|
1.
|
Scelo G and Brennan P: The epidemiology of
bladder and kidney cancer. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 4:205–217. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
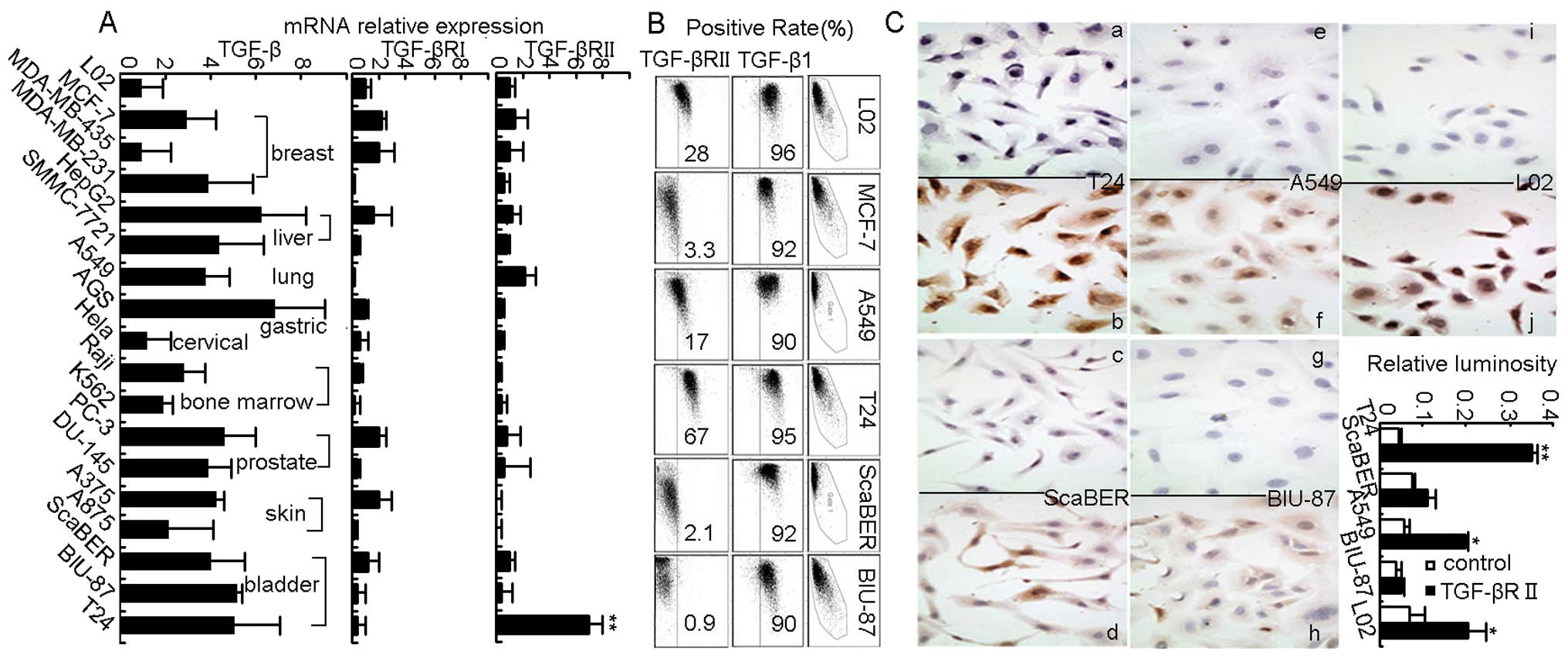
2.
|
Niu HT, Shao SX, Zhang ZL, et al:
Quantitative risk stratification and individual comprehensive
therapy for invasive bladder cancers in China. Int Urol Nephrol.
41:571–577. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
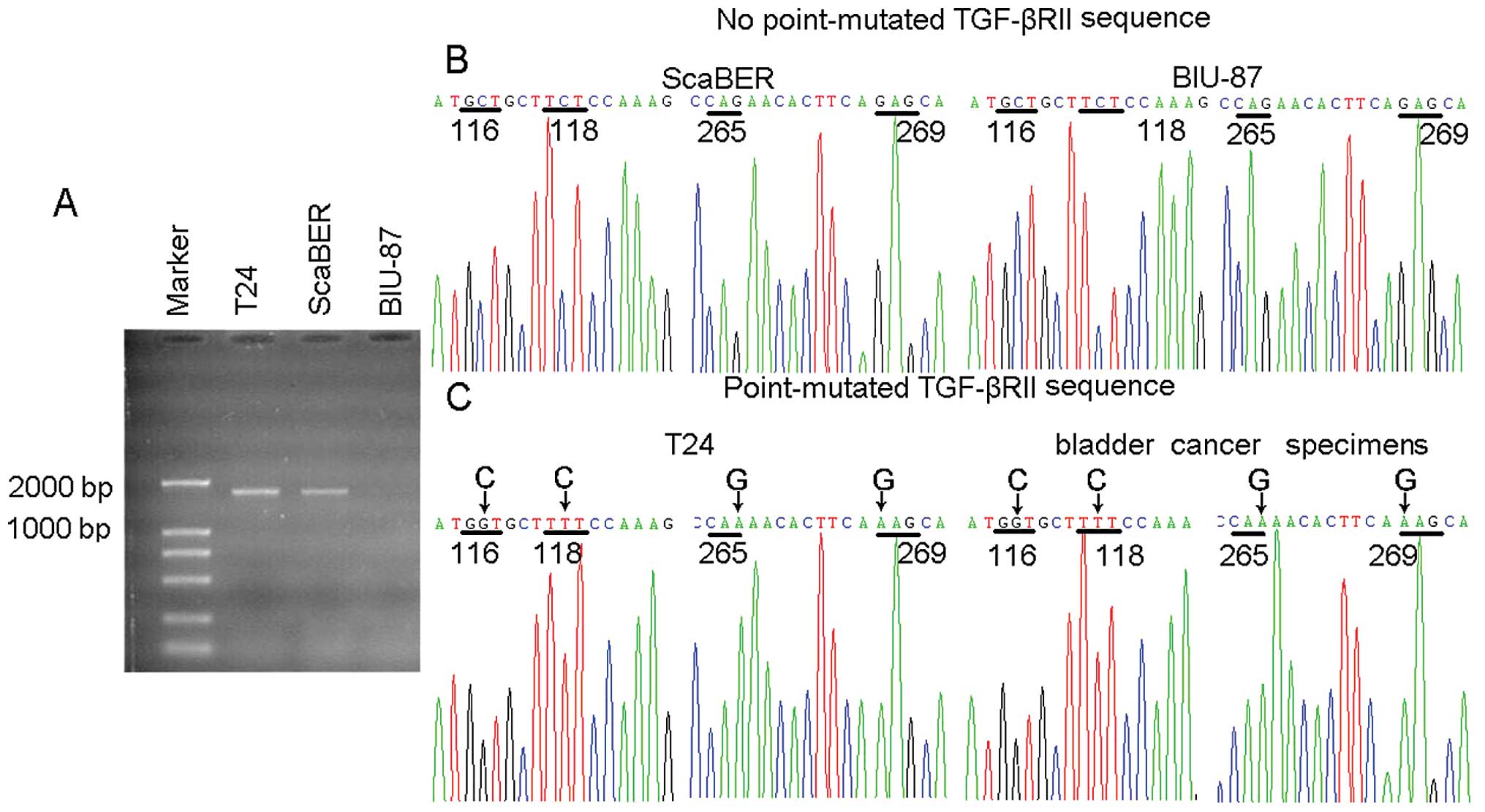
|
Carthon BC, Wolchok JD, Yuan J, et al:
Preoperative CTLA-4 blockade: tolerability and immune monitoring in
the setting of a presurgical clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res.
16:2861–2871. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Havaleshko DM, Smith SC, Cho H, et al:
Comparison of global versus epidermal growth factor receptor
pathway profiling for prediction of lapatinib sensitivity in
bladder cancer. Neoplasia. 11:1185–1193. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
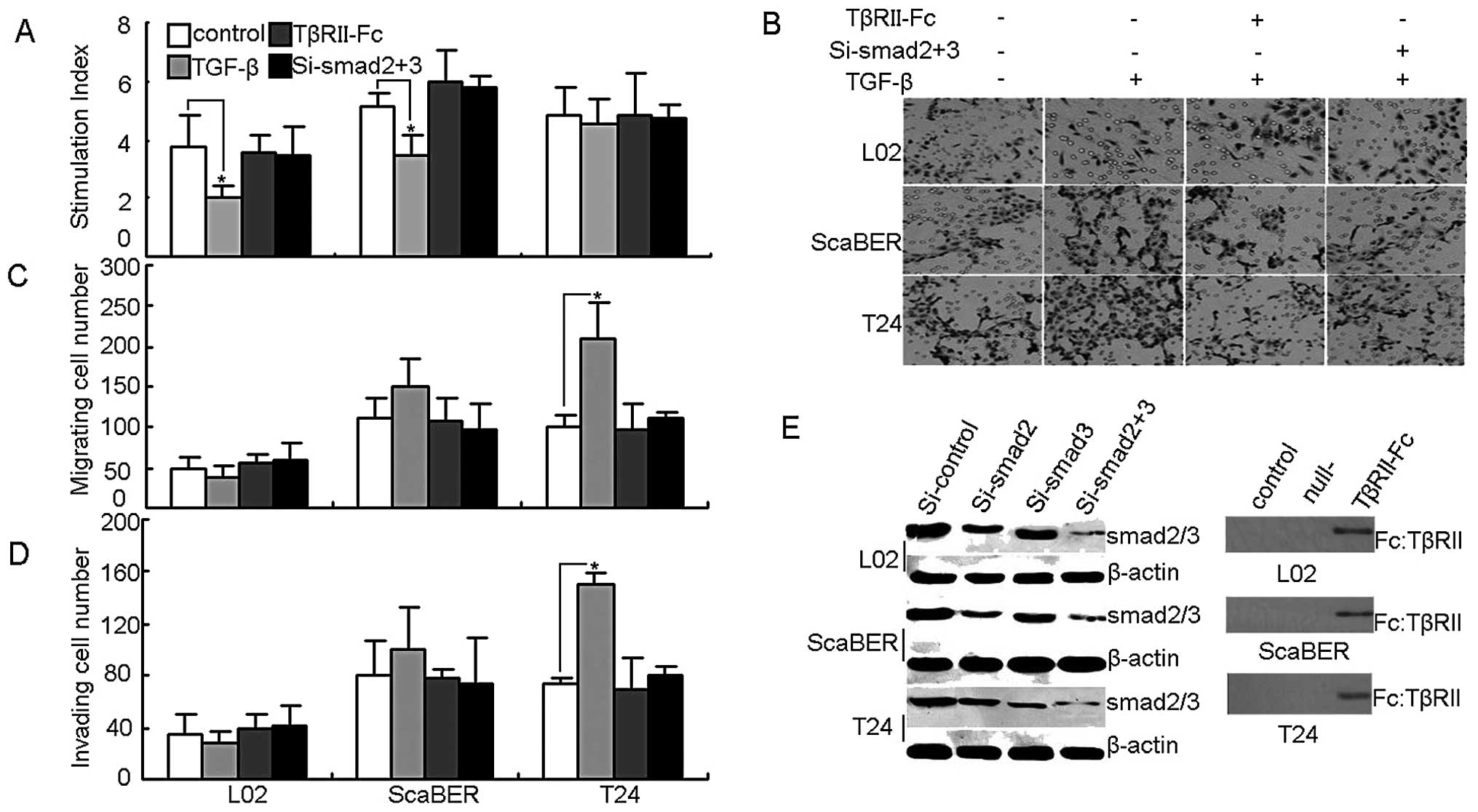
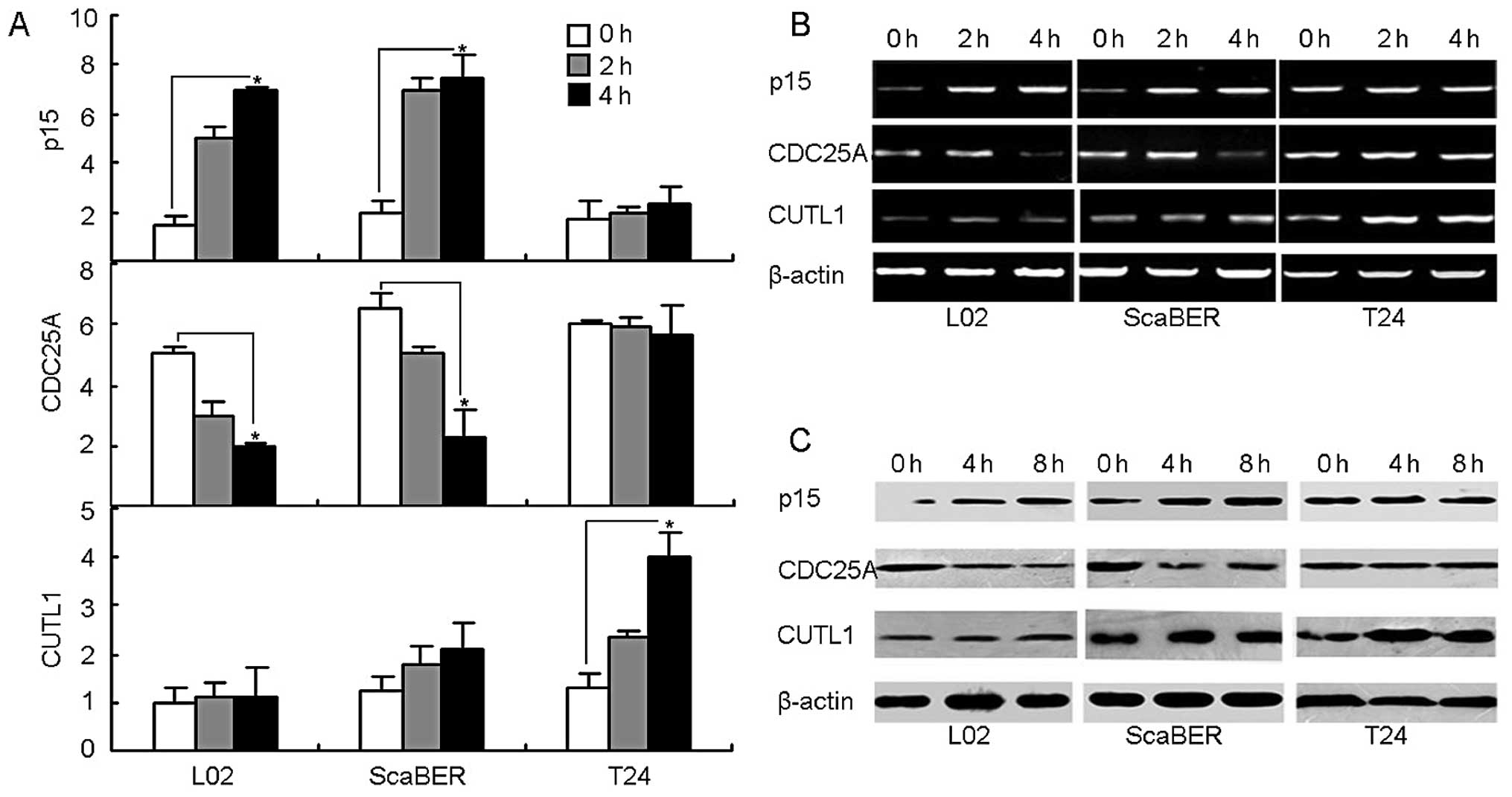
|
|
5.
|
Vaughn DJ, Srinivas S, Stadler WM, et al:
Vinflunine in platinum-pretreated patients with locally advanced or
metastatic urothelial carcinoma: results of a large phase 2 study.
Cancer. 115:4110–4117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Calabro F, Lorusso V, Rosati G, et al:
Gemcitabine and paclitaxel every 2 weeks in patients with
previously untreated urothelial carcinoma. Cancer. 115:2652–2659.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Milowsky MI, Nanus DM, Maluf FC, et al:
Final results of sequential doxorubicin plus gemcitabine and
ifosfamide, paclitaxel, and cisplatin chemotherapy in patients with
metastatic or locally advanced transitional cell carcinoma of the
urothelium. J Clin Oncol. 27:4062–4067. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Kim JH, Shariat SF, Kim IY, Menesses-Diaz
A, Tokunaga H, Wheeler TM and Lerner SP: Predictive value of
expression of transforming growth factor-beta(1) and its receptors
in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Cancer.
92:1475–1483. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hung TT, Wang H, Kingsley EA, Risbridger
GP and Russell PJ: Molecular profiling of bladder cancer:
involvement of the TGF-beta pathway in bladder cancer progression.
Cancer Lett. 265:27–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Champelovier P, El Atifi M, Mantel F,
Rostaing B, Simon A, Berger F and Seigneurin D: In vitro tumoral
progression of human bladder carcinoma: role for TGFbeta. Eur Urol.
48:846–851. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Helmy A, Hammam OA, El Lithy TR and El
Deen Wishahi MM: The role of TGF-beta-1 protein and TGF-beta-R-1
receptor in immune escape mechanism in bladder cancer. Med Gen Med.
9:342007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Shi Y and Massague J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Rahimi RA and Leof EB: TGF-beta signaling:
a tale of two responses. J Cell Biochem. 102:593–608. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Fukai Y, Fukuchi M, Masuda N, Osawa H,
Kato H, Nakajima T and Kuwano H: Reduced expression of transforming
growth factor-beta receptors is an unfavorable prognostic factor in
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
104:161–166. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Levy L and Hill CS: Alterations in
components of the TGF-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:41–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Lynch MA, Nakashima R, Song H, DeGroff VL,
Wang D, Enomoto T and Weghorst CM: Mutational analysis of the
transforming growth factor beta receptor type II gene in human
ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:4227–4232. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Garrigue-Antar L, Souza RF, Vellucci VF,
Meltzer SJ and Reiss M: Loss of transforming growth factor-beta
type II receptor gene expression in primary human esophageal
cancer. Lab Invest. 75:263–272. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Zhang HT, Chen XF, Wang MH, et al:
Defective expression of transforming growth factor beta receptor
type II is associated with CpG methylated promoter in primary
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2359–2367. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Gobbi H, Arteaga CL, Jensen RA, et al:
Loss of expression of transforming growth factor beta type II
receptor correlates with high tumour grade in human breast in-situ
and invasive carcinomas. Histopathology. 36:168–177. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kim IY, Ahn HJ, Lang S, Oefelein MG, Oyasu
R, Kozlowski JM and Lee C: Loss of expression of transforming
growth factor-beta receptors is associated with poor prognosis in
prostate cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 4:1625–1630.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kim IY, Ahn HJ, Zelner DJ, et al: Loss of
expression of transforming growth factor beta type I and type II
receptors correlates with tumor grade in human prostate cancer
tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 2:1255–1261. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Massague J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: Tumour
microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:506–520. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Zhao XP, Huang YY, Huang Y, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 upregulates the expression of CXC
chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:347–354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Zhou Y, Wang S, Ma JW, et al: Hepatitis B
virus protein X induced expression of the CXC chemokine IP-10 is
mediated through activation of NF-kappaB and increases migration of
leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 285:12159–12168. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Huang B, Zhao J, Shen S, et al: Listeria
monocytogenes promotes tumor growth via tumor cell toll-like
receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res. 67:4346–4352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Huang B, Lei Z, Zhang GM, et al:
SCF-mediated mast cell infiltration and activation exacerbate the
inflammation and immunosuppression in tumor microenvironment.
Blood. 112:1269–1279. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Han M, Li AY, Meng F, et al: Synergistic
co-operation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B
with activator protein 1 in angiotensin II-induced angiotensinogen
gene activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS J.
276:1720–1728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Brown K and Bhowmick NA: Linking
TGF-beta-mediated Cdc25A inhibition and cytoskeletal regulation
through RhoA/p160(ROCK) signaling. Cell Cycle. 3:408–410. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Feng XH, Lin X and Derynck R: Smad2, Smad3
and Smad4 cooperate with Sp1 to induce p15(Ink4B) transcription in
response to TGF-beta. EMBO J. 19:5178–5193. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Seoane J, Pouponnot C, Staller P, Schader
M, Eilers M and Massague J: TGFbeta influences Myc, Miz-1 and Smad
to control the CDK inhibitor p15INK4b. Nat Cell Biol. 3:400–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Aleksic T, Bechtel M, Krndija D, et al:
CUTL1 promotes tumor cell migration by decreasing
proteasome-mediated Src degradation. Oncogene. 26:5939–5949. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Michl P and Downward J: CUTL1: a key
mediator of TGFbeta-induced tumor invasion. Cell Cycle. 5:132–134.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Michl P, Ramjaun AR, Pardo OE, et al:
CUTL1 is a target of TGF(beta) signaling that enhances cancer cell
motility and invasiveness. Cancer Cell. 7:521–532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Grady WM, Myeroff LL, Swinler SE, et al:
Mutational inactivation of transforming growth factor beta receptor
type II in microsatellite stable colon cancers. Cancer Res.
59:320–324. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Izumoto S, Arita N, Ohnishi T, et al:
Microsatellite instability and mutated type II transforming growth
factor-beta receptor gene in gliomas. Cancer Lett. 112:251–256.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Nagai M, Kawarada Y, Watanabe M, et al:
Analysis of micro-satellite instability, TGF-beta type II receptor
gene mutations and hMSH2 and hMLH1 allele losses in
pancreaticobiliary maljunction-associated biliary tract tumors.
Anticancer Res. 19:1765–1768. 1999.
|
|
39.
|
Tani M, Takenoshita S, Kohno T, Hagiwara
K, Nagamachi Y, Harris CC and Yokota J: Infrequent mutations of the
transforming growth factor beta-type II receptor gene at chromosome
3p22 in human lung cancers with chromosome 3p deletions.
Carcinogenesis. 18:1119–1121. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Wu MS, Lee CW, Shun CT, Wang HP, Lee WJ,
Sheu JC and Lin JT: Clinicopathological significance of altered
loci of replication error and microsatellite instability-associated
mutations in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 58:1494–1497. 1998.
|
|
41.
|
Bharathy S, Xie W, Yingling JM and Reiss
M: Cancer-associated transforming growth factor beta type II
receptor gene mutant causes activation of bone morphogenic
protein-Smads and invasive phenotype. Cancer Res. 68:1656–1666.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42.
|
Eder IE, Stenzl A, Hobisch A, Cronauer MV,
Bartsch G and Klocker H: Transforming growth factors-beta 1 and
beta 2 in serum and urine from patients with bladder carcinoma. J
Urol. 156:953–957. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Eder IE, Stenzl A, Hobisch A, Cronauer MV,
Bartsch G and Klocker H: Expression of transforming growth factors
beta 1, beta 2 and beta 3 in human bladder carcinomas. Br J Cancer.
75:1753–1760. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Geiser AG, Burmester JK, Webbink R,
Roberts AB and Sporn MB: Inhibition of growth by transforming
growth factor-beta following fusion of two nonresponsive human
carcinoma cell lines. Implication of the type II receptor in growth
inhibitory responses. J Biol Chem. 267:2588–2593. 1992.
|
|
45.
|
Izadifar V, de Boer WI, Muscatelli-Groux
B, Maille P, van der Kwast TH and Chopin DK: Expression of
transforming growth factor beta1 and its receptors in normal human
urothelium and human transitional cell carcinomas. Hum Pathol.
30:372–377. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
McGarvey TW, Tait E, Tomaszewski JE and
Malkowicz SB: Expression of transforming growth factor-beta
receptors and related cell-cycle components in transitional-cell
carcinoma of the bladder. Mol Urol. 3:371–380. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Li F, Goncalves J, Faughnan K, et al:
Targeted inhibition of wound-induced PAI-1 expression alters
migration and differentiation in human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp
Cell Res. 258:245–253. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Providence KM and Higgins PJ: PAI-1
expression is required for epithelial cell migration in two
distinct phases of in vitro wound repair. J Cell Physiol.
200:297–308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|