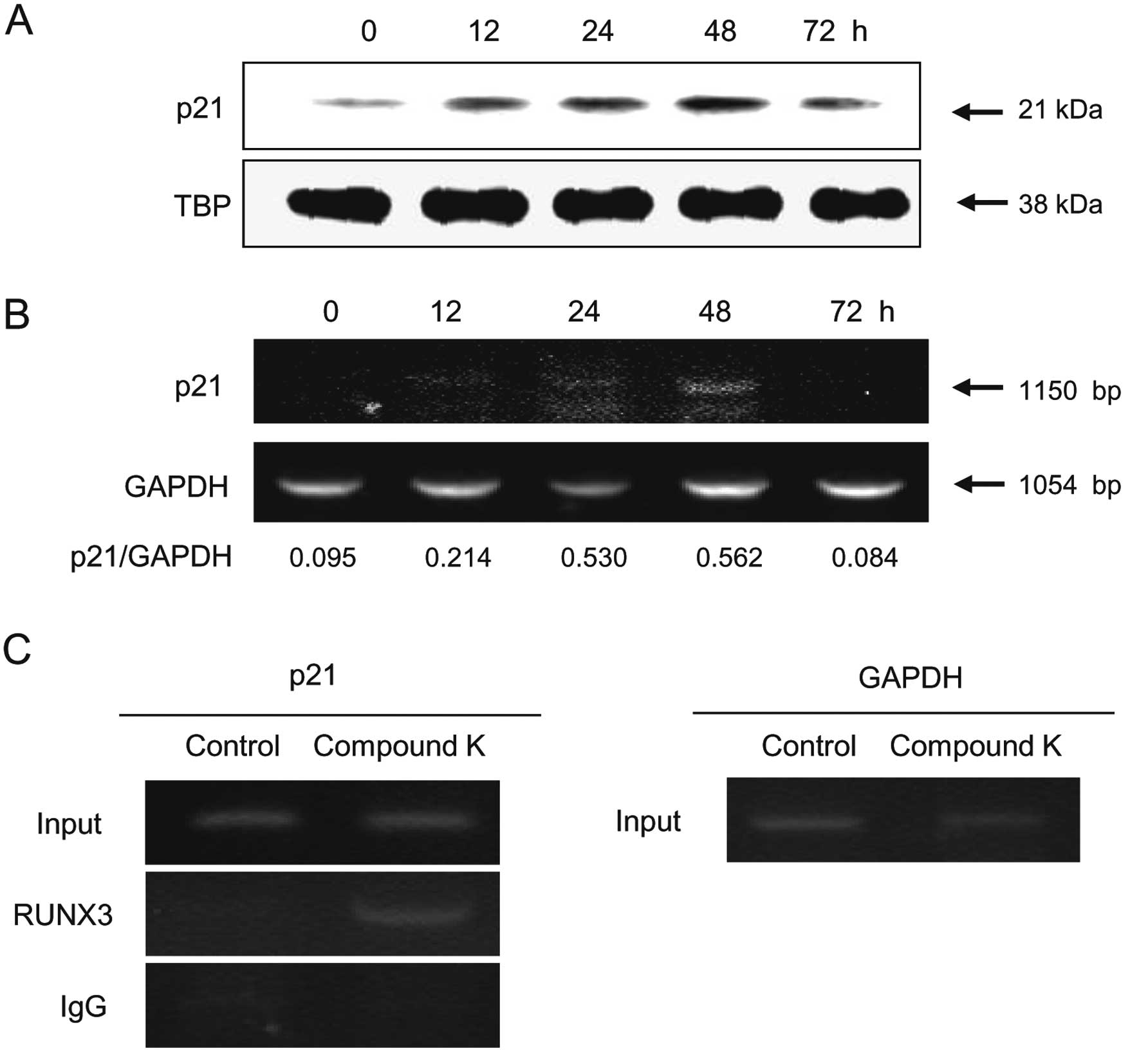
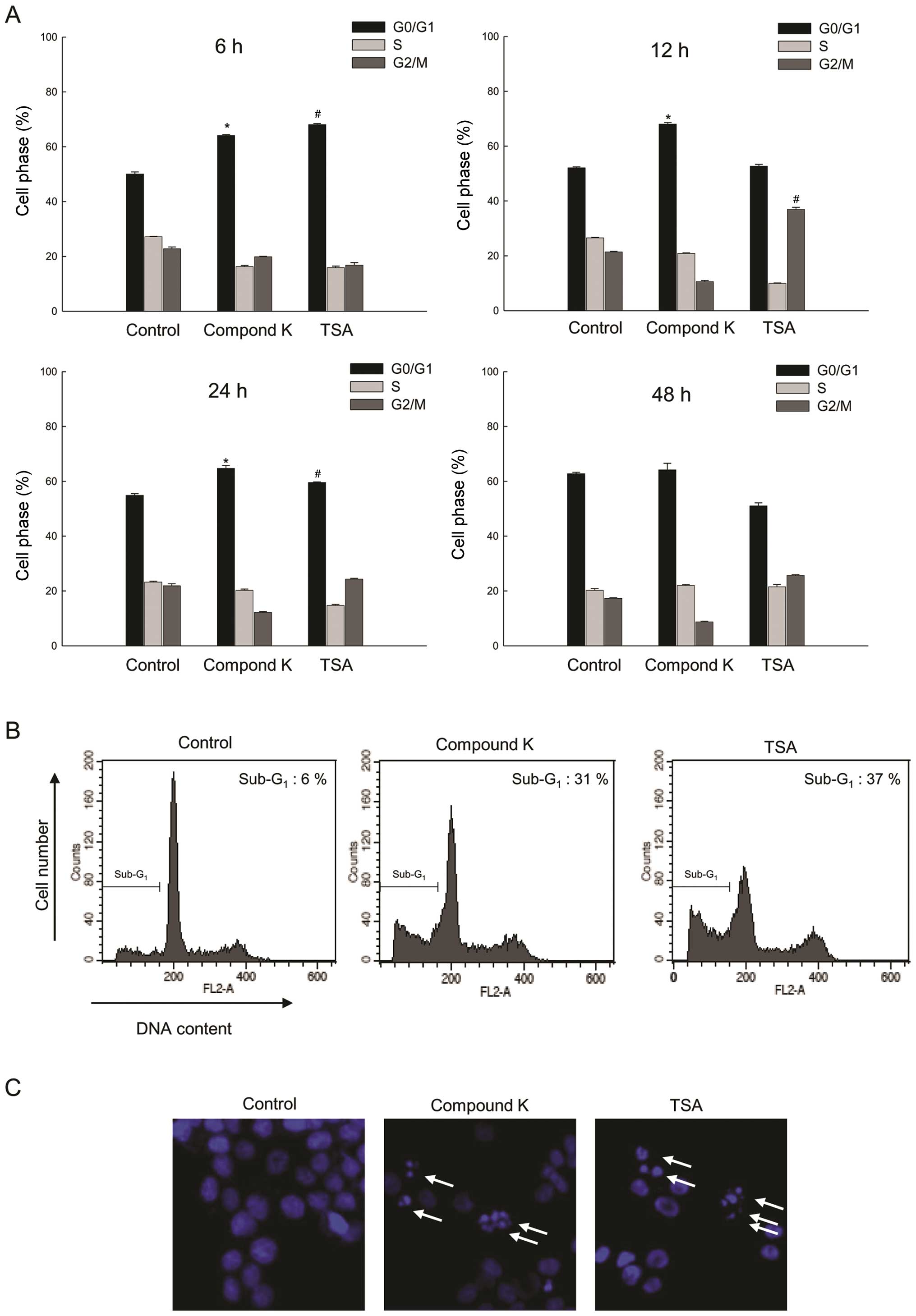
|
1.
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Gallinari P, Di Marco S, Jones P, Pallaoro
M and Steinkühler C: HDACs, histone deacetylation and gene
transcription: from molecular biology to cancer therapeutics. Cell
Res. 17:195–211. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Wilson AJ, Byun DS, Popova N, Murray LB,
L’Italien K, Sowa Y, Arango D, Velcich A, Augenlicht LH and
Mariadason JM: Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and other class I
HDACs regulate colon cell maturation and p21 expression and are
deregulated in human colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 281:13548–13558.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Nakagawa M, Oda Y, Eguchi T, Aishima S,
Yao T, Hosoi F, Basaki Y, Ono M, Kuwano M, Tanaka M and Tsuneyoshi
M: Expression profile of class I histone deacetylases in human
cancer tissues. Oncol Rep. 18:769–774. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ishihama K, Yamakawa M, Semba S, Takeda H,
Kawata S, Kimura S and Kimura W: Expression of HDAC1 and CBP/p300
in human colorectal carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 60:1205–1210. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Zhu P, Martin E, Mengwasser J, Schlag P,
Janssen KP and Göttlicher M: Induction of HDAC2 expression upon
loss of APC in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 5:455–463.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Huang BH, Laban M, Leung CH, Lee L, Lee
CK, Salto-Tellez M, Raju GC and Hooi SC: Inhibition of histone
deacetylase 2 increases apoptosis and p21(Cipl/WAFl) expression,
independent of histone deacetylase 1. Cell Death Differ.
12:395–404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Giannini R and Cavallini A: Expression
analysis of a subset of coregulators and three nuclear receptors in
human colorectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 25:4287–4292.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Weichert W, Röske A, Niesporek S, Noske A,
Buckendahl AC, Dietel M, Gekeler V, Boehm M, Beckers T and Denkert
C: Class I histone deacetylase expression has independent
prognostic impact in human colorectal cancer: specific role of
class I histone deacetylases in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1669–1677. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Beckers T, Stephan C, Jung K, Fritzsche
FR, Niesporek S, Denkert C, Dietel M and Kristiansen G: Histone
deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in prostate cancer and
HDAC2 expression is associated with shorter PSA relapse time after
radical prostatectomy. Br J Cancer. 98:604–610. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Spurling CC, Godman CA, Noonan EJ,
Rasmussen TP, Rosenberg DW and Giardina C: HDAC3 overexpression and
colon cancer cell proliferation and differentiation. Mol Carcinog.
47:137–147. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Archer SY, Meng S, Shei A and Hodin RA:
p21WAF-1 is required for butyrate-mediated growth
inhibition of colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:6791–6796. 1998.
|
|
14.
|
Finnin MS, Donigian JR, Cohen A, Richon
VM, Rifkind RA, Marks PA, Breslow R and Pavletich NP: Structures of
a histone deacetylase homologue bound to the TSA and SAHA
inhibitors. Nature. 401:188–193. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Myzak MC and Dashwood RH: Histone
deacetylases as targets for dietary cancer preventive agents:
lessons learned with butyrate, diallyl disulfide and sulforaphane.
Curr Drug Targets. 7:443–445. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bruserud Ø, Stapnes C, Ersvaer E, Gjertsen
BT and Ryningen A: Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer
treatment: a review of the clinical toxicity and the modulation of
gene expression in cancer cells. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 8:388–400.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Levanon D, Brenner O, Negreanu V, Bettoun
D, Woolf E, Eilam R, Lotem J, Gat U, Otto F, Speck N and Groner Y:
Spatial and temporal expression pattern of Runx3 (Aml2) and Runxl
(Amll) indicates non-redundant functions during mouse
embryogenesis. Mech Dev. 109:413–417. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Woolf E, Xiao C, Fainaru O, Lotem J, Rosen
D, Negreanu V, Bernstein Y, Goldenberg D, Brenner O, Berke G,
Levanon D and Groner Y: Runx3 and Runxl are required for CD8 T cell
development during thymopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:7731–7736. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Choi JK, Lee YH, Kim HM, Li LS, Kim H,
Chang J, Ito Y, Lee KY and Bae SC: Transcriptional silencing of the
RUNX3 gene by CpG hypermethylation is associated with lung cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 314:223–228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Chuang LS and Ito Y: RUNX3 is
multifunctional in carcinogenesis of multiple solid tumors.
Oncogene. 29:2605–2615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ragnarsson G, Eiriksdottir G,
Johannsdottir JT, Jonasson JG, Egilsson V and Ingvarsson S: Loss of
heterozygosity at chromosome 1p in different solid human tumours:
association with survival. Br J Cancer. 79:1468–1474. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Tanaka K, Yanoshita R, Konishi M, Oshimura
M, Maeda Y, Mori T and Miyaki M: Suppression of tumourigenicity in
human colon carcinoma cells by introduction of normal chromosome
1p36 region. Oncogene. 8:2253–2258. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Herman JG and Baylin SB: Gene silencing in
cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med.
349:2042–2054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Li QL, Ito K, Sakakura C, Fukamachi H,
Inoue Ki, Chi XZ, Lee KY, Nomura S, Lee CW, Han SB, Kim HM, Kim WJ,
Yamamoto H, Yamashita N, Yano T, Ikeda T, Itohara S, Inazawa J, Abe
T, Hagiwara A, Yamagishi H, Ooe A, Kaneda A, Sugimura T, Ushijima
T, Bae SC and Ito Y: Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3
expression and gastric cancer. Cell. 109:113–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Goel A, Arnold CN, Tassone P, Chang DK,
Niedzwiecki D, Dowell JM, Wasserman L, Compton C, Mayer RJ,
Bertagnolli MM and Boland CR: Epigenetic inactivation of RUNX3 in
microsatellite unstable sporadic colon cancers. Int J Cancer.
112:754–759. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Fujii S, Ito K, Ito Y and Ochiai A:
Enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) down-regulates RUNX3 by
increasing histone H3 methylation. J Biol Chem. 283:17324–17332.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lee SH, Kim J, Kim WH and Lee YM: Hypoxic
silencing of tumor suppressor RUNX3 by histone modification in
gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:184–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Hong SY, Cho JY and Seo DW: Ginsenoside
Rp1 inhibits proliferation and migration of human lung cancer
cells. Biomole Ther. 19:411–418. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Park JW, Lee JC, Ann S, Seo DW, Choi WS,
Yoo YH, Park SK, Choi JY, Um SH, Ahn SH and Han JW: A fermented
ginseng extract, BST204, inhibits proliferation and motility of
human colon cancer cells. Biomole Ther. 19:211–217. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Seo EY and Kim WK: Red ginseng extract
reduced metastasis of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J
Gins Res. 35:315–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Akao T, Kanaoka M and Kobashi K:
Appearance of Compound K, a major metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 by
intestinal bacteria, in rat plasma after oral
administration-measurement of Compound K by enzyme immunoassay.
Biol Pharm Bull. 21:245–249. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Hasegawa H, Sung JH and Huh JH: Ginseng
intestinal bacterial metabolite IH901 as a new anti-metastatic
agent. Arch Pharm Res. 20:539–544. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Quan LH, Cheng LQ, Kim HB, Kim JH, Son NR,
Kim SY, Jin HO and Yang DC: Bioconversion of Ginsenoside Rd into
Compound K by Lactobacillus pentosus DC101 isolated from
Kimchi. J Gins Res. 34:288–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Kang KA, Kim YW, Kim SU, Chae S, Koh YS,
Kim HS, Choo MK, Kim DH and Hyun JW: G1 phase arrest of the cell
cycle by a ginseng metabolite, Compound K, in U937 human monocytic
leukamia cells. Arch Pharm Res. 28:685–690. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Kang KA, Lim HK, Kim SU, Kim YW, Kim WT,
Chung HS, Choo MK, Kim DH, Kim HS, Shim MJ, Chung MH and Hyun JW:
Induction of apoptosis by ginseng saponin metabolite in U937 human
monocytic leukemia cells. J Food Biochem. 29:27–40. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Chae S, Kang KA, Chang WY, Kim MJ, Lee SJ,
Lee YS, Kim HS, Kim DH and Hyun JW: Effect of Compound K, a
metabolite of ginseng saponin, combined with gamma-ray radiation in
human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J Agric Food Chem.
57:5777–5782. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Kim AD, Kang KA, Zhang R, Lim CM, Kim HS,
Kim DH, Jeon YJ, Lee CH, Park J, Chang WY and Hyun JW: Ginseng
saponin metabolite induces apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
through the modulation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 30:134–140. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Kang KA, Kim HS, Kim DH and Hyun JW: The
role of a ginseng saponin metabolite as a DNA methyltransferase
inhibitor in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:228–236.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Ito K, Lim AC, Salto-Tellez M, Motoda L,
Osato M, Chuang LS, Lee CW, Voon DC, Koo JK, Wang H, Fukamachi H
and Ito Y: RUNX3 attenuates beta-catenin/T cell factors in
intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 14:226–237. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Ku JL, Kang SB, Shin YK, Kang HC, Hong SH,
Kim IJ, Shin JH, Han IO and Park JG: Promoter hypermethylation
downregulates RUNX3 gene expression in colorectal cancer cell
lines. Oncogene. 23:6736–6742. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Yano T, Ito K, Fukamachi H, Chi XZ, Wee
HJ, Inoue K, Ida H, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Bae SC and Ito Y: The
RUNX3 tumor suppressor upregulates Bim in gastric epithelial cells
undergoing transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biol. 26:4474–4488. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Tong DD, Jiang Y, Li M, Kong D, Meng XN,
Zhao YZ, Jin Y, Bai J, Fu SB and Geng JS: RUNX3 inhibits cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis by TGF-beta-dependent and
-independent mechanisms in human colon carcinoma cells.
Pathobiology. 76:163–169. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Kodach LL, Jacobs RJ, Heijmans J, van
Noesel CJ, Langers AM, Verspaget HW, Hommes DW, Offerhaus GJ, van
den Brink GR and Hardwick JC: The role of EZH2 and DNA methylation
in the silencing of the tumour suppressor RUNX3 in colorectal
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:1567–1575. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Jones PA: DNA methylation and cancer.
Oncogene. 21:5358–5360. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Counts JL and Goodman JI: Alterations in
DNA methylation may play a variety of roles in carcinogenesis.
Cell. 83:13–15. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47.
|
Shibata S: Chemistry and cancer preventing
activities of ginseng saponins and some related triterpenoid
compounds. J Korean Med Sci. 16:S28–S37. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Wang L, Zou X, Berger AD, Twiss C, Peng Y,
Li Y, Chiu J, Guo H, Satagopan J, Wilton A, Gerald W, Basch R, Wang
Z, Osman I and Lee P: Increased expression of histone deacetylaces
(HDACs) and inhibition of prostate cancer growth and invasion by
HDAC inhibitor SAHA. Am J Transl Res. 1:62–71. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Patra SK, Patra A and Dahiya R: Histone
deacetylase and DNA methyltransferase in human prostate cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 287:705–713. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Halkidou K, Gaughan L, Cook S, Leung HY,
Neal D and Robson CN: Upregulation and nuclear recruitment of HDAC1
in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Prostate. 59:177–189. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Yang XJ and Seto E: Collaborative spirit
of histone deacetylases in regulating chromatin structure and gene
expression. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 13:143–153. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Kim DH, Kim M and Kwon HJ: Histone
deacetylase in carcinogenesis and its inhibitors as anti-cancer
agents. J Biochem Mol Biol. 36:110–119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Buchwald M, Krämer OH and Heinzel T: HDACi
- targets beyond chromatin. Cancer Lett. 280:160–167. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Mellert HS, Stanek TJ, Sykes SM, Rauscher
FJ III, Schultz DC and McMahon SB: Deacetylation of the DNA-binding
domain regulates p53-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
286:4264–4270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Oh ET, Park MT, Choi BH, Ro S, Choi EK,
Jeong SY and Park HJ: Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor CG200745
induces clonogenic cell death by modulating acetylation of p53 in
cancer cells. Invest New Drugs. 30:435–442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|