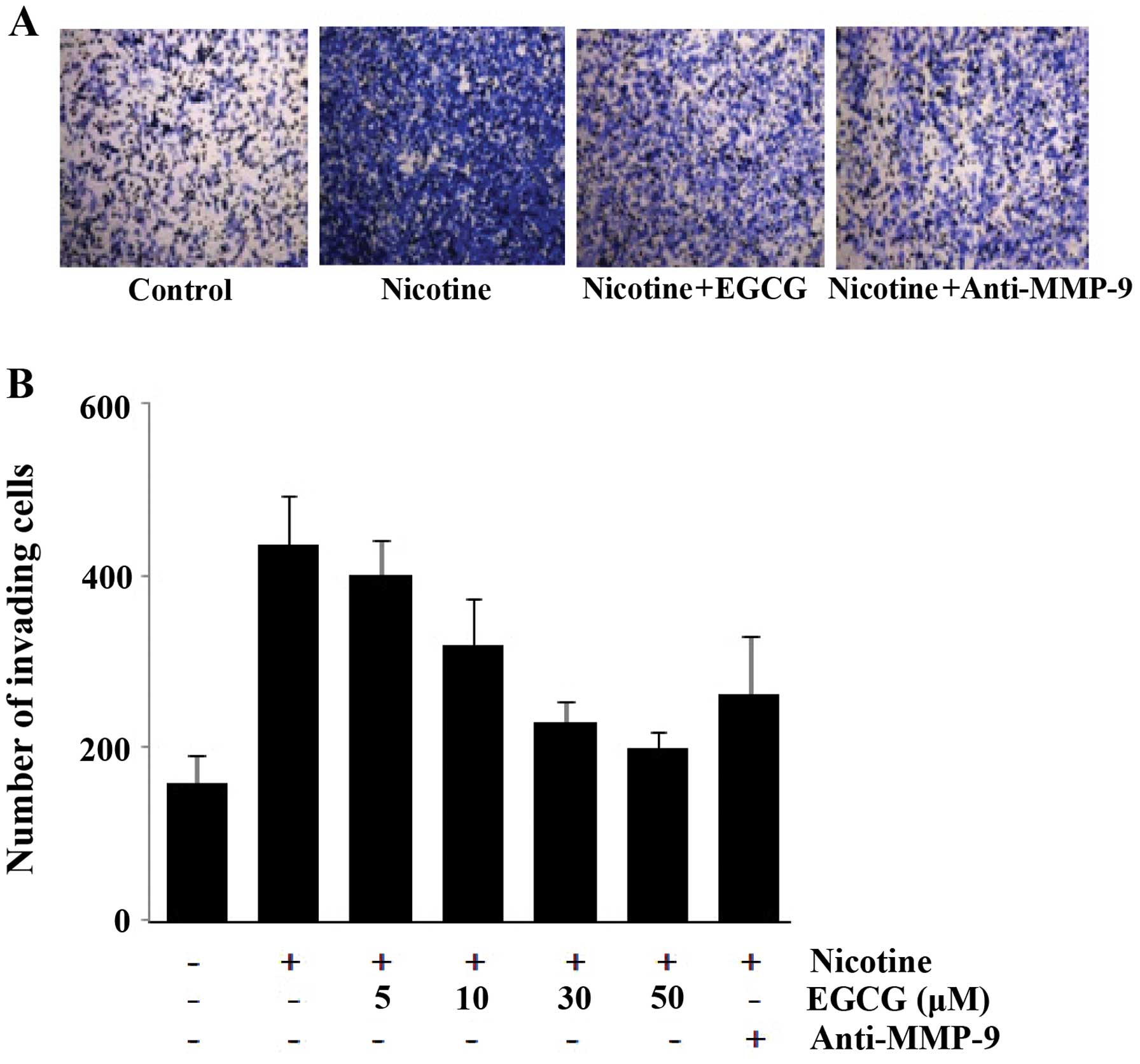
|
1
|
Brunnemann KD and Hoffmann D: Analytical
studies on tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines in tobacco and tobacco
smoke. Crit Rev Toxicol. 21:235–240. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davis R, Rizwani W, Banerjee S, Kovacs M,
Haura E, Coppola D and Chellappan S: Nicotine promotes tumor growth
and metastasis in mouse models of lung cancer. PLoS One.
4:e75242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ji BT, Chow WH, Hsing AW, McLaughlin JK,
Dai Q, Gao YT, Blot WJ and Fraumeni JF Jr: Green tea consumption
and the risk of pancreatic and colorectal cancers. Int J Cancer.
70:255–258. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stoner GD and Mukhtar H: Polyphenols as
cancer chemopreventive agents. J Cell Biochem (Suppl). 22:169–180.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Paschka AG, Butler R and Young CY:
Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines by the green
tea component, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Lett.
130:1–7. 1998.
|
|
6
|
Jung YD, Kim MS, Shin BA, Chay KO, Ahn BW,
Liu W, Bucana CD, Gallick GE and Ellis LM: EGCG, a major component
of green tea, inhibits tumour growth by inhibiting VEGF induction
in human colon carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 84:844–850. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sen T, Dutta A and Chatterjee A:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) downregulates gelatinase-B
(MMP-9) by involvement of FAK/ERK/NFkappaB and AP-1 in the human
breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Anticancer Drugs. 21:632–644.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim MH, Jung MA, Hwang YS, Jeong M, Kim
SM, Ahn SJ, Shin BA, Ahn BW and Jung YD: Regulation of urokinase
plasminogen activator by epigallocatechin-3-gallate in human
fibrosarcoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 487:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen JZ, Zheng XF, Wei EQ and Kwan CY:
Green tea catechins evoke a phasic contraction in rat aorta via
H2O2-mediated multiple-signalling pathways.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 30:88–95. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung YD and Ellis LM: Inhibition of tumour
invasion and angiogenesis by epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a
major component of green tea. Int J Exp Pathol. 82:309–316. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Parsons SL, Watson SA, Brown PD, Collins
HM and Steele RJ: Matrix metalloproteinases. Br J Surg. 84:160–166.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chandler S, Miller KM, Clements JM, Lury
J, Corkill D, Anthony DC, Adams SE and Gearing AJ: Matrix
metalloproteinases, tumor necrosis factor and multiple sclerosis:
an overview. J Neuroimmunol. 72:155–161. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ogata Y, Pratta MA, Nagase H and Arner EC:
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (92-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase)
is induced in rabbit articular chondrocytes by cotreatment with
interleukin 1 beta and a protein kinase C activator. Exp Cell Res.
201:245–249. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ma Z, Qin H and Benveniste EN:
Transcriptional suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene
expression by IFN-gamma and IFN-beta: critical role of STAT-1alpha.
J Immunol. 167:5150–5159. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vartak DG and Gemeinhart RA: Matrix
metalloproteases: underutilized targets for drug delivery. J Drug
Target. 15:1–20. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV,
Papatsoris AG and Papavassiliou AG: Matrix metalloproteinase
inhibitors as anticancer agents. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
40:1156–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF and Liotta LA:
General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer. 80:1529–1537. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mehlen P and Puisieux A: Metastasis: a
question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:449–458. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arii S, Mise M, Harada T, Furutani M,
Ishigami S, Niwano M, Mizumoto M, Fukumoto M and Imamura M:
Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene in hepatocellular
carcinoma with invasive potential. Hepatology. 24:316–322. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Klein G, Vellenga E, Fraaije MW, Kamps WA
and de Bont ES: The possible role of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in cancer, e.g acute leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 50:87–100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shin SY, Kim JH, Baker A, Lim Y and Lee
YH: Transcription factor Egr-1 is essential for maximal matrix
metalloproteinase-9 transcription by tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Mol Cancer Res. 8:507–519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McKinsey TA, Brockman JA, Scherer DC,
Al-Murrani SW, Green PL and Ballard DW: Inactivation of IkappaBbeta
by the tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: a
potential mechanism for constitutive induction of NF-kappaB. Mol
Cell Biol. 16:2083–2090. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Geleziunas R, Ferrell S, Lin X, Mu Y,
Cunningham ET Jr, Grant M, Connelly MA, Hambor JE, Marcu KB and
Greene WC: Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax induction of
NF-kappaB involves activation of the IkappaB kinase alpha
(IKKalpha) and IKKbeta cellular kinases. Mol Cell Biol.
18:5157–5165. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hwang YS, Jeong M, Park JS, Kim MH, Lee
DB, Shin BA, Mukaida N, Ellis LM, Kim HR, Ahn BW and Jung YD:
Interleukin-1beta stimulates IL-8 expression through MAP kinase and
ROS signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncogene.
23:6603–6611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mizuma M, Katayose Y, Yamamoto K, Shiraso
S, Sasaki T, Yabuuchi S, Oda A, Masuda K, Rikiyama T, Onogawa T,
Ohtsuka H, Motoi F, Egawa S and Unno M: Up-regulated
p27Kip1 reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inhibits
invasion of human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
28:2669–2677. 2008.
|
|
26
|
Poulsen HE, Jensen BR, Weimann A, Jensen
SA, Sørensen M and Loft S: Antioxidants, DNA damage and gene
expression. Free Radic Res. 33:33–39. 2000.
|
|
27
|
Park MJ, Lee JY, Kwak HJ, Park CM, Lee HC,
Woo SH, Jin HO, Han CJ, An S, Lee SH, Chung HY, Park IC, Hong SI
and Rhee CH: Arsenic trioxide (As2O3)
inhibits invasion of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells: role of
nuclear factor-kappaB and reactive oxygen species. J Cell Bochem.
95:955–969. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tobar N, Villar V and Santibanez JF:
ROS-NFkappaB mediates TGF-beta1-induced expression of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator, matrix metalloproteinase-9
and cell invasion. Mol Cell Biochem. 340:195–202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim HS, Kim MH, Jeong M, Hwang YS, Lim SH,
Shin BA, Ahn BW and Jung YD: EGCG blocks tumor promoter-induced
MMP-9 expression via suppression of MAPK and AP-1 activation in
human gastric AGS cells. Anticancer Res. 24:747–753.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hipskind RA and Bilbe G: MAP kinase
signaling cascades and gene expression in osteoblasts. Front
Biosci. 3:804–816. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guedea AL, Schrick C, Guzman YF,
Leaderbrand K, Jovasevic V, Corcoran KA, Tronson NC and Radulovic
J: ERK-associated changes of AP-1 proteins during fear extinction.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 47:137–144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iwasaka C, Tanaka K, Abe M and Sato Y:
Ets-1 regulates angiogenesis by inducing the expression of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase-1
and the migration of vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol.
169:522–531. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hong MH, Kim MH, Chang HJ, Kim NH, Shin
BA, Ahn BW and Jung YD: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits
monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression in endothelial cells via
blocking NF-kappaB signaling. Life Sci. 80:1957–1965. 2007.
|
|
34
|
Wittel UA, Momi N, Seifert G, Wiech T,
Hopt UT and Batra SK: The pathobiological impact of cigarette smoke
on pancreatic cancer development (Review). Int J Oncol. 41:5–14.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen RJ, Chang LW, Lin P and Wang YJ:
Epigenetic effects and molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis
induced by cigarette smoke: an overview. J Oncol.
2011:6549312011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jacob-Ferreira AL, Palei AC, Cau SB,
Moreno H Jr, Martinez ML, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Gerlach RF and
Tanus-Santos JE: Evidence for the involvement of matrix
metalloproteinases in the cardiovascular effects produced by
nicotine. Eur J Pharmacol. 627:216–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Noda M, Oh J, Takahashi R, Kondo S,
Kitayama H and Takahashi C: RECK: a novel suppressor of malignancy
linking oncogenic signaling to extracellular matrix remodeling.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 22:167–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee HY, Park KS, Kim MK, Lee T, Ryu SH,
Woo KJ, Kwon TK and Bae YS: A small compound that inhibits tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9
upregulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 336:716–722. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brenneisen P, Briviba K, Wlaschek M, Wenk
J and Scharffetter-Kochanek K: Hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2) increases the steady-state mRNA levels
of collagenase/MMP-1 in human dermal fibroblasts. Free Radic Biol
Med. 22:515–524. 1997.
|
|
41
|
Asano H, Horinouchi T, Mai Y, Sawada O,
Fujii S, Nishiya T, Minami M, Katayama T, Iwanaga T, Terada K and
Miwa S: Nicotine- and tar-free cigarette smoke induces cell damage
through reactive oxygen species newly generated by PKC-dependent
activation of NADPH oxidase. J Pharmacol Sci. 118:275–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Okabe S, Suganuma M, Hayashi M, Sueoka E,
Komori A and Fujiki H: Mechanisms of growth inhibition of human
lung cancer cell line, PC-9, by tea polyphenols. Jpn J Cancer Res.
88:639–643. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Graham HN: Green tea composition,
consumption and polyphenol chemistry. Prev Med. 21:334–350. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang G, Miura Y and Yagasaki K:
Suppression of adhesion and invasion of hepatoma cells in culture
by tea compounds through antioxidative activity. Cancer Lett.
159:169–173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sato H and Seiki M: Regulatory mechanism
of 92 kDa type IV collagenase gene expression which is associated
with invasiveness of tumor cells. Oncogene. 8:395–405.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
van Dam H and Castellazzi M: Distinct
roles of Jun: Fos and Jun: ATF dimers in oncogenesis. Oncogene.
20:2453–2464. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Besirli CG, Wagner EF and Johnson EM Jr:
The limited role of NH2-terminal c-Jun phosphorylation
in neuronal apoptosis: identification of the nuclear pore complex
as a potential target of the JNK pathway. J Cell Biol. 170:401–411.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gum R, Wang H, Lengyel E, Juarez J and
Boyd D: Regulation of 92 kDa type IV collagenase expression by the
jun aminoterminal kinase- and the extracellular signal-regulated
kinase-dependent signaling cascades. Oncogene. 14:1481–1493. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Simon C, Simon M, Vucelic G, Hicks MJ,
Plinkert PK, Koitschev A and Zenner HP: The p38 SAPK pathway
regulates the expression of the MMP-9 collagenase via
AP-1-dependent promoter activation. Exp Cell Res. 271:344–355.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|