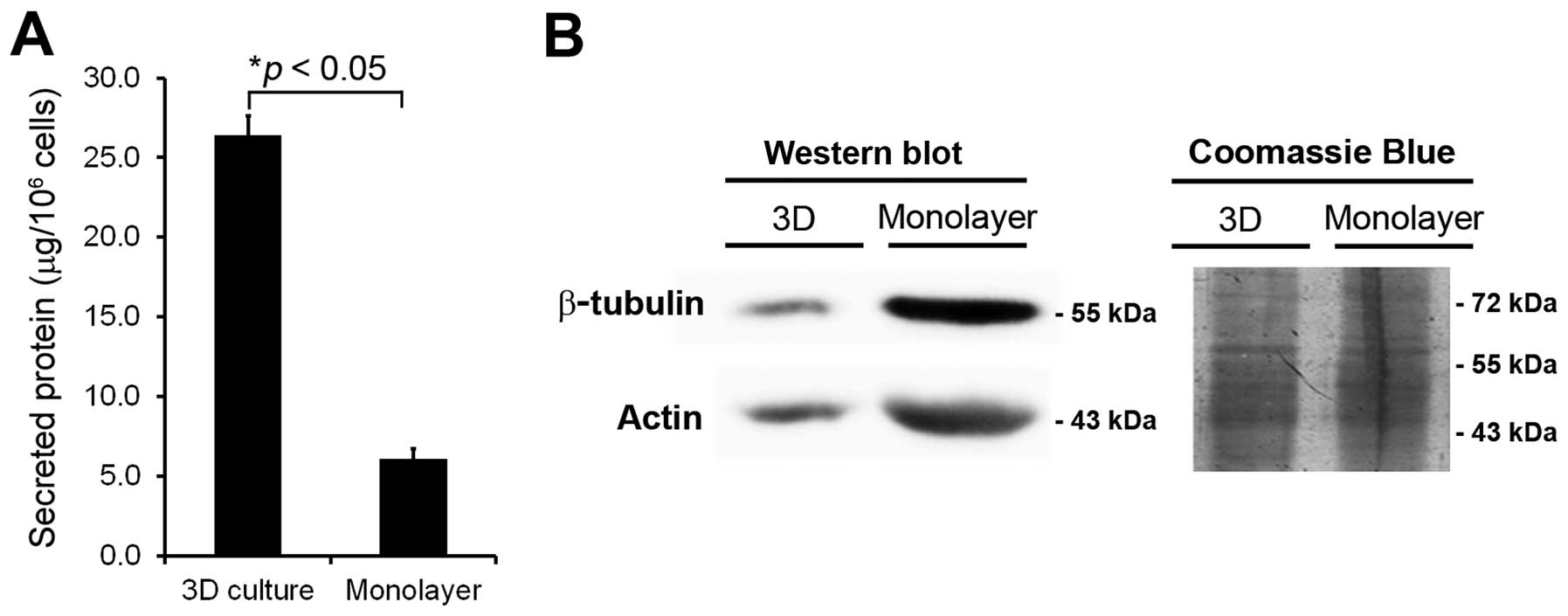
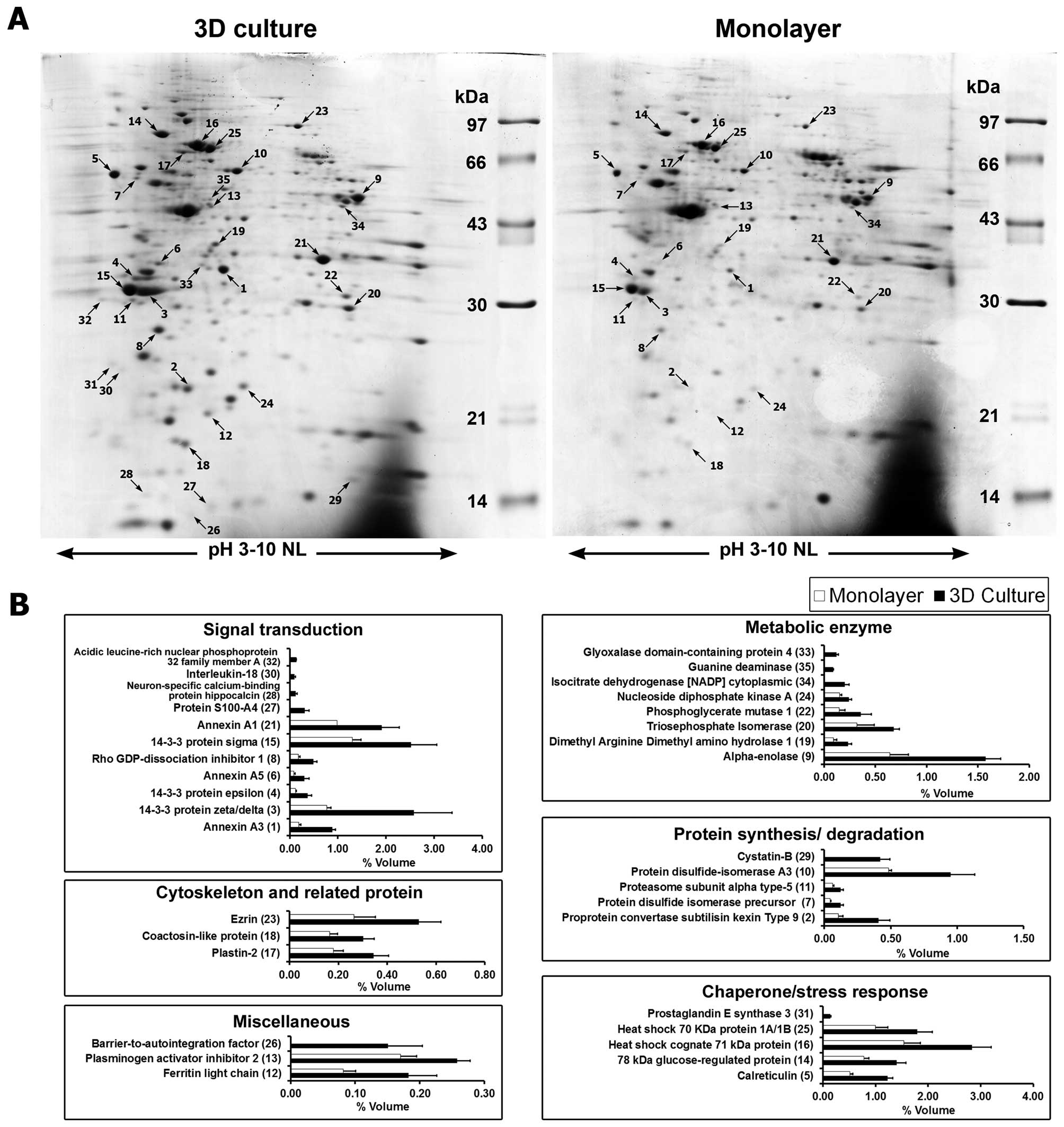
|
1
|
Khan SA, Thomas HC, Davidson BR and
Taylor-Robinson SD: Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 366:1303–1314.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khan SA, Toledano MB and Taylor-Robinson
SD: Epidemiology, risk factors, and pathogenesis of
cholangiocarcinoma. HPB. 10:77–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sripa B, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P, et al:
Liver fluke induces cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS Med. 4:e2012007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leelawat K, Narong S, Wannaprasert J and
Ratanashu-ek T: Prospective study of MMP7 serum levels in the
diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
16:4697–4703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mott JL and Gores GJ: Targeting IL-6 in
cholangiocarcinoma therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 102:2171–2172.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shigehara K, Yokomuro S, Ishibashi O, et
al: Real-time PCR-based analysis of the human bile microRNAome
identifies miR-9 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for biliary
tract cancer. PLoS One. 6:e235842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Makridakis M and Vlahou A: Secretome
proteomics for discovery of cancer biomarkers. J Proteomics.
73:2291–2305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Srisomsap C, Sawangareetrakul P,
Subhasitanont P, et al: Proteomic analysis of cholangiocarcinoma
cell line. Proteomics. 4:1135–1144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Srisomsap C, Sawangareetrakul P,
Subhasitanont P, et al: Proteomic studies of cholangiocarcinoma and
hepatocellular carcinoma cell secretomes. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:4371432010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hutmacher DW, Loessner D, Rizzi S, Kaplan
DL, Mooney DJ and Clements JA: Can tissue engineering concepts
advance tumor biology research? Trends Biotechnol. 28:125–133.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pampaloni F, Reynaud EG and Stelzer EH:
The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live
tissue. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:839–845. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamada KM and Cukierman E: Modeling tissue
morphogenesis and cancer in 3D. Cell. 130:601–610. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weigelt B and Bissell MJ: The need for
complex 3D culture models to unravel novel pathways and identify
accurate biomarkers in breast cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
69–70:42–51. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sirisinha S, Tengchaisri T, Boonpucknavig
S, Prempracha N, Ratanarapee S and Pausawasdi A: Establishment and
characterization of a cholangiocarcinoma cell line from a Thai
patient with intrahepatic bile duct cancer. Asian Pac J Allergy
Immunol. 9:153–157. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Laohathai K and Bhamarapravati N:
Culturing of human hepatocellular carcinoma. A simple and
reproducible method. Am J Pathol. 118:203–208. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weeraphan C, Diskul-Na-Ayudthaya P,
Chiablaem K, et al: Effective enrichment of cholangiocarcinoma
secretomes using the hollow fiber bioreactor culture system.
Talanta. 99:294–301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pruksakorn D, Lirdprapamongkol K,
Chokchaichamnankit D, et al: Metabolic alteration of HepG2 in
scaffold-based 3-D culture: proteomic approach. Proteomics.
10:3896–3904. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khongmanee A, Lirdprapamongkol K, Tit-oon
P, Chokchaichamnankit D, Svasti J and Srisomsap C: Proteomic
analysis reveals important role of 14-3-3sigma in anoikis
resistance of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Proteomics. 13:3157–3166.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cardinale V, Carpino G, Reid L, Gaudio E
and Alvaro D: Multiple cells of origin in cholangiocarcinoma
underlie biological, epidemiological and clinical heterogeneity.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:94–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiarini LB, Takiya CM, Borojevic R and
Monteiro AN: Long-term culture of cholangiocytes from liver
fibro-granulomatous lesions. BMC Gastroenterol. 6:132006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mall AS, Tyler MG, Ho SB, et al: The
expression of MUC mucin in cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
206:805–809. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haeuptle MT, Suard YL, Bogenmann E, Reggio
H, Racine L and Kraehenbuhl JP: Effect of cell shape change on the
function and differentiation of rabbit mammary cells in culture. J
Cell Biol. 96:1425–1434. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Perathoner A, Pirkebner D, Brandacher G,
et al: 14-3-3sigma expression is an independent prognostic
parameter for poor survival in colorectal carcinoma patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:3274–3279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou WH, Tang F, Xu J, et al: Aberrant
upregulation of 14-3-3σ expression serves as an inferior prognostic
biomarker for gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 11:3972011.
|
|
25
|
Santini MT, Rainaldi G, Romano R, et al:
MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells grown in monolayer and as
three-dimensional tumor spheroids present a different metabolic
profile: a (1)H NMR study. FEBS Lett. 557:148–154. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Thongwatchara P, Promwikorn W, Srisomsap
C, Chokchaichamnankit D, Boonyaphiphat P and Thongsuksai P:
Differential protein expression in primary breast cancer and
matched axillary node metastasis. Oncol Rep. 26:185–191.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoshida A, Okamoto N, Tozawa-Ono A, et al:
Proteomic analysis of differential protein expression by brain
metastases of gynecological malignancies. Hum Cell. 26:56–66. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren F, Wu H, Lei Y, et al: Quantitative
proteomics identification of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 as a novel
therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
9:812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yonglitthipagon P, Pairojkul C,
Bhudhisawasdi V, Mulvenna J, Loukas A and Sripa B: Proteomics-based
identification of alphaenolase as a potential prognostic marker in
cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Biochem. 45:827–834. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shinomiya H: Plastin family of
actin-bundling proteins: its functions in leukocytes, neurons,
intestines, and cancer. Int J Cell Biol. 2012:2134922012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kang S, Shim HS, Lee JS, et al: Molecular
proteomics imaging of tumor interfaces by mass spectrometry. J
Proteome Res. 9:1157–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ang CS and Nice EC: Targeted in-gel MRM: a
hypothesis driven approach for colorectal cancer biomarker
discovery in human feces. J Proteome Res. 9:4346–4355. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin CS, Park T, Chen ZP and Leavitt J:
Human plastin genes. Comparative gene structure, chromosome
location, and differential expression in normal and neoplastic
cells. J Biol Chem. 268:2781–2792. 1993.
|
|
34
|
Park T, Chen ZP and Leavitt J: Activation
of the leukocyte plastin gene occurs in most human cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 54:1775–1781. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saenz-Lopez P, Carretero R, Vazquez F, et
al: Impact of interleukin-18 polymorphisms-607 and -137 on clinical
characteristics of renal cell carcinoma patients. Hum Immunol.
71:309–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tangkijvanich P, Thong-Ngam D, Mahachai V,
Theamboonlers A and Poovorawan Y: Role of serum interleukin-18 as a
prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World
J Gastroenterol. 13:4345–4349. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|