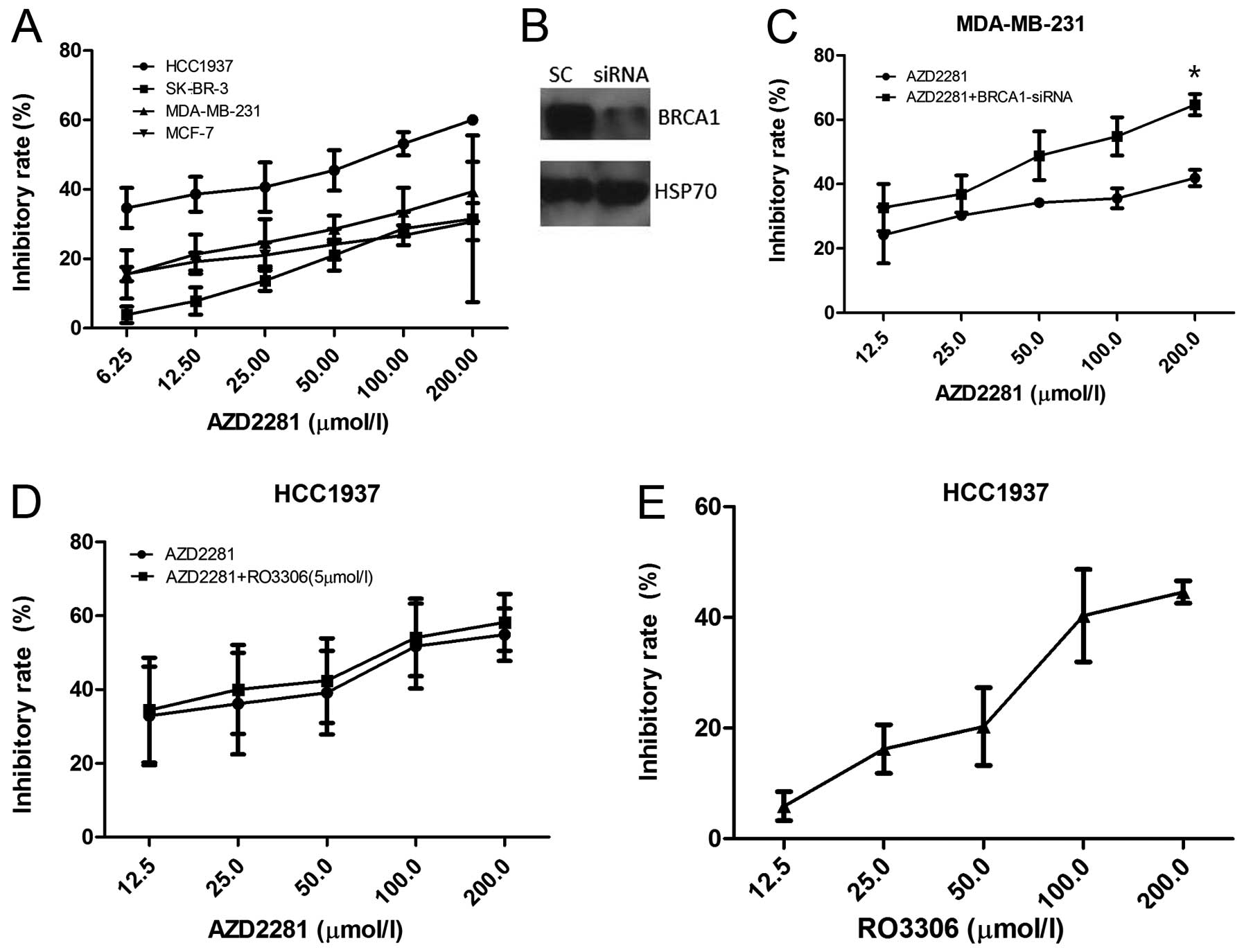
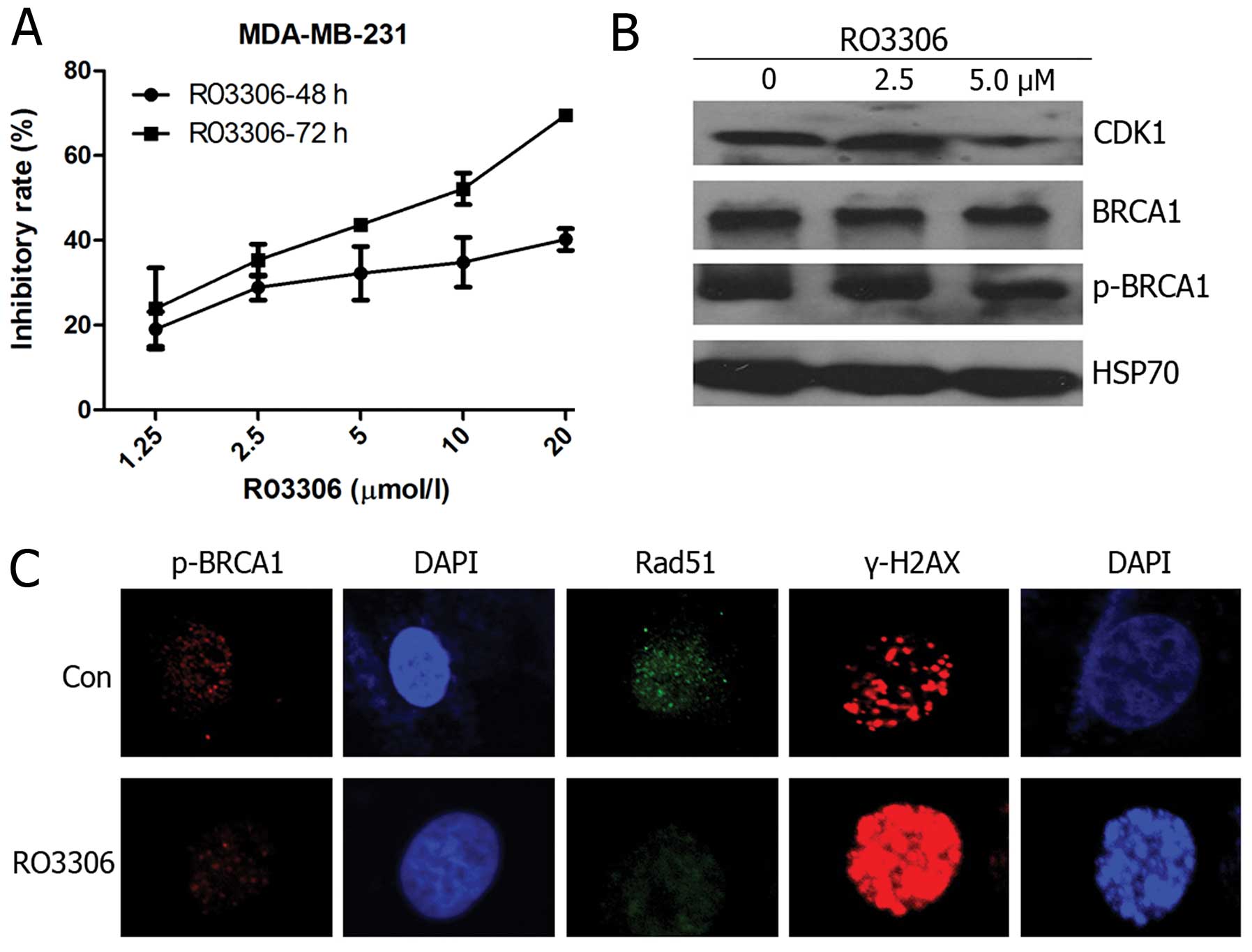
|
1.
|
Gucalp A and Traina TA: Triple-negative
breast cancer: adjuvant therapeutic options. Chemother Res Pract.
2011:6962082011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Moynahan ME, Chiu JW, Koller BH and Jasin
M: Brca1 controls homology-directed DNA repair. Mol Cell.
4:511–518. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Zhang J and Powell SN: The role of the
BRCA1 tumor suppressor in DNA double-strand break repair. Mol
Cancer Res. 3:531–539. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hartman AR and Ford JM: BRCA1 induces DNA
damage recognition factors and enhances nucleotide excision repair.
Nat Genet. 32:180–184. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Alli E, Sharma VB, Sunderesakumar P and
Ford JM: Defective repair of oxidative DNA damage in
triple-negative breast cancer confers sensitivity to inhibition of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cancer Res. 69:3589–3596. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
McCabe N, Turner NC, Lord CJ, Kluzek K,
Bialkowska A, Swift S, Giavara S, O’Connor MJ, Tutt AN, Zdzienicka
MZ, Smith GC and Ashworth A: Deficiency in the repair of DNA damage
by homologous recombination and sensitivity to poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase inhibition. Cancer Res. 66:8109–8115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ashworth A: A synthetic lethal therapeutic
approach: poly(ADP) ribose polymerase inhibitors for the treatment
of cancers deficient in DNA double-strand break repair. J Clin
Oncol. 26:3785–3790. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Tutt A, Robson M, Garber JE, Domchek SM,
Audeh MW, Weitzel JN, Friedlander M, Arun B, Loman N, Schmutzler
RK, Wardley A, Mitchell G, Earl H, Wickens M and Carmichael J: Oral
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in patients with
BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and advanced breast cancer: a
proof-of-concept trial. Lancet. 376:235–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, Tutt A, Wu P,
Mergui-Roelvink M, Mortimer P, Swaisland H, Lau A, O’Connor MJ,
Ashworth A, Carmichael J, Kaye SB, Schellens JH and de Bono JS:
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA
mutation carriers. N Engl J Med. 361:123–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Wooster R and Weber BL: Breast and ovarian
cancer. N Engl J Med. 348:2339–2347. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Morgan DO: Principles of CDK regulation.
Nature. 374:131–134. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Vassilev LT, Tovar C, Chen S, Knezevic D,
Zhao X, Sun H, Heimbrook DC and Chen L: Selective small-molecule
inhibitor reveals critical mitotic functions of human CDK1. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:10660–10665. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Goga A, Yang D, Tward AD, Morgan DO and
Bishop JM: Inhibition of CDK1 as a potential therapy for tumors
over-expressing MYC. Nat Med. 13:820–827. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kojima K, Shimanuki M, Shikami M, Andreeff
M and Nakakuma H: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 inhibitor RO-3306
enhances p53-mediated Bax activation and mitochondrial apoptosis in
AML. Cancer Sci. 100:1128–1136. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Johnson N, Cai D, Kennedy RD, Pathania S,
Arora M, Li YC, D’Andrea AD, Parvin JD and Shapiro GI: Cdkl
participates in BRCA1-dependent S phase checkpoint control in
response to DNA damage. Mol Cell. 35:327–339. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Johnson N, Li YC, Walton ZE, Cheng KA, Li
D, Rodig SJ, Moreau LA, Unitt C, Bronson RT, Thomas HD, Newell DR,
D’Andrea AD, Curtin NJ, Wong KK and Shapiro GI: Compromised CDK1
activity sensitizes BRCA-proficient cancers to PARP inhibition. Nat
Med. 17:875–882. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Gartner EM, Burger AM and Lorusso PM:
Poly(adp-ribose) polymerase inhibitors: a novel drug class with a
promising future. Cancer J. 16:83–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Paull TT, Rogakou EP, Yamazaki V,
Kirchgessner CU, Gellert M and Bonner WM: A critical role for
histone H2AX in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after
DNA damage. Curr Biol. 10:886–895. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Turner NC and Reis-Filho JS: Basal-like
breast cancer and the BRCA1 phenotype. Oncogene. 25:5846–5853.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Gudmundsdottir K and Ashworth A: The roles
of BRCA1 and BRCA2 and associated proteins in the maintenance of
genomic stability. Oncogene. 25:5864–5874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D,
Futreal PA, Harshman K, Tavtigian S, Liu Q, Cochran C, Bennett LM
and Ding W: A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer
susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 266:66–71. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Amé JC, Spenlehauer C and de Murcia G: The
PARP super-family. Bioessays. 26:882–893. 2004.
|
|
24.
|
Turner N, Tutt A and Ashworth A: Hallmarks
of ‘BRCAness’ in sporadic cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:814–819.
2004.
|
|
25.
|
Ira G, Pellicioli A, Balijja A, Wang X,
Fiorani S, Carotenuto W, Liberi G, Bressan D, Wan L, Hollingsworth
NM, Haber JE and Foiani M: DNA end resection, homologous
recombination and DNA damage checkpoint activation require CDK1.
Nature. 431:1011–1017. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Santamaría D, Barrière C, Cerqueira A,
Hunt S, Tardy C, Newton K, Cáceres JF, Dubus P, Malumbres M and
Barbacid M: Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle.
Nature. 448:811–815. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kimbung S, Biskup E, Johansson I, Aaltonen
K, Ottosson-Wadlund A, Gruvberger-Saal S, Cunliffe H, Fadeel B,
Loman N, Berglund P and Hedenfalk I: Co-targeting of the PI3K
pathway improves the response of BRCA1 deficient breast cancer
cells to PARP1 inhibition. Cancer Lett. 319:232–241. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Drew Y, Mulligan EA, Vong WT, Thomas HD,
Kahn S, Kyle S, Mukhopadhyay A, Los G, Hostomsky Z, Plummer ER,
Edmondson RJ and Curtin NJ: Therapeutic potential of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibito AG014699 in human cancers with
mutated or methylated BRCA1 or BRCA2. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:334–346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Mendes-Pereira AM, Martin SA, Brough R,
McCarthy A, Taylor JR, Kim JS, Waldman T, Lord CJ and Ashworth A:
Synthetic lethal targeting of PTEN mutant cells with PARP
inhibitors. EMBO Mol Med. 1:315–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Inbar-Rozensal D, Castiel A, Visochek L,
Castel D, Dantzer F, Izraeli S and Cohen-Armon M: A selective
eradication of human nonhereditary breast cancer cells by
phenanthridine-derived polyADP-ribose polymerase inhibitors. Breast
Cancer Res. 11:R782009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Payton M, Chung G, Yakowec P, Wong A,
Powers D, Xiong L, Zhang N, Leal J, Bush TL, Santora V, Askew B,
Tasker A, Radinsky R, Kendall R and Coats S: Discovery and
evaluation of dual CDK1 and CDK2 inhibitors. Cancer Res.
66:4299–4308. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Gao LL, Li FR, Jiao P, Yang MF, Zhou XJ,
Si YH, Jiang WJ and Zheng TT: Paris chinensis dioscin induces G2/M
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901
cells. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4389–4395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Cuervo AM: Autophagy: in sickness and in
health. Trends Cell Biol. 14:70–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|