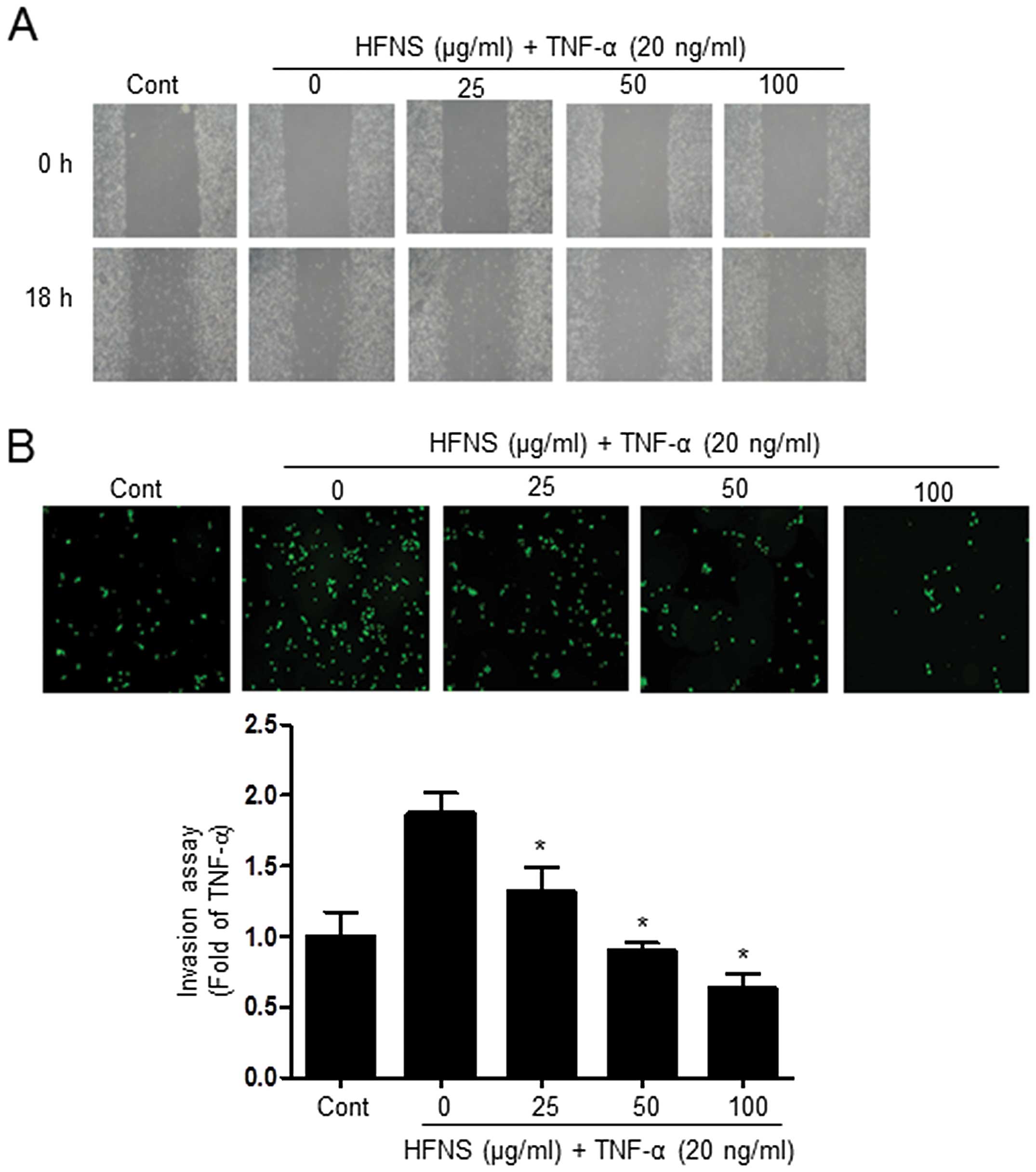
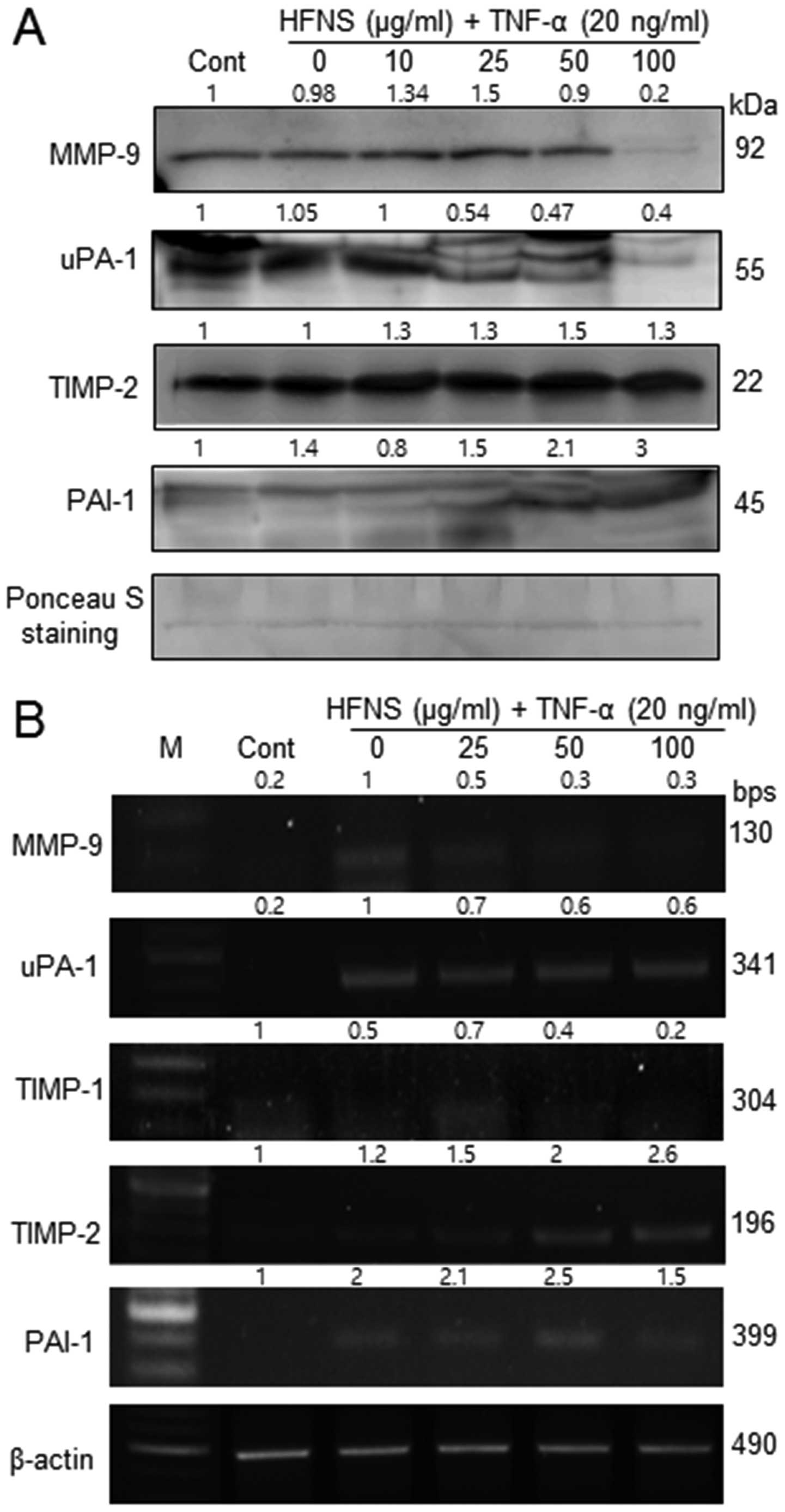
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kreusel KM, Bechrakis NE, Wiegel T, Krause
L and Foerster MH: Incidence and clinical characteristics of
symptomatic choroidal metastasis from lung cancer. Acta Ophthalmol.
86:515–519. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang HL, Kuo YH, Tsai CT, et al:
Anti-metastatic activities of Antrodia camphorata against human
breast cancer cells mediated through suppression of the MAPK
signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:290–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fidler IJ: Orthotopic implantation of
human colon carcinomas into nude mice provides a valuable model for
the biology and therapy of metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
10:229–243. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yilmaz M, Christofori G and Lehembre F:
Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol
Med. 13:535–541. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sliva D, English D, Lyons D and Lloyd FP
Jr: Protein kinase C induces motility of breast cancers by
upregulating secretion of urokinase-type plasminogen activator
through activation of AP-1 and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 290:552–557. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zheng H, Takahashi H, Murai Y, et al:
Expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF are closely linked to growth,
invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 26:3579–3583. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Westermarck J and Kahari VM: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J.
13:781–792. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Quaranta M, Daniele A, Coviello M, et al:
MMP-2, MMP-9, VEGF and CA 15.3 in breast cancer. Anticancer Res.
27:3593–3600. 2007.
|
|
10
|
Folgueras AR, Pendas AM, Sanchez LM and
Lopez-Otin C: Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: from new
functions to improved inhibition strategies. Int J Dev Biol.
48:411–424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Look M, van Putten W, Duffy M, et al:
Pooled analysis of prognostic impact of uPA and PAI-1 in breast
cancer patients. Thromb Haemost. 90:538–548. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rosen EM, Goldberg ID, Liu D, et al: Tumor
necrosis factor stimulates epithelial tumor cell motility. Cancer
Res. 51:5315–5321. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hagemann T, Wilson J, Kulbe H, et al:
Macrophages induce invasiveness of epithelial cancer cells via
NF-kappa B and JNK. J Immunol. 175:1197–1205. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chazaud B, Ricoux R, Christov C, Plonquet
A, Gherardi RK and Barlovatz-Meimon G: Promigratory effect of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 on invasive breast cancer cell
populations. Am J Pathol. 160:237–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases in cell signaling: metalloproteinase-independent
biological activities. Sci Signal. 1:re62008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lijnen HR: Pleiotropic functions of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Thromb Haemost. 3:35–45. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rose P, Huang Q, Ong CN and Whiteman M:
Broccoli and watercress suppress matrix metalloproteinase-9
activity and invasiveness of human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 209:105–113. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi S and Singh SV: Bax and Bak are
required for apoptosis induction by sulforaphane, a cruciferous
vegetable-derived cancer chemopreventive agent. Cancer Res.
65:2035–2043. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ho YC, Yang SF, Peng CY, Chou MY and Chang
YC: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the invasion of human oral
cancer cells and decreases the productions of matrix
metalloproteinases and urokinase-plasminogen activator. J Oral
Pathol Med. 36:588–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seo HS, DeNardo DG, Jacquot Y, et al:
Stimulatory effect of genistein and apigenin on the growth of
breast cancer cells correlates with their ability to activate ER
alpha. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 99:121–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang J, Grieb B, Thyagarajan A and Sliva
D: Ganoderic acids suppress growth and invasive behavior of breast
cancer cells by modulating AP-1 and NF-kappaB signaling. Int J Mol
Med. 21:577–584. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sliva D, Jedinak A, Kawasaki J, Harvey K
and Slivova V: Phellinus linteus suppresses growth,
angiogenesis and invasive behaviour of breast cancer cells through
the inhibition of AKT signalling. Br J Cancer. 98:1348–1356. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kim HG, Yoon DH, Lee WH, et al:
Phellinus linteus inhibits inflammatory mediators by
suppressing redox-based NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation in
lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophage. J Ethnopharmacol.
114:307–315. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Godio RP, Fouces R, Gudina EJ and Martin
JF: Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of the
antitumor clavaric acid-producing basidiomycete Hypholoma
sublateritium. Curr Genet. 46:287–294. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Godio RP, Fouces R and Martin JF: A
squalene epoxidase is involved in biosynthesis of both the
antitumor compound clavaric acid and sterols in the basidiomycete
H. sublateritium. Chem Biol. 14:1334–1346. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Godio RP and Martin JF: Modified
oxidosqualene cyclases in the formation of bioactive secondary
metabolites: biosynthesis of the antitumor clavaric acid. Fungal
Genet Biol. 46:232–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi S, Jang HJ, Choi JY, Kim MS, Lee YR,
Kim HS, Choi SW, Jeon BH, Won SI, Kim TW and Choi JW: Antioxidant
and anticancer activity of fractions of the ethanol extract of
Naematoloma sublateritium. J Med Plants Res. 6:92012.
|
|
28
|
Lee YR, Kim KM, Jeon BH, Choi JW and Choi
S: The n-butanol fraction of Naematoloma sublateritium
suppresses the inflammatory response through downregulation of
NF-kappaB in human endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 29:801–808.
2012.
|
|
29
|
Kajanne R, Miettinen P, Mehlem A, et al:
EGF-R regulates MMP function in fibroblasts through MAPK and AP-1
pathways. J Cel Physiol. 212:489–497. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cohen M, Meisser A, Haenggeli L and
Bischof P: Involvement of MAPK pathway in TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9
expression in human trophoblastic cells. Mol Hum Reprod.
12:225–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leber TM and Balkwill FR: Regulation of
monocyte MMP-9 production by TNF-alpha and a tumour-derived soluble
factor (MMPSF). Br J Cancer. 78:724–732. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stuelten CH, DaCosta Byfield S, Arany PR,
Karpova TS, Stetler-Stevenson WG and Roberts AB: Breast cancer
cells induce stromal fibroblasts to express MMP-9 via secretion of
TNF-alpha and TGF-beta. J Cell Sci. 118:2143–2153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG, Lichtinghagen R
and Sommerhoff CP: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in breast
cancer cell lines of different tumorigenicity. Anticancer Res.
21:3821–3828. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
John A and Tuszynski G: The role of matrix
metalloproteinases in tumor angiogenesis and tumor metastasis.
Pathol Oncol Res. 7:14–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee EJ, Kim WJ and Moon SK: Cordycepin
suppresses TNF-alpha-induced invasion, migration and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression in human bladder cancer cells.
Phytother Res. 24:1755–1761. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yaoita Y, Matsuki K, Iijima T, et al: New
sterols and triterpenoids from four edible mushrooms. Chem Pharm
Bull. 49:589–594. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chavez KJ, Garimella SV and Lipkowitz S:
Triple negative breast cancer cell lines: one tool in the search
for better treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis.
32:35–48. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|