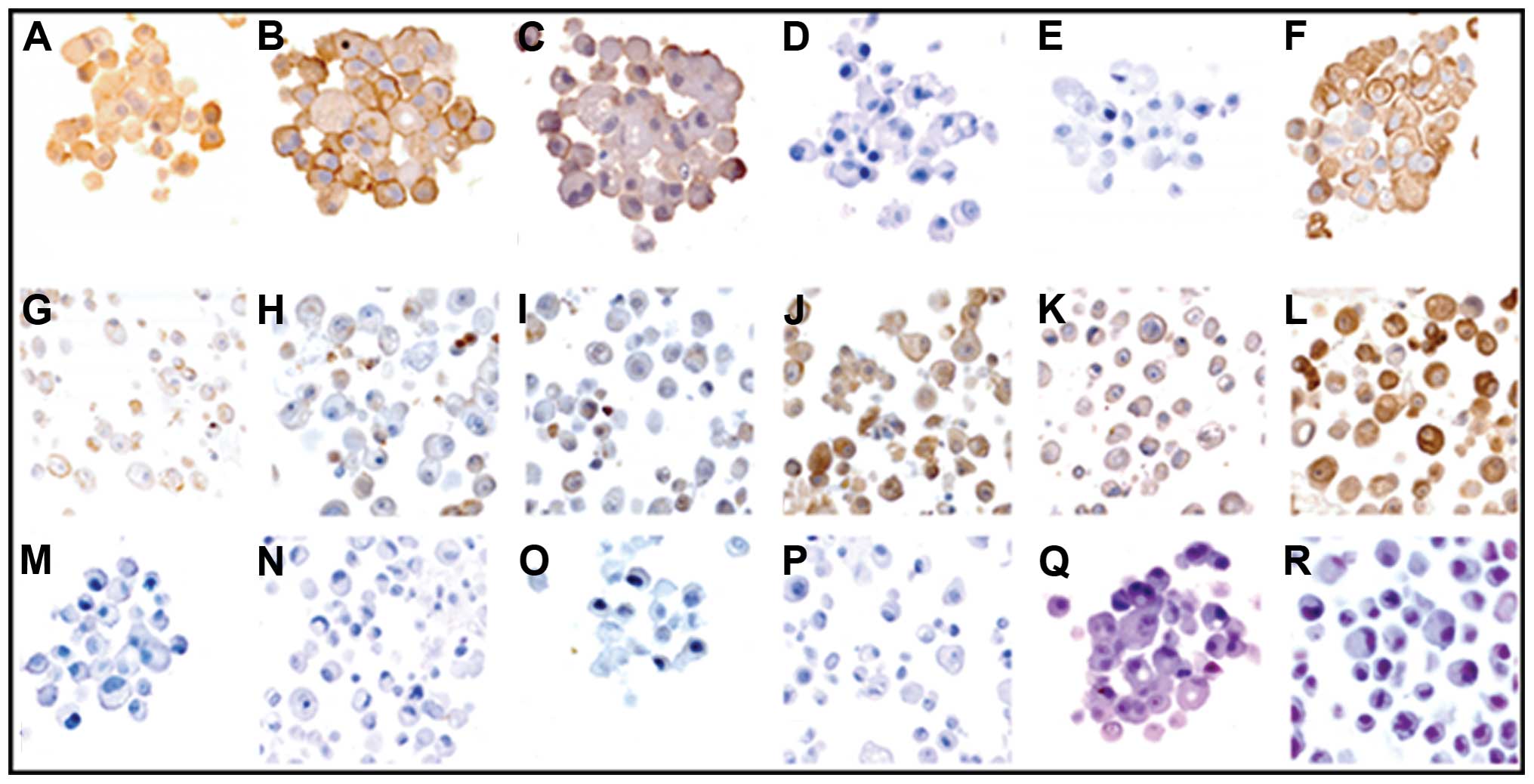
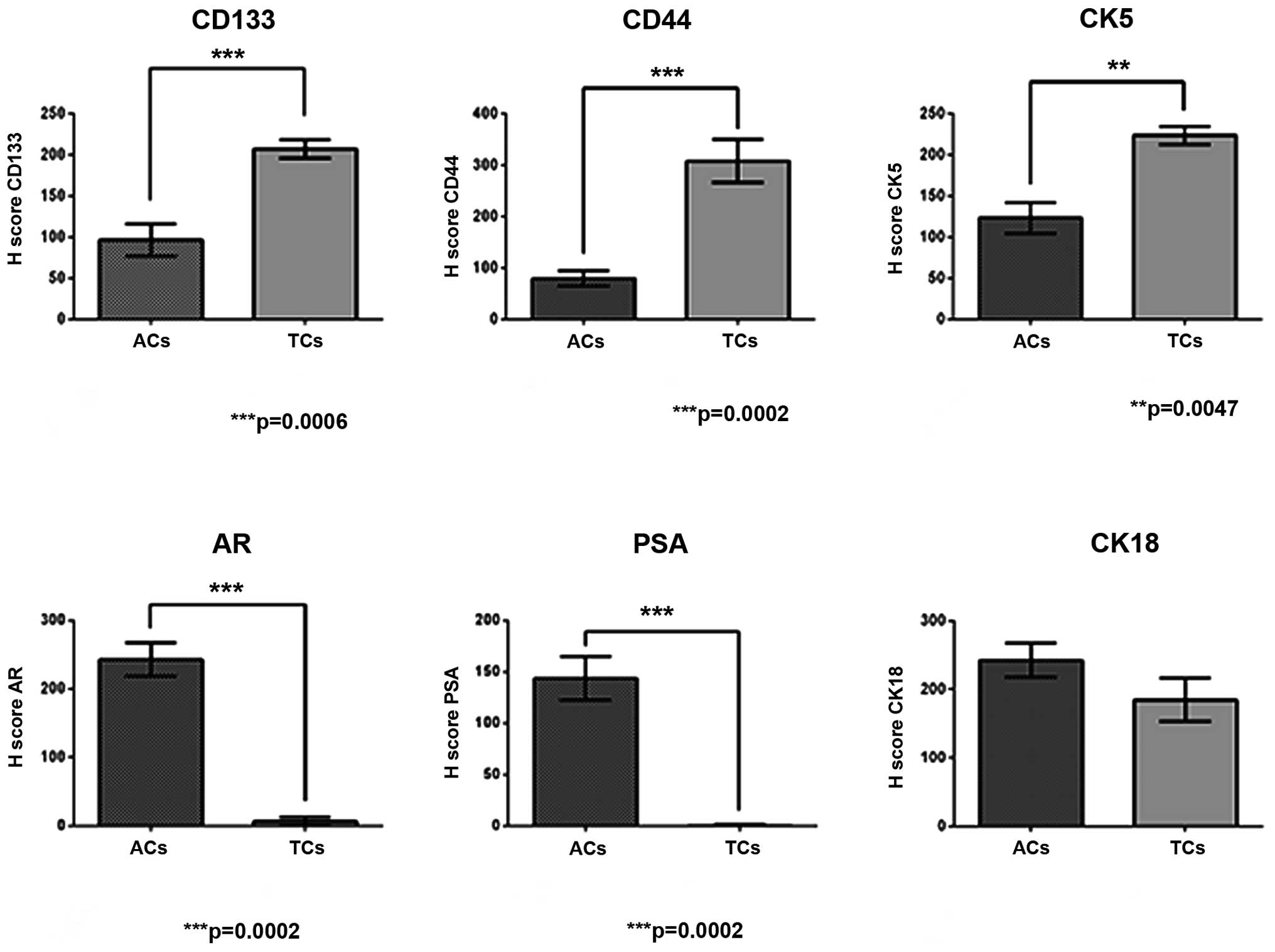
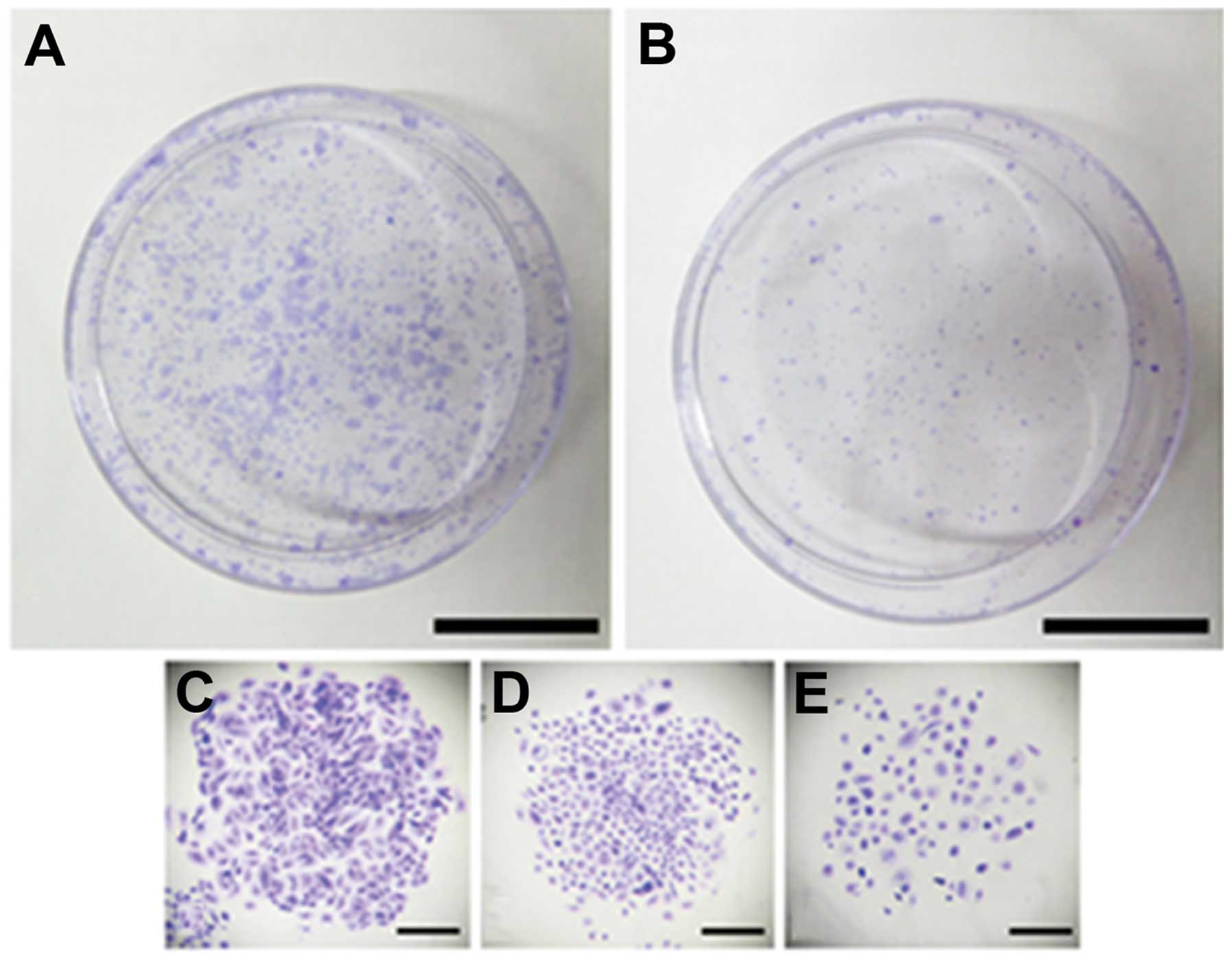
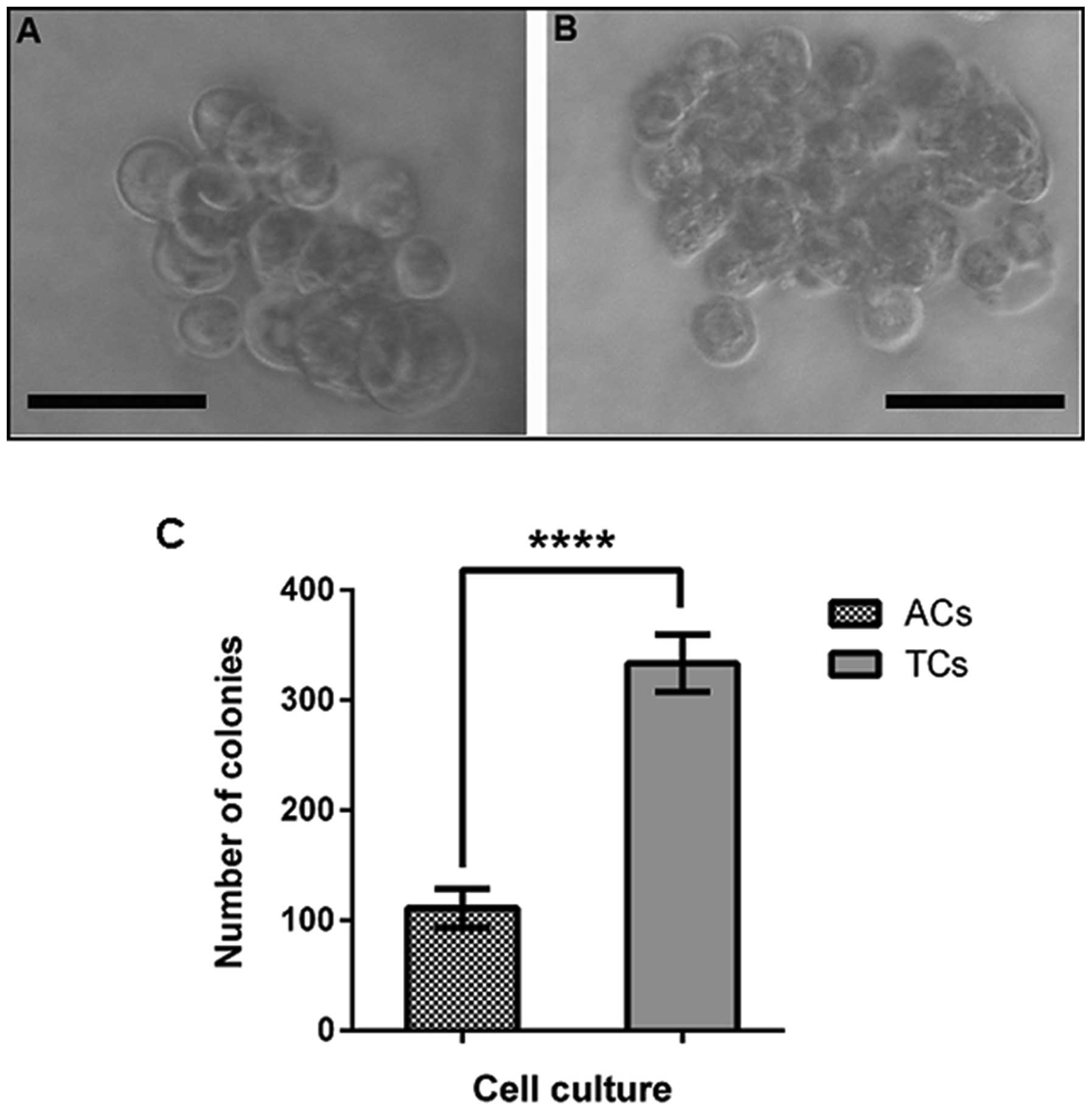
|
1
|
Nagler C, Zanker KS and Dittmar T: Cell
fusion, drug resistance and recurrence CSCs. Adv Exp Med Biol.
714:173–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barnhart BC and Simon MC: Metastasis and
stem cell pathways. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:261–271. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kuhn NZ and Tuan RS: Regulation of
stemness and stem cell niche of mesenchymal stem cells:
implications in tumorigenesis and metastasis. J Cell Physiol.
222:268–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayashida T, Jinno H, Kitagawa Y, et al:
Cooperation of cancer stem cell properties and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the establishment of breast
cancer metastasis. J Oncol. 2011:5914272011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sampieri K and Fodde R: Cancer stem cells
and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:187–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen SF, Chang YC, Nieh S, et al:
Nonadhesive culture system as a model of rapid sphere formation
with cancer stem cell properties. PLoS One. 7:e318642012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tu SM and Lin SH: Prostate cancer stem
cells. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 10:69–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li H and Tang DG: Prostate cancer stem
cells and their potential roles in metastasis. J Surg Oncol.
103:558–562. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tirino V, Desiderio V, Paino F, et al:
Cancer stem cells in solid tumors: an overview and new approaches
for their isolation and characterization. FASEB J. 27:13–24. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sugihara E and Saya H: Complexity of
cancer stem cells. Int J Cancer. 132:1249–1259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Filho MS and Nor JE: The biology
of head and neck cancer stem cells. Oral Oncol. 48:1–9. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Castellon EA, Valenzuela R, Lillo J, et
al: Molecular signature of cancer stem cells isolated from prostate
carcinoma and expression of stem markers in different Gleason
grades and metastasis. Biol Res. 45:297–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fukaya R, Ohta S, Yamaguchi M, et al:
Isolation of cancer stem-like cells from a side population of a
human glioblastoma cell line, SK-MG-1. Cancer Lett. 291:150–157.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hiraga T, Ito S and Nakamura H: Side
population in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells exhibits cancer
stem cell-like properties without higher bone-metastatic potential.
Oncol Rep. 25:289–296. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Bleau AM, Huse JT and Holland EC: The
ABCG2 resistance network of glioblastoma. Cell Cycle. 8:2936–2944.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Corcoran C, Rani S, O’Brien K, et al:
Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: evaluating associated
phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via
exosomes. PLoS One. 7:e509992012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Singh S, Chitkara D, Mehrazin R, et al:
Chemoresistance in prostate cancer cells is regulated by miRNAs and
Hedgehog pathway. PLoS One. 7:e400212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Semenas J, Allegrucci C, Boorjian SA, et
al: Overcoming drug resistance and treating advanced prostate
cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 13:1308–1323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cooperberg MR, Small EJ, D’Amico A, et al:
The evolving role of androgen deprivation therapy in the management
of prostate cancer. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 55:219–238.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Buyyounouski MK: Androgen deprivation
therapy in high-risk prostate cancer. Oncology (Williston Park).
24:806–809. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Petrylak DP: Current state of
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Am J Manag Care. 19(Suppl
18): S358–S365. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sanchez C, Mercado A, Contreras HR, et al:
Chemotherapy sensitivity recovery of prostate cancer cells by
functional inhibition and knock down of multidrug resistance
proteins. Prostate. 71:1810–1817. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sanchez C, Mendoza P, Contreras HR, et al:
Expression of multidrug resistance proteins in prostate cancer is
related with cell sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs. Prostate.
69:1448–1459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kerfoot C, Huang W and Rotenberg SA:
Immunohistochemical analysis of advanced human breast carcinomas
reveals downregulation of protein kinase C alpha. J Histochem
Cytochem. 52:419–422. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, et al:
Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc. 1:2315–2319. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Chen X, Calhoun-Davis T, et al: PC3
human prostate carcinoma cell holoclones contain self-renewing
tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 68:1820–1825. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Jiao M, Li L, et al: Tumorspheres
derived from prostate cancer cells possess chemoresistant and
cancer stem cell properties. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:675–686.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bisson I and Prowse DM: WNT signaling
regulates self-renewal and differentiation of prostate cancer cells
with stem cell characteristics. Cell Res. 19:683–697. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Freitas DP, Teixeira CA, Santos-Silva F,
et al: Therapy-induced enrichment of putative lung cancer stem-like
cells. Int J Cancer. 134:1270–1278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ratajczak M, Tarnowski M, Staniszewska M,
et al: Mechanisms of cancer metastasis: involvement of cancer stem
cells? Minerva Med. 101:179–191. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Rycaj K, Liu X, et al: New
insights into prostate cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle. 12:579–586.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Miki J: Investigations of prostate
epithelial stem cells and prostate cancer stem cells. Int J Urol.
17:139–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Huang X, Zheng X, et al:
Enrichment of prostate cancer stem-like cells from human prostate
cancer cell lines by culture in serum-free medium and
chemoradiotherapy. Int J Biol Sci. 9:472–479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Garraway IP, Sun W, Tran CP, et al: Human
prostate sphere-forming cells represent a subset of basal
epithelial cells capable of glandular regeneration in vivo.
Prostate. 70:491–501. 2010.
|
|
36
|
Sutton LM, Han JS, Molberg KH, et al:
Intratumoral expression level of epidermal growth factor receptor
and cytokeratin 5/6 is significantly associated with nodal and
distant metastases in patients with basal-like triple-negative
breast carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 134:782–787. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
de Silva Rudland S, Platt-Higgins A,
Winstanley JH, et al: Statistical association of basal cell
keratins with metastasis-inducing proteins in a prognostically
unfavorable group of sporadic breast cancers. Am J Pathol.
179:1061–1072. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Celia-Terrassa T, Meca-Cortes O, Mateo F,
et al: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition can suppress major
attributes of human epithelial tumor-initiating cells. J Clin
Invest. 122:1849–1868. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun-Davis T,
Schneider-Broussard R, et al: Hierarchical organization of prostate
cancer cells in xenograft tumors: the
CD44+alpha2beta1+cell population is enriched
in tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 67:6796–6805. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun T,
Schneider-Broussard R, et al: Highly purified
CD44+prostate cancer cells from xenograft human tumors
are enriched in tumorigenic and metastatic progenitor cells.
Oncogene. 25:1696–1708. 2006.
|
|
41
|
Kee N, Sivalingam S, Boonstra R, et al:
The utility of Ki-67 and BrdU as proliferative markers of adult
neurogenesis. J Neurosci Methods. 115:97–105. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Coltrera MD and Gown AM: PCNA/cyclin
expression and BrdU uptake define different subpopulations in
different cell lines. J Histochem Cytochem. 39:23–30. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Staszkiewicz J, Gimble J, Cain C, et al:
Flow cytometric and immunohistochemical detection of in vivo
BrdU-labeled cells in mouse fat depots. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
378:539–544. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|