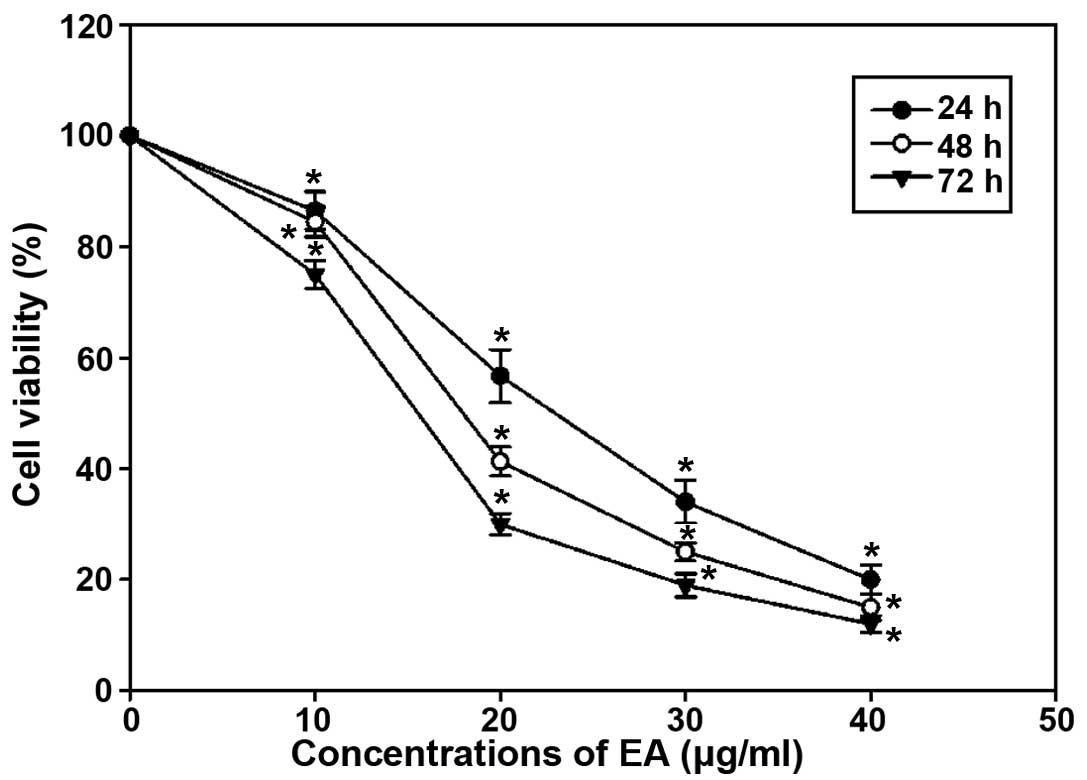
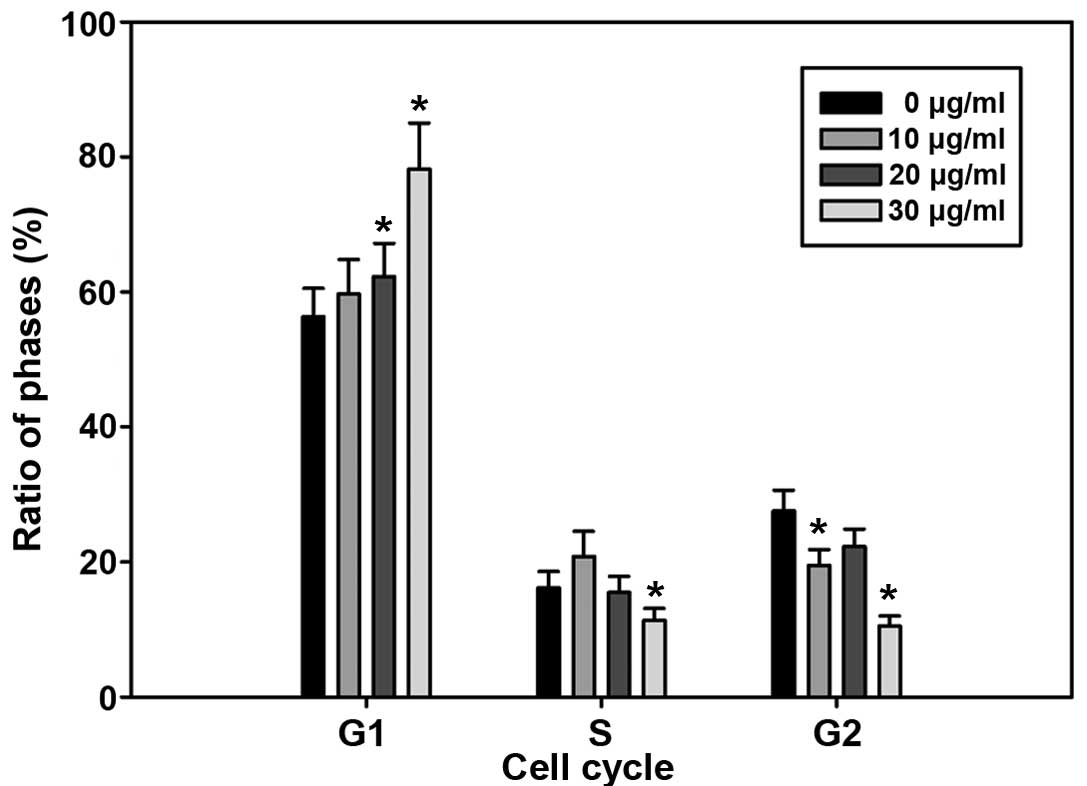
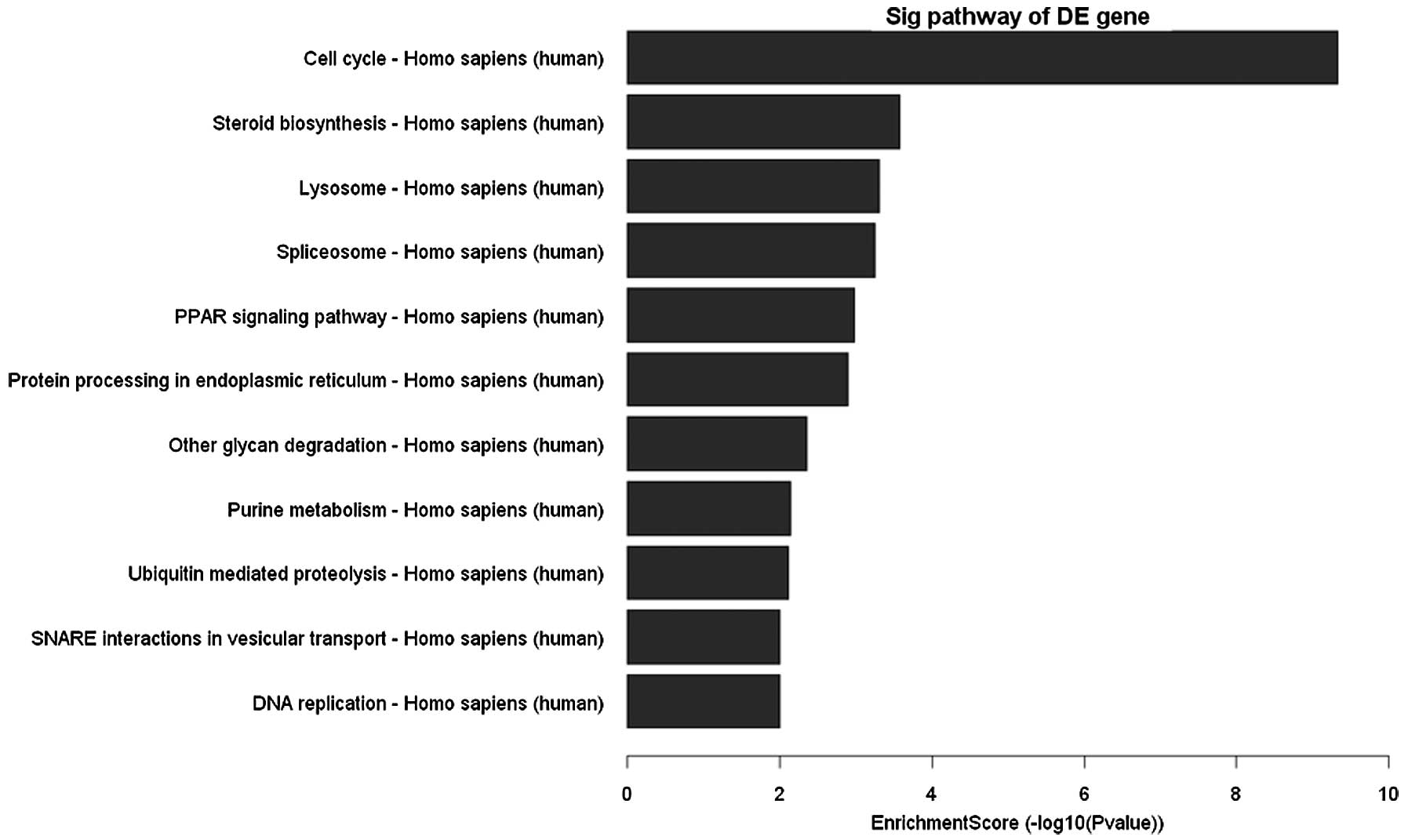
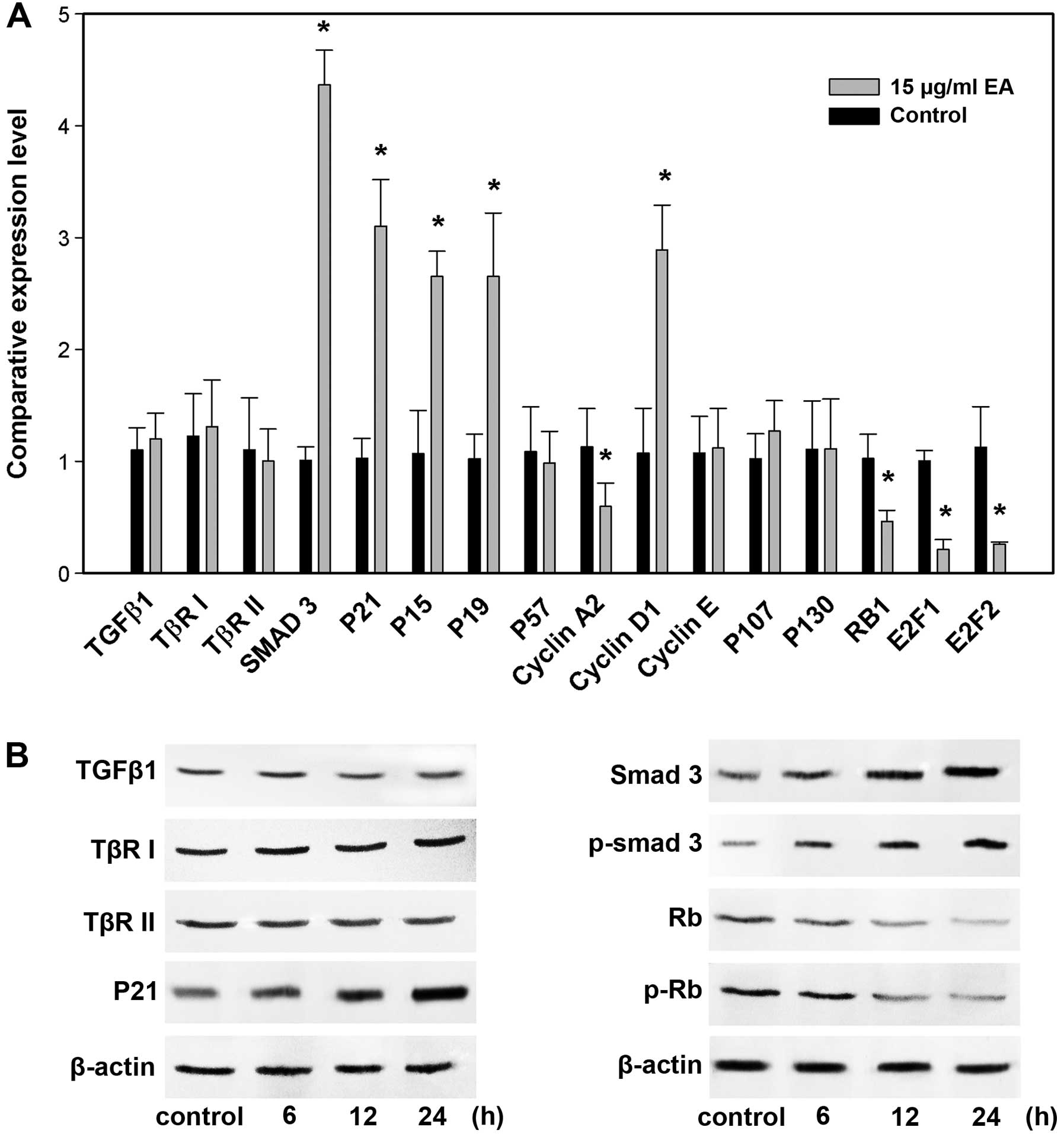
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dai Z, Nair V, Khan M and Ciolino HP:
Pomegranate extract inhibits the proliferation and viability of
MMTV-Wnt-1 mouse mammary cancer stem cells in vitro. Oncol Rep.
24:1087–1091. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Larrosa M, Tomas-Barberan FA and Espin JC:
The dietary hydrolysable tannin punicalagin releases ellagic acid
that induces apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells
by using the mitochondrial pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 17:611–625.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seeram NP, Adams LS, Henning SM, et al: In
vitro antiproliferative, apoptotic and antioxidant activities of
punicalagin, ellagic acid and a total pomegranate tannin extract
are enhanced in combination with other polyphenols as found in
pomegranate juice. J Nutr Biochem. 16:360–367. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herrera MC and Luque de Castro MD:
Ultrasound-assisted extraction for the analysis of phenolic
compounds in strawberries. Anal Bioanal Chem. 379:1106–1112.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsao DA, Chang HJ, Lin CY, et al: Gene
expression profiles for predicting the efficacy of the anticancer
drug 5-fluorouracil in breast cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 29:285–293.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berger E, Rome S, Vega N, Ciancia C and
Vidal H: Transcriptome profiling in response to adiponectin in
human cancer-derived cells. Physiol Genomics. 42A:61–70. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poulogiannis G, Luo F and Arends MJ: RAS
signalling in the colorectum in health and disease. Cell Commun
Adhes. 19:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Areshkov PO, Avdieiev SS, Balynska OV,
Leroith D and Kavsan VM: Two closely related human members of
chitinase-like family, CHI3L1 and CHI3L2, activate ERK1/2 in 293
and U373 cells but have the different influence on cell
proliferation. Int J Biol Sci. 8:39–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang KF, Zhang GD, Huang YQ and Diao Y:
Wogonin induces apoptosis and down-regulates survivin in human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells by modulating PI3K-AKT pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:334–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rodriguez-Berriguete G, Fraile B,
Martinez-Onsurbe P, Olmedilla G, Paniagua R and Royuela M: MAP
kinases and prostate cancer. J Signal Transduct. 2012:1691702012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang CY, Tsai AC, Peng CY, et al:
Dehydrocostuslactone suppresses angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo
through inhibition of Akt/GSK-3beta and mTOR signaling pathways.
PLoS One. 7:e311952012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cirera-Salinas D, Pauta M, Allen RM, et
al: Mir-33 regulates cell proliferation and cell cycle progression.
Cell Cycle. 11:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong Y, Ganther HE, Stewart C and Ip C:
Identification of molecular targets associated with
selenium-induced growth inhibition in human breast cells using cDNA
microarrays. Cancer Res. 62:708–714. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uhlmann F, Bouchoux C and Lopez-Aviles S:
A quantitative model for cyclin-dependent kinase control of the
cell cycle: revisited. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
366:3572–3583. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu B, Lane ME and Wadler S: SU9516, a
cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor, promotes accumulation of high
molecular weight E2F complexes in human colon carcinoma cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 64:1091–1100. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maiti B, Li J, de Bruin A, et al: Cloning
and characterization of mouse E2F8, a novel mammalian E2F family
member capable of blocking cellular proliferation. J Biol Chem.
280:18211–18220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng L, Rossi F, Fang W, Mori T and
Cobrinik D: Cdk2-dependent phosphorylation and functional
inactivation of the pRB-related p130 protein in pRB(−),
p16INK4A(+) tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 275:30317–30325.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Muller H, Moroni MC, Vigo E, Petersen BO,
Bartek J and Helin K: Induction of S-phase entry by E2F
transcription factors depends on their nuclear localization. Mol
Cell Biol. 17:5508–5520. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gui T, Sun Y, Shimokado A and Muragaki Y:
The roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in
TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Signal
Transduct. 2012:2892432012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pardali E and Ten Dijke P: TGFbeta
signaling and cardiovascular diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 8:195–213.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Attisano L and Wrana JL: Signal
transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science. 296:1646–1647.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Siegel PM and Massague J: Cytostatic and
apoptotic actions of TGF-beta in homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:807–821. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S and Heldin
CH: Smad regulation in TGF-beta signal transduction. J Cell Sci.
114:4359–4369. 2001.
|
|
26
|
de Caestecker MP, Piek E and Roberts AB:
Role of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1388–1402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Levy L and Hill CS: Alterations in
components of the TGF-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:41–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen CR, Kang Y, Siegel PM and Massague J:
E2F4/5 and p107 as Smad cofactors linking the TGFbeta receptor to
c-myc repression. Cell. 110:19–32. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Coffey RJ Jr, Bascom CC, Sipes NJ,
Graves-Deal R, Weissman BE and Moses HL: Selective inhibition of
growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by
transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 8:3088–3093.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pietenpol JA, Holt JT, Stein RW and Moses
HL: Transforming growth factor beta 1 suppression of c-myc gene
transcription: role in inhibition of keratinocyte proliferation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:3758–3762. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hannon GJ and Beach D: p15INK4B is a
potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature.
371:257–261. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Warner BJ, Blain SW, Seoane J and Massague
J: Myc downregulation by transforming growth factor beta required
for activation of the p15Ink4b G1 arrest
pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 19:5913–5922. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, et al:
p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth
factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev.
8:9–22. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Laiho M, DeCaprio JA, Ludlow JW,
Livingston DM and Massague J: Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked
to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell.
62:175–185. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ramos C, Becerril C, Montano M, et al:
FGF-1 reverts epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by
TGF-{beta}1 through MAPK/ERK kinase pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 299:L222–L231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Derynck R: TGF-beta-receptor-mediated
signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 19:548–553. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Claudio PP, Tonini T and Giordano A: The
retinoblastoma family: twins or distant cousins? Genome Biol.
3:reviews3012. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Coqueret O: New roles for p21 and p27
cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends
Cell Biol. 13:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ko TC, Sheng HM, Reisman D, Thompson EA
and Beauchamp RD: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibits cyclin
D1 expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene. 10:177–184.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Massague J and Polyak K: Mammalian
antiproliferative signals and their targets. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
5:91–96. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Robson CN, Gnanapragasam V, Byrne RL,
Collins AT and Neal DE: Transforming growth factor-beta1
up-regulates p15, p21 and p27 and blocks cell cycling in G1 in
human prostate epithelium. J Endocrinol. 160:257–266. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cam H and Dynlacht BD: Emerging roles for
E2F: beyond the G1/S transition and DNA replication. Cancer Cell.
3:311–316. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Brehm A, Miska EA, McCance DJ, Reid JL,
Bannister AJ and Kouzarides T: Retinoblastoma protein recruits
histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature. 391:597–601.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Groisman R, Naguibneva
I, et al: Retinoblastoma protein represses transcription by
recruiting a histone deacetylase. Nature. 391:601–605. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|