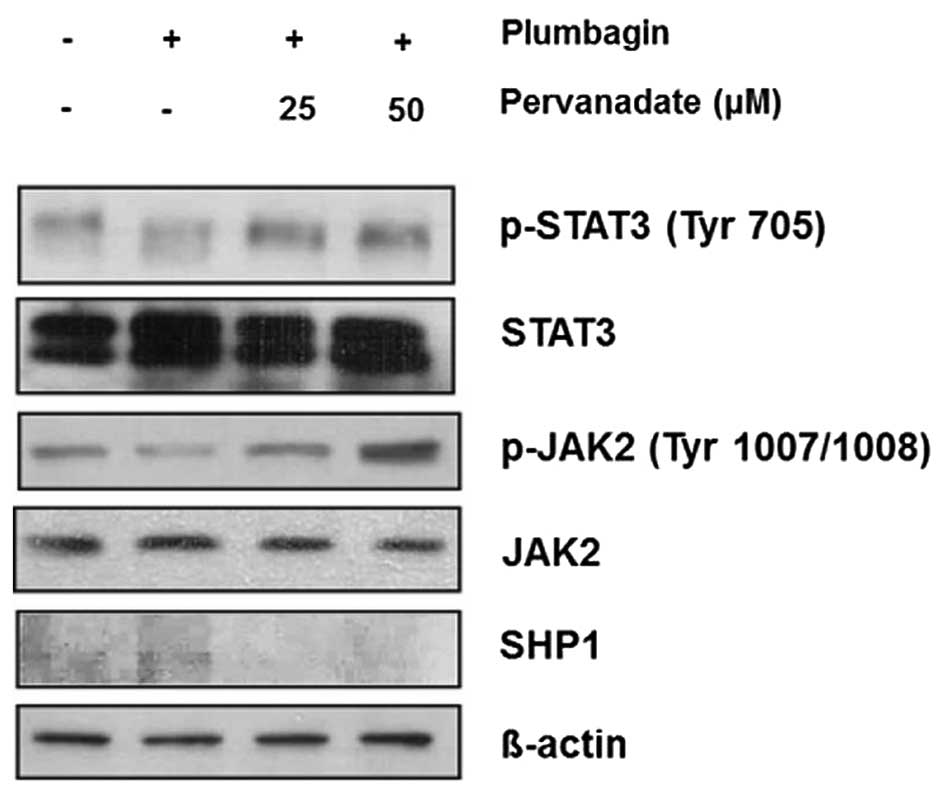
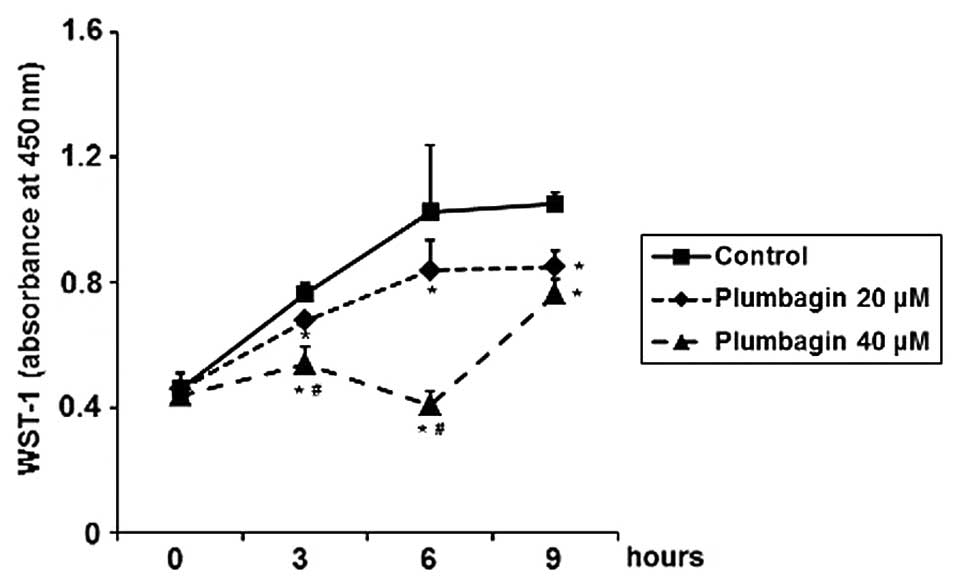
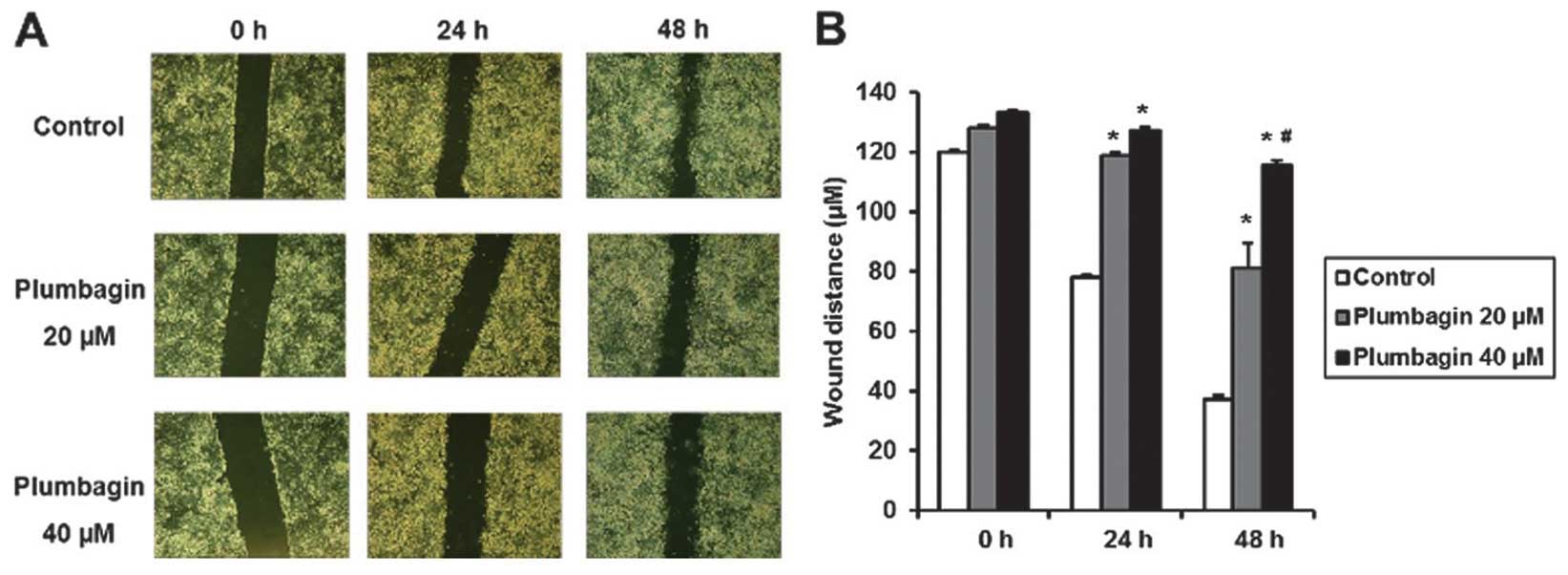
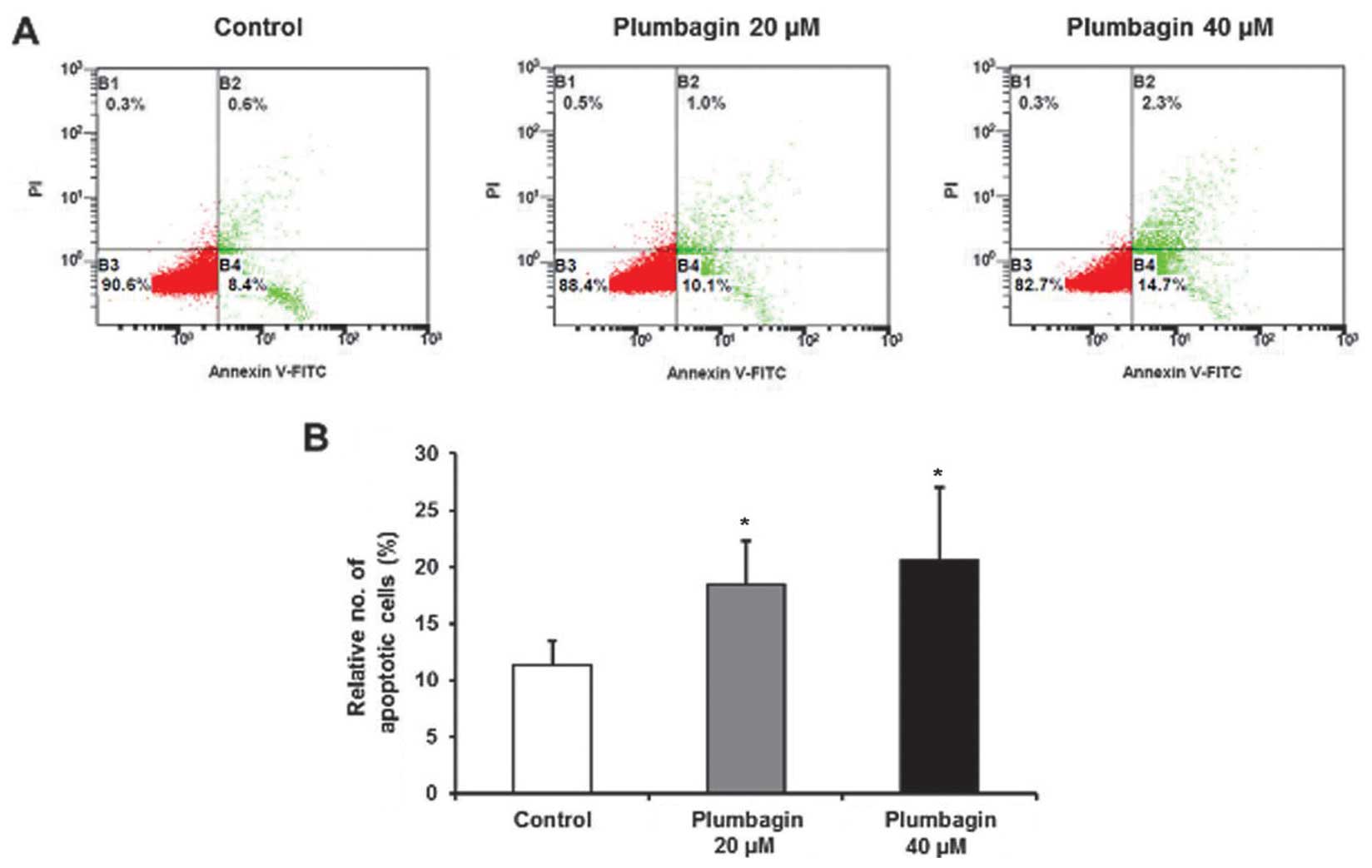
|
1
|
Sandur SK, Ichikawa H, Sethi G, Ahn KS and
Aggarwal BB: Plumbagin (5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone)
suppresses NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-regulated gene
products through modulation of p65 and IkappaBalpha kinase
activation, leading to potentiation of apoptosis induced by
cytokine and chemotherapeutic agents. J Biol Chem. 281:17023–17033.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sugie S, Okamoto K, Rahman KM, Tanaka T,
Kawai K, Yamahara J and Mori H: Inhibitory effects of plumbagin and
juglone on azoxymethane-induced intestinal carcinogenesis in rats.
Cancer Lett. 127:177–183. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuo PL, Hsu YL and Cho CY: Plumbagin
induces G2-M arrest and autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mammalian
target of rapamycin pathway in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 5:3209–3221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hsu YL, Cho CY, Kuo PL, Huang YT and Lin
CC: Plumbagin (5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A549 cells through p53
accumulation via c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated phosphorylation
at serine 15 in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
318:484–494. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang CC, Chiang YM, Sung SC, Hsu YL, Chang
JK and Kuo PL: Plumbagin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
through reactive oxygen species/c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways in
human melanoma A375.S2 cells. Cancer Lett. 259:82–98. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Powolny AA and Singh SV: Plumbagin-induced
apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells is associated with
modulation of cellular redox status and generation of reactive
oxygen species. Pharm Res. 25:2171–2180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hafeez BB, Jamal MS, Fischer JW, Mustafa A
and Verma AK: Plumbagin, a plant derived natural agent inhibits the
growth of pancreatic cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo via
targeting EGFR, Stat3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int J Cancer.
131:2175–2186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Manu KA, Shanmugam MK, Rajendran P, Li F,
Ramachandran L, Hay HS, Kannaiyan R, Swamy SN, Vali S, Kapoor S, et
al: Plumbagin inhibits invasion and migration of breast and gastric
cancer cells by downregulating the expression of chemokine receptor
CXCR4. Mol Cancer. 10:1072011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Shen L, Lu FR, Qin Y, Chen R, Li J,
Li Y, Zhan HZ and He YQ: Plumbagin inhibits cell growth and
potentiates apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells in vitro
through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
33:242–249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sung B and Aggarwal
BB: 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, a vitamin K3 analogue,
suppresses STAT3 activation pathway through induction of protein
tyrosine phosphatase, SHP-1: Potential role in chemosensitization.
Mol Cancer Res. 8:107–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Z, Lee H, Lee E, Kang SK, Nam JM and
Lee M: Responsive nematic gels from the self-assembly of aqueous
nanofibres. Nat Commun. 2:4592011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dallol A, Agathanggelou A, Tommasi S,
Pfeifer GP, Maher ER and Latif F: Involvement of the RASSF1A tumor
suppressor gene in controlling cell migration. Cancer Res.
65:7653–7659. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiong H, Chen ZF, Liang QC, Du W, Chen HM,
Su WY, Chen GQ, Han ZG and Fang JY: Inhibition of DNA
methyl-transferase induces G2 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
human colorectal cancer cells via inhibition of JAK2/STAT3/STAT5
signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 13:3668–3679. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lin MT, Lin BR, Chang CC, Chu CY, Su HJ,
Chen ST, Jeng YM and Kuo ML: IL-6 induces AGS gastric cancer cell
invasion via activation of the c-Src/RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway.
Int J Cancer. 120:2600–2608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu BH, Chen HY, Zhan WH, Wang CY, Cai SR,
Wang Z, Zhang CH and He YL: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits
VEGF expression induced by IL-6 via Stat3 in gastric cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 17:2315–2325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rhee YH, Jeong SJ, Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Koh W,
Jung JH, Kim SH and Sung-Hoon K: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling and
induction of SHP1 mediate antiangiogenic and antitumor activities
of ergosterol peroxide in U266 multiple myeloma cells. BMC Cancer.
12:282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JH, Chiang SY, Nam D, Chung WS, Lee J,
Na YS, Sethi G and Ahn KS: Capillarisin inhibits constitutive and
inducible STAT3 activation through induction of SHP-1 and SHP-2
tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett. 345:140–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jackson CB and Giraud AS: STAT3 as a
prognostic marker in human gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:505–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim JA, Lee EK, Park SJ, Kim ND, Hyun DH,
Lee CG, Lee JH, Yang KM, Heo K and Son TG: Novel anti-cancer role
of naphthazarin in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
40:157–162. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Wang J, Lin L, He L, Wu Y, Zhang
L, Yi Z, Chen Y, Pang X and Liu M: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling
pathway by nitidine chloride suppressed the angiogenesis and growth
of human gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:277–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jia Y, Liu D, Xiao D, Ma X, Han S, Zheng
Y, Sun S, Zhang M, Gao H, Cui X, et al: Expression of AFP and STAT3
is involved in arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis and inhibition of
proliferation in AFP-producing gastric cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e547742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim MJ, Nam HJ, Kim HP, Han SW, Im SA, Kim
TY, Oh DY and Bang YJ: OPB-31121, a novel small molecular
inhibitor, disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and exhibits an
antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
335:145–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katsha A, Arras J, Soutto M, Belkhiri A
and El-Rifai W: AURKA regulates JAK2-STAT3 activity in human
gastric and esophageal cancers. Mol Oncol. 8:1419–1428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
López-Ruiz P, Rodriguez-Ubreva J, Cariaga
AE, Cortes MA and Colás B: SHP-1 in cell-cycle regulation.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:89–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Somani AK and Siminovitch KA:
Roles of the SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase in the negative regulation
of cell signalling. Semin Immunol. 12:361–378. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu C, Sun M, Liu L and Zhou GW: The
function of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in cancer. Gene.
306:1–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han Y, Amin HM, Franko B, Frantz C, Shi X
and Lai R: Loss of SHP1 enhances JAK3/STAT3 signaling and decreases
proteosome degradation of JAK3 and NPM-ALK in ALK+ anaplastic
large-cell lymphoma. Blood. 108:2796–2803. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oka T, Ouchida M, Koyama M, Ogama Y,
Takada S, Nakatani Y, Tanaka T, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Ohara N, et
al: Gene silencing of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP1 gene by
aberrant methylation in leukemias/lymphomas. Cancer Res.
62:6390–6394. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koyama M, Oka T, Ouchida M, Nakatani Y,
Nishiuchi R, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Akagi T and Seino Y: Activated
proliferation of B-cell lymphomas/leukemias with the SHP1 gene
silencing by aberrant CpG methylation. Lab Invest. 83:1849–1858.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chim CS, Fung TK, Cheung WC, Liang R and
Kwong YL: SOCS1 and SHP1 hypermethylation in multiple myeloma:
Implications for epigenetic activation of the Jak/STAT pathway.
Blood. 103:4630–4635. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ruchusatsawat K, Wongpiyabovorn J,
Shuangshoti S, Hirankarn N and Mutirangura A: SHP-1 promoter 2
methylation in normal epithelial tissues and demethylation in
psoriasis. J Mol Med (Berl). 84:175–182. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bernal C, Aguayo F, Villarroel C, Vargas
M, Díaz I, Ossandon FJ, Santibáñez E, Palma M, Aravena E,
Barrientos C, et al: Reprimo as a potential biomarker for early
detection in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6264–6269. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ksiaa F, Ziadi S, Amara K, Korbi S and
Trimeche M: Biological significance of promoter hypermethylation of
tumor-related genes in patients with gastric carcinoma. Clin Chim
Acta. 404:128–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giraud AS, Menheniott TR and Judd LM:
Targeting STAT3 in gastric cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:889–901. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Souma Y, Nishida T, Serada S, Iwahori K,
Takahashi T, Fujimoto M, Ripley B, Nakajima K, Miyazaki Y, Mori M,
et al: Antiproliferative effect of SOCS-1 through the suppression
of STAT3 and p38 MAPK activation in gastric cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 131:1287–1296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Inagaki-Ohara K, Mayuzumi H, Kato S,
Minokoshi Y, Otsubo T, Kawamura YI, Dohi T, Matsuzaki G and
Yoshimura A: Enhancement of leptin receptor signaling by SOCS3
deficiency induces development of gastric tumors in mice. Oncogene.
33:74–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tenev T, Böhmer SA, Kaufmann R, Frese S,
Bittorf T, Beckers T and Böhmer FD: Perinuclear localization of the
protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 and inhibition of epidermal
growth factor-stimulated STAT1/3 activation in A431 cells. Eur J
Cell Biol. 79:261–271. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim H and Baumann H: Dual signaling role
of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in regulating expression
of acute-phase plasma proteins by interleukin-6 cytokine receptors
in hepatic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 19:5326–5338. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gunaje JJ and Bhat GJ: Involvement of
tyrosine phosphatase PTP1D in the inhibition of
interleukin-6-induced Stat3 signaling by alpha-thrombin. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 288:252–257. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Irie-Sasaki J, Sasaki T, Matsumoto W,
Opavsky A, Cheng M, Welstead G, Griffiths E, Krawczyk C, Richardson
CD, Aitken K, et al: CD45 is a JAK phosphatase and negatively
regulates cytokine receptor signalling. Nature. 409:349–354. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee IO, Kim JH, Choi YJ, Pillinger MH, Kim
SY, Blaser MJ and Lee YC: Helicobacter pylori CagA phosphorylation
status determines the gp130-activated SHP2/ERK and JAK/STAT signal
transduction pathways in gastric epithelial cells. J Biol Chem.
285:16042–16050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jiang J, Jin MS, Kong F, Wang YP, Jia ZF,
Cao DH, Ma HX, Suo J and Cao XY: Increased expression of tyrosine
phosphatase SHP-2 in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:575–580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim JS, Shin OR, Kim HK, Cho YS, An CH,
Lim KW and Kim SS: Overexpression of protein phosphatase
non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) in gastric carcinomas. Dig Dis Sci.
55:1565–1569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jiménez DJ, Montaña JS, Alvarez D and
Baena S: A novel cold active esterase derived from Colombian high
Andean forest soil metagenome. World J Microbiol Biotechnol.
28:361–370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gu X, Cun Y, Li M, Qing Y, Jin F, Zhong Z,
Dai N, Qian C, Sui J and Wang D: Human apurinic/apyrimidinic
endonuclease siRNA inhibits the angiogenesis induced by X-ray
irradiation in lung cancer cells. Int J Med Sci. 10:870–882. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
McTavish N, Copeland LA, Saville MK,
Perkins ND and Spruce BA: Proenkephalin assists stress-activated
apoptosis through transcriptional repression of NF-kappaB- and
p53-regulated gene targets. Cell Death Differ. 14:1700–1710. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Takei Y, Kadomatsu K, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S
and Muramatsu T: A small interfering RNA targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res.
64:3365–3370. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rivera MN, Kim WJ, Wells J, Stone A,
Burger A, Coffman EJ, Zhang J and Haber DA: The tumor suppressor
WTX shuttles to the nucleus and modulates WT1 activity. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:8338–8343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|