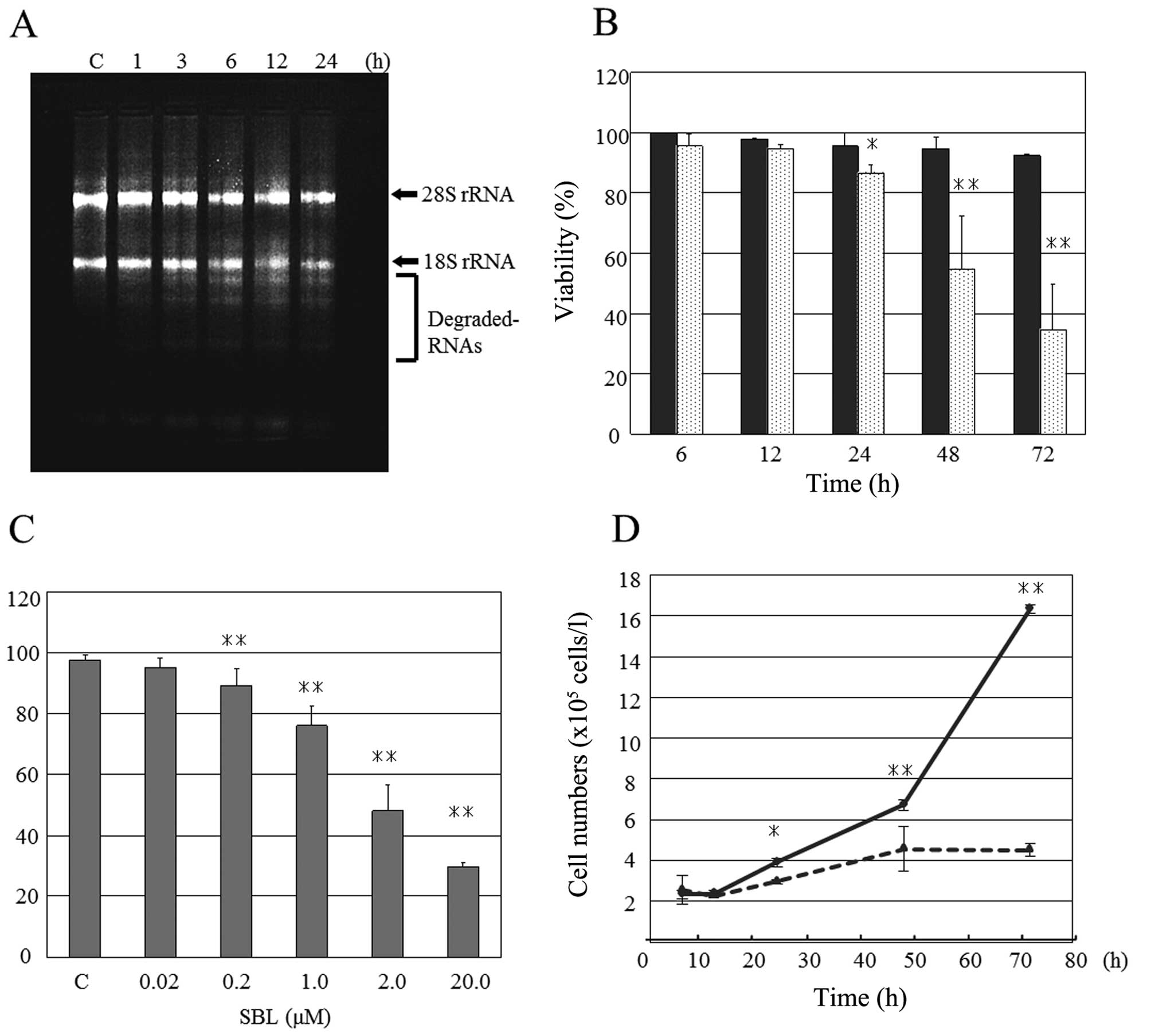
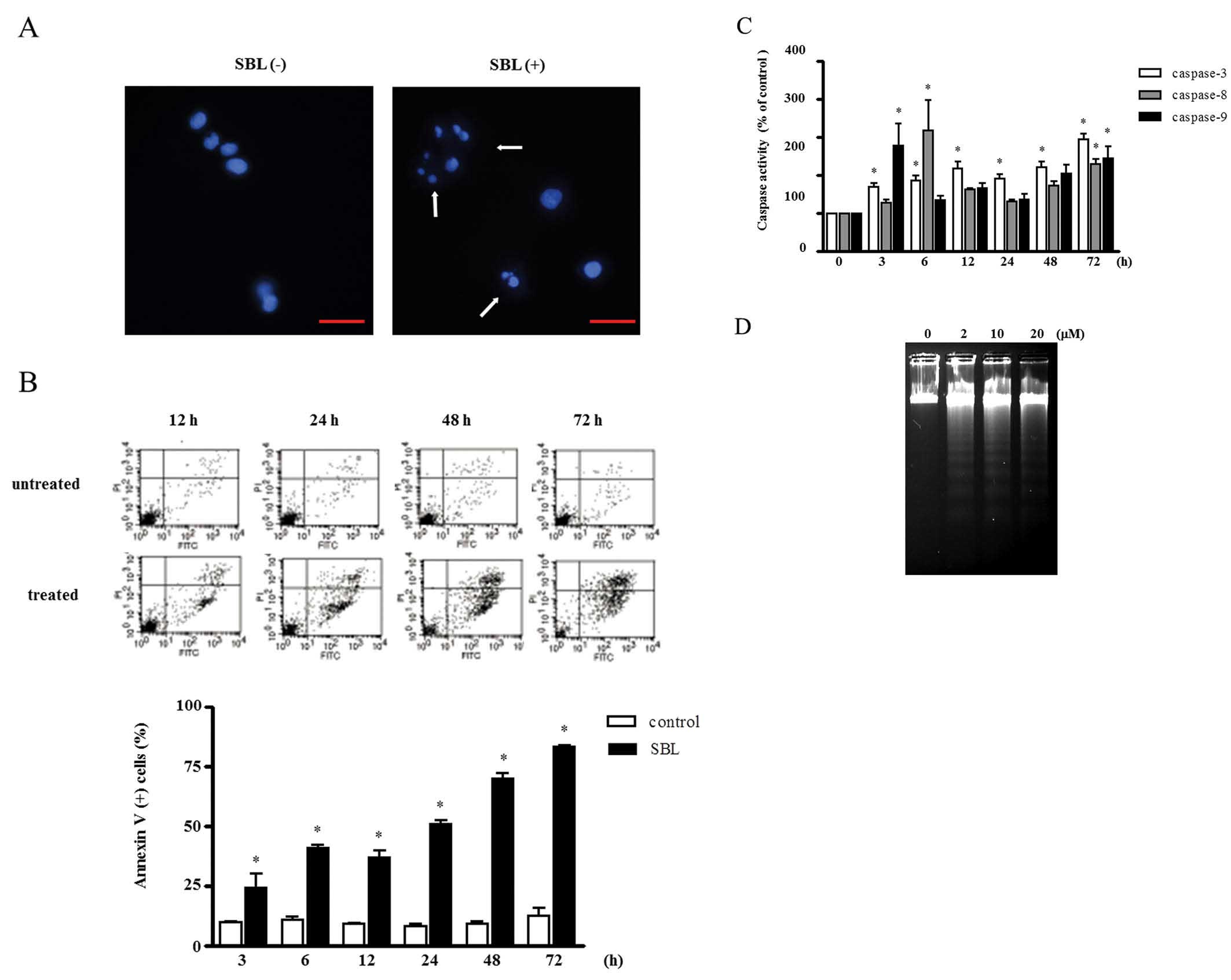
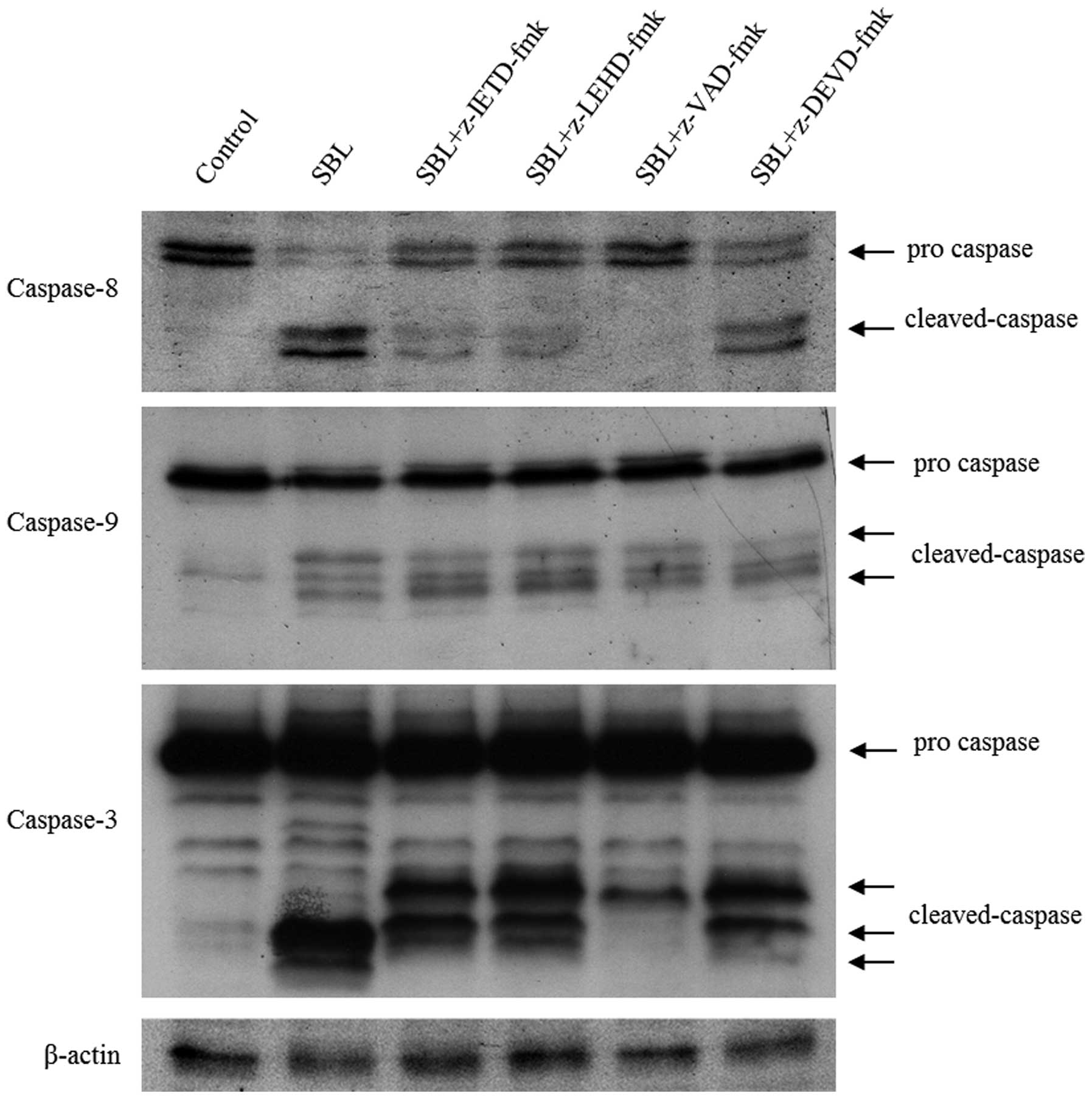
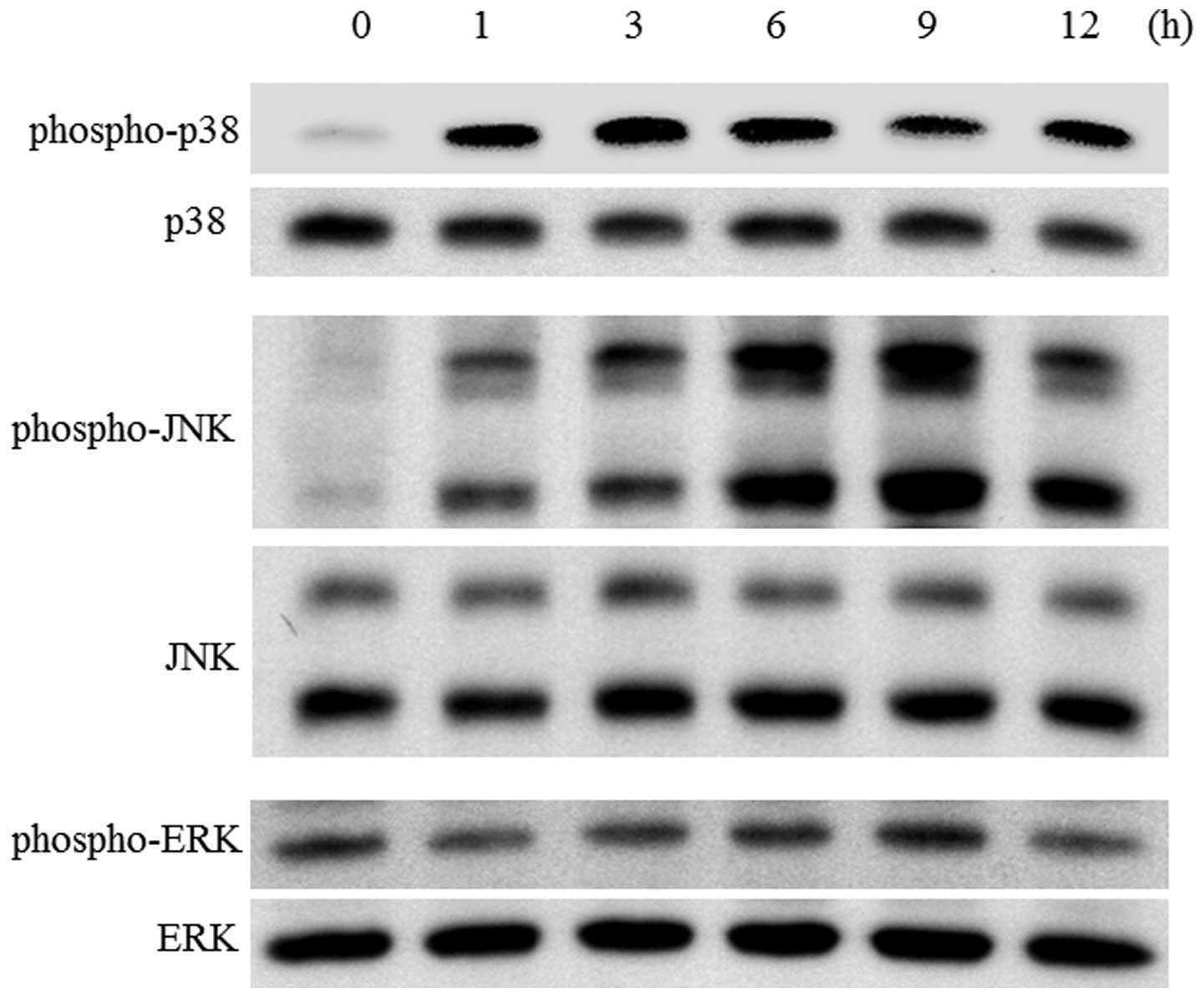
|
1.
|
Costanzi J, Sidransky D, Navon A and
Goldsweig H: Ribonucleases as a novel pro-apoptotic anticancer
strategy: review of the preclinical and clinical data for
ranpirnase. Cancer Invest. 23:643–650. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Deshpande RA and Shankar V: Ribonucleases
from T2 family. Crit Rev Microbiol. 28:79–122. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Fang EF, Zhang CZ, Fong WP and Ng TB:
RNase MC2: a new Momordica charantia ribonuclease that
induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells associated with activation
of MAPKs and induction of caspase pathways. Apoptosis. 17:377–387.
2012.
|
|
4.
|
D’Alessio G: New and cryptic biological
messages from RNases. Trends Cell Biol. 3:106–109. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Raines RT: Ribonuclease A. Chem Rev.
98:1045–1066. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Ita M, Halicka HD, Tanaka T, Kurose A,
Ardelt B, Shogen K and Darzynkiewicz Z: Remarkable enhancement of
cytotoxicity of onconase and cepharanthine when used in combination
on various tumor cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1104–1108. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Rybak SM, Pearson JW, Fogler WE, Volker K,
Spence SE, Newton DL, Mikulski SM, Ardelt W, Riggs CW, Kung HF and
Longo DL: Enhancement of vincristine cytotoxicity in drug-resistant
cells by simultaneous treatment with onconase, an antitumor
ribonuclease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 88:747–753. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kim DH, Kim EJ, Kalota A, Gewirtz AM,
Glickson J, Shogen K and Lee I: Possible mechanisms of improved
radiation response by cytotoxic RNase, Onconase, on A549 human lung
cancer xenografts of nude mice. Adv Exp Med Biol. 599:53–59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Halicka HD, Murakami T, Papageorgio CN,
Mittelman A, Mikulski SM, Shogen K and Darzynkiewicz Z: Induction
of differentiation of leukaemic (HL-60) or prostate cancer (LNCaP,
JCA-1) cells potentiates apoptosis triggered by onconase. Cell
Prolif. 33:407–417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Tsai SY, Hsieh TC, Ardelt B, Darzynkiewicz
Z and Wu JM: Combined effects of onconase and IFN-beta on
proliferation, macromolecular syntheses and expression of STAT-1 in
JCA-1 cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 20:891–896. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Mikulski SM, Viera A, Darzynkiewicz Z and
Shogen K: Synergism between a novel amphibian oocyte ribonuclease
And lovastatin in inducing cytostatic and cytotoxic effects in
human lung and pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Br J Cancer.
66:304–310. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Rutkoski TJ, Kink JA, Strong LE, Schilling
CI and Raines RT: Antitumor activity of ribonuclease multimers
created by site-specific covalent tethering. Bioconjug Chem.
21:1691–1702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Haigis MC, Kurten EL and Raines RT:
Ribonuclease inhibitor as an intracellular sentry. Nucleic Acids
Res. 31:1024–1032. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Ledoux L and Brachet J: Remarks on
preparations of ribonuclease from different manufacturing sources.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 16:2901955.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ledoux L: Action of ribonuclease on
neoplastic growth. II. Action on Landschutz ascites cells in vitro.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 20:369–377. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Darzynkiewicz Z, Carter SP, Mikulski SM,
Ardelt WJ and Shogen K: Cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of Pannon
(P-30 Protein), a novel anticancer agent. Cell Tissue Kinet.
21:169–182. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Easty DM, Ledoux L and Ambrose EJ: The
action of ribonuclease on neoplastic growth. III. Studies by
interference microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 20:528–537. 1956.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Telford IR, Kemp JF, Taylor EF and Yeaman
MW: Effect of ribonuclease on survival of ascites tumor bearing
mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 100:829–831. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ledoux L: Action of ribonuclease on two
solid tumours in vivo. Nature. 176:36–37. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Ardelt W, Mikulski SM and Shogen K: Amino
acid sequence of an anti-tumor protein from Rana pipiens
oocytes and early embryos. Homology to pancreatic ribonucleases. J
Biol Chem. 266:245–251. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ledoux L and Revell SH: Action of
ribonuclease on neoplastic growth. I. Chemical aspects of normal
tumour growth: the Landschutz ascites tumour. Biochim Biophys Acta.
18:416–426. 1955.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Aleksandrowicz J, Urbanczyk J, Ostrowska A
and Sierko J: Further research on the activity of ribonucleases in
the blood and urine of patients suffering from proliferative
hemocytopathia. Blood. 13:652–664. 1958.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Vert A, Castro J, Ruiz-Martinez S, Tubert
P, Escribano D, Ribo M, Vilanova M and Benito A: Generation of new
cytotoxic human ribonuclease variants directed to the nucleus. Mol
Pharm. 9:2894–2902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Fang EF and Ng TB: Ribonucleases of
different origins with a wide spectrum of medicinal applications.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1815:65–74. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Castro J, Ribo M, Navarro S, Nogues MV,
Vilanova M and Benito A: A human ribonuclease induces apoptosis
associated with p21WAF1/CIP1 induction and JNK inactivation. BMC
Cancer. 11:92011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kawauchi H, Sakakibara F and Watanabe K:
Agglutinins of frog eggs: a new class of proteins causing
preferential agglutination of tumor cells. Experientia. 31:364–365.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Sakakibara F, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi G and
Ise H: Egg lectin of Rana japonica and its receptor
glycoprotein of Ehrlich tumor cells. Cancer Res. 39:1347–1352.
1979.
|
|
28.
|
Nitta K, Takayanagi G, Kawauchi H and
Hakomori S: Isolation and characterization of Rana
catesbeiana lectin and demonstration of the lectin-binding
glycoprotein of rodent and human tumor cell membranes. Cancer Res.
47:4877–4883. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Titani K, Takio K, Kuwada M, Nitta K,
Sakakibara F, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi G and Hakomori S: Amino acid
sequence of sialic acid binding lectin from frog (Rana
catesbeiana) eggs. Biochemistry. 26:2189–2194. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Kamiya Y, Oyama F, Oyama R, Sakakibara F,
Nitta K, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y and Titani K: Amino acid sequence
of a lectin from Japanese frog (Rana japonica) eggs. J
Biochem. 108:139–143. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Nitta K, Oyama F, Oyama R, Sekiguchi K,
Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y, Hakomori S and Titani K: Ribonuclease
activity of sialic acid-binding lectin from Rana catesbeiana
eggs. Glycobiology. 3:37–45. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Okabe Y, Katayama N, Iwama M, Watanabe H,
Ohgi K, Irie M, Nitta K, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y, Oyama F, et al:
Comparative base specificity, stability, and lectin activity of two
lectins from eggs of Rana catesbeiana and R. japonica
and liver ribonuclease from R catesbeiana. J Biochem.
109:786–790. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Nitta K, Ozaki K, Ishikawa M, Furusawa S,
Hosono M, Kawauchi H, Sasaki K, Takayanagi Y, Tsuiki S and Hakomori
S: Inhibition of cell proliferation by Rana catesbeiana and
Rana japonica lectins belonging to the ribonuclease
superfamily. Cancer Res. 54:920–927. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Nitta K, Ozaki K, Tsukamoto Y, Furusawa S,
Ohkubo Y, Takimoto H, Murata R, Hosono M, Hikichi N, Sasaki K, et
al: Characterization of a Rana catesbeiana lectin-resistant
mutant of leukemia P388 cells. Cancer Res. 54:928–934. 1994.
|
|
35.
|
Nitta K, Ozaki K, Tsukamoto Y, Hosono M,
Ogawakonno Y, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y, Tsuiki S and Hakomori S:
Catalytic lectin (leczyme) from bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana)
eggs. Int J Oncol. 9:19–23. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Liao YD: A pyrimidine-guanine
sequence-specific ribonuclease from Rana catesbeiana
(bullfrog) oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 20:1371–1377. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Liao YD, Huang HC, Leu YJ, Wei CW, Tang PC
and Wang SC: Purification and cloning of cytotoxic ribonucleases
from Rana catesbeiana (bullfrog). Nucleic Acids Res.
28:4097–4104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Tang CH, Hu CC, Wei CW and Wang JJ:
Synergism of Rana catesbeiana ribonuclease And IFN-gamma
triggers distinct death machineries in different human cancer
cells. FEBS Lett. 579:265–270. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K, Ohkura
Y and Ueno K: A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt
as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability.
Talanta. 44:1299–1305. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Liao YD, Huang HC, Chan HJ and Kuo SJ:
Large-scale preparation of a ribonuclease from Rana
catesbeiana (bullfrog) oocytes and characterization of its
specific cytotoxic activity against tumor cells. Protein Expr
Purif. 7:194–202. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Hu CC, Lee YH, Tang CH, Cheng JT and Wang
JJ: Synergistic cytotoxicity of Rana catesbeiana
ribonuclease And IFN-gamma on hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 280:1229–1236. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Thomas H and Coley HM: Overcoming
multidrug resistance in cancer: an update on the clinical strategy
of inhibiting P-glycoprotein. Cancer Control. 10:159–165.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna CA,
Ramachandra M, Pastan I and Gottesman MM: Biochemical, cellular,
and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 39:361–398. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Krishna R and Mayer LD: Multidrug
resistance (MDR) in cancer. Mechanisms, reversal using modulators
of MDR and the role of MDR modulators in influencing the
pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs. Eur J Pharm Sci. 11:265–283.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Stavrovskaya AA: Cellular mechanisms of
multidrug resistance of tumor cells. Biochemistry (Mosc).
65:95–106. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Ozben T: Mechanisms and strategies to
overcome multiple drug resistance in cancer. FEBS Lett.
580:2903–2909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Castro J, Ribo M, Puig T, Colomer R,
Vilanova M and Benito A: A cytotoxic ribonuclease reduces the
expression level of P-glycoprotein in multidrug-resistant cell
lines. Invest New Drugs. 30:880–888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Grutter MG: Caspases: key players in
programmed cell death. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 10:649–655. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Mansouri A, Ridgway LD, Korapati AL, Zhang
Q, Tian L, Wang Y, Siddik ZH, Mills GB and Claret FX: Sustained
activation of JNK/p38 MAPK pathways in response to cisplatin leads
to Fas ligand induction and cell death in ovarian carcinoma cells.
J Biol Chem. 278:19245–19256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Bunyard P, Handley M, Pollara G, Rutault
K, Wood I, Chaudry M, Alderman C, Foreman J, Katz DR and Chain BM:
Ribotoxic stress activates p38 and JNK kinases and modulates the
antigen-presenting activity of dendritic cells. Mol Immunol.
39:815–827. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
He K, Zhou HR and Pestka JJ: Mechanisms
for ribotoxin-induced ribosomal RNA cleavage. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 265:10–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Iordanov MS, Wong J, Newton DL, Rybak SM,
Bright RK, Flavell RA, Davis RJ and Magun BE: Differential
requirement for the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun
NH(2)-terminal kinase in RNA damage-induced apoptosis in primary
and in immortalized fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun.
4:122–128. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54.
|
Fang EF, Zhang CZ, Zhang L, Fong WP and Ng
TB: In vitro and in vivo anticarcinogenic effects of RNase MC2, a
ribonuclease isolated from dietary bitter gourd, toward human liver
cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1351–1360. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Dasmahapatra G, Lembersky D, Kramer L,
Fisher RI, Friedberg J, Dent P and Grant S: The pan-HDAC inhibitor
vorinostat potentiates the activity of the proteasome inhibitor
carfilzomib in human DLBCL cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood.
115:4478–4487. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Chen J, Rusnak M, Luedtke RR and Sidhu A:
D1 dopamine receptor mediates dopamine-induced cytotoxicity via the
ERK signal cascade. J Biol Chem. 279:39317–39330. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y,
Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch
M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE,
Bollag G and Trail PA: BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral
antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor
tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis.
Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Wolf BB and Green DR: Suicidal tendencies:
apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J Biol Chem.
274:20049–20052. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Kuwana T, Smith JJ, Muzio M, Dixit V,
Newmeyer DD and Kornbluth S: Apoptosis induction by caspase-8 is
amplified through the mitochondrial release of cytochrome c.
J Biol Chem. 273:16589–16594. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome
c release from mitochondria in response to activation of
cell surface death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Schendel SL, Azimov R, Pawlowski K, Godzik
A, Kagan BL and Reed JC: Ion channel activity of the BH3 only Bcl-2
family member, BID. J Biol Chem. 274:21932–21936. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T,
Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and
Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to
mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Viswanath V, Wu Y, Boonplueang R, Chen S,
Stevenson FF, Yantiri F, Yang L, Beal MF and Andersen JK: Caspase-9
activation results in downstream caspase-8 activation and bid
cleavage in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced
Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci. 21:9519–9528. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|