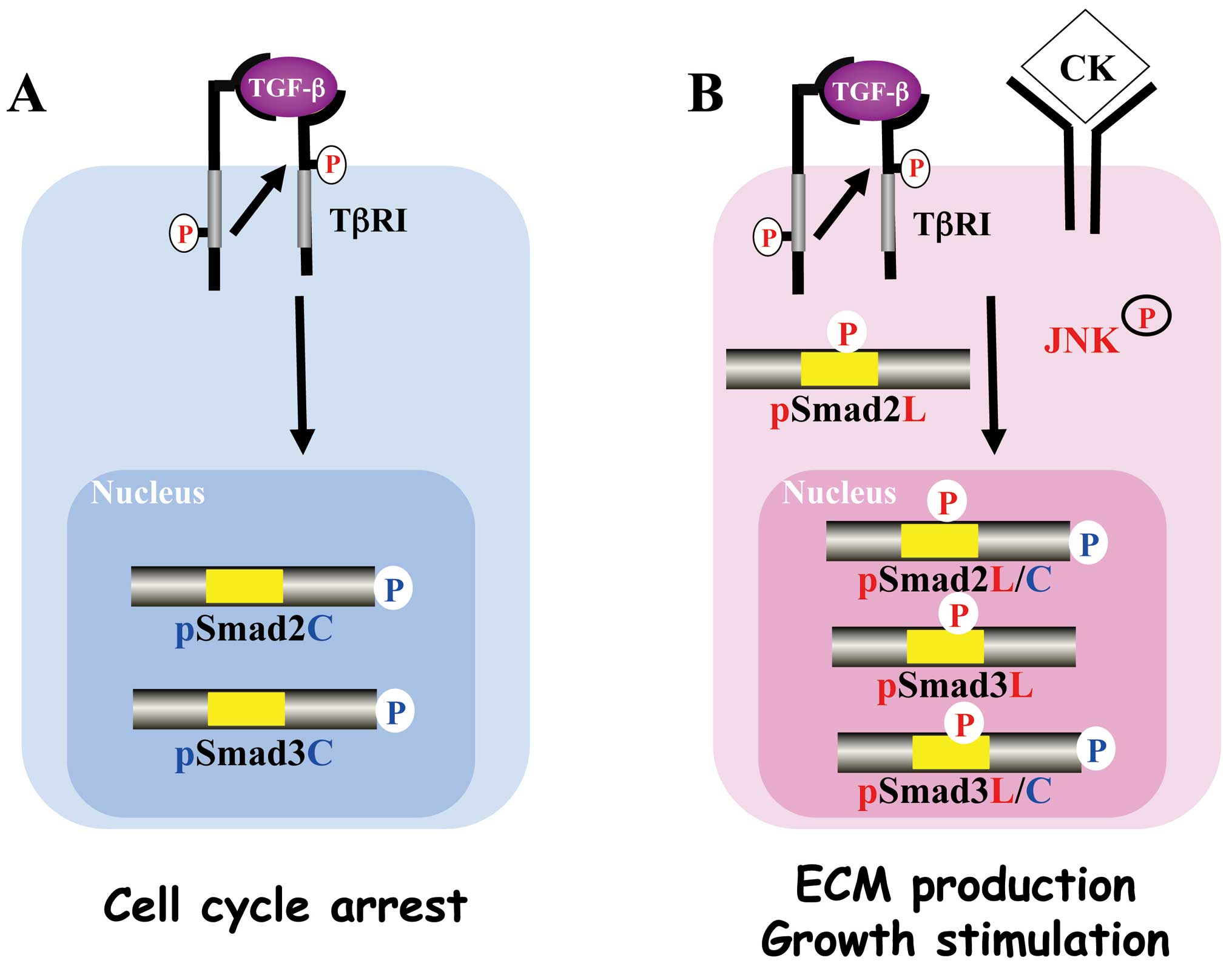
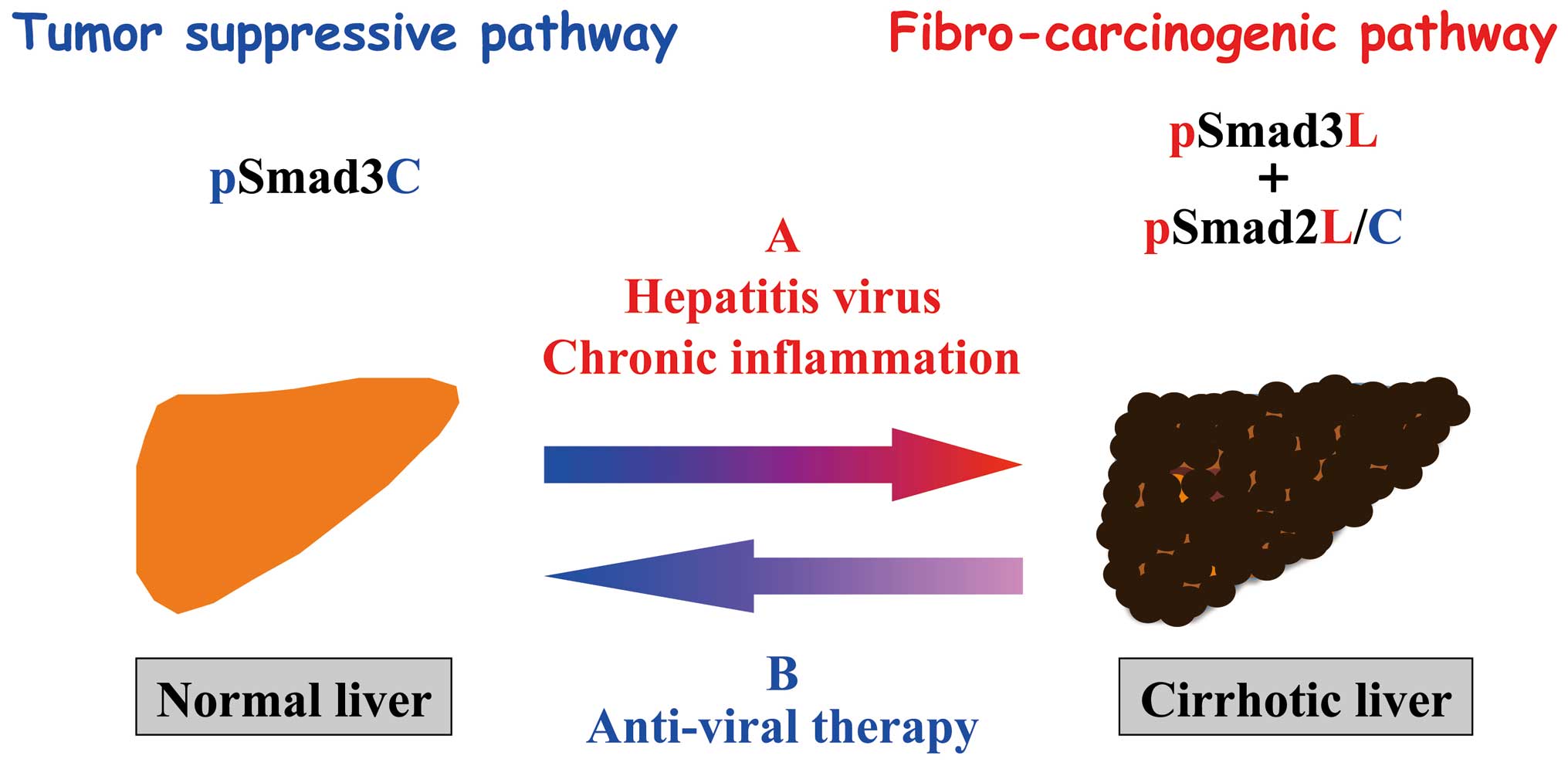
|
1
|
Dooley S and Ten Dijke P: TGF-beta in
progression of liver disease. Cell Tissue Res. 347:245–256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pinzani M and Macias-Barragan J: Update on
the pathophysiology of liver fibrosis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 4:459–472. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Date M, Matsuzaki K, Matsushita M, et al:
Differential expression of transforming growth factor-beta and its
receptors in hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells of rat liver
after CCl4 administration. J Hepatol. 28:572–581. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Date M, Matsuzaki K, Matsushita M, Tahashi
Y, Furukawa F and Inoue K: Modulation of transforming growth factor
beta function in hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells in rat
liver injury. Gut. 46:719–724. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kisseleva T and Brenner DA: Mechanisms of
fibrogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 233:109–122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Moses HL and Serra R: Regulation of
differentiation by TGF-beta. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 6:581–586. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roberts AB and Sporn MB: The transforming
growth factor-βs. Peptide Growth Factors and Their Receptors I
Berlin: Springer; pp. 419–472. 1990
|
|
8
|
Bellam N and Pasche B: Tgf-beta signaling
alterations and colon cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 155:85–103. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matsuzaki K: Smad phosphoisoform signaling
specificity: the right place at the right time. Carcinogenesis.
32:1578–1588. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsuzaki K: Smad phosphoisoform signals
in acute and chronic liver injury: similarities and differences
between epithelial and mesenchymal cells. Cell Tissue Res.
347:225–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Derynck R and Miyazono K: The TGF-β
Signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; NY: 2008
|
|
12
|
Shi Y and Massague J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J, Timokhina I and
Massague J: A mechanism of repression of TGFbeta/Smad signaling by
oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 13:804–816. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsuura I, Denissova NG, Wang G, He D,
Long J and Liu F: Cyclin-dependent kinases regulate the
antiproliferative function of Smads. Nature. 430:226–231. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsuzaki K, Kitano C, Murata M, et al:
Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylated at both linker and COOH-terminal
regions transmit malignant TGF-beta signal in later stages of human
colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5321–5330. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kamaraju AK and Roberts AB: Role of
Rho/ROCK and p38 MAP kinase pathways in transforming growth
factor-beta-mediated Smad-dependent growth inhibition of human
breast carcinoma cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 280:1024–1036. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wicks SJ, Lui S, Abdel-Wahab N, Mason RM
and Chantry A: Inactivation of smad-transforming growth factor beta
signaling by Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:8103–8111. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Furukawa F, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, et al:
p38 MAPK mediates fibrogenic signal through Smad3 phosphorylation
in rat myofibroblasts. Hepatology. 38:879–889. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mori S, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, Furukawa
F, et al: TGF-beta and HGF transmit the signals through
JNK-dependent Smad2/3 phosphorylation at the linker regions.
Oncogene. 23:7416–7429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ho J, Cocolakis E, Dumas VM, Posner BI,
Laporte SA and Lebrun JJ: The G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2
is a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGFbeta signal transduction.
EMBO J. 24:3247–3258. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Millet C, Yamashita M, Heller M, Yu LR,
Veenstra TD and Zhang YE: A negative feedback control of
transforming growth factor-beta signaling by glycogen synthase
kinase 3-mediated Smad3 linker phosphorylation at Ser-204. J Biol
Chem. 284:19808–19816. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alarcon C, Zaromytidou AI, Xi Q, et al:
Nuclear CDKs drive Smad transcriptional activation and turnover in
BMP and TGF-beta pathways. Cell. 139:757–769. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsuzaki K: Smad phospho-isoforms direct
context-dependent TGF-beta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
24:385–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamagata H, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, et al:
Acceleration of Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylation via c-Jun
NH(2)-terminal kinase during human colorectal carcinogenesis.
Cancer Res. 65:157–165. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sekimoto G, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, et al:
Reversible Smad-dependent signaling between tumor suppression and
oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 67:5090–5096. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yoshida K, Matsuzaki K, Mori S, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta and platelet-derived growth factor
signal via c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent Smad2/3
phosphorylation in rat hepatic stellate cells after acute liver
injury. Am J Pathol. 166:1029–1039. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Matsuzaki K, Murata M, Yoshida K, et al:
Chronic inflammation associated with hepatitis C virus infection
perturbs hepatic transforming growth factor beta signaling,
promoting cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
46:48–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Murata M, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, et al:
Hepatitis B virus X protein shifts human hepatic transforming
growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling from tumor suppression to
oncogenesis in early chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 49:1203–1217.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nagata H, Hatano E, Tada M, et al:
Inhibition of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase switches Smad3 signaling
from oncogenesis to tumor-suppression in rat hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:1944–1953. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawamata S, Matsuzaki K, Murata M, et al:
Oncogenic Smad3 signaling induced by chronic inflammation is an
early event in ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:683–695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamaguchi T, Matsuzaki K, Inokuchi R, et
al: Phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3 signaling: Shifting between
tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatol Res. 43:1327–1342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deng YR, Yoshida K, Jin Q, et al:
Reversible phospho-Smad3 signaling between tumor-suppression and
fibro-carcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B infection. Clin Exp
Immunol. 176:102–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heldin CH, Miyazono K and ten Dijke P:
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD
proteins. Nature. 390:465–471. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miyazono K: Positive and negative
regulation of TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Sci. 113:1101–1109.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Moren A, et al:
Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta
signalling. Nature. 389:631–635. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hayashi H, Abdollah S, Qiu Y, et al: The
MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFbeta receptor and
functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell.
89:1165–1173. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Massague J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin X, Duan X, Liang YY, et al: PPM1A
functions as a Smad phosphatase to terminate TGFbeta signaling.
Cell. 125:915–928. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hill CS: Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of
Smad proteins. Cell Res. 19:36–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Piek EJW, Heyer J, Escalante-Alcalde D, et
al: Functional characterization of transforming growth factor beta
signaling in Smad2- and Smad3-deficient fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
276:19945–19953. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang YFX, We R and Derynck R:
Receptor-associated Mad homologues synergize as effectors of the
TGF-beta response. Nature. 383:168–172. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu XSY, Constantinescu SN, Karam E,
Weinberg RA and Lodish HF: Transforming growth factor beta-induced
phosphorylation of Smad3 is required for growth inhibition and
transcriptional induction in epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:10669–10674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Velden JL AJ, Guala AS, Badura EC and
Janssen-Heininger YM: c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 promotes
transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition via control of linker phosphorylation and
transcriptional activity of Smad3. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
44:571–581. 2011.
|
|
45
|
Hirashima YKH, Suzuki M, Tanaka Y,
Kanayama N and Terao T: Transforming growth factor-beta1 produced
by ovarian cancer cell line HRA stimulates attachment and invasion
through an up-regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1
in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
278:26793–26802. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hu PF, Chen H, Zhong W, Lin Y, Zhang X,
Chen YX and Xie WF: Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against
PAI-1 mRNA ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in rats. J Hepatol.
51:102–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu F: Smad3 phosphorylation by
cyclin-dependent kinases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:9–17.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wang G, Matsuura I, He D and Liu F:
Transforming growth factor-{beta}-inducible phosphorylation of
Smad3. J Biol Chem. 284:9663–9673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hayashida T, Decaestecker M and Schnaper
HW: Cross-talk between ERK MAP kinase and Smad signaling pathways
enhances TGF-beta-dependent responses in human mesangial cells.
FASEB J. 17:1576–1578. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang YE: Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta
signaling. Cell Res. 19:128–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Landstrom M: The TAK1-TRAF6 signalling
pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:585–589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sorrentino A, Thakur N, Grimsby S, et al:
The type I TGF-beta receptor engages TRAF6 to activate TAK1 in a
receptor kinase-independent manner. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1199–1207.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yamashita M, Fatyol K, Jin C, Wang X, Liu
Z and Zhang YE: TRAF6 mediates Smad-independent activation of JNK
and p38 by TGF-beta. Mol Cell. 31:918–924. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Seki E, Brenner DA and Karin M: A liver
full of JNK: signaling in regulation of cell function and disease
pathogenesis, and clinical approaches. Gastroenterology.
143:307–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kodama Y, Kisseleva T, Iwaisako K, et al:
c-Jun N-terminal kinase-1 from hematopoietic cells mediates
progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis
in mice. Gastroenterology. 137:1467–1477.e5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hui L, Zatloukal K, Scheuch H, Stepniak E
and Wagner EF: Proliferation of human HCC cells and chemically
induced mouse liver cancers requires JNK1-dependent p21
downregulation. J Clin Invest. 118:3943–3953. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Michalopoulos GK and DeFrances MC: Liver
regeneration. Science. 276:60–66. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Dooley JS, Lok ASF, Burroughs AK and
Heathcote EJ: Sherlock’s Disease of the Liver and Biliary System.
12th edition. Wiley-Blackwell; 2011
|
|
59
|
Tahashi Y, Matsuzaki K, Date M, et al:
Differential regulation of TGF-beta signal in hepatic stellate
cells between acute and chronic rat liver injury. Hepatology.
35:49–61. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yoshida K and Matsuzaki K: Differential
regulation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling in hepatic stellate cells
between acute and chronic liver injuries. Front Physiol. 3:532012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of disease:
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and therapeutic implications. Nat
Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:98–105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Friedman SL: Evolving challenges in
hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:425–436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rockey DC, Housset CN and Friedman SL:
Activation-dependent contractility of rat hepatic lipocytes in
culture and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 92:1795–1804. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Brenner DA, Waterboer T, Choi SK, et al:
New aspects of hepatic fibrosis. J Hepatol. 32:32–38. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Marra F: Chemokines in liver inflammation
and fibrosis. Front Biosci. 7:d1899–d1914. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Reimann T, Hempel U, Krautwald S, Axmann
A, Scheibe R, Seidel D and Wenzel KW: Transforming growth
factor-beta1 induces activation of Ras, Raf-1, MEK and MAPK in rat
hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett. 403:57–60. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pinzani M, Gesualdo L, Sabbah GM and
Abboud HE: Effects of platelet-derived growth factor and other
polypeptide mitogens on DNA synthesis and growth of cultured rat
liver fat-storing cells. J Clin Invest. 84:1786–1793. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rockey DC, Fouassier L, Chung JJ, Carayon
A, Vallee P, Rey C and Housset C: Cellular localization of
endothelin-1 and increased production in liver injury in the rat:
potential for autocrine and paracrine effects on stellate cells.
Hepatology. 27:472–480. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Marra F, Arrighi MC, Fazi M, et al:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation differentially
regulates platelet-derived growth factor’s actions in hepatic
stellate cells, and is induced by in vivo liver injury in the rat.
Hepatology. 30:951–958. 1999.
|
|
71
|
Nouchi T, Tanaka Y, Tsukada T, Sato C and
Marumo F: Appearance of alpha-smooth-muscle-actin-positive cells in
hepatic fibrosis. Liver. 11:100–105. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Schmitt-Graff A, Kruger S, Bochard F,
Gabbiani G and Denk H: Modulation of alpha smooth muscle actin and
desmin expression in perisinusoidal cells of normal and diseased
human livers. Am J Pathol. 138:1233–1242. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pinzani M, Milani S, Herbst H, et al:
Expression of platelet-derived growth factor and its receptors in
normal human liver and during active hepatic fibrogenesis. Am J
Pathol. 148:785–800. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dooley S, Delvoux B, Lahme B,
Mangasser-Stephan K and Gressner AM: Modulation of transforming
growth factor beta response and signaling during
transdifferentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells to
myofibroblasts. Hepatology. 31:1094–1106. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Stopa M, Anhuf D, Terstegen L, Gatsios P,
Gressner AM and Dooley S: Participation of Smad2, Smad3, and Smad4
in transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-induced activation of
Smad7. THE TGF-beta response element of the promoter requires
functional Smad binding element and E-box sequences for
transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 275:29308–29317. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Breitkopf K, et al:
Smad7 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver
fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology. 125:178–191. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Weng HL, Liu Y, Chen JL, et al: The
etiology of liver damage imparts cytokines transforming growth
factor beta1 or interleukin- 13 as driving forces in fibrogenesis.
Hepatology. 50:230–243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Parkin DM, Pisani P and Ferlay J: Global
cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin. 49:33–64. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J and Borras J:
Epidemiology of primary liver cancer. Semin Liver Dis. 19:271–285.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Shiraha H, Yamamoto K and Namba M: Human
hepatocyte carcinogenesis (Review). Int J Oncol. 42:1133–1138.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jiang Z, Jhunjhunwala S, Liu J, et al: The
effects of hepatitis B virus integration into the genomes of
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Genome Res. 22:593–601. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Brechot C, Pourcel C, Louise A, Rain B and
Tiollais P: Presence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences
in cellular DNA of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature.
286:533–535. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Shafritz DA, Shouval D, Sherman HI,
Hadziyannis SJ and Kew MC: Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA
into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver disease and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies
and post-mortem tissue specimens. N Engl J Med. 305:1067–1073.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Bonilla Guerrero R and Roberts LR: The
role of hepatitis B virus integrations in the pathogenesis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 42:760–777. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Feitelson MA and Lee J: Hepatitis B virus
integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
252:157–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Terradillos O, Billet O, Renard CA, Levy
R, Molina T, Briand P and Buendia MA: The hepatitis B virus X gene
potentiates c-myc-induced liver oncogenesis in transgenic mice.
Oncogene. 14:395–404. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Feitelson MA: c-myc overexpression in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Hum Pathol. 35:1299–1302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hayashi J, Aoki H, Kajino K, Moriyama M,
Arakawa Y and Hino O: Hepatitis C virus core protein activates the
MAPK/ERK cascade synergistically with tumor promoter TPA, but not
with epidermal growth factor or transforming growth factor alpha.
Hepatology. 32:958–961. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Erhardt A, Hassan M, Heintges T and
Haussinger D: Hepatitis C virus core protein induces cell
proliferation and activates ERK, JNK, and p38 MAP kinases together
with the MAP kinase phosphatase MKP-1 in a HepG2 Tet-Off cell line.
Virology. 292:272–284. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
He Y, Nakao H, Tan SL, et al: Subversion
of cell signaling pathways by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A
protein via interaction with Grb2 and P85 phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase. J Virol. 76:9207–9217. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Qadri I, Iwahashi M, Capasso JM, Hopken
MW, Flores S, Schaack J and Simon FR: Induced oxidative stress and
activated expression of manganese superoxide dismutase during
hepatitis C virus replication: role of JNK, p38 MAPK and AP-1.
Biochem J. 378:919–928. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhao LJ, Wang L, Ren H, Cao J, Li L, Ke JS
and Qi ZT: Hepatitis C virus E2 protein promotes human hepatoma
cell proliferation through the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway via
cellular receptors. Exp Cell Res. 305:23–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Hassan M, Ghozlan H and Abdel-Kader O:
Activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway is
essential for the stimulation of hepatitis C virus (HCV)
non-structural protein 3 (NS3)-mediated cell growth. Virology.
333:324–336. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Choi SH and Hwang SB: Modulation of the
transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction pathway by
hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein. J Biol Chem.
281:7468–7478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hassan M, Selimovic D, Ghozlan H and
Abdel-Kader O: Hepatitis C virus core protein triggers hepatic
angiogenesis by a mechanism including multiple pathways.
Hepatology. 49:1469–1482. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Park KJ, Choi SH, Choi DH, Park JM, Yie
SW, Lee SY and Hwang SB: Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein modulates
c-Jun N-terminal kinase through interaction with tumor necrosis
factor receptor-associated factor 2. J Biol Chem. 278:30711–30718.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lin W, Tsai WL, Shao RX, Wu G, Peng LF,
Barlow LL, Chung WJ, et al: Hepatitis C virus regulates
transforming growth factor beta1 production through the generation
of reactive oxygen species in a nuclear factor kappaB-dependent
manner. Gastroenterology. 138:2509–2518. 2518.e12010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Moriya K, Yotsuyanagi H, Shintani Y, Fujie
H, Ishibashi K, Matsuura Y, Miyamura T, et al: Hepatitis C virus
core protein induces hepatic steatosis in transgenic mice. J Gen
Virol. 78:1527–1531. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Moriya K, Fujie H, Shintani Y, Yotsuyanagi
H, Tsutsumi T, Ishibashi K, Matsuura Y, et al: The core protein of
hepatitis C virus induces hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic
mice. Nat Med. 4:1065–1067. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lerat H, Honda M, Beard MR, Loesch K, Sun
J, Yang Y, Okuda M, et al: Steatosis and liver cancer in transgenic
mice expressing the structural and nonstructural proteins of
hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology. 122:352–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Dzieran J, Fabian J, Feng T, et al:
Comparative analysis of TGF-beta/Smad signaling dependent
cytostasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. PLoS One.
8:e722522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Dienstag JL, Schiff ER, Wright TL, et al:
Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the
United States. N Engl J Med. 341:1256–1263. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, et al:
Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e
antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 348:808–816.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chang TT, Gish RG, de Man R, et al: A
comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic
hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 354:1001–1010. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Lai CL, Gane E, Liaw YF, et al:
Telbivudine versus lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
N Engl J Med. 357:2576–2588. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Khakoo S, Glue P, Grellier L, et al:
Ribavirin and interferon alfa-2b in chronic hepatitis C: assessment
of possible pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions. Br J
Clin Pharmacol. 46:563–570. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Shiratori Y, Imazeki F, Moriyama M, et al:
Histologic improvement of fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C who
have sustained response to interferon therapy. Ann Intern Med.
132:517–524. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Morgan TR, Ghany MG, Kim HY, et al:
Outcome of sustained virological responders with histologically
advanced chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 52:833–844. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yoshida H, Shiratori Y, Moriyama M, et al:
Interferon therapy reduces the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma:
national surveillance program of cirrhotic and noncirrhotic
patients with chronic hepatitis C in Japan. IHIT Study Group.
Inhibition of Hepatocarcinogenesis by Interferon Therapy. Ann
Intern Med. 131:174–181. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Suzuki Y, Kumada H, Ikeda K, et al:
Histological changes in liver biopsies after one year of lamivudine
treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. J
Hepatol. 30:743–748. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|