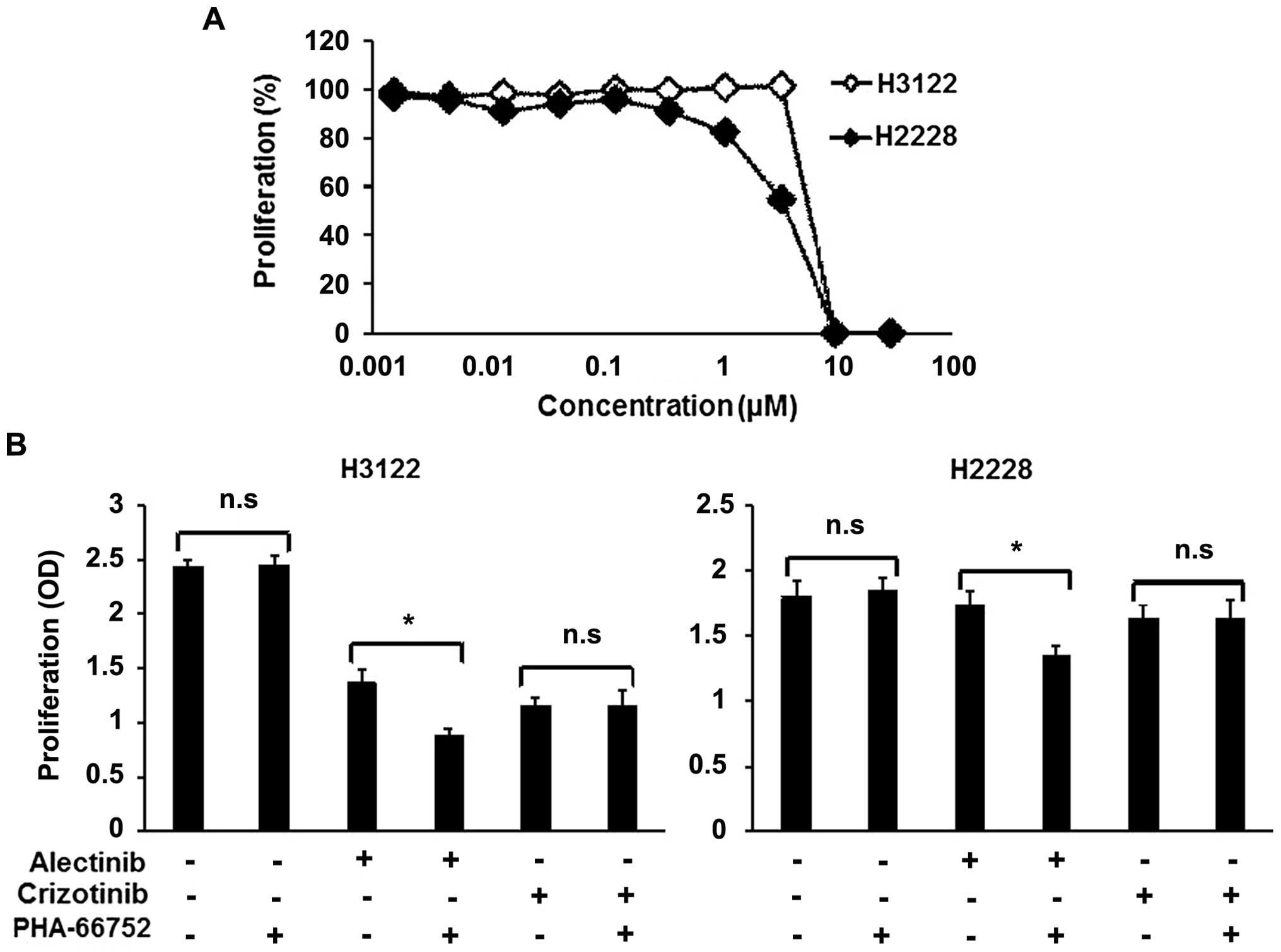
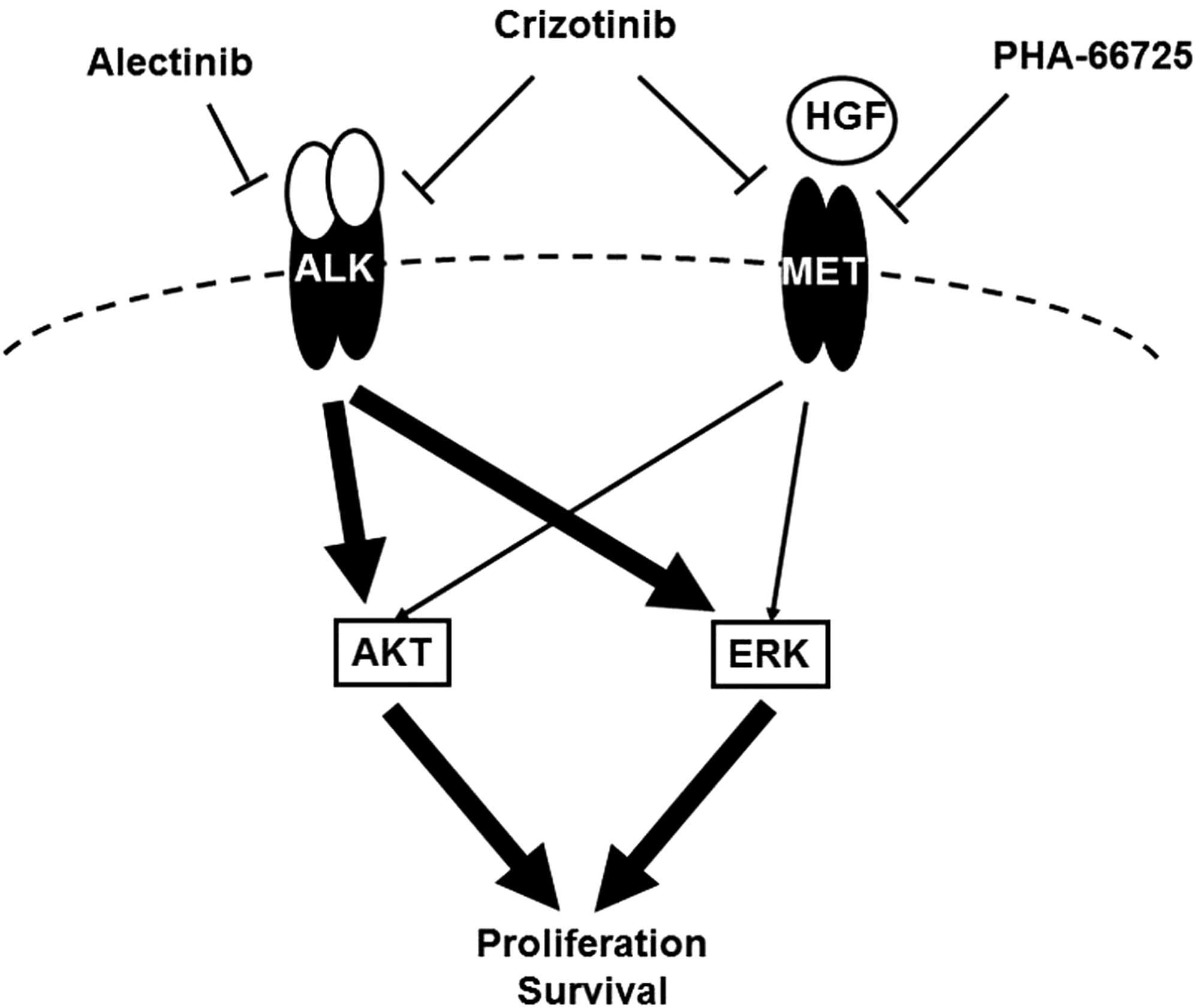
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, et al:
Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J
Clin. 62:220–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et
al: Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 346:92–98. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ohe Y, Ohashi Y, Kubota K, et al:
Randomized phase III study of cisplatin plus irinotecan versus
carboplatin plus paclitaxel, cisplatin plus gemcitabine, and
cisplatin plus vinorelbine for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer:
Four-Arm Cooperative Study in Japan. Ann Oncol. 18:317–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Weinstein IB: Cancer: addiction to
oncogenes - the Achilles heal of cancer. Science. 297:63–64. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pao W and Girard N: New driver mutations
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 12:175–180. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al: EGFR
mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to
gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al:
Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor
underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, et al: EGF
receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never
smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib
and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:13306–13311. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al:
Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al:
Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, et al:
Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:2385–2394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seto T, Kiura K, Nishio M, et al:
CH5424802 (RO5424802) for patients with ALK-rearranged advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-001JP study): a single-arm,
open-label, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Oncol. 14:590–598. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al:
EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK
inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 363:1734–1739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Katayama R, Shaw AT, Khan TM, et al:
Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung
Cancers. Sci Transl Med. 4:120ra172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katayama R, Khan TM, Benes C, et al:
Therapeutic strategies to overcome crizotinib resistance in
non-small cell lung cancers harboring the fusion oncogene EML4-ALK.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:7535–7540. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cui JJ, Tran-Dubé M, Shen H, et al:
Structure based drug design of crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent
and selective dual inhibitor of mesenchymal-epithelial transition
factor (c-MET) kinase and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). J Med
Chem. 54:6342–6363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakamoto H, Tsukaguchi T, Hiroshima S, et
al: CH5424802, a selective ALK inhibitor capable of blocking the
resistant gatekeeper mutant. Cancer Cell. 19:679–690. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kodama T, Tsukaguchi T, Yoshida M, Kondoh
O and Sakamoto H: Selective ALK inhibitor alectinib with potent
antitumor activity in models of crizotinib resistance. Cancer Lett.
351:215–221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Friboulet L, Li N, Katayama R, et al: The
ALK inhibitor ceritinib overcomes crizotinib resistance in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 4:662–673. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peters S and Adjei AA: MET: a promising
anticancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 9:314–326. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gherardi E, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C and
Vande Woude G: Targeting MET in cancer: rationale and progress. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:89–103. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Corso S and Giordano S: Cell-autonomous
and non-cell-autonomous mechanisms of HGF/MET-driven resistance to
targeted therapies: from basic research to a clinical perspective.
Cancer Discov. 3:978–992. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sadiq AA and Salgia R: MET as a possible
target for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:1089–1096.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et
al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer
by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yano S, Wang W, Li Q, et al: Hepatocyte
growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma
with epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer
Res. 68:9479–9487. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arao T, Fukumoto H, Takeda M, Tamura T,
Saijo N and Nishio K: Small in-frame deletion in the epidermal
growth factor receptor as a target for ZD6474. Cancer Res.
64:9101–9104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Hamaguchi T, et al:
FGFR2 gene amplification and clinicopathological features in
gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:727–327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanizaki J, Okamoto I, Okabe T, et al:
Activation of HER family signaling as a mechanism of acquired
resistance to ALK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:6219–6226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamaguchi N, Lucena-Araujo AR, Nakayama S,
et al: Dual ALK and EGFR inhibition targets a mechanism of acquired
resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib in ALK
rearranged lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 83:37–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim HR, Kim WS, Choi YJ, Choi CM, Rho JK
and Lee JC: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition leads to crizotinib
resistance in H2228 lung cancer cells with EML4-ALK translocation.
Mol Oncol. 7:1093–1102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamada T, Takeuchi S, Nakade J, et al:
Paracrine receptor activation by microenvironment triggers bypass
survival signals and ALK inhibitor resistance in EML4-ALK lung
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 18:3592–3602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Feng Y, Minca EC, Lanigan C, et al: High
MET receptor expression but not gene amplification in ALK 2p23
rearrangement positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
9:646–653. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gouji T, Takashi S, Mitsuhiro T and Yukito
I: Crizotinib can overcome acquired resistance to CH5424802: is
amplification of the MET gene a key factor? J Thorac Oncol.
9:e27–e28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Voena C, Di Giacomo F, Panizza E, et al:
The EGFR family members sustain the neoplastic phenotype of
ALK+ lung adenocarcinoma via EGR1. Oncogenesis.
2:e432013. View Article : Google Scholar
|