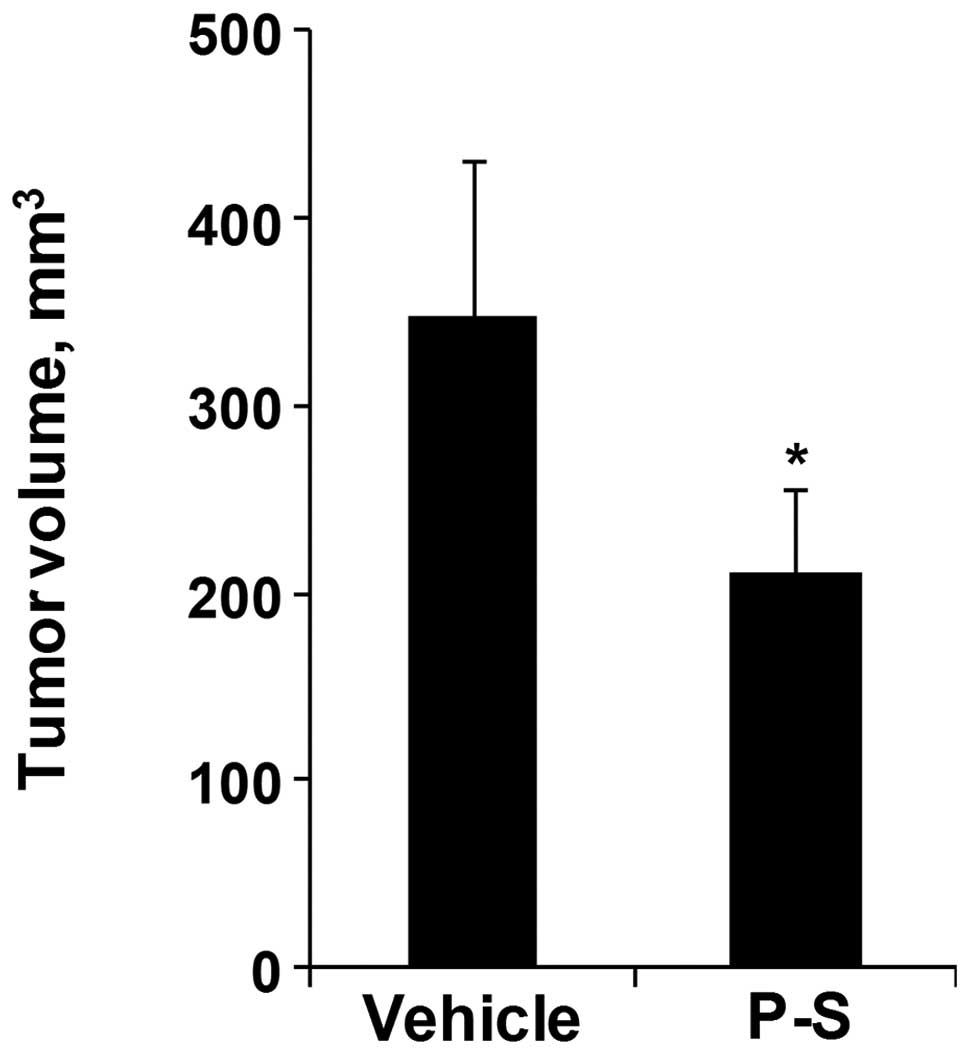
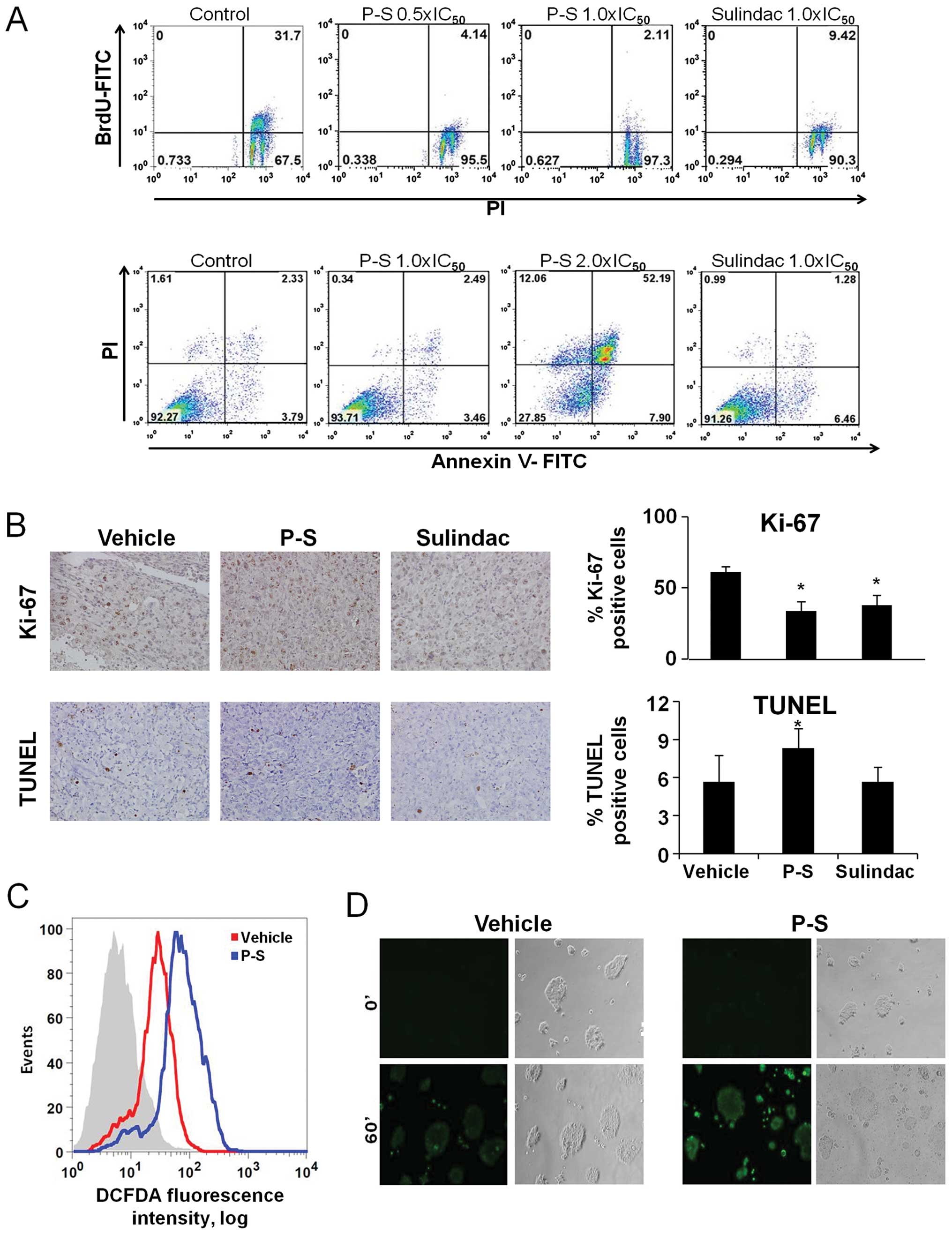
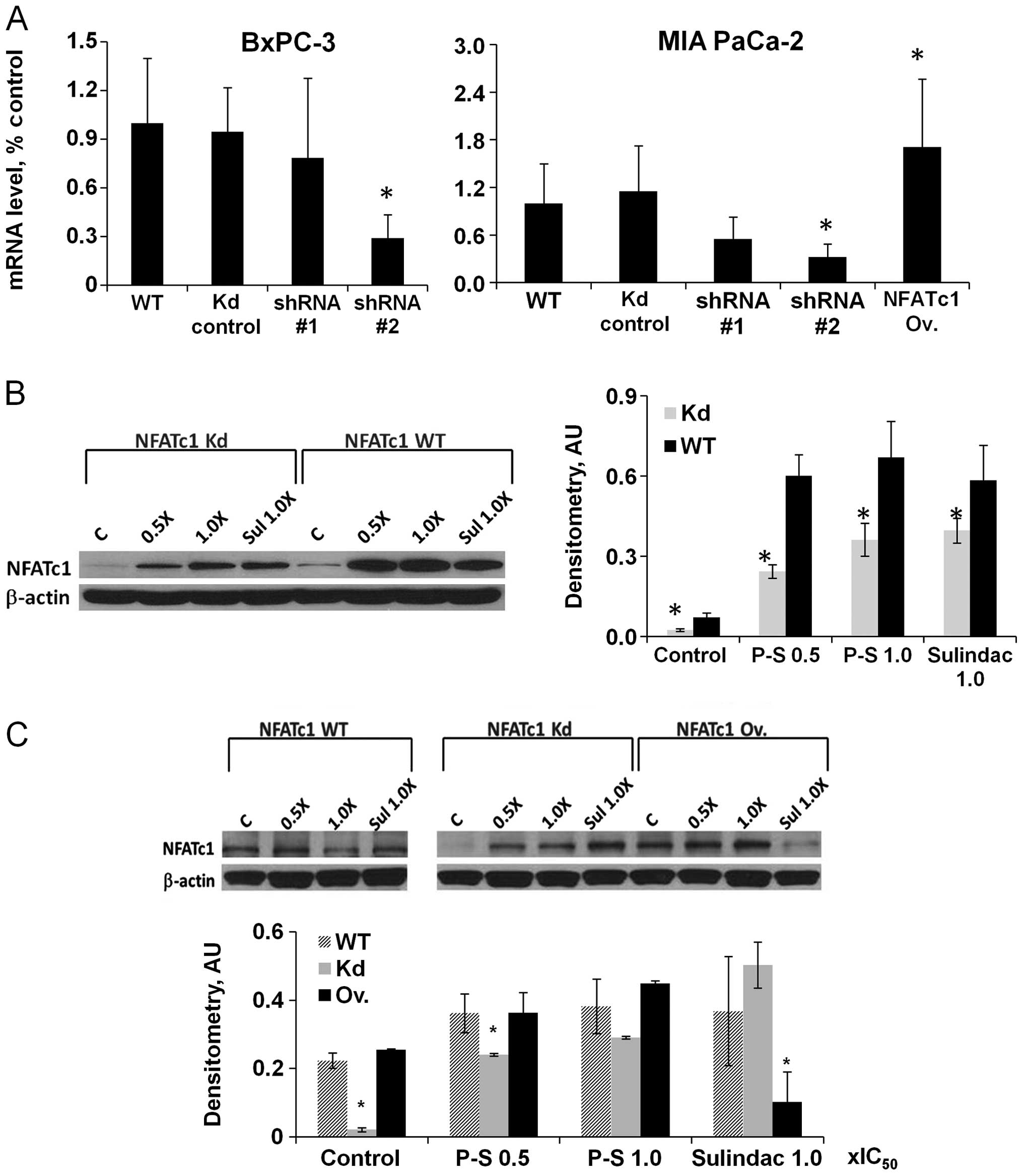
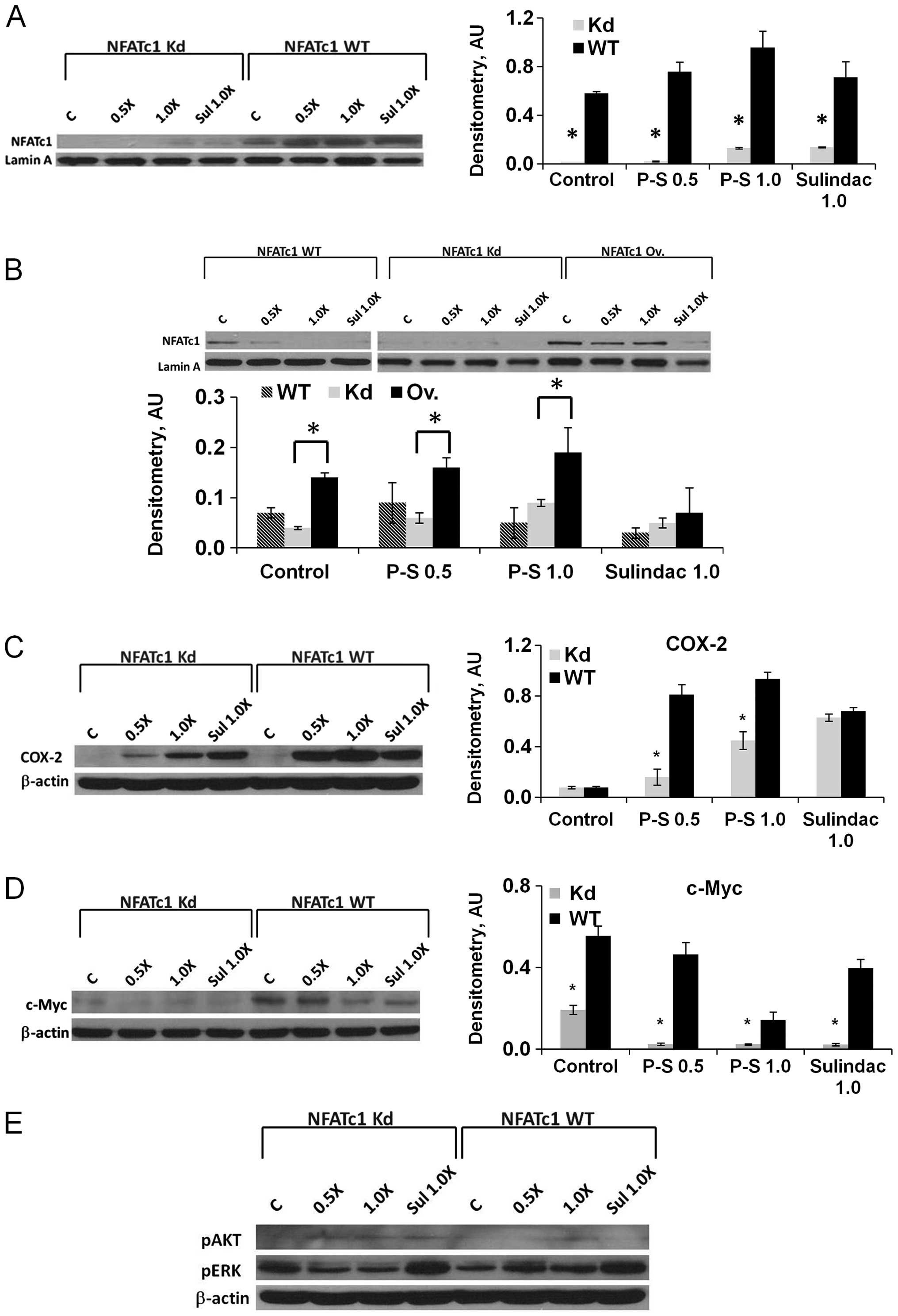
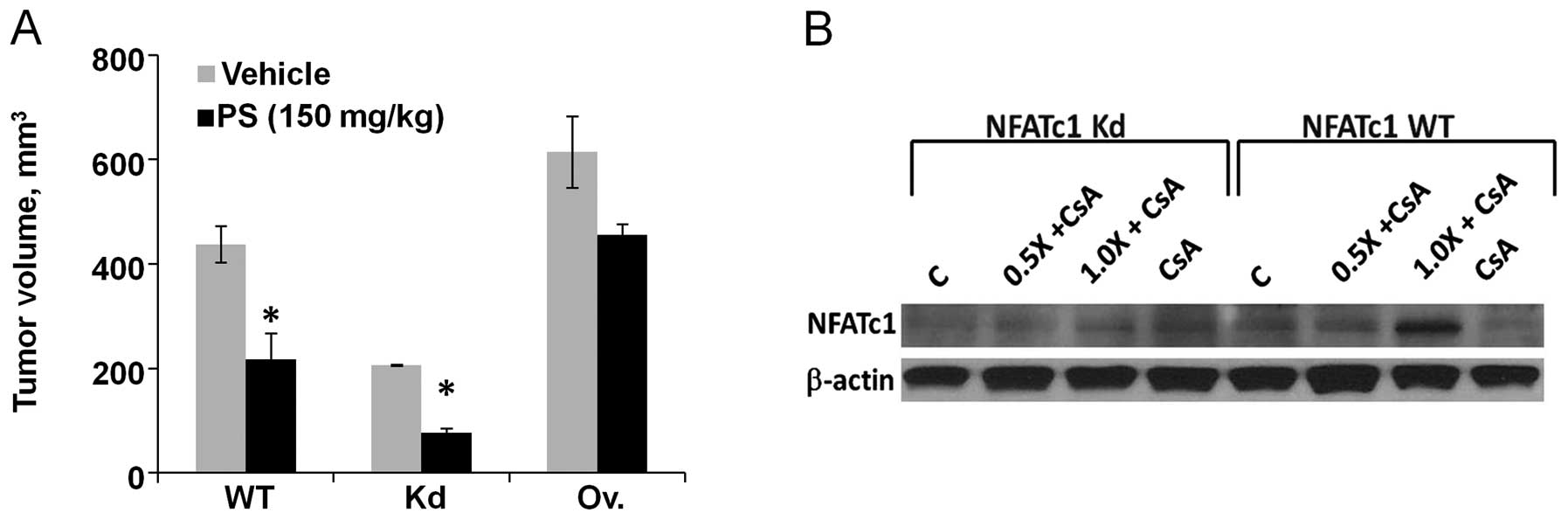
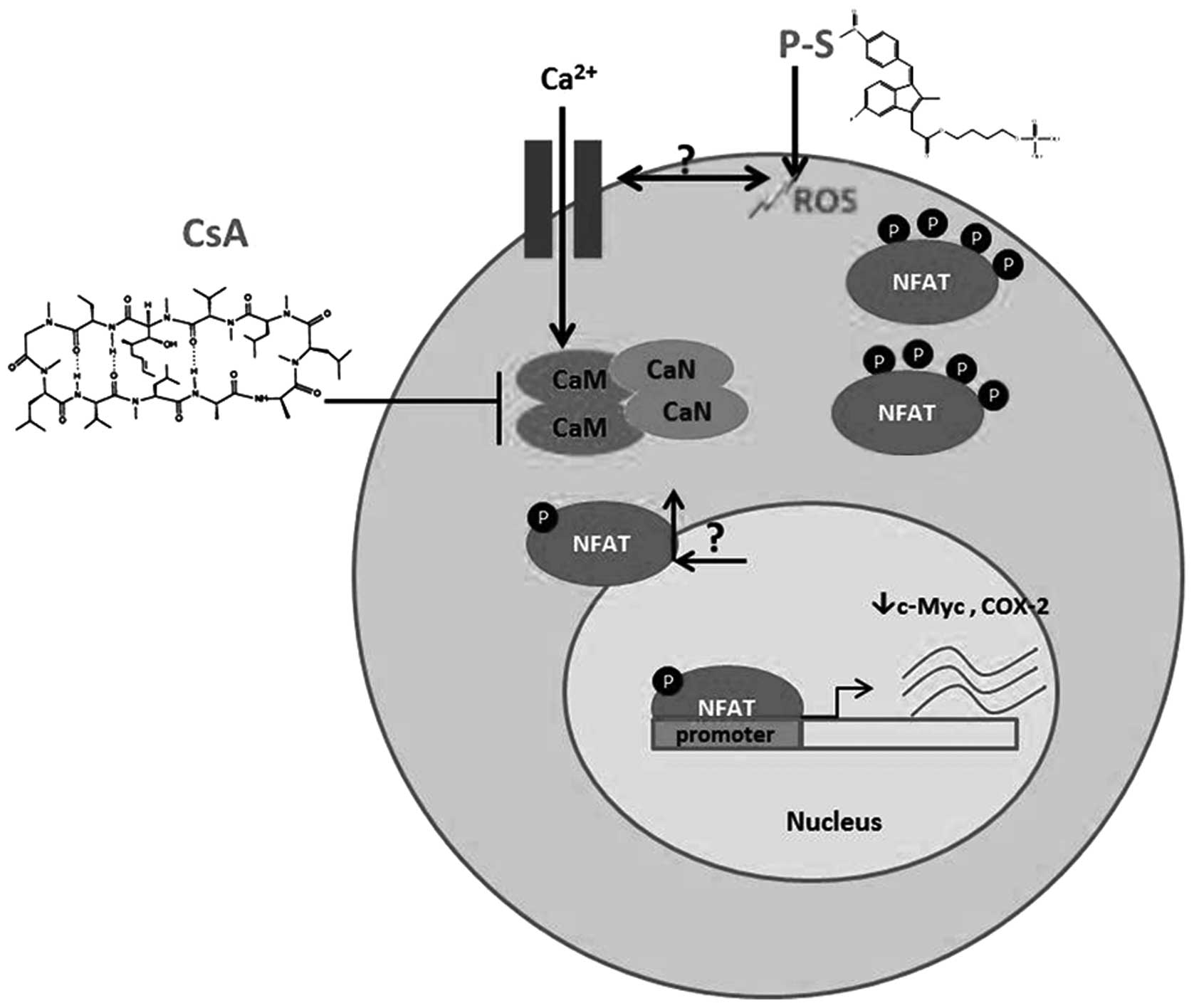
|
1.
|
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R and Abbruzzese JL:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 363:1049–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Hezel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ,
Bardeesy N and Depinho RA: Genetics and biology of pancreatic
ductal adeno-carcinoma. Genes Dev. 20:1218–1249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Bardeesy N and DePinho RA: Pancreatic
cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:897–909. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Wolfe MM, Lichtenstein DR and Singh G:
Gastrointestinal toxicity of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N
Engl J Med. 340:1888–1899. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Molina MA, Sitja-Arnau M, Lemoine MG,
Frazier ML and Sinicrope FA: Increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression
in human pancreatic carcinomas and cell lines: growth inhibition by
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cancer Res. 59:4356–4362.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yip-Schneider MT, Wu H, Ralstin M,
Yiannoutsos C, Crooks PA, Neelakantan S, Noble S, Nakshatri H,
Sweeney CJ and Schmidt CM: Suppression of pancreatic tumor growth
by combination chemotherapy with sulindac and LC-1 is associated
with cyclin D1 inhibition in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1736–1744.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Yip-Schneider MT, Nakshatri H, Sweeney CJ,
Marshall MS, Wiebke EA and Schmidt CM: Parthenolide and sulindac
cooperate to mediate growth suppression and inhibit the nuclear
factor-kappa B pathway in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:587–594. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Yip-Schneider MT and Schmidt CM: MEK
inhibition of pancreatic carcinoma cells by U0126 and its effect in
combination with sulindac. Pancreas. 7:337–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Huang L, Zhu C, Sun Y, Xie G, Mackenzie
GG, Qiao G, Komninou D and Rigas B: Phospho-sulindac (OXT-922)
inhibits the growth of human colon cancer cell lines: a
redox/polyamine-dependent effect. Carcinogenesis. 31:1982–1990.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Mackenzie GG, Sun Y, Huang L, Xie G,
Ouyang N, Gupta RC, Johnson F, Komninou D, Kopelovich L and Rigas
B: Phosphosulindac (OXT-328), a novel sulindac derivative, is safe
and effective in colon cancer prevention in mice. Gastroenterology.
139:1320–1332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Xie G, Nie T, Mackenzie GG, Sun Y, Huang
L, Ouyang N, Alston N, Zhu C, Murray OT, Constantinides PP,
Kopelovich L and Rigas B: The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of
phosphosulindac (OXT-328) and the effect of
difluoromethylornithine. Br J Pharmacol. 165:2152–2166. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Muller MR and Rao A: NFAT, immunity and
cancer: a transcription factor comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
10:645–656. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Mancini M and Toker A: NFAT proteins:
emerging roles in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:810–820.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Cippa PE, Kraus AK, Lindenmeyer MT, Chen
J, Guimezanes A, Bardwell PD, Wekerle T, Wuthrich RP and Fehr T:
Resistance to ABT-737 in activated T lymphocytes: molecular
mechanisms and reversibility by inhibition of the calcineurin-NFAT
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2992012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Gregory MA, Phang TL, Neviani P,
Alvarez-Calderon F, Eide CA, O’Hare T, Zaberezhnyy V, Williams RT,
Druker BJ, Perrotti D and Degregori J: Wnt/Ca2+/NFAT
signaling maintains survival of Ph+leukemia cells upon
inhibition of Bcr-Abl. Cancer Cell. 18:74–87. 2010.
|
|
16.
|
Sun Y and Rigas B: The thioredoxin system
mediates redox-induced cell death in human colon cancer cells:
implications for the mechanism of action of anticancer agents.
Cancer Res. 68:8269–8277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Ouyang N, Williams JL, Tsioulias GJ, Gao
J, Iatropoulos MJ, Kopelovich L, Kashfi K and Rigas B: Nitric
oxide-donating aspirin prevents pancreatic cancer in a hamster
tumor model. Cancer Res. 66:4503–4511. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Sun Y, Huang L, Mackenzie GG and Rigas B:
Oxidative stress mediates through apoptosis the anticancer effect
of phosphononsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: implications for
the role of oxidative stress in the action of anticancer agents. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 338:775–783. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Nie T, Wong CC, Alston N, Aro P,
Constantinides PP and Rigas B: Phospho-ibuprofen (MDC-917)
incorporated in nano-carriers: Anti-cancer activity in vitro and in
vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 166:991–1001. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Buchholz M, Schatz A, Wagner M, Michl P,
Linhart T, Adler G, Gress TM and Ellenrieder V: Overexpression of
c-myc in pancreatic cancer caused by ectopic activation of NFATc1
and the Ca2+/calcineurin signaling pathway. EMBO J.
25:3714–3724. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Duque J, Fresno M and Iniguez MA:
Expression and function of the nuclear factor of activated T cells
in colon carcinoma cells: involvement in the regulation of
cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 280:8686–8693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Cao Z and Li Y: Chemical induction of
cellular antioxidants affords marked protection against oxidative
injury in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
292:50–57. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J and Rao A:
Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes
Dev. 17:2205–2232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|