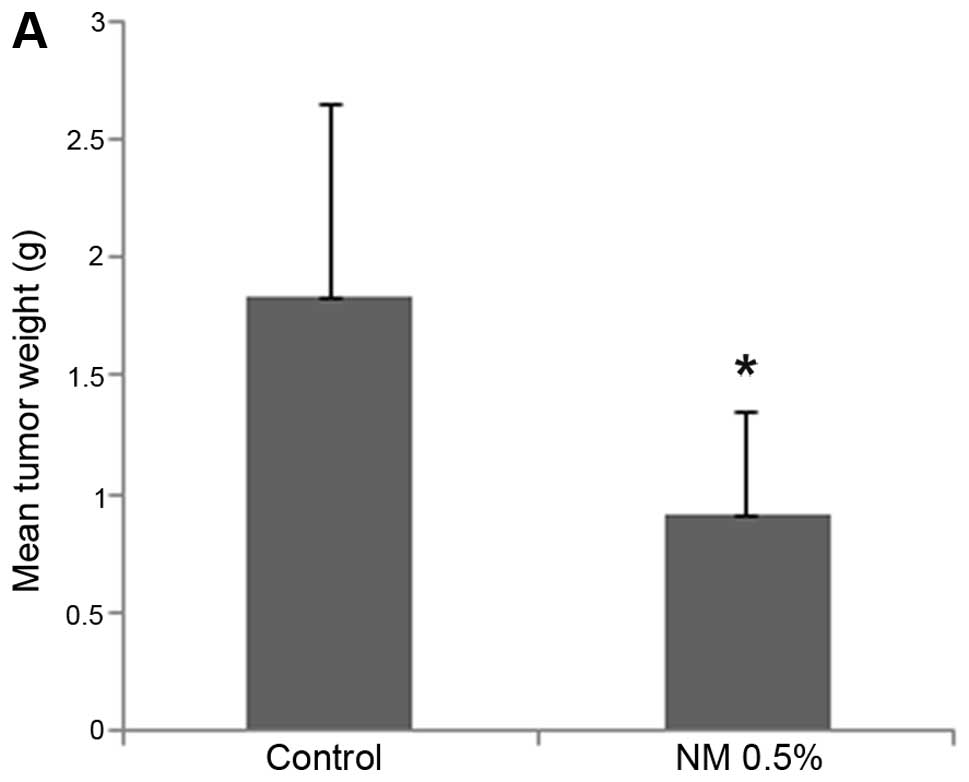
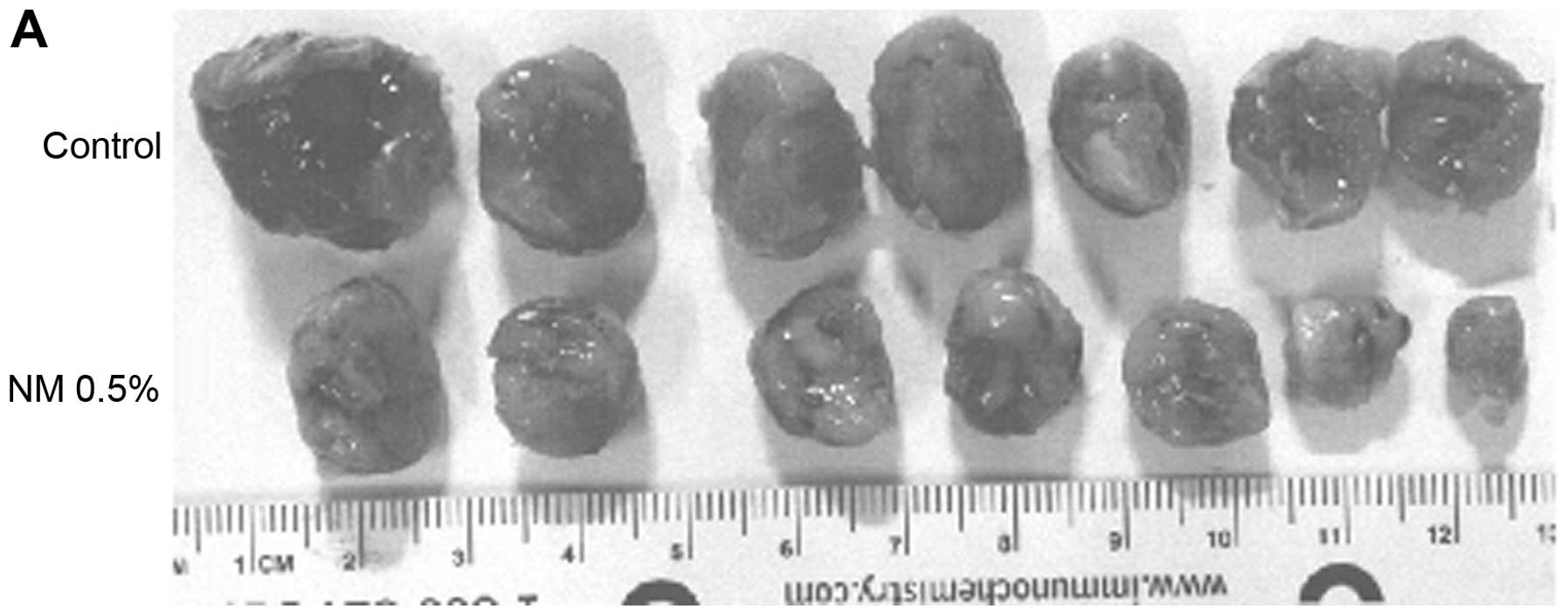
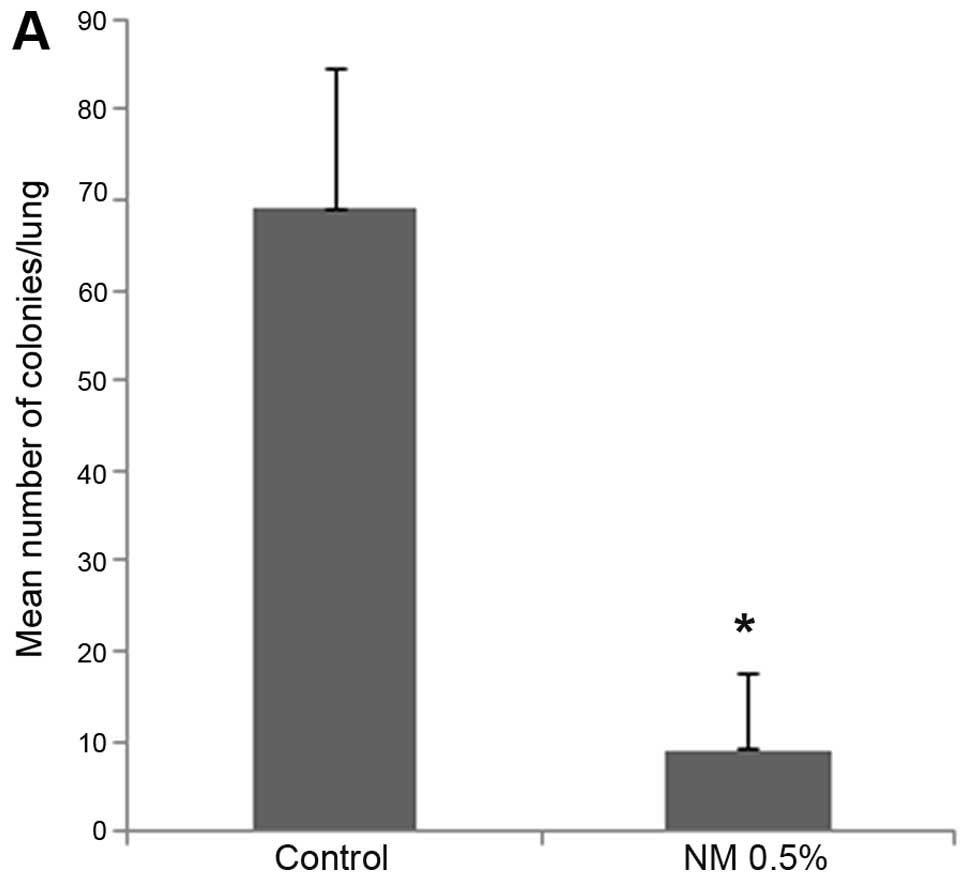
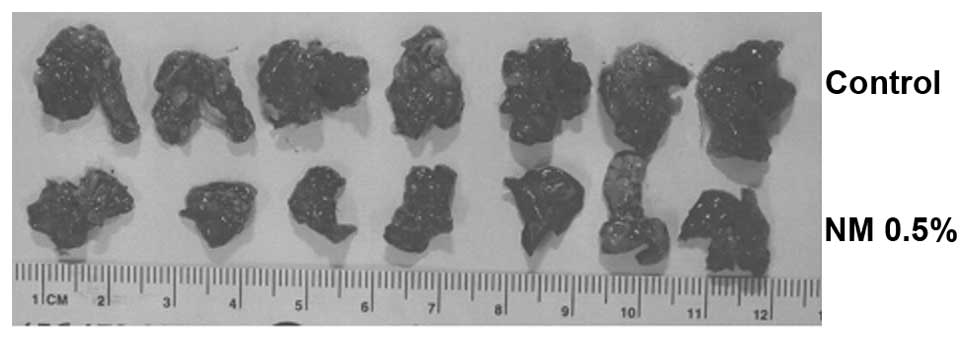
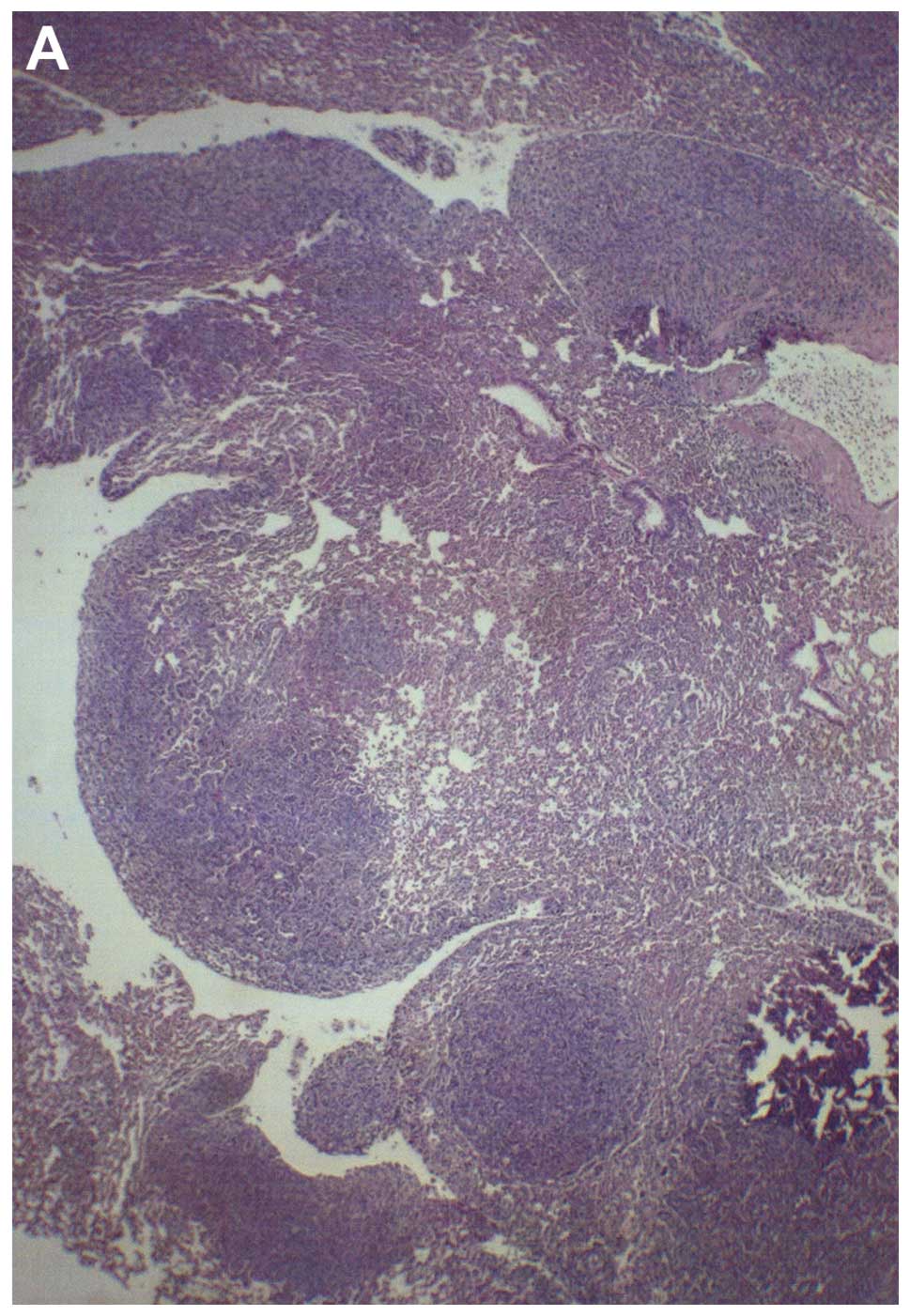
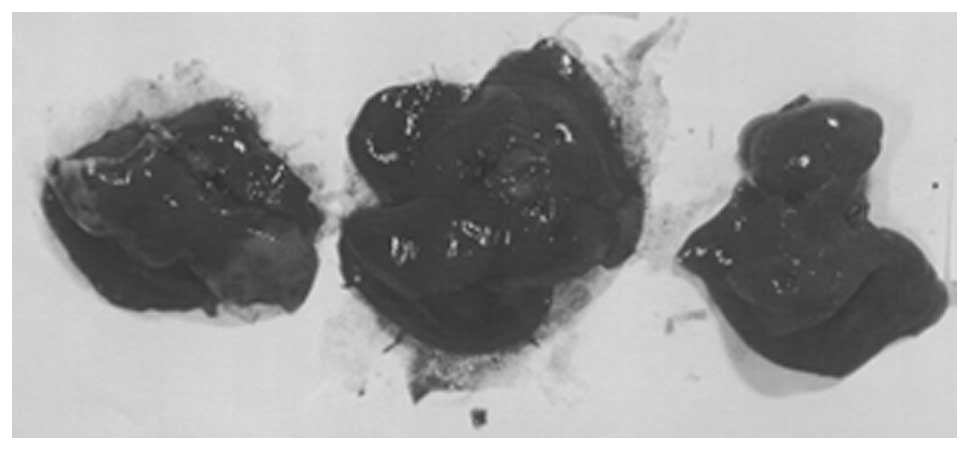
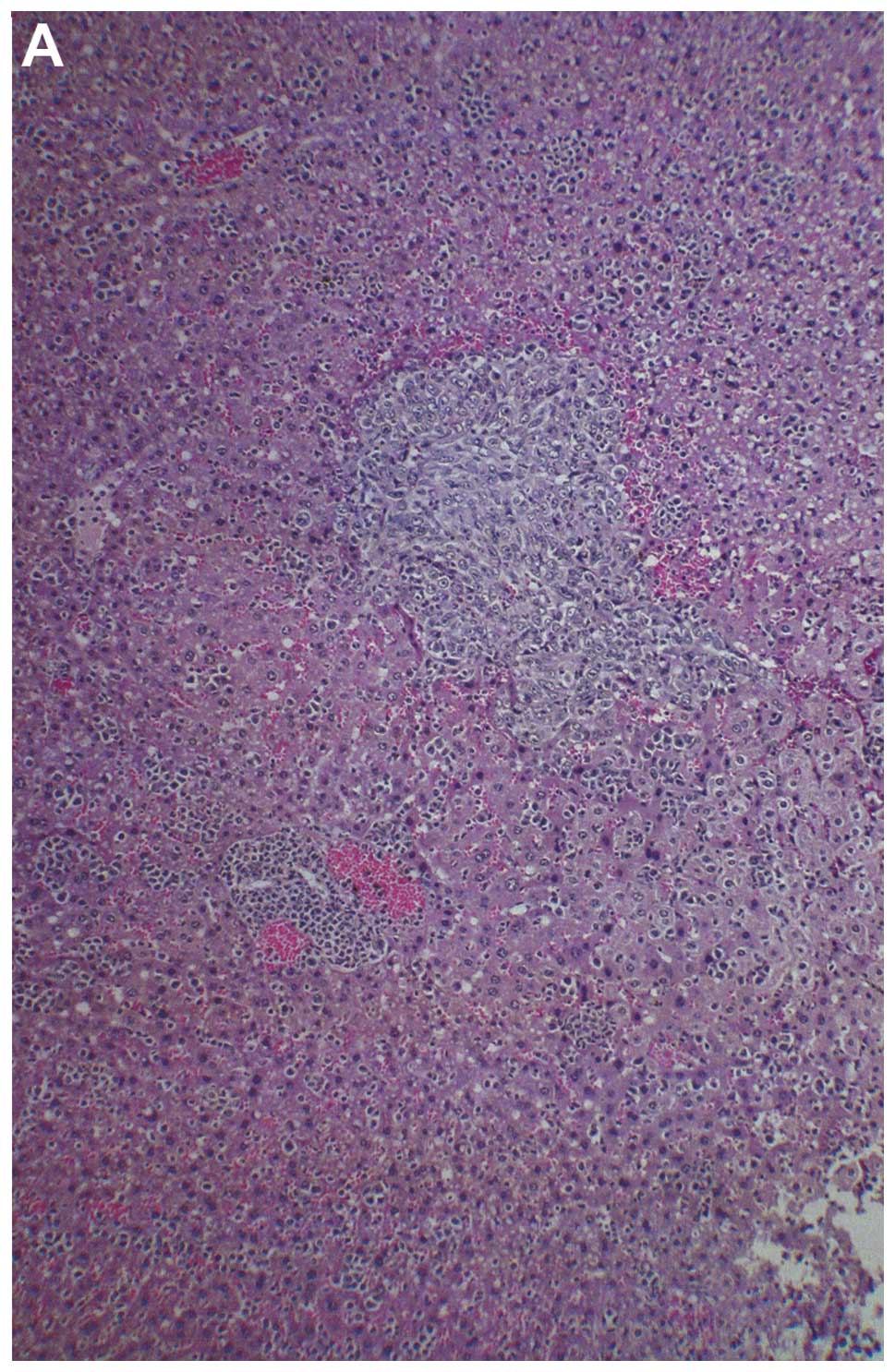
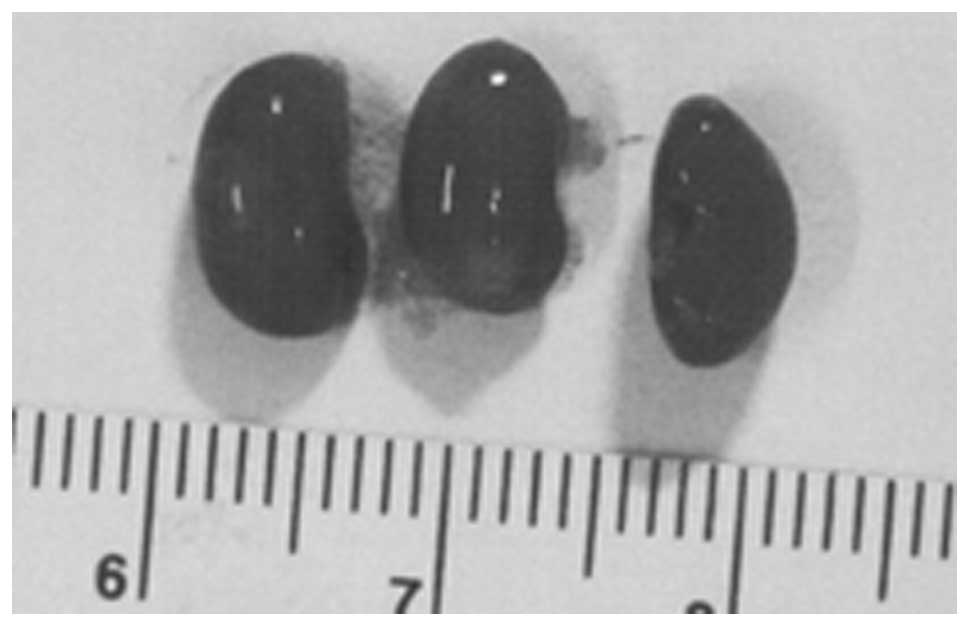
|
1.
|
American Cancer Society: Breast cancer:
what are the key statistics about breast cancer? http://www.cancer.org/cancer/breastcancer/detailedguide/breast-cancer-key-statistics).
Accessed 10/9/13. Last Medical Review: 09/11/2013. Last Revised:
10/01/2013.
|
|
2.
|
Ali SM, Harvey HA and Lipton A: Metastatic
breast cancer: overview of treatment. Clin Orthop. 414(Suppl):
132–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Fidler IJ: Molecular biology of cancer:
invasion and metastasis. Cancer: Principles and Practice of
Oncology. 5th edition. De Vita VT, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA:
Lippincott-Raven; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 135–152. 1997
|
|
4.
|
Rath M and Pauling L: Plasmin-induced
proteolysis and the role of apoprotein(a), lysine and synthetic
analogs. Orthomolecular Med. 7:17–23. 1992.
|
|
5.
|
Niedzwiecki A, Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T and
Rath M: Micronutrient synergy - a new tool in effective control of
metastasis and other key mechanisms of cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 29:529–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Bibby MC: Orthotopic models of cancer for
preclinical drug evaluation: advantages and disadvantages. Eur J
Cancer. 40:852–857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Eccles SA, Box G, Court W, Sandle J and
Dean CJ: Preclinical models for the evaluation of targeted
therapies of metastatic disease. Cell Biophys. 24–25:279–291.
1994.
|
|
8.
|
Hoffman RM: Orthotopic metastatic mouse
models for anti-cancer drug discovery and evaluation: a bridge to
the clinic. Invest New Drugs. 17:343–359. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Vernon E, Bakewell SJ and Chodash LA:
Deciphering the molecular basis of breast cancer metastasis with
mouse models. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 8:199–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Tao K, Fang M, Aloy J and Sahagian GG:
Imagable 4T1 model for the study of late stage breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 8:2282008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Aslakson CJ and Miller FR: Selective
events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the
sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary
tumor. Cancer Res. 52:1399–1405. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bonfil RD, Bustuabad OD, Ruggiero RA,
Meiss RP and Pasqualini CD: Tumor necrosis can facilitate the
appearance of metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 6:121–129. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Bonfil RD, Medina PA, Gómez DE, Farías E,
Lazarowski A, Lucero Gritti MF, Meiss RP and Bustuabad OD:
Expression of gelatinase/type IV collagenase in tumor necrosis
correlates with cell detachment and tumor invasion. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 10:211–220. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Cha J, Roomi MW, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T,
Niedzwiecki A and Rath M: Ascorbate supplementation inhibits growth
and metastasis of B16FO melanoma and 4T1 breast cancer cells in
vitamin C deficient mice. Int J Oncol. 42:55–64. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG, Lichtinghagen R
and Sommerhoff CP: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in breast
cancer cell lines of different tumorigenicity. Anticancer Res.
6A:3821–3828. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Pellikainen JM, Ropponen KM, Kataja VV,
Kellokoski JK, Eskelinen MJ and Kosma VM: Expression of matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer with a special
reference to activator protein-2, HER-2, and prognosis. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:7621–7628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Connolly EM, Harmey JH, O'Grady T, Foley
D, Roche-Nagle G, Kay E and Bouchier-Hayes DJ: Cyclo-oxygenase
inhibition reduces tumour growth and metastasis in an orthotopic
model of breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 87:231–237. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Denardo DG, Johansson M and Coussans LM:
Immune cells as mediators of solid tumor metastasis. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 27:11–18. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
van Kempen LC, de Visser KE and Coussens
LM: Inflammation, proteases and cancer. Eur J Cancer. 42:728–734.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Roomi NW, Rath M
and Niedzwiecki A: Inhibition of growth and expression of
inflammation mediators in human leukemic cell line. Exp Oncol.
35:180–186. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Niedzwiecki A and
Rath M: Pleiotropic effects of a micronutrient mixture on critical
parameters of bladder cancer. Bladder Cancer Etymology, Diagnosis
and Treatments. Nilsson WE: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.; New
York: 2009
|
|
22.
|
Sun Z, Chen YH, Wang P, Zhang J, Gurewich
V, Zhang P and Liu JN: The blockage of high-affinity lysine binding
sites of plasminogen by EACA significantly inhibits
prourokinase-induced plasminogen activation. Biochem Biophys Acta.
1596:182–192. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Valcic S, Timmermann BN, Alberts DS,
Wachter GA, Krutzsch M, Wymer J and Guillen JM: Inhibitory effect
of six green tea catechins and caffeine on the growth of four
selected human tumor cell lines. Anticancer Drugs. 7:461–468. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Mukhtar H and Ahmed N: Tea polyphenols:
prevention of cancer and optimizing health. Am J Clin Nutr.
71:S1698–S1702. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Yang GY, Liao J, Kim K, Yurtow EJ and Yang
CS: Inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer
cell lines by tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis. 19:611–616. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Taniguchi S, Fujiki H, Kobayashi H, Go H,
Miyado K, Sadano H and Shimikawa R: Effect of (−) epigallocatechin
gallate, the main constituent of green tea, on lung metastasis with
mouse B16 melanoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 65:51–54. 1992.
|
|
27.
|
Hara Y: Green tea: Health Benefits and
Applications. Marcel Dekker; New York, Basel: 2001, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Kawakami S, Kageyama Y, Fujii Y, Kihara K
and Oshima H: Inhibitory effects of N-acetyl cysteine on invasion
and MMP 9 production of T24 human bladder cancer cells. Anticancer
Res. 21:213–219. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Morini M, Cai T, Aluigi MG, Noonan DM,
Masiello L, De Floro S, D’Agostinin F, Albini A and Fassima G: The
role of the thiol N-acetyl cysteine in the prevention of tumor
invasion and angiogenesis. Int J Biol Markers. 14:268–271.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Yoon SO, Kim MM and Chung AS: Inhibitory
effects of selenite on invasion of HT 1080 tumor cells. J Biol
Chem. 276:20085–20092. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Naidu KA, Karl RC and Coppola D:
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effect of ascorbyl stearate in
human pancreatic cancer cells: association with decreased
expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Dig Dis Sci.
48:230–237. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Anthony HM and Schorah CJ: Severe
hypovitaminosis C in lung-cancer patients: the utilization of
vitamin C in surgical repair and lymphocyte-related host
resistance. Br J Cancer. 46:354–367. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Maramag C, Menon M, Balaji KC, Reddy PG
and Laxmanan S: Effect of vitamin C on prostate cancer cells in
vitro: effect on cell number, viability and DNA synthesis.
Prostate. 32:188–195. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Koh WS, Lee SJ, Lee H, Park C, Park MH,
Kim WS, Yoon SS, Park K, Hong SI, Chung MH and Park CH:
Differential effects and transport kinetics of ascorbate
derivatives in leukemic cell lines. Anticancer Res. 8:2487–2493.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC, Mitchell JB,
Corpe CP, Buettner GR, Shacter E and Levine M: Pharmacologic
ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: Action
as a pro-drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13604–13609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Nunez C, Ortiz de Apodaca Y and Ruiz A:
Ascorbic acid in the plasma and blood cells of women with breast
cancer. The effect of consumption of food with an elevated content
of this vitamin. Nutr Hosp. 10:368–372. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Kurbacher CM, Wagner U, Kolster B,
Andreotti PE, Krebs D and Bruckner HW: Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
improves the antineoplastic activity of doxorubicin, cisplatin and
paclitaxel in human breast carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Lett.
103:183–189. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Cooke JP and Dzau VJ: Nitric oxide
synthase: role in the genesis of vascular disease. Annu Rev Med.
48:489–509. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|