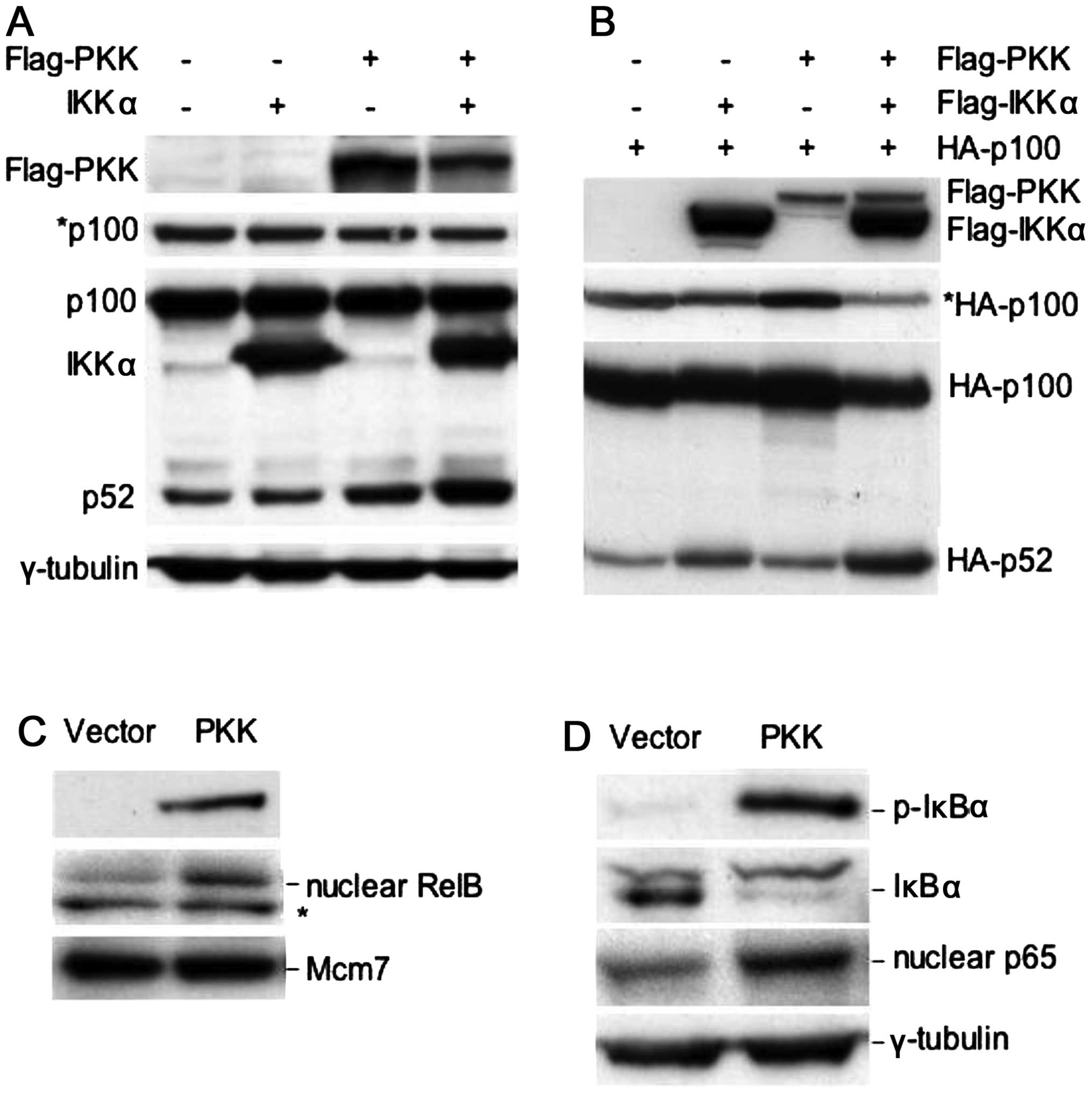
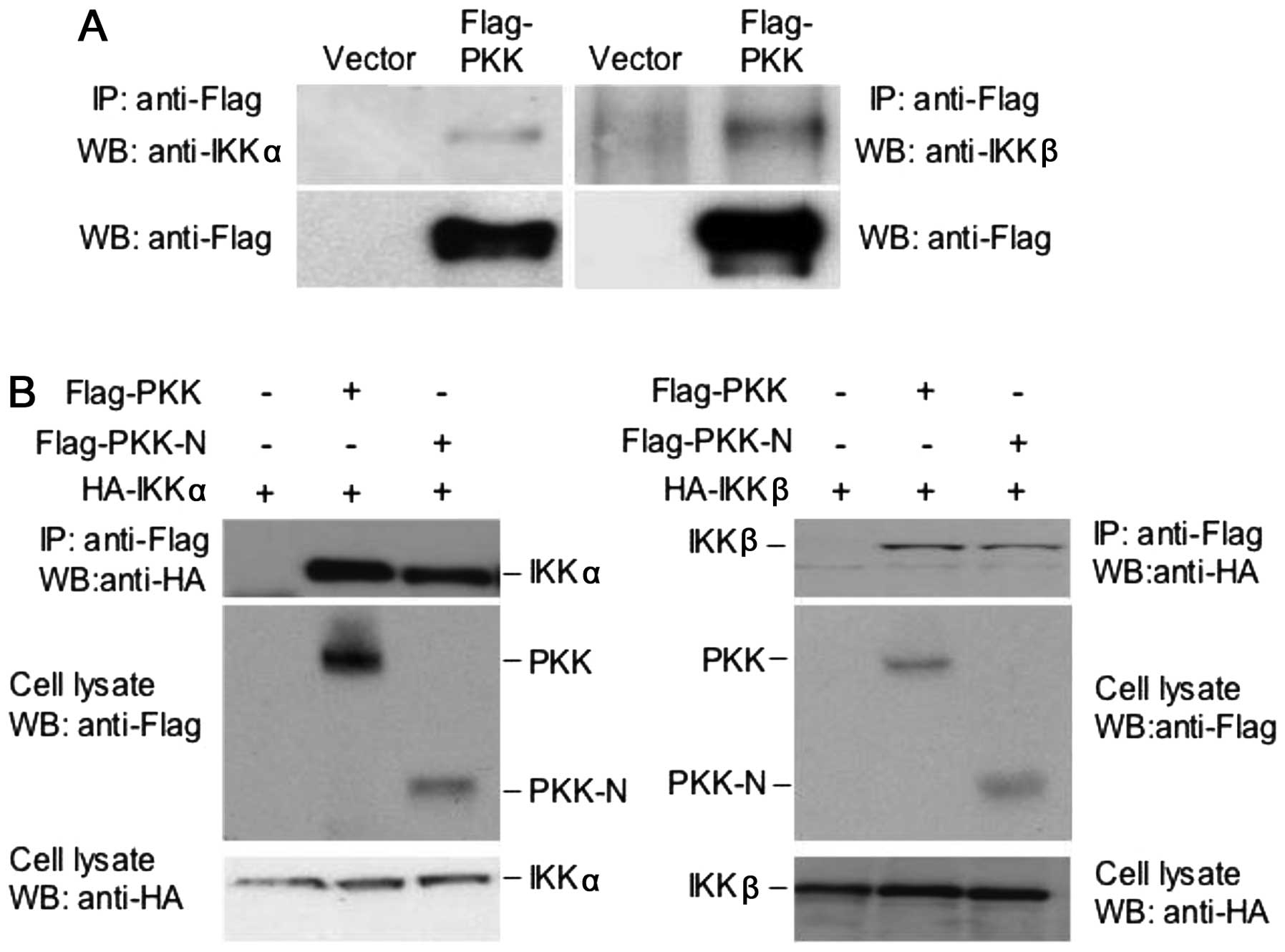
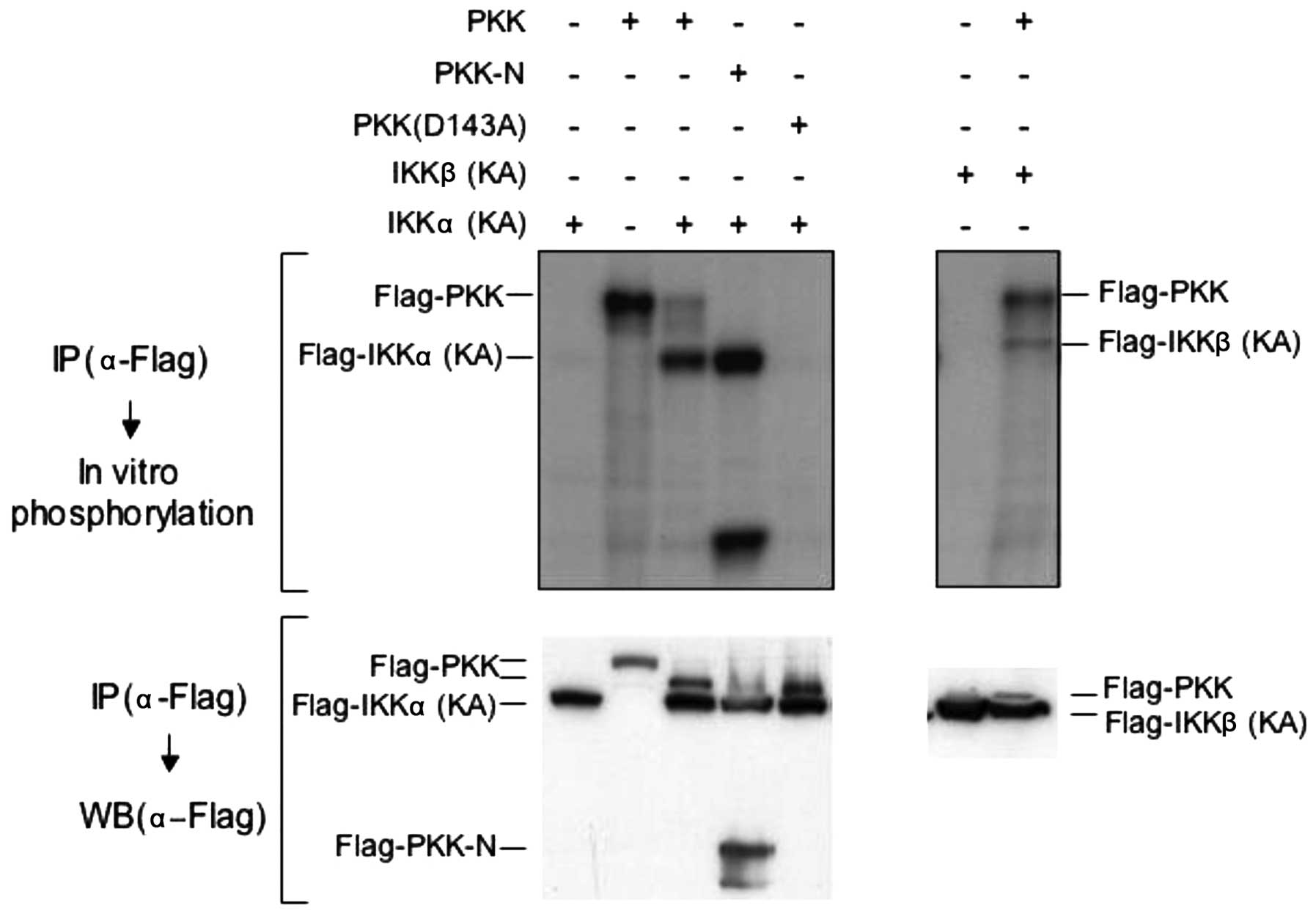
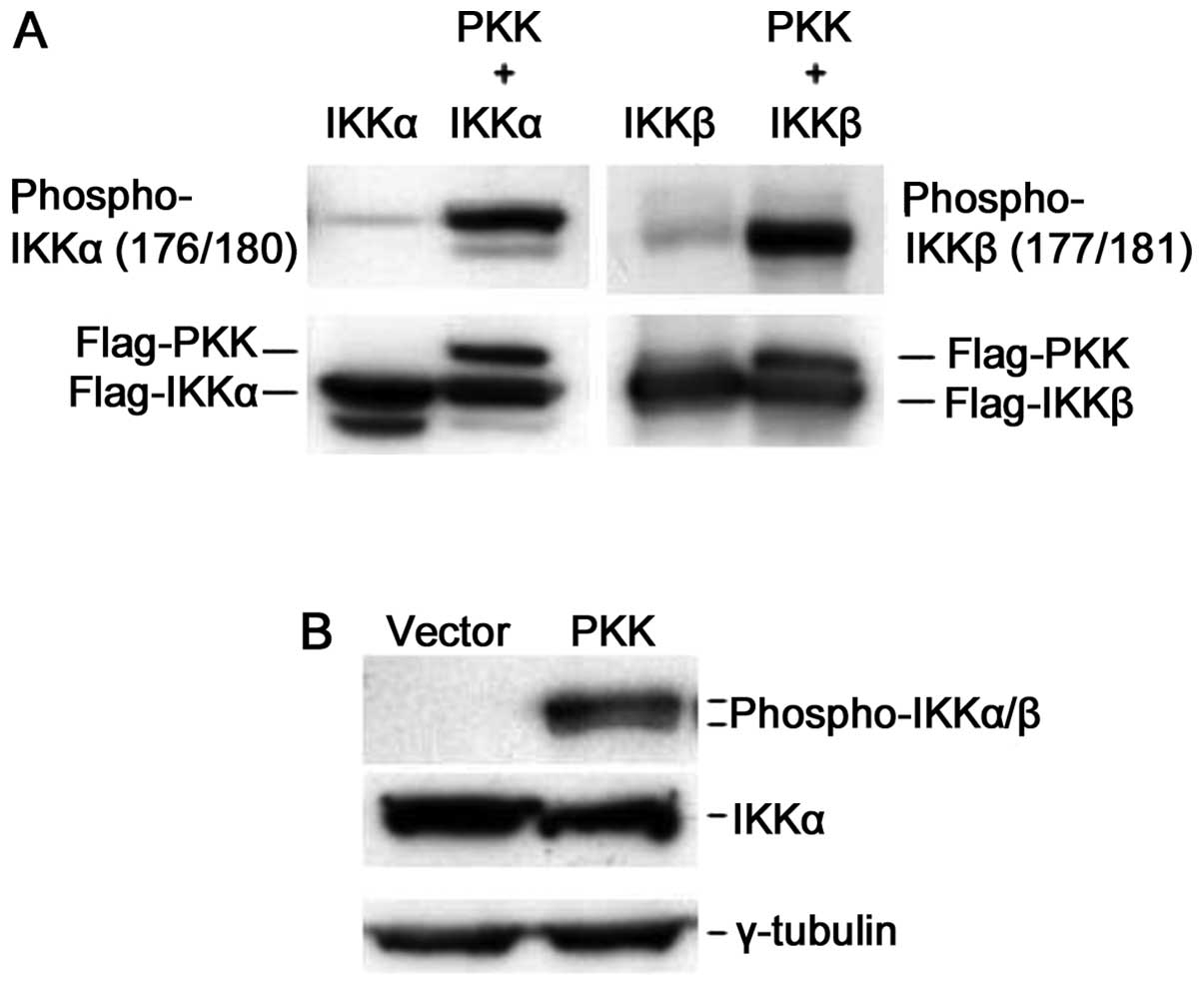
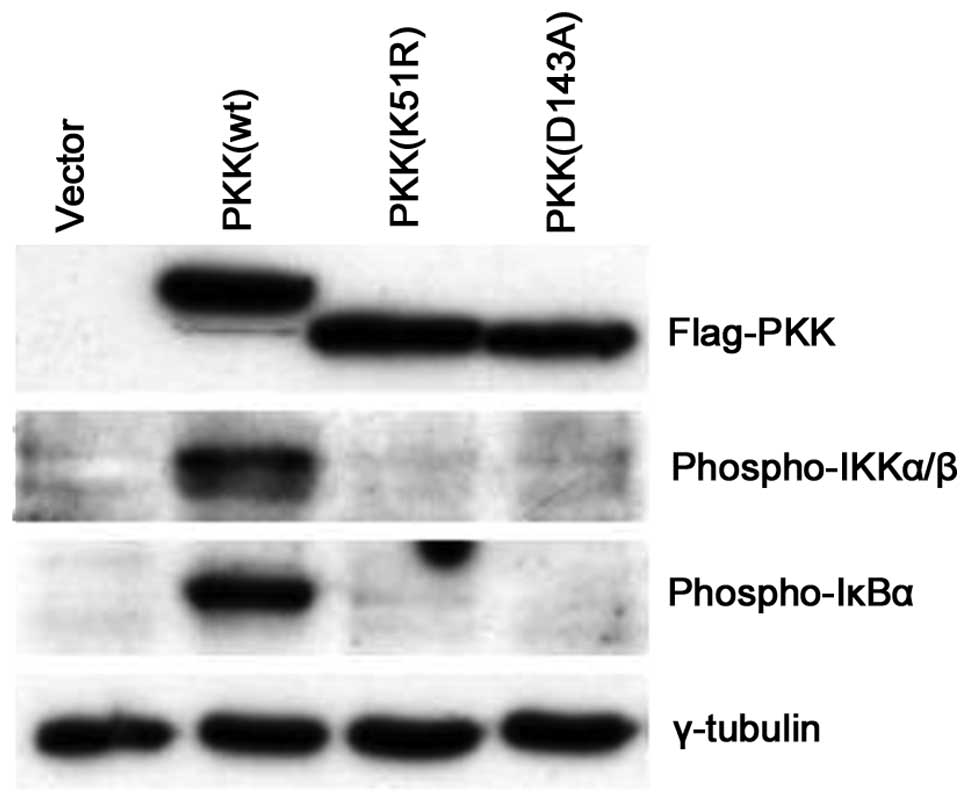
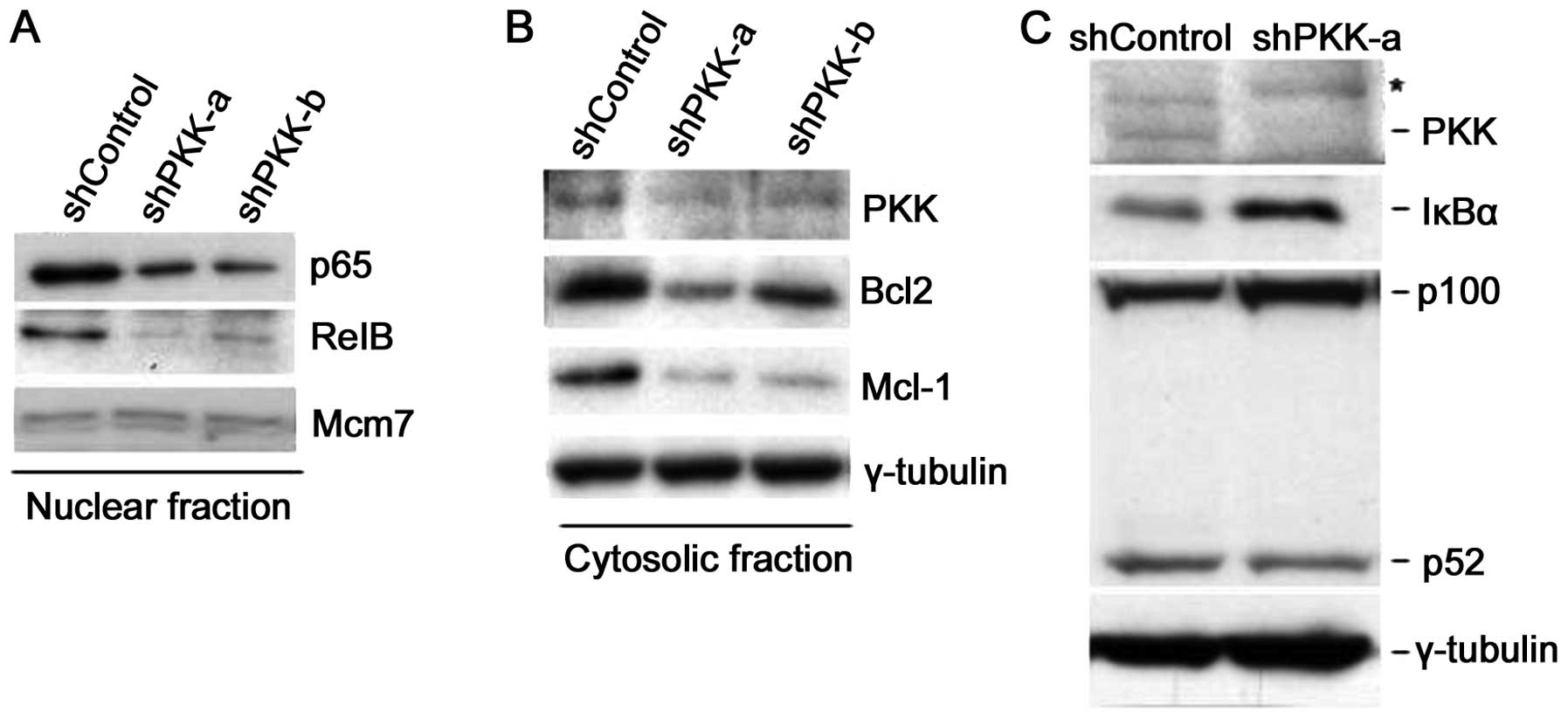
|
1
|
Schreiber J, Jenner RG, Murray HL, Gerber
GK, Gifford DK and Young RA: Coordinated binding of NF-kappaB
family members in the response of human cells to
lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:5899–5904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bonizz G and Karin M: The two NF-kappaB
activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity.
Trends Immunol. 25:280–288. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappaB: the
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: IkappaB kinases:
key regulators of the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends Biochem Sci.
29:72–79. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ling L, Cao Z and Goeddel DV:
NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activates IKK-alpha by phosphorylation of
Ser-176. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:3792–3797. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu Y, Baud V, Oga T, Kim KI, Yoshida K and
Karin M: IKKalpha controls formation of the epidermis independently
of NF-kappaB. Nature. 410:710–714. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Delhase M, Hayakawa M, Chen Y and Karin M:
Positive and negative regulation of IkappaB kinase activity through
IKKbeta subunit phosphorylation. Science. 284:309–313. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bahr C, Rohwer A, Stempka L, Rincke G,
Marks F and Gschwendt M: DIK, a novel protein kinase that interacts
with protein kinase Cdelta. Cloning, characterization, and gene
analysis. J Biol Chem. 275:36350–36357. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen L, Haider K, Ponda M, Cariappa A,
Rowitch D and Pillai S: Protein kinase C-associated kinase (PKK), a
novel membrane-associated, ankyrin repeat-containing protein
kinase. J Biol Chem. 276:21737–21744. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meylan E and Tschopp J: The RIP kinases:
crucial integrators of cellular stress. Trends Biochem Sci.
30:151–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meylan E, Martinon F, Thome M, Gschwendt M
and Tschopp J: RIP4 (DIK/PKK), a novel member of the RIP kinase
family, activates NF-kappa B and is processed during apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 3:1201–1208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moran ST, Haider K, Ow Y, Milton P, Chen L
and Pillai S: Protein kinase C-associated kinase can activate
NFkappaB in both a kinase-dependent and a kinase-independent
manner. J Biol Chem. 278:21526–21533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Muto A, Ruland J, McAllister-Lucas LM,
Lucas PC, Yamaoka S, Chen FF, Lin A, Mak TW, Nunez G and Inohara N:
Protein kinase C-associated kinase (PKK) mediates Bcl10-independent
NF-kappa B activation induced by phorbol ester. J Biol Chem.
277:31871–31876. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Woronicz JD, Gao X, Cao Z, Rothe M and
Goeddel DV: IkappaB kinase-beta: NF-kappaB activation and complex
formation with IkappaB kinase-alpha and NIK. Science. 278:866–869.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao J, Dynlacht B, Imai T, Hori T and
Harlow E: Expression of NPAT, a novel substrate of cyclin E-CDK2,
promotes S-phase entry. Genes Dev. 12:456–461. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hannon GJ and Rossi JJ: Unlocking the
potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature.
431:371–378. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huppi K, Martin SE and Caplen NJ: Defining
and assaying RNAi in mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 17:1–10. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li ZW, Rickert RC and Karin M: Genetic
dissection of antigen receptor induced-NF-kappaB activation. Mol
Immunol. 41:701–714. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shim JH, Xiao C, Paschal AE, Bailey ST,
Rao P, Hayden MS, Lee KY, Bussey C, Steckel M, Tanaka N, Yamada G,
Akira S, Matsumoto K and Ghosh S: TA K1, but not TA B1 or TA B2,
plays an essential role in multiple signaling pathways in vivo.
Genes Dev. 19:2668–2681. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Saijo K, Mecklenbrauker I, Santana A,
Leitger M, Schmed C and Tarakhovsky A: Protein kinase C beta
controls nuclear factor kappaB activation in B cells through
selective regulation of the IkappaB kinase alpha. J Exp Med.
195:1647–1652. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu PW, Huang BC, Shen M, Quast J, Chan E,
Xu X, Nolan GP, Payan DG and Luo Y: Identification of RIP3, a
RIP-like kinase that activates apoptosis and NFkappaB. Curr Biol.
9:539–542. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kasof GM, Prosser JC, Liu D, Lorenzi MV
and Gomes BC: The RIP-like kinase, RIP3, induces apoptosis and
NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and localizes to mitochondria. FEBS
Lett. 473:285–291. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McCarthy JV, Ni J and Dixit VM: RIP2 is a
novel NF-kappaB-activating and cell death-inducing kinase. J Biol
Chem. 273:16968–16975. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kelliher MA, Grimm S, Ishida Y, Kuo F,
Stanger BZ and Leder P: The death domain kinase RIP mediates the
TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity. 8:297–303. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsu H, Huang J, Shu HB, Baichwal V and
Goeddel DV: TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to
the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity. 4:387–396. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cariappa A, Chen L, Haider K, Tang M,
Nebelitskiy E, Moran ST and Pillai S: A catalytically inactive form
of protein kinase C-associated kinase/receptor interacting protein
4, a protein kinase C beta-associated kinase that mediates NF-kappa
B activation, interferes with early B cell development. J Immunol.
171:1875–1880. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Holland P, Willis C, Kanaly S, Glaccum M,
Warren A, Charrier K, Murison J, Derry J, Virca G, Bird T and
Peschon J: RIP4 is an ankyrin repeat-containing kinase essential
for keratinocyte differentiation. Curr Biol. 12:1424–1428. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moran ST, Cariappa A, Liu H, Boboila C,
Shi HN, Holland PM, Peschon JJ and Pillai S: Protein kinase
C-associated kinase is not required for the development of
peripheral B lymphocyte populations. Mol Immunol. 43:1694–1699.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jimi E and Ghosh S: Role of nuclear
factor-kappaB in the immune system and bone. Immunol Rev.
208:80–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim HJ, Hawke N and Baldwin AS: NF-kappaB
and IKK as therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Differ.
13:738–747. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Q, Withoff S and Verma IM:
Inflammation-associated cancer: NF-kappaB is the lynchpin. Trends
Immunol. 26:318–325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim SW, Oleksyn DW, Rossi RM, Jordan CT,
Sanz I, Chen L and Zhao J: Protein kinase C-associated kinase is
required for NF-kappaB signaling and survival in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma cells. Blood. 111:1644–1653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|