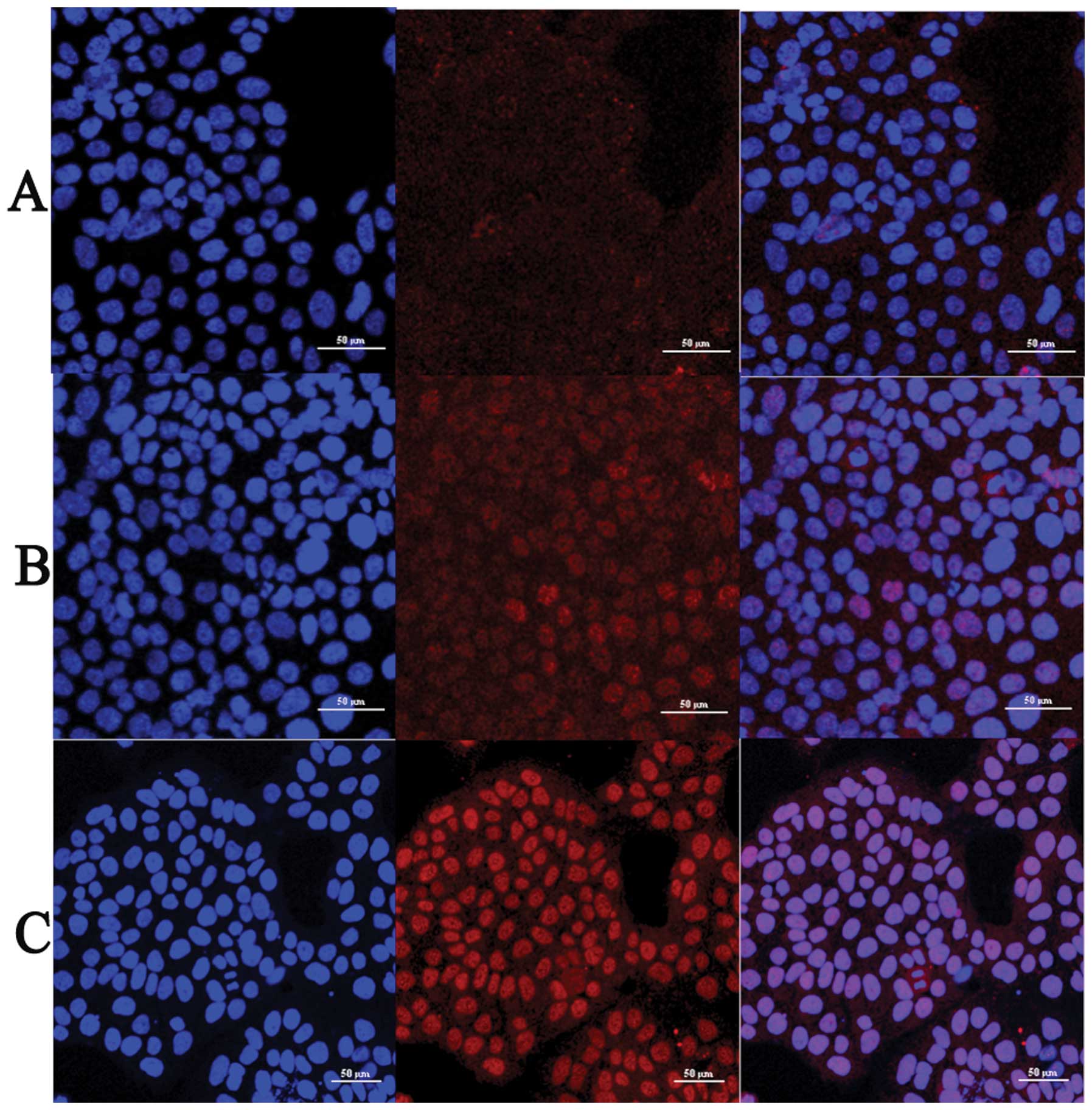
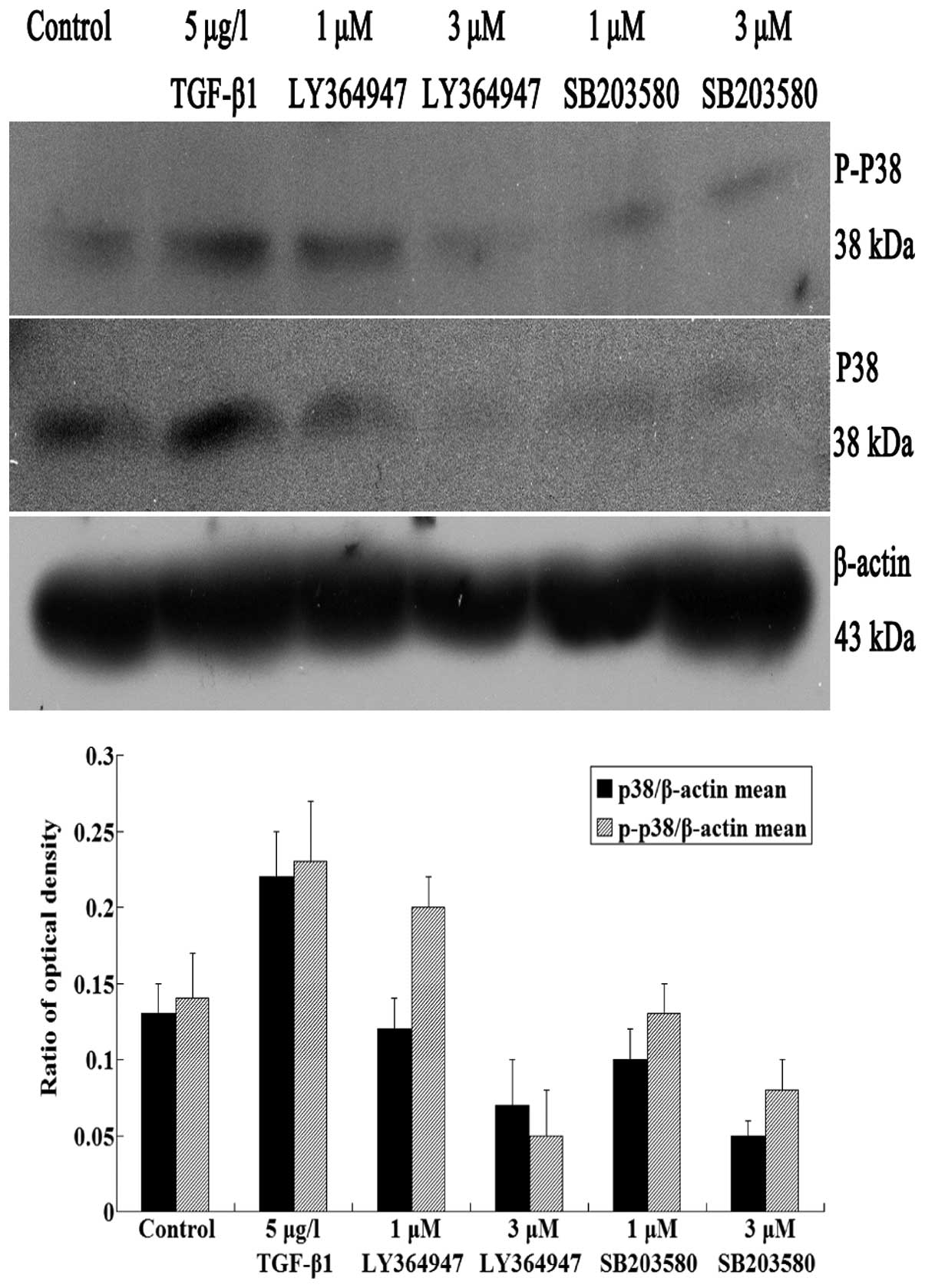
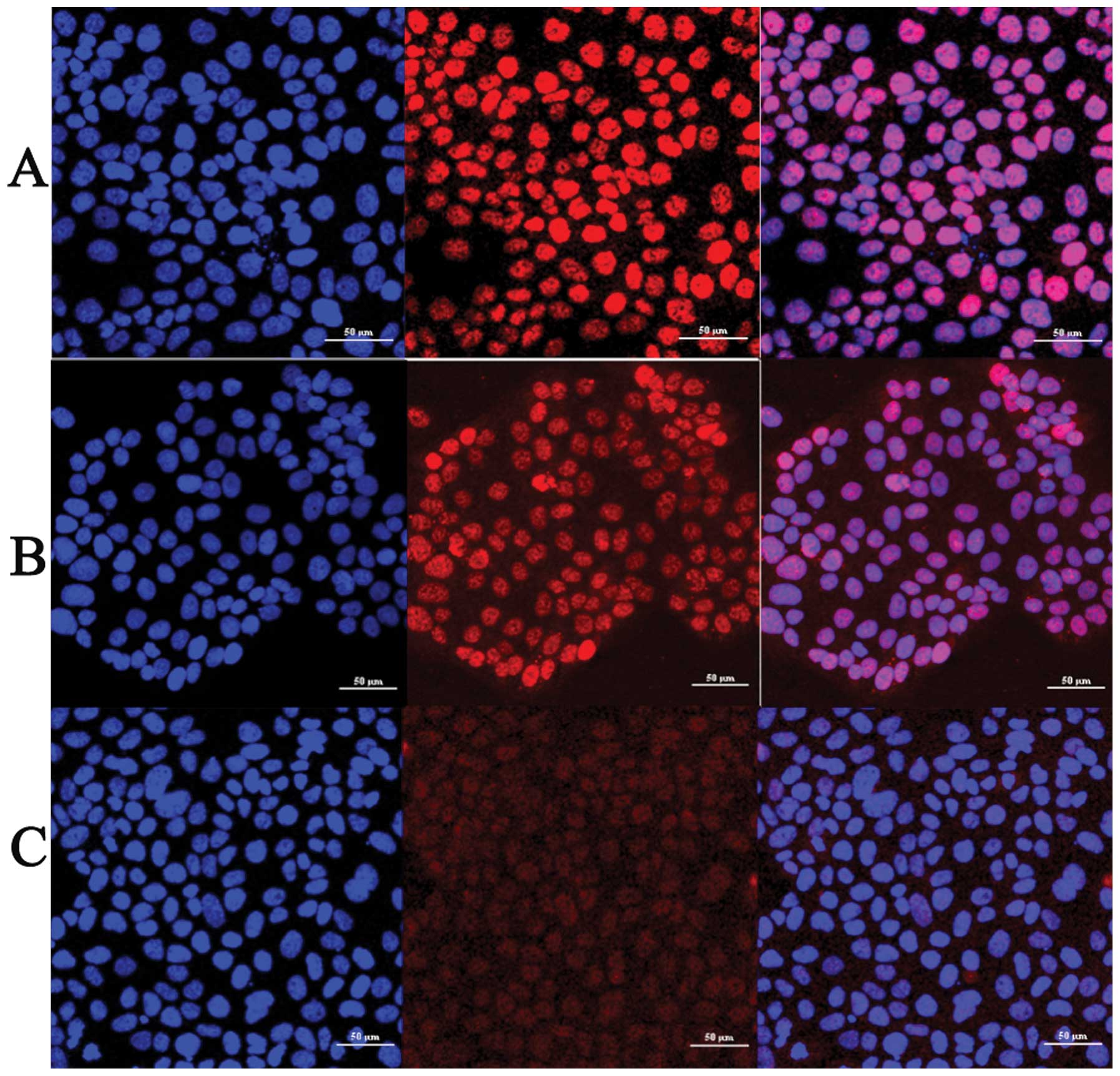
|
1.
|
McGee J and Covens A: Gestational
trophoblastic disease: hydatidiform mole, nonmetastatic and
metastatic gestational trophoblastic tumor: diagnosis and
management. Comprehensive Gynecology. 6th edition. Lentz GM, Lobo
RA, Gershenson DM and Katz VL: Mosby Elsevier; Philadelphia, PA:
chapter 35,. 2012
|
|
2.
|
Braunstein GD: Endocrine changes in
pregnancy. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Melmed S, Polonsky
KS, Larsen PR and Kronenberg HM: 12th edition. Saunders Elsevier;
Philadelphia, PA: chapter 21,. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Yamamoto E, Ino K, Yamamoto T, Sumigama S,
Nawa A, Nomura S and Kikkawa F: A pure nongestational
choriocarcinoma of the ovary diagnosed with short tandem repeat
analysis: case report and review of the literature. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 17:254–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Fu Y, O’Connor LM, Shepherd TG and
Nachtigal MW: The p38 MAPK inhibitor, PD169316, inhibits
transforming growth factor beta-induced Smad signaling in human
ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 310:391–397.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Li Y, Xu Q, Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi C and Tan
Y: The impact of TGF-β1 on the mRNA expression of TβR I, TβR II,
Smad4 and the invasiveness of the JEG-3 placental choriocarcinoma
cell line. Oncol Lett. 4:1344–1348. 2012.
|
|
6.
|
Watanabe H, de Caestecker MP and Yamada Y:
Transcriptional cross-talk between Smad, ERK1/2, and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways regulates transforming
growth factor-β-induced aggrecan gene expression in chondrogenic
ATDC5 cells. J Biol Chem. 276:466–473. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: Cellular
context-dependent ‘colors’ of transforming growth factor-β
signaling. Cancer Sci. 101:306–312. 2010.
|
|
8.
|
Nickl-Jockschat T, Arslan F, Doerfelt A,
Bogdahn U, Bosserhoff A and Hau P: An imbalance between Smad and
MAPK pathways is responsible for TGF-β tumor promoting effects in
high-grade gliomas. Int J Oncol. 30:499–507. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Chapnick DA, Warner L, Bernet J, Rao T and
Liu X: Partners in crime: the TGFβ and MAPK pathways in cancer
progression. Cell Biosci. 1:42–49. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Coulthard LR, White DE, Jones DL,
McDermott MF and Burchill SA: p38(MAPK): stress responses from
molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 15:369–379.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Takekawa M, Kubota Y, Nakamura T and
Ichikawa K: Regulation of stress-activated MAP kinase pathways
during cell fate decisions. Nagoya J Med Sci. 73:1–14.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Cuenda A and Rousseau S: p38 MAP-kinases
pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:1358–1375. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Shiryaev A and Moens U: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase p38 and MK2, MK3 and MK5: ménage à trois or ménage à
quatre? Cell Signal. 22:1185–1192. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Freund A, Patil CK and Campisi J: p38MAPK
is a novel DNA damage response-independent regulator of the
senescence-associated secretory phenotype. EMBO J. 30:1536–1548.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Li J, Deane JA, Campanale NV, Bertram JF
and Ricardo SD: Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
and TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway rescues bone marrow-derived
peritubular capillary endothelial cells in adriamycin-induced
nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 10:2799–2811. 2006.
|
|
16.
|
Gui T, Sun Y, Shimokado A and Muragaki Y:
The roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Signal
Transduct. 12:1155–1165. 2012.
|
|
17.
|
Kolosova I, Nethery D and Kern JA: Role of
Smad2/3 and p38 MAP kinase in TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of pulmonary epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol.
226:1248–1254. 2011.
|
|
18.
|
Undevia NS, Dorscheid DR, Marroquin BA, et
al: Smad and p38-MAPK signaling mediates apoptotic effects of
transforming growth factor-β in human airway epithelial cells. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 287:L515–L524. 2004.
|
|
19.
|
Dziembowska M, Danilkiewicz M, Wesolowska
A, et al: Crosstalk between Smad and p38MAPK signalling in
transforming growth factor beta signal transduction in human
glioblastoma cells. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 354:1101–1106. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Tsukada S, Westwick JK, Ikejima K, et al:
SMAD and p38 MAPK signaling pathways independently regulate α1(I)
collagen gene expression in unstimulated and transforming growth
factor-β-stimulated hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem.
280:10055–10064. 2005.
|
|
21.
|
Han YC, Zeng XX, Wang R, Zhao Y, Li BL and
Song M: Correlation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal
transduction pathway to uPA expression in breast cancer. Ai Zheng.
26:48–53. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Zhang X-Z, Huang D, Wu F, et al:
Experimental study on role of TGF-β1/p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway to renal interstitial fibrosis and intervention
mechanisms of Kang Xianling Decoction. China J Traditional Chinese
Medicine Pharmacy. 26:245–248. 2011.
|
|
23.
|
Chen YX, Weng ZH and Zhang SL: Notch3
regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:1397–1403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Vyas B, Ishikawa K, Duflo S, Chen X and
Thibeault SL: Inhibitory effects of HGF and IL-6 on TGF-β1 mediated
vocal fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation. Ann Otol Rhinol
Laryngol. 119:350–357. 2010.
|
|
25.
|
Kashiwagi Y, Horie K, Kanno C, Inomata M,
et al: Trichostatin A-induced TGF-β type II receptor expression in
retinoblastoma cell lines. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:679–685.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Meng XM, Huang XR, Chung AC, Qin W, Shao
X, et al: Smad2 protects against TGF-β/Smad3-mediated renal
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1477–1487. 2010.
|
|
27.
|
Goldstein DP and Berkowitz RS: Gestational
trophoblastic disease. Abeloff’s Clinical Oncology. 4th edition.
Abeloff MD, Armitage JO, Niederhuber JE, Kastan MB and McKenna WG:
Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 94–112.
2008
|
|
28.
|
Gerulath AH and Toronto: Gestational
Trophoblastic Disease. Sogc Clinic Practice Guidelines. 114:1–6.
2002.
|
|
29.
|
Denkert C, Darb-Esfahani S, Loibl S,
Anagnostopoulos I and Jöhrens K: Anti-cancer immune response
mechanisms in neoadjuvant and targeted therapy. Semin Immunopathol.
33:341–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Giampieri S, Pinner S and Sahai E:
Intravital imaging illuminates transforming growth factor beta
signaling switches during metastasis. Cancer Res. 70:3435–3439.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Tsai S, Hollenbeck ST, Ryer EJ, Edlin R,
Yamanouchi D, Kundi R, Wang C, Liu B and Kent KC: TGF-β through
Smad3 signaling stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and neointimal formation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 297:H540–H549. 2009.
|
|
32.
|
Javelaud D and Mauviel A: Crosstalk
mechanisms between the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways
and Smad signaling downstream of TGF-β: implications for
carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 24:5742–5750. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK and
Arteaga CL: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for
TGFβ-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration.
J Cell Sci. 115:3193–3206. 2002.
|
|
34.
|
Furukawa F, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, Tahashi
Y, et al: p38 MAPK mediates fibrogenic signal through Smad3
phosphorylation in rat myofibroblasts. Hepatology. 38:879–889.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Ungefroren H, Groth S, Sebens S, Lehnert
H, Gieseler F and Fändrich F: Differential roles of Smad2 and Smad3
in the regulation of TGF-β1-mediated growth inhibition and cell
migration in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells: control by
Racl. Mol Cancer. 10:671–679. 2011.
|
|
36.
|
Grzmil M, Morin P Jr, Lino MM, et al: MAP
kinase-interacting kinase 1 regulates SMAD2-dependent TGF-β
signaling pathway in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 71:2392–2402.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|