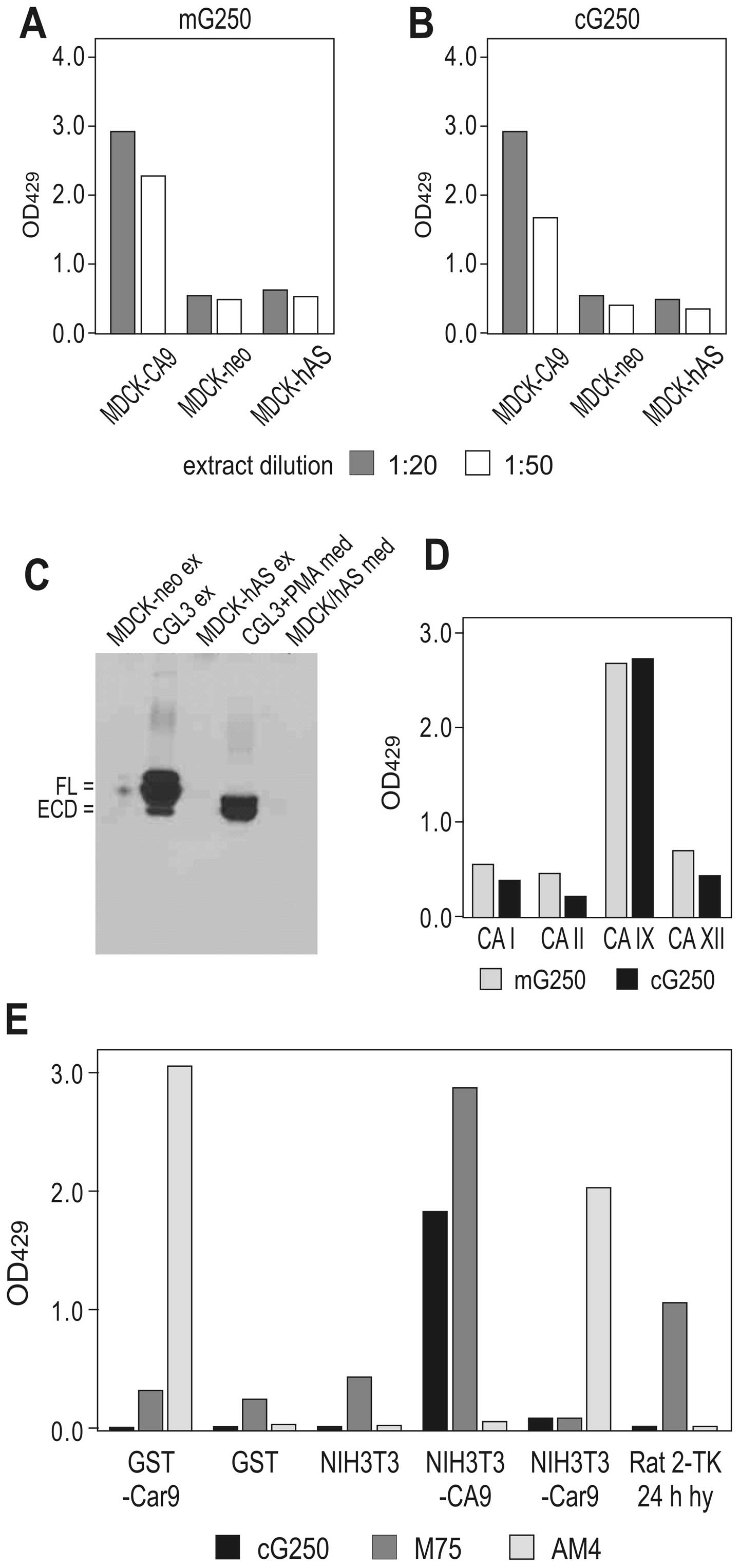
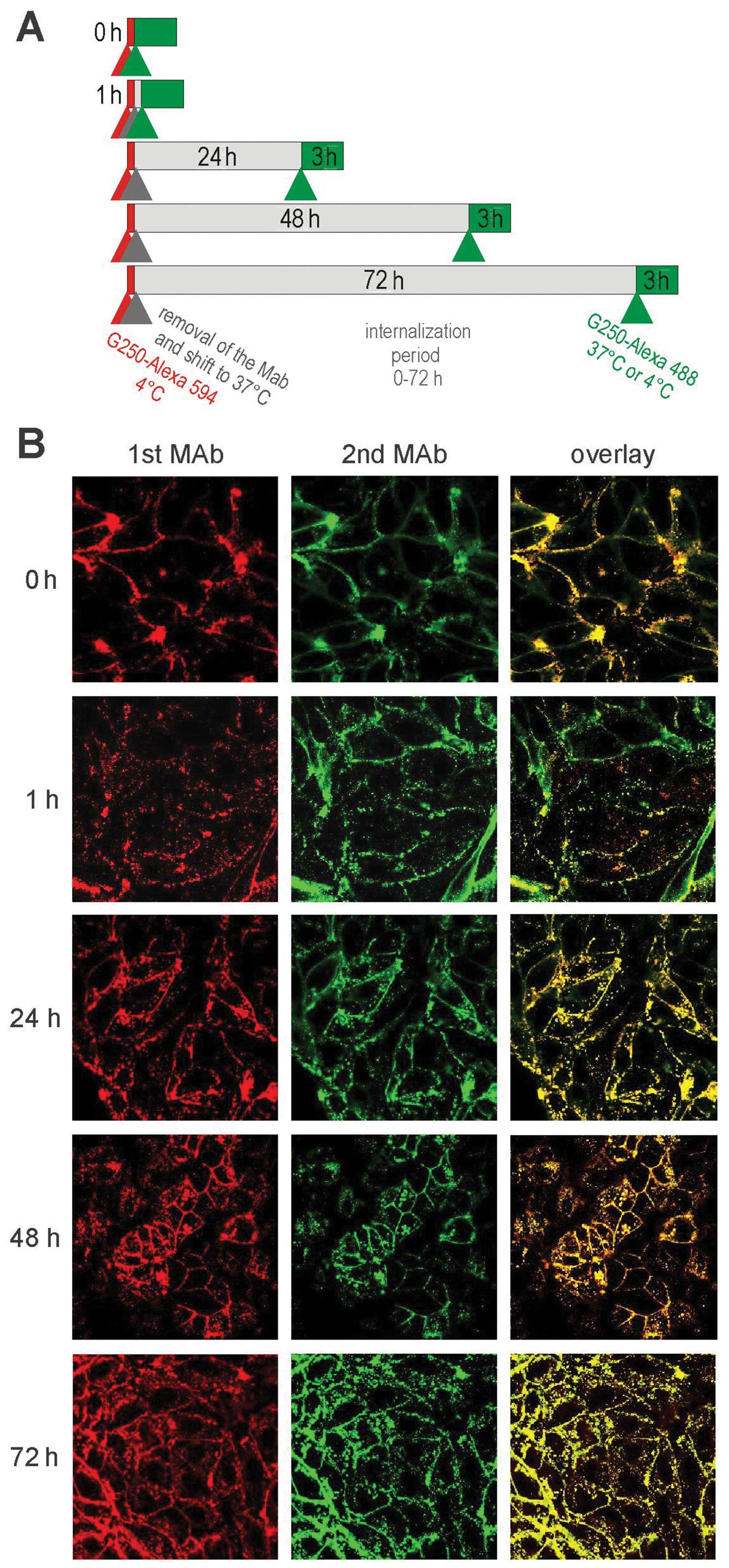
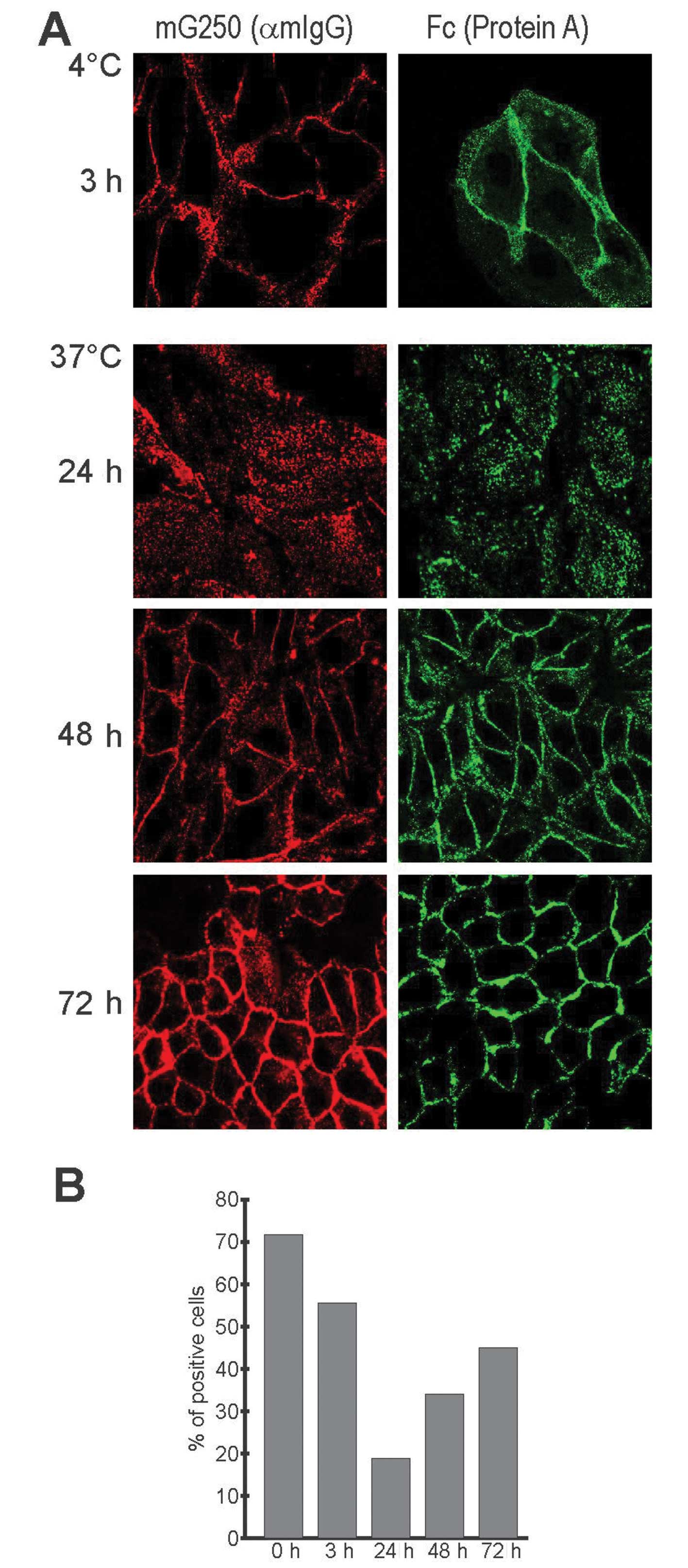
|
1
|
Pastorekova S, Parkkila S, Pastorek J and
Supuran CT: Carbonic anhydrases: current state of the art,
therapeutic applications and future prospects. J Enzyme Inhib Med
Chem. 19:199–229. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pastoreková S, Parkkila S, Parkkila AK,
Opavský R, Zelník V, Saarnio J and Pastorek J: Carbonic anhydrase
IX, MN/CA IX: analysis of stomach complementary DNA sequence and
expression in human and rat alimentary tracts. Gastroenterology.
112:398–408. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pastorekova S, Parkkila S and Zavada J:
Tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases and their clinical
significance. Adv Clin Chem. 42:167–216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, Murray
PG, Morgan NV, Sowter HM, Wykoff CC, Maher ER, Harris AL, Ratcliffe
PJ and Maxwell PH: HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL
kidneys: evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in
the nephron. Cancer Cell. 1:459–468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Potter C and Harris AL: Hypoxia inducible
carbonic anhydrase IX, marker of tumour hypoxia, survival pathway
and therapy target. Cell Cycle. 3:164–167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wykoff CC, Beasley NJ, Watson PH, Turner
KJ, Pastorek J, Sibtain A, Wilson GD, Turley H, Talks KL, Maxwell
PH, et al: Hypoxia-inducible regulation of tumor-associated
carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res. 60:7075–7083. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Svastová E, Hulíková A, Rafajová M,
Zat’ovicová M, Gibadulinová A, Casini A, Cecchi A, Scozzafava A,
Supuran CT, Pastorek J and Pastoreková S: Hypoxia activates the
capacity of tumour-associated carbonic anhydrase IX to acidify
extracellular pH. FEBS Lett. 577:439–445. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ditte P, Dequiedt F, Svastova E, Hulikova
A, Ohradanova-Repic A, Zatovicova M, Csaderova L, Kopacek J,
Supuran CT, Pastorekova S and Pastorek J: Phosphorylation of
carbonic anhydrase IX controls its ability to mediate extracellular
acidification in hypoxic tumors. Cancer Res. 71:7558–7567. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dorai T, Sawczuk IS, Pastorek J, Wiernik
PH and Dutcher JP: The role of carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression
in kidney cancer. Eur J Cancer. 41:2935–2947. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiche J, Ilc K, Laferrière J, Trottier E,
Dayan F, Mazure NM, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur J:
Hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase IX and XII promote tumour cell
growth by counteracting acidosis through the regulation of the
intracellular pH. Cancer Res. 69:358–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dubois L, Peeters S, Lieuwes NG, Geusens
N, Thiry A, Wigfield S, Carta F, McIntyre A, Scozzafava A, Dogné
JM, et al: Specific inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX activity
enhances the in vivo therapeutic effect of tumour irradiation.
Radiother Oncol. 99:424–431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McIntyre A, Patiar S, Wigfield S, Li JL,
Ledaki I, Turley H, Leek R, Snell C, Gatter K, Sly WS, et al:
Carbonic anhydrase IX promotes tumour growth and necrosis in vivo
and inhibition enhances anti-VEGF therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3100–3111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Svastová E, Zilka N, Zat’ovicová M,
Gibadulinová A, Ciampor F, Pastorek J and Pastoreková S: Carbonic
anhydrase reduces E-cadherin-mediated adhesion of MDCK cells via
interaction with beta-catenin. Exp Cell Res. 290:332–345.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Svastova E, Witarski W, Csaderova L, Kosik
I, Skvarkova L, Hulikova A, Zatovicova M, Barathova M, Kopacek J,
Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX interacts with
bicarbonate transporters in lamellipodia and increases cell
migration via its catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 287:3392–3402.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Csaderova L, Debreova M, Radvak P, Stano
M, Vrestiakova M, Kopacek J, Pastorekova S and Svastova E: The
effect of carbonic anhydrase IX on focal contacts during cell
spreading and migration. Front Physiol. 4:2712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Závada J, Závadová Z, Pastoreková S,
Ciampor F, Pastorek J and Zelník V: Expression of MaTu-MN protein
in human tumor cultures and in clinical specimens. Int J Cancer.
54:268–274. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zatovicova M, Jelenska L, Hulikova A,
Csaderova L, Ditte Z, Ditte P, Goliasova T, Pastorek J and
Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX as an anticancer therapy
target: preclinical evaluation of internalizing monoclonal antibody
directed to catalytic domain. Curr Pharm Des. 16:3255–3263. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lou Y, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Chia S,
Ostlund C, Ahmadi A, Kyle A, Auf dem Keller U, Leung S, Huntsman D,
et al: Targeting tumor hypoxia: suppression of breast tumour growth
and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer
Res. 71:3364–3376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rafajová M, Zatovicová M, Kettmann R,
Pastorek J and Pastoreková S: Induction by hypoxia combined with
low glucose or low bicarbonate and high posttranslational stability
upon reoxygenation contribute to carbonic anhydrase IX expression
in cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 24:995–1004. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zatovicova M, Sedlakova O, Svastova E,
Ohradanova A, Ciampor F, Arribas J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S:
Ectodomain shedding of the hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX is
a metalloprotease-dependent process regulated by TACE/ADAM17. Br J
Cancer. 93:1267–1276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zatovičová M and Pastorekova S: Modulation
of cell surface density of carbonic anhydrase IX by shedding of the
ectodomain and endocytosis. Acta Virol. 57:257–264. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oosterwijk E, Ruiter DJ, Hoedemaeker PJ,
Pauwels EK, Jonas U, Zwartendijk J and Warnaar SO: Monoclonal
antibody G 250 recognizes a determinant present in renal-cell
carcinoma and absent from normal kidney. Int J Cancer. 38:489–494.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oosterwijk-Wakka JC, Boerman OC, Mulders
PF and Oosterwijk E: Application of monoclonal antibody G250
recognizing carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 14:11402–11423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zat’ovicová M, Tarábková K, Svastová E,
Gibadulinová A, Mucha V, Jakubícková L, Biesová Z, Rafajová M,
Ortova Gut M, Parkkila S, et al: Monoclonal antibodies generated in
carbonic anhydrase IX-deficient mice recognize different domains of
tumour-associated hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX. J Immunol
Methods. 282:117–134. 2003.
|
|
25
|
Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Molecular
mechanisms regulating expression and function of cancer-associated
anhydrase IX. The Tumour Microenvironment. Bagley RG: Springer New
York: Humana Press, NY; pp. 59–90. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu C, Lo A, Yammanuru A, Tallarico AS,
Brady K, Murakami A, Barteneva N, Zhu Q and Marasco WA: Unique
biological properties of catalytic domain directed human anti-CAIX
antibodies discovered through phage-display technology. PLoS One.
5:e96252010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Murri-Plesko MT, Hulikova A, Oosterwijk E,
Scott AM, Zortea A, Harris AL, Ritter G, Old L, Bauer S, Swietach P
and Renner C: Antibody inhibiting enzymatic activity of
tumour-associated carbonic anhydrase isoform IX. Eur J Pharmacol.
657:173–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Supuran CT: Carbonic anhydrases: novel
therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 7:168–181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gnarra JR, Tory K, Weng Y, Schmidt L, Wei
MH, Li H, Latif F, Liu S, Chen F, Duh FM, et al: Mutations of the
VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 7:85–90.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ivanov SV, Kuzmin I, Wei MH, Pack S, Geil
L, Johnson BE, Stanbridge EJ and Lerman MI: Down-regulation of
transmembrane carbonic anhydrases in renal cell carcinoma cell
lines by wild-type von Hippel-Lindau transgenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:12596–12601. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wiesener MS, Münchenhagen PM, Berger I,
Morgan NV, Roigas J, Schwiertz A, Jürgensen JS, Gruber G, Maxwell
PH, Löning SA, et al: Constitutive activation of hypoxia-inducible
genes related to overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
in clear cell renal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 61:5215–5222.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MGB, Sowter HM,
Mandriota SJ, Li JL, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL and Ratcliffe
PJ: Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)
and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol
Cell Biol. 25:5675–5686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bui MH, Seligson D, Han KR, Pantuck AJ,
Dorey FJ, Huang Y, Horvath S, Leibovich BC, Chopra S, Liao SY, et
al: Carbonic anhydrase IX is an independent predictor of survival
in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis
and therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 9:802–811. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brouwers AH, Frielink C, Oosterwijk E,
Oyen WJ, Corstens FH and Boerman OC: Interferons can upregulate the
expression of the tumor associated antigen G250-MN/CA IX, a
potential target for (radio)immunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 18:539–547. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Atkins M, Regan M, McDermott D, Mier J,
Stanbridge E, Youmans A, Febbo P, Upton M, Lechpammer M and
Signoretti S: Carbonic anhydrase IX expression predicts outcome of
interleukin 2 therapy for renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3714–3721. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chrastina A, Závada J, Parkkila S, Kaluz
S, Kaluzová M, Rajcáni J, Pastorek J and Pastoreková S:
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of 125I-labeled monoclonal
antibody M75 specific for carbonic anhydrase IX, an intrinsic
marker of hypoxia, in nude mice xenografted with human colorectal
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 105:873–881. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pastorek J, Pastoreková S, Callebaut I,
Mornon JP, Zelník V, Opavský R, Zat’ovicová M, Liao S, Portetelle
D, Stanbridge EJ, et al: Cloning and characterization of MN, a
human tumor-associated protein with a domain homologous to carbonic
anhydrase and a putative helix-loop-helix DNA binding segment.
Oncogene. 9:2877–2888. 1994.
|
|
38
|
Grabmaier K, Vissers JL, De Weijert MC,
Oosterwijk-Wakka JC, Van Bokhoven A, Brakenhoff RH, Noessner E,
Mulders PA, Merkx G, Figdor CG, et al: Molecular cloning and
immunogenicity of renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250. Int
J Cancer. 85:865–870. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oosterwijk E, Bander NH, Divgi CR, Welt S,
Wakka JC, Finn RD, Carswell EA, Larson SM, Warnaar SO, Fleuren GJ,
et al: Antibody localization in human renal cell carcinoma: a phase
I study of monoclonal antibody G250. J Clin Oncol. 11:738–750.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Steffens MG, Boerman OC, Oosterwijk-Wakka
JC, Oosterhof GO, Witjes JA, Koenders EB, Oyen WJ, Buijs WC,
Debruyne FM, Corstens FH and Oosterwijk E: Targeting of renal cell
carcinoma with iodine-131-labeled chimeric monoclonal antibody
G250. J Clin Oncol. 15:1529–1537. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bleumer I, Knuth A, Oosterwijk E, Hofmann
R, Varga Z, Lamers C, Kruit W, Melchior S, Mala C, Ullrich S, et
al: A phase II trial of chimeric monoclonal antibody G250 for
advanced renal cell carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer. 90:985–990.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bleumer I, Oosterwijk E, Oosterwijk-Wakka
JC, Völler MC, Melchior S, Warnaar SO, Mala C, Beck J and Mulders
PF: A clinical trial with chimeric monoclonal antibody WX-G250 and
low dose interleukin-2 pulsing scheme for advanced renal cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 175:57–62. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Siebels M, Rohrmann K, Oberneder R,
Stahler M, Haseke N, Beck J, Hofmann R, Kindler M, Kloepfer P and
Stief C: A clinical phase I/II trial with the monoclonal antibody
cG250 (RENCAREX®) and interferon-alpha-2a in metastatic
renal cell carcinoma patients. World J Urol. 29:121–126. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Belldegrun AS, Chamie K, Kloepfer P, Fall
B, Bevan P, Störkel S, Wilhelm O and Pantuck AJ: ARISER: a
randomized double blind phase III study to evaluate adjuvant cG250
treatment versus placebo in patients with high-risk ccRCC - results
and implications for adjuvant clinical trials. J Clin Oncol.
31(Suppl; abs. 4507)2013.
|
|
45
|
Takacova M, Barathova M, Hulikova A,
Ohradanova A, Kopacek J, Parkkila S, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S and
Zatovicova M: Hypoxia-inducible expression of the mouse carbonic
anhydrase IX demonstrated by new monoclonal antibodies. Int J
Oncol. 31:1103–1110. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Barathova M, Takacova M, Holotnakova T,
Gibadulinova A, Ohradanova A, Zatovicova M, Hulikova A, Kopacek J,
Parkkila S, Supuran CT, et al: Alternative splicing variant of the
hypoxia marker carbonic anhydrase IX expressed independently of
hypoxia and tumour phenotype. Br J Cancer. 98:129–136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Závada J, Závadová Z, Zat’ovicová M, Hyrsl
L and Kawaciuk I: Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) in
the serum and urine of renal carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer.
89:1067–1071. 2003.
|
|
48
|
Hyrsl L, Zavada J, Zavadova Z, Kawaciuk I,
Vesely S and Skapa P: Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX)
in transitional cell carcinoma of urinary tract. Neoplasma.
56:298–302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou GX, Ireland J, Rayman P, Finke J and
Zhou M: Quantification of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in serum
and tissue of renal cell carcinoma patients using enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay: prognostic and diagnostic potentials. Urology.
75:257–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kock L, Mahner S, Choschzick M, Eulenburg
C, Milde-Langosch K, Schwarz J, Jaenicke F, Müller V and Woelber L:
Serum carbonic anhydrase IX and its prognostic relevance in vulvar
cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 21:141–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Müller V, Riethdorf S, Rack B, Janni W,
Fasching PA, Solomayer E, Aktas B, Kasimir-Bauer S, Zeitz J, Pantel
K, et al: Prospective evaluation of serum tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase 1 and carbonic anhydrase IX in correlation to
circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:R712011.
|
|
52
|
Gigante M, Li G, Ferlay C, Perol D, Blanc
E, Paul S, Zhao A, Tostain J, Escudier B, Negrier S and Genin C:
Prognostic value of serum CA9 in patients with metastatic clear
cell renal cell carcinoma under targeted therapy. Anticancer Res.
32:5447–5451. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Takacova M, Bartosova M, Skvarkova L,
Zatovicova M, Vidlickova I, Csaderova L, Barathova M, Breza J Jr,
Bujdak P, Pastorek J, et al: Carbonic anhydrase IX is a clinically
significant tissue and serum biomarker associated with renal cell
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 5:191–197. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Alterio V, Hilvo M, Di Fiore A, Supuran
CT, Pan P, Parkkila S, Scaloni A, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S, Pedone
C, et al: Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the
tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:16233–16238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dubois L, Lieuwes NG, Maresca A, Thiry A,
Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Wouters BG and Lambin P: Imaging of CA IX
with fluorescent labelled sulfonamides distinguishes hypoxic and
(re)-oxygenated cells in a xenograft tumour model. Radiother Oncol.
92:423–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dürrbach A, Angevin E, Poncet P, Rouleau
M, Chavanel G, Chapel A, Thierry D, Gorter A, Hirsch R, Charpentier
B, et al: Antibody-mediated endocytosis of G250 tumor-associated
antigen allows targeted gene transfer to human renal cell carcinoma
in vitro. Cancer Gene Ther. 6:564–571. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Grantab R, Sivananthan S and Tannock IF:
The penetration of anticancer drugs through tumour tissue as a
function of cellular adhesion and packing density of tumour cells.
Cancer Res. 66:1033–1039. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Sorkin A and von Zastrow M: Endocytosis
and signalling: intertwining molecular networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 10:609–622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Surfus JE, Hank JA, Oosterwijk E, Welt S,
Lindstrom MJ, Albertini MR, Schiller JH and Sondel PM:
Anti-renal-cell carcinoma chimeric antibody G250 facilitates
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity with in vitro and in vivo
interleukin-2-activated effectors. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor
Immunol. 19:184–191. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu Z, Smyth FE, Renner C, Lee FT,
Oosterwijk E and Scott AM: Anti-renal cell carcinoma chimeric
antibody G250: cytokine enhancement of in vitro antibody-dependent
cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 51:171–177. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Divgi CR, Pandit-Taskar N, Jungbluth AA,
Reuter VE, Gönen M, Ruan S, Pierre C, Nagel A, Pryma DA, Humm J, et
al: Preoperative characterisation of clear-cell renal carcinoma
using iodine-124-labelled antibody chimeric G250
(124I-cG250) and PET in patients with renal masses: a
phase I trial. Lancet Oncol. 8:304–310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Beasley NJ, Wykoff CC, Watson PH, Leek R,
Turley H, Gatter K, Pastorek J, Cox GJ, Ratcliffe P and Harris AL:
Carbonic anhydrase IX, an endogenous hypoxia marker, expression in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its relationship to
hypoxia, necrosis and microvessel density. Cancer Res.
61:5262–5267. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Turner KJ, Crew JP, Wykoff CC, Watson PH,
Poulsom R, Pastorek J, Ratcliffe PJ, Cranston D and Harris AL: The
hypoxia-inducible genes VEGF and CA9 are differentially regulated
in superficial vs invasive bladder cancer. Br J Cancer.
86:1276–1282. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Swinson DE, Jones JL, Cox G, Richardson D,
Harris AL and O’Byrne KJ: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in non
small cell lung cancer: relation to growth factor, protease and
apoptosis pathways. Int J Cancer. 111:43–50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Olive PL, Aquino-Parsons C, MacPhail SH,
Laio S, Raleigh JA, Lerman MI and Stanbridge EJ: Carbonic anhydrase
9 as an endogenous marker for hypoxic cells in cervical cancer.
Cancer Res. 61:8924–8929. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|