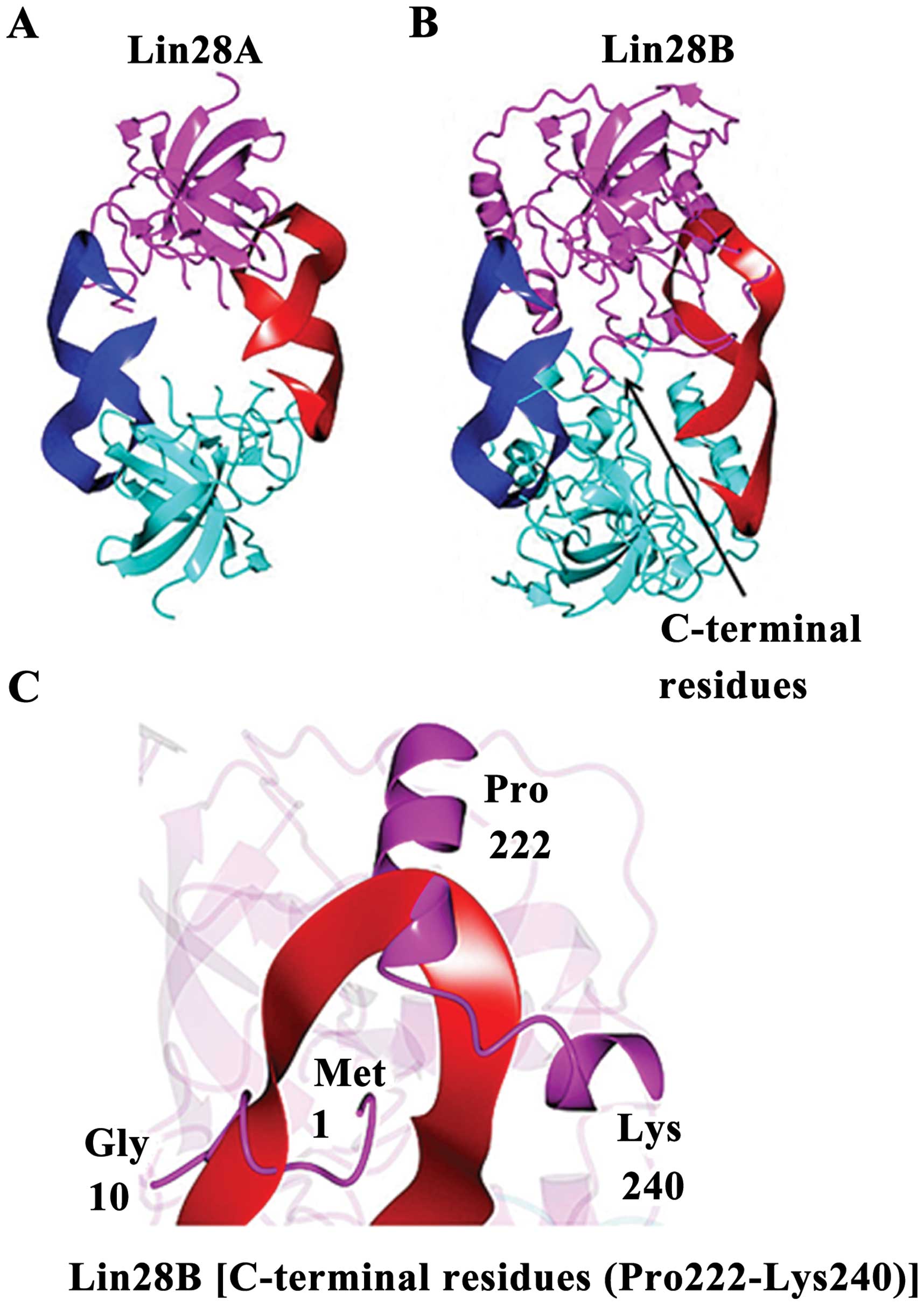
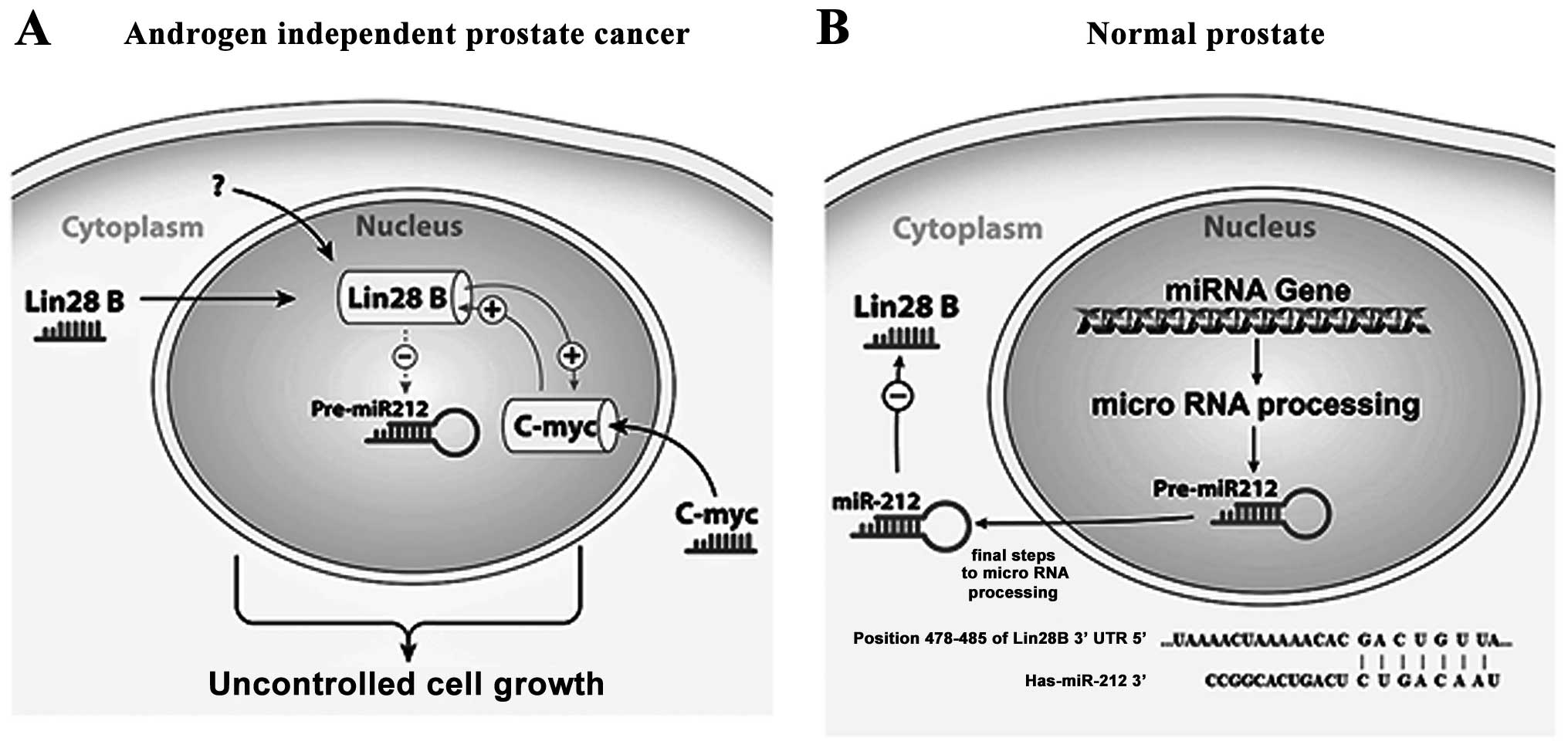
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Crawford ED, Stone NN, Yu EY, et al:
Challenges and recommendations for early identification of
metastatic disease in prostate cancer. Urology. 83:664–669. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Trendel JA: The hurdle of antiandrogen
drug resistance: drug design strategies. Expert Opin Drug Discov.
8:1491–1501. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L, Primrose
JN and Packham G: MicroRNAs: key players in carcinogenesis and
novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:339–347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ritchie W, Rasko JE and Flamant S:
MicroRNA target prediction and validation. Adv Exp Med Biol.
774:39–53. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lovat F, Valeri N and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in the pathogenesis of cancer. Semin Oncol. 38:724–733. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hafner M, Max KE, Bandaru P, et al:
Identification of mRNAs bound and regulated by human LIN28 proteins
and molecular requirements for RNA recognition. RNA. 19:613–626.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou J, Ng SB and Chng WJ: LIN28/LIN28B:
an emerging oncogenic driver in cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:973–978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gaytan F, Sangiao-Alvarellos S,
Manfredi-Lozano M, et al: Distinct expression patterns predict
differential roles of the miRNA-binding proteins, Lin28 and Lin28b,
in the mouse testis: studies during postnatal development and in a
model of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Endocrinology.
154:1321–1336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tummala R, Nadiminty N, Lou W, et al:
Lin28 promotes growth of prostate cancer cells and activates the
androgen receptor. Am J Pathol. 183:288–295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Roy A, Kucukural A and Zhang Y: I-TASSER:
a unified platform for automated protein structure and function
prediction. Nat Protoc. 5:725–738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walter BA, Valera VA, Pinto PA and Merino
MJ: Comprehensive microRNA profiling of prostate cancer. J Cancer.
4:350–357. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Incoronato M, Urso L, Portela A, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of miR-212 expression in lung cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e277222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu B, Wang N, Wang X, et al: MiR-146a
suppresses tumor growth and progression by targeting EGFR pathway
and in a p-ERK-dependent manner in castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Prostate. 72:1171–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jones CI, Zabolotskaya MV, King AJ, et al:
Identification of circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers
for use in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer. 107:1987–1996. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Endo Y, Toyama T, Takahashi S, et al:
miR-1290 and its potential targets are associated with
characteristics of estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:91–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Sand D, et al:
Comparative microarray analysis of microRNA expression profiles in
primary cutaneous malignant melanoma, cutaneous malignant melanoma
metastases, and benign melanocytic nevi. Cell Tissue Res.
351:85–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nurul-Syakima AM, Yoke-Kqueen C, Sabariah
AR, Shiran MS, Singh A and Learn-Han L: Differential microRNA
expression and identification of putative miRNA targets and
pathways in head and neck cancers. Int J Mol Med. 28:327–336.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Z, Zhang H, Zhang P, Li J, Shan Z and
Teng W: Upregulation of miR-2861 and miR-451 expression in
papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. Med Oncol.
30:5772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu K, Liang X, Cui D, Wu Y, Shi W and Liu
J: miR-1915 inhibits Bcl-2 to modulate multidrug resistance by
increasing drug-sensitivity in human colorectal carcinoma cells.
Mol Carcinog. 52:70–78. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu H, Li S, Cui X, et al: The
overexpression of hypomethylated miR-663 induces chemotherapy
resistance in human breast cancer cells by targeting heparin
sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2). J Biol Chem. 288:10973–10985. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
An J, Pan Y, Yan Z, et al: MiR-23a in
amplified 19p13.13 loci targets metallothionein 2A and promotes
growth in gastric cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 114:2160–2169.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li JH, Xiao X, Zhang YN, et al: MicroRNA
miR-886-5p inhibits apoptosis by down-regulating Bax expression in
human cervical carcinoma cells. Gynecol Oncol. 120:145–151. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ferrajoli A, Shanafelt TD, Ivan C, et al:
Prognostic value of miR-155 in individuals with monoclonal B-cell
lymphocytosis and patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Blood. 122:1891–1899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oh JS, Kim JJ, Byun JY and Kim IA:
Lin28-let7 modulates radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with
activation of K-Ras. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:5–8. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cui MH, Hou XL, Lei XY, et al:
Upregulation of microRNA 181c expression in gastric cancer tissues
and plasma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3063–3066. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang L, Lin C, Song L, et al:
MicroRNA-30e* promotes human glioma cell invasiveness in
an orthotopic xenotransplantation model by disrupting the
NF-κB/IκBα negative feedback loop. J Clin Invest. 122:33–47.
2012.
|
|
29
|
Kashat M, Azzouz L, Sarkar SH, Kong D, Li
Y and Sarkar FH: Inactivation of AR and Notch-1 signaling by
miR-34a attenuates prostate cancer aggressiveness. Am J Transl Res.
4:432–442. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, et al:
Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Man YG, Fu SW, Liu AJ, et al: Aberrant
expression of chromogranin A, miR-146a, and miR-146b-5p in prostate
structures with focally disrupted basal cell layers: an early sign
of invasion and hormone-refractory cancer? Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 8:235–244. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bray I, Tivnan A, Bryan K, et al:
MicroRNA-542-5p as a novel tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma.
Cancer Lett. 303:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang L, Li Y, Cheng M, et al: A functional
polymorphism at microRNA-629-binding site in the 3′-untranslated
region of NBS1 gene confers an increased risk of lung cancer in
Southern and Eastern Chinese population. Carcinogenesis.
33:338–347. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ali PS, Ghoshdastider U, Hoffmann J,
Brutschy B and Filipek S: Recognition of the let-7g miRNA precursor
by human Lin28B. FEBS Lett. 586:3986–3990. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nam Y, Chen C, Gregory RI, Chou JJ and
Sliz P: Molecular basis for interaction of let-7 microRNAs with
Lin28. Cell. 147:1080–1091. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nadiminty N, Tummala R, Lou W, et al:
MicroRNA let-7c is downregulated in prostate cancer and suppresses
prostate cancer growth. PLoS One. 7:e328322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vencio EF, Nelson AM, Cavanaugh C, et al:
Reprogramming of prostate cancer-associated stromal cells to
embryonic stem-like. Prostate. 72:1453–1463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, et al:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mechanistically linked with
stem cell signatures in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One.
5:e124452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|