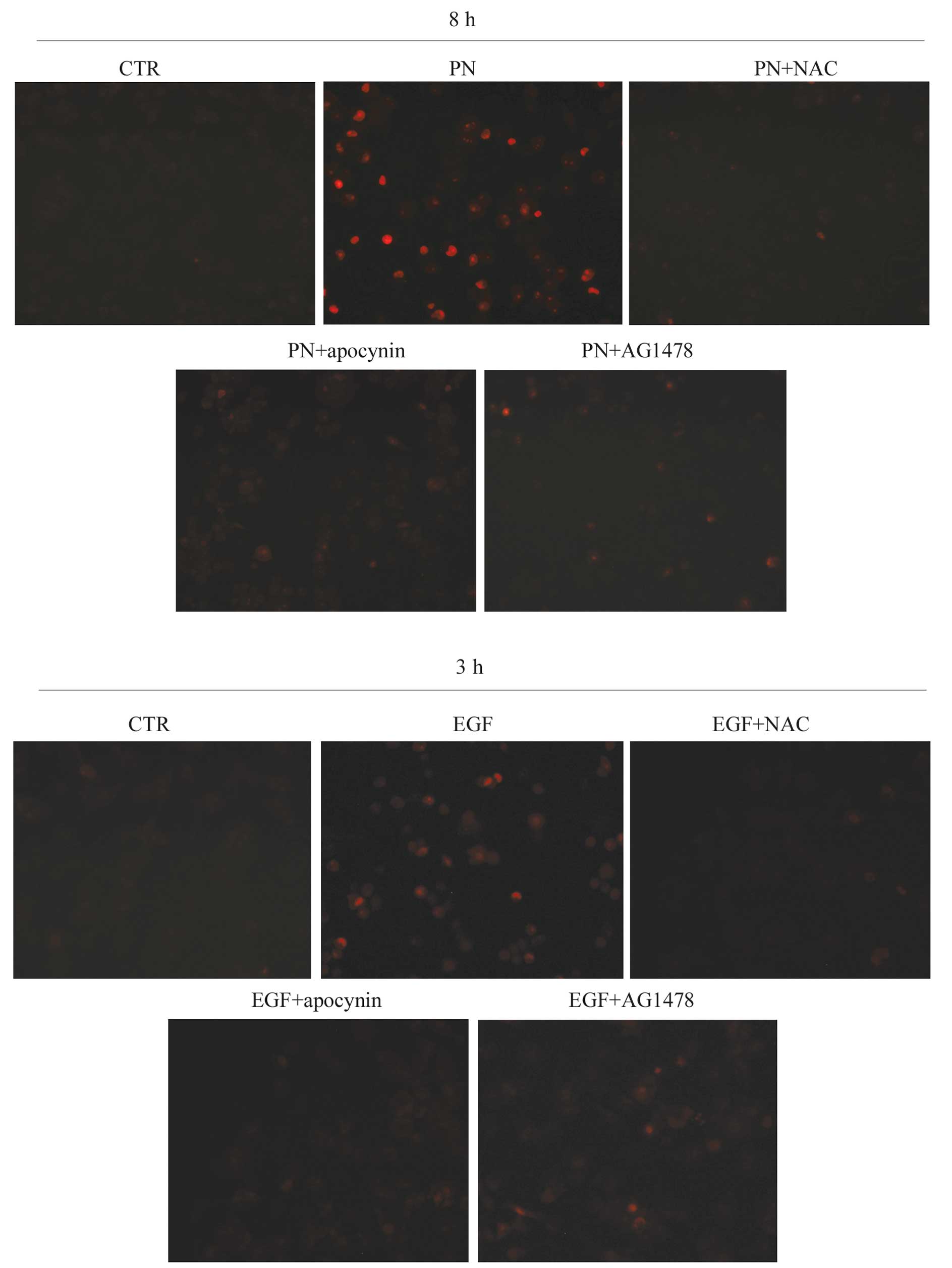
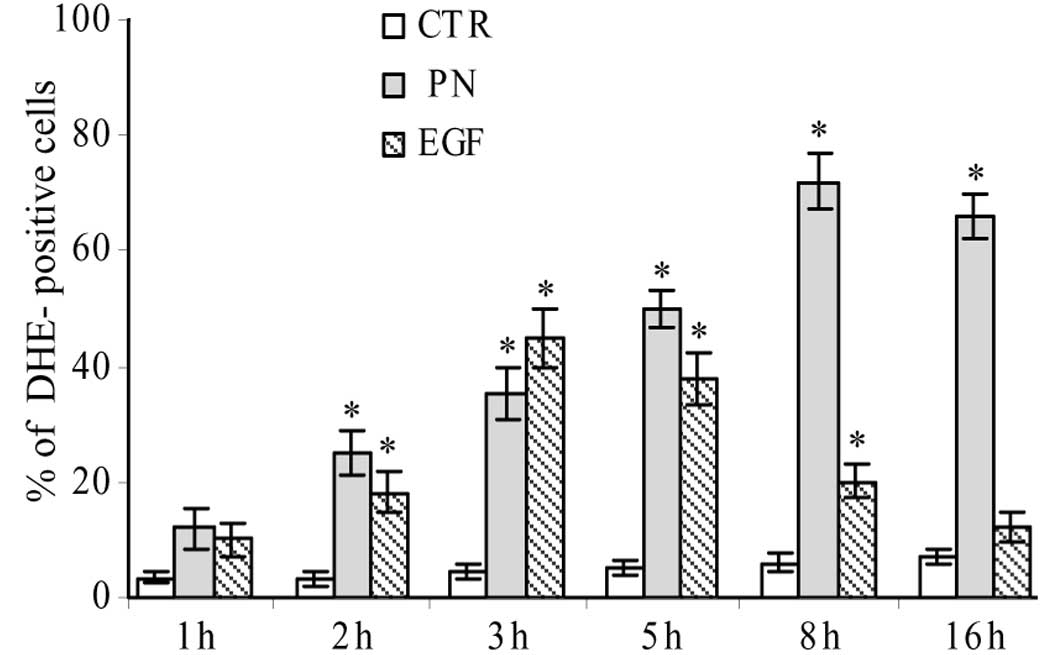
|
1.
|
Ghantous A, Sinjab A, Herceg Z and
Darwiche N: Parthenolide: from plant shoots to cancer roots. Drug
Discov Today. 18:894–905. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kim SL, Trang KT, Kim SH, Kim IH, Lee SO,
Lee ST, Kim DG and Kim SW: Parthenolide suppresses tumor growth in
a xenograft model of colorectal cancer cells by inducing
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 41:1547–1553.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Yip-Schneider MT, Nakshatri H, Sweeney CJ,
Marshall MS, Wiebke EA and Schmidt CM: Parthenolide and sulindac
cooperate to mediate growth suppression and inhibit the nuclear
factor-kappa B pathway in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:587–594. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Sun Y, St Clair DK, Xu Y, Crooks PA and St
Clair WH: A NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signaling pathway
mediates the selective radiosensitization effect of parthenolide in
prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:2880–2890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Wang W, Adachi M, Kawamura R, Sakamoto H,
Hayashi T, Ishida T, Imai K and Shinomura Y: Parthenolide-induced
apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells involves reactive oxygen
species generation and cell sensitivity depends on catalase
activity. Apoptosis. 11:2225–2235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
D’Anneo A, Carlisi D, Lauricella M,
Emanuele S, Di Fiore R, Vento R and Tesoriere G: Parthenolide
induces caspase-independent and AIF-mediated cell death in human
osteosarcoma and melanoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 228:952–967.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
D’Anneo A, Carlisi D, Lauricella M, Puleio
R, Martinez R, Di Bella S, Di Marco P, Emanuele S, Di Fiore R,
Guercio A, Vento R and Tesoriere G: Parthenolide generates reactive
oxygen species and autophagy in MDA-MB-231 cells A soluble
parthenolide analogue inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in a
xenograft model of breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. (In press).
|
|
8.
|
Bazley LA and Gullick WJ: The epidermal
growth factor receptor family. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:17–27. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Hölsken A, Gebhardt M, Buchfelder M,
Fahlbusch R, Blümcke I and Buslei R: EGFR signaling regulates tumor
cell migration in craniopharyngiomas. Clin Cancer Res.
17:4367–4377. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Zhang J, Li H, Wang J, Dong Z, Mian S and
Yu FS: Role of EGFR transactivation in preventing apoptosis in
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected human corneal epithelial
cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 45:2569–2576. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
van Cruijsen H, Giaccone G and Hoekman K:
Epidermal growth factor receptor and angiogenesis: opportunities
for combined anticancer strategies. Int J Cancer. 118:883–888.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Macias A, Azavedo E, Hagerstrom T,
Klintenberg C, Perez R and Skoog L: Prognostic significance of the
receptor for epidermal growth factor in human mammary carcinomas.
Anticancer Res. 7:459–464. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Sequist LV, Joshi VA, Jänne PA, Muzikansky
A, Fidias P, Meyerson M, Haber DA, Kucherlapati R, Johnson BE and
Lynch TJ: Response to treatment and survival of patients with
non-small cell lung cancer undergoing somatic EGFR mutation
testing. Oncologist. 12:90–98. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bae YS, Kang SW, Seo MS, Baines IC, Tekle
E, Chock PB and Rhee SG: Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced
generation of hydrogen peroxide. Role in EGF receptor-mediated
tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 272:217–221. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Cuddihy SL, Winterbourn CC and Hampton MB:
Assessment of redox changes to hydrogen peroxide-sensitive proteins
during EGF signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:167–174. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Truong TH and Carroll KS: Redox regulation
of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through cysteine
oxidation. Biochemistry. 51:9954–9965. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Chiarugi P, Pani G, Giannoni E, Taddei L,
Colavitti R, Raugei G, Symons M, Borrello S, Galeotti T and Ramponi
G: Reactive oxygen species as essential mediators of cell adhesion:
the oxidative inhibition of a FAK tyrosine phosphatase is required
for cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 161:933–944. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Jagadeesha DK, Takapoo M, Banfi B, Bhalla
RC and Miller FJ Jr: Nox1 transactivation of epidermal growth
factor receptor promotes N-cadherin shedding and smooth muscle cell
migration. Cardiovasc Res. 93:406–413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Giuliano M, Lauricella M, Calvaruso G,
Carabillò M, Emanuele S, Vento R and Tesoriere G: The apoptotic
effects and synergistic interaction of sodium butyrate and MG132 in
human retinoblastoma Y79 cells. Cancer Res. 59:5586–5595.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Voldborg BR, Damstrup L, Spang-Thomsen M
and Poulsen HS: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and EGFR
mutations, function and possible role in clinical trials. Ann
Oncol. 8:1197–1206. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Paletta-Silva R, Rocco-Machado N and
Meyer-Fernandes JR: NADPH oxidase biology and the regulation of
tyrosine kinase receptor signaling and cancer drug cytotoxicity.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:3683–3704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hordijk PL: Regulation of NADPH oxidases:
the role of Rac proteins. Circ Res. 98:453–462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Boudreau HE, Casterline BW, Rada B,
Korzeniowska A and Leto TL: Nox4 involvement in TGF-beta and
SMAD3-driven induction of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and migration of breast epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:1489–1499. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Wu F, Tyml K and Wilson JX: iNOS
expression requires NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signaling in
microvascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 117:207–214. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Zhua XF, Liua ZC, Xiea BF, Lia ZM, Fenga
GK, Yangb D and Zeng YX: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478
inhibits cell proliferation and arrests cell cycle in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 169:27–32. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Schlessinger J: Ligand-induced,
receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor.
Cell. 110:669–672. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H,
Takahashi T and Mitsudomi T: Mutations of epidermal growth factor
receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications.
Cancer Res. 64:8919–8923. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Rampaul RS, Pinder SE, Nicholson RI,
Gullick WJ, Robertson JF and Ellis IO: Clinical value of epidermal
growth factor receptor expression in primary breast cancer. Adv
Anat Pathol. 12:271–273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Lauricella M, Ciraolo A, Carlisi D, Vento
R and Tesoriere G: SAHA/TRAIL combination induces detachment and
anoikis of MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochimie.
94:287–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Lee CS, Hall RE, Alexander IE, Koga M,
Shine J and Sutherland RL: Inverse relationship between estrogen
receptor and epidermal growth factor. Growth Factors. 3:97–103.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Gamou S and Shimizu N: Hydrogen peroxide
preferentially enhances the tyrosine phosphorylation of epidermal
growth factor receptor. FEBS Lett. 357:161–164. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Haj FG, Markova B, Klaman LD, Bohmer FD
and Neel BG: Regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by
protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B. J Biol Chem. 278:739–744. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Chiarugi P: PTPs versus PTKs: the redox
side of the coin. Free Radic Res. 39:353–364. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Paulsen CE, Truong TH, Garcia FJ, Homann
A, Gupta V, Leonard SE and Carroll KS: Peroxide-dependent
sulfenylation of the EGFR catalytic site enhances kinase activity.
Nat Chem Biol. 8:57–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Tamas P, Solti Z, Bauer P, Illes A, Sipeki
S, Bauer A, Farago A, Downward J and Buday L: Mechanism of
epidermal growth factor regulation of Vav2, a guanine nucleotide
exchange factor for Rac. J Biol Chem. 278:5163–5171. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Sheng ZG, Huang W, Liu YX, Yuan Y and Zhu
BZ: Ofloxacin induces apoptosis via β1 integrin-EGFR-Rac1-Nox2
pathway in microencapsulated chondrocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
267:74–87. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|