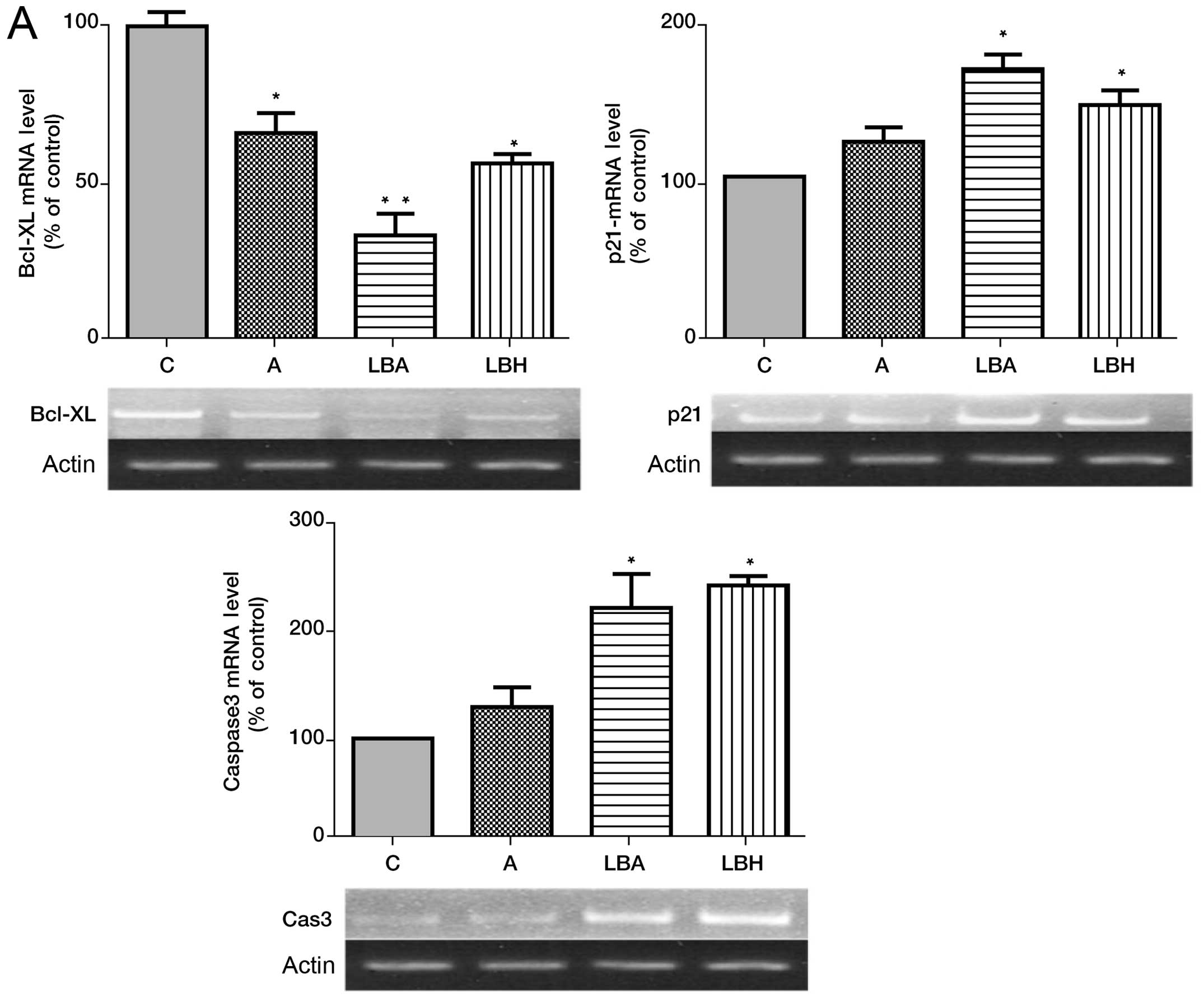
|
1
|
Feinberg AP and Tycko B: The history of
cancer epigenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:143–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bolden JE, Peart MJ and Johnstone RW:
Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 5:769–784. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cameron EE, Bachman KE, Myohanen S, Herman
JG and Baylin SB: Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase
inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat
Genet. 21:103–107. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gore SD, Baylin S and Sugar E: Combined
DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibition in the
treatment of myeloid neoplasms. Cancer Res. 66:6361–6369. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Griffiths EA and Gore SD: DNA
methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors in the
treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Hematol. 45:23–30.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang H, Hoshino K, Sanchez-Gonzalez B,
Kantarjian H and Garcia-Manero G: Antileukemia activity of the
combination of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine with valproic acid. Leuk Res.
29:739–748. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shaker S, Bernstein M, Momparler LF and
Momparler RL: Preclinical evaluation of antineoplastic activity of
inhibitors of DNA methylation (5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine) and histone
deacetylation (trichostatin A, depsipeptide) in combination against
myeloid leukemic cells. Leuk Res. 27:437–444. 2003.
|
|
8
|
Liu HB, Mayes PA, Perlmutter P, McKendrick
JJ and Dear AE: The anti-leukemic effect and molecular mechanisms
of novel hydroxamate and benzamide histone deacetylase inhibitors
with 5-aza-cytidine. Int J Oncol. 38:1421–1425. 2011.
|
|
9
|
Shen L, Kantarjian H, Guo Y, Lin E, Shan
J, Huang X, Berry D, Ahmed S, Zhu W, Pierce S, Kondo Y, Oki Y,
Jelinek J, Saba H, Estey E and Issa JP: DNA methylation predicts
survival and response to therapy in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 28:605–613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fandy TE, Herman JG, Kerns P, Jiemjit A,
Sugar EA, Choi SH, Yang AS, Aucott T, Dauses T, Odchimar-Reissig R,
Licht J, McConnell MJ, Nasrallah C, Kim MK, Zhang W, Sun Y, Murgo
A, Espinoza-Delgado I, Oteiza K, Owoeye I, Silverman LR, Gore SD
and Carraway HE: Early epigenetic changes and DNA damage do not
predict clinical response in an overlapping schedule of
5-azacytidine and entinostat in patients with myeloid malignancies.
Blood. 114:2764–2773. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Prince HM, Bishton MJ and Harrison SJ:
Clinical studies of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:3958–3969. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lane AA and Chabner BA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
27:5459–5468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu HB, Voso MT, Gumiero D, Duong J,
McKendrick JJ and Dear AE: The anti-leukemic effect of a novel
histone deacetylase inhibitor MCT-1 and 5-aza-cytidine involves
augmentation of Nur77 and inhibition of MMP-9 expression. Int J
Oncol. 34:573–579. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan P, Wei A, Mithraprabhu S, Cummings N,
Liu H, Perugini M, Reed K, Avery S, Patil S, Walker P, Mollee P,
Grigg A, D’Andrea R, Dear A and Spencer A: Dual epigenetic
targeting with panobinostat and azacitidine in acute myeloid
leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood Cancer J.
4:e1702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheson BD, Greenberg PL, Bennett JM, et
al: Clinical application and proposal for modification of the
International Working Group (IWG) response criteria in
myelodysplasia. Blood. 108:419–425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mullican SE, Zhang S, Konopleva M, Ruvolo
V, Andreeff M, Millbrant J and Conneely OM: Abrogation of nuclear
receptors Nr4a3 and Nr4a1 leads to development of acute myeloid
leukemia. Nat Med. 13:730–735. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E,
et al: Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of conventional
care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk myelodysplastic
syndromes: a randomised, open-label, phase III study. Lancet Oncol.
10:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tan PT and Wei AH: The epigenomics
revolution in myelodysplasia: a clinico-pathological perspective.
Pathology. 243:536–546. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matthews GM, Lefebure M, Doyle MA, Shortt
J, Ellul J, Chesi M, Banks KM, Vidacs E, Faulkner D, Atadja P,
Bergsagel PL and Johnstone RW: Preclinical screening of histone
deacetylase inhibitors combined with ABT-737, rhTRAIL/MD5-1 or
5-azacytidine using syngeneic Vk*MYC multiple myeloma. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e7982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giles F, Fischer T, Cortes J,
Garcia-Manero G, Beck J, Ravandi F, Masson E, Rae P, Laird G,
Sharma S, Kantarjian H, Dugan M, Albitar M and Bhalla K: A phase 1
study of intravenous LBH589, a novel cinnamic hydroxamic acid
analogue histone deacetylase inhibitor, in patients with refractory
hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4628–4635. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xiao Y, Wang J, Song H, Zou P, Zhou D and
Liu L: CD34+ cells from patients with myelodysplastic
syndrome present different p21 dependent premature senescence. Leuk
Res. 37:333–340. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Link PA, Baer MR, James SR, Jones DA and
Karpf AR: p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase (p53R2/RRM2B) is a
DNA hypomethylation-independent decitabine gene target that
correlates with clinical response in myelodysplastic syndrome/acute
myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 68:9358–9366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhou L, Ruvolo VR, McQueen T, Chen W,
Samudio IJ, Conneely O, Konopleva M and Andreeff M: HDAC inhibition
by SNDX-275 (Entinostat) restores expression of silenced
leukemia-associated transcription factors Nur77 and Nor1 and of key
pro-apoptotic proteins in AML. Leukemia. 27:1358–1368. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sonnemann J, Hartwig M, Plath A, Saravana
Kumar K, Muller C and Beck JF: Histone deacetylase inhibitors
require caspase activity to induce apoptosis in lung and prostate
carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 232:148–160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ekert PG and Vaux DL: The mitochondrial
death squad: hardened killers or innocent bystanders? Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 17:626–630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin B, Kolluri SK, Lin F, Liu W, Han YH,
Cao X, Dawson MI, Reed JC and Zhang XK: Conversion of Bcl-2 from
protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor
Nur77/TR3. Cell. 116:527–540. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Uchida T, Kinoshita T, Nagai H, Nakahara
Y, Saito H, Hotta T and Murate T: Hypermethylation of the
p15INK4B gene in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood.
90:1403–1409. 1997.
|
|
28
|
Daskalakis M, Nguyen TT, Nguyen C,
Guldberg P, Kohler G, Wijermans P, Jones PA and Lübbert M:
Demethylation of a hypermethylated P15/INK4B gene in patients with
myelodysplastic syndrome by 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine)
treatment. Blood. 100:2957–2964. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hitomi T, Matsuzaki Y, Yokota T, Takaoka Y
and Sakai T: p15(INK4B) in HDAC inhibitor-induced growth arrest.
FEBS Lett. 554:347–350. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Soriano AO, Yang H, Faderl S, Estrov Z,
Giles F, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Wierda WG, Ouzounian S, Quezada A,
Pierce S, Estey EH, Issa JP, Kantarjian HM and Garcia-Manero G:
Safety and clinical activity of the combination of 5-azacytidine,
valproic acid, and all-trans retinoic acid in acute myeloid
leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 110:2302–2308. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian HM,
Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Yang H, Rosner G, Verstovsek S, Rytting M,
Wierda WG, Ravandi F, Koller C, Xiao L, Faderl S, Estrov Z, Cortes
J, O’brien S, Estey E, Bueso-Ramos C, Fiorentino J, Jabbour E and
Issa JP: Phase 1/2 study of the combination of
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine with valproic acid in patients with
leukemia. Blood. 108:3271–3279. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|