|
1
|
The World Health Organization. Cancer,
Fact Sheet No. 297. February. 2014
|
|
2
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer. Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence
worldwide in 2012. Globocan 2012. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Gupta SC, Sundaram C, Reuter S and
Aggarwal BB: Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a
therapeutic strategy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:775–787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo JL, Kamata H and Karin M:
IKK/NF-kappaB signaling: balancing life and death - a new approach
to cancer therapy. J Clin Invest. 115:2625–2632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kozakai N, Kikuchi E, Hasegawa M, Suzuki
E, Ide H, Miyajima A, Horiguchi Y, Nakashima J, Umezawa K,
Shigematsu N and Oya M: Enhancement of radiosensitivity by a unique
novel NF-κB inhibitor, DHMEQ, in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer.
107:652–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun XF and Zhang H: NFκB and NFκBI
polymorphisms in relation to susceptibility of tumour and other
diseases. Histol Histopathol. 22:1387–1398. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
St-Germain ME, Gagnon V, Parent S and
Asselin E: Regulation of COX-2 protein expression by Akt in
endometrial cancer cells is mediated through NF-kappaB/IkappaB
pathway. Mol Cancer. 3:1–11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Monks NR and Pardee AB: Targeting the
NF-kappa B pathway in estrogen receptor negative MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells using small inhibitory RNAs. J Cell Biochem.
98:221–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jang BC, Sanchez T, Schaefers HJ, Trifan
OC, Liu CH, Creminon C, Huang CK and Hla T: Serum
withdrawal-induced post-transcriptional stabilization of
cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in MDA-MB-231 mammary carcinoma cells
requires the activity of the p38 stress-activated protein kinase. J
Biol Chem. 275:39507–39515. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karin M, Yamamoto Y and Wang QM: The IKK
NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 3:17–26. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Orlowski RZ and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB
as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 8:385–389. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY,
Pestell RG and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB controls cell growth and
differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:5785–5799. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dannenberg AJ, Altorki NK, Boyle JO, Dang
C, Howe LR, Weksler BB and Subbaramaiah K: Cyclo-oxygenase 2: a
pharmacological target for the prevention of cancer. Lancet Oncol.
2:544–551. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Thun MJ, Henley SJ and Patrono C:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as anticancer agents:
mechanistic, pharmacologic, and clinical issues. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 94:252–266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu B, Shi ZL, Feng J and Tao HM:
Celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, induces apoptosis in human
osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 via down-regulation of PI3K/Akt. Cell
Biol Int. 32:494–501. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Leng J, Han C, Demetris AJ, Michalopoulos
GK and Wu T: Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
cell growth through Akt activation: evidence for Akt inhibition in
celecoxib-induced apoptosis. Hepatology. 38:756–768. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Half E, Sun Y and Sinicrope FA: Anti-EGFR
and ErbB-2 antibodies attenuate cyclooxygenase-2 expression and
cooperatively inhibit survival of human colon cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 251:237–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Park MK, Hwang SY, Kim JO, Kwack MH, Kim
JC, Kim MK and Sung YK: NS398 inhibits the growth of Hep3B human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via caspase-independent apoptosis.
Mol Cells. 17:45–50. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reddy L, Odhav B and Bhoola KD: Natural
products for cancer prevention: a global perspective. Pharmacol
Ther. 99:1–13. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giovino GA: The tobacco epidemic in the
United States. Am J Prev Med. 33:S318–S326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aggarwal BB and Shishodia S: Molecular
targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 71:1397–1421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boileau TW, Liao Z, Kim S, Lemeshow S,
Erdman JW Jr and Clinton SK: Prostate carcinogenesis in
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (NMU)-testosterone-treated rats fed tomato
powder, lycopene, or energy-restricted diets. J Natl Cancer Inst.
95:1578–1586. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Halicka D, Ita M, Tanaka T, Kurose A and
Darzynkiewicz Z: Biscoclaurine alkaloid cepharanthine protects DNA
in TK6 lymphoblastoid cells from constitutive oxidative damage.
Pharmacol Rep. 60:93–100. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kikukawa Y, Okuno Y, Tatetsu H, Nakamura
M, Harada N, Ueno S, Kamizaki Y, Mitsuya H and Hata H: Induction of
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in myeloma cells by cepharanthine,
a biscoclaurine alkaloid. Int J Oncol. 33:807–814. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meng LH, Zhang H, Hayward L, Takemura H,
Shao RG and Pommier Y: Tetrandrine induces early G1 arrest in human
colon carcinoma cells by down-regulating the activity and inducing
the degradation of G1-S-specific cyclin-dependent kinases and by
inducing p53 and p21Cip1. Cancer Res. 64:9086–9092.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park D-H, Xu HD, Shim J, Li Y-C, Lee J-H,
Cho S-C, Han S-S, Lee Y-L, Lee M-J and Kwon S-W: Stephania delavayi
Diels. inhibits breast carcinoma proliferation through the p38MAPK/
NF-κB/COX-2 pathway. Oncol Rep. 26:833–841. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nawawi A, Nakamura N, Meselhy MR, Hattori
M, Kurokawa M, Shiraki K, Kashiwaba N and Ono M: In vivo antiviral
activity of Stephania cepharantha against herpes simplex virus
type-1. Phytother Res. 15:497–500. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma CM, Nakamura N, Hattori M, Kawahata T
and Otake T: Inhibitory effects of triterpene-azidothymidine
conjugates on proliferation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
and its protease. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 50:877–880. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ma CM, Nakamura N, Miyashiro H, Hattori M,
Komatsu K, Kawahata T and Otake T: Screening of Chinese and
Mongolian herbal drugs for anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1
(HIV-1) activity. Phytother Res. 16:186–189. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Baba M: Inhibitors of HIV-1 gene
expression and transcription. Curr Top Med Chem. 4:871–882. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu WK, Wang XK and Che CT: Cytotoxic
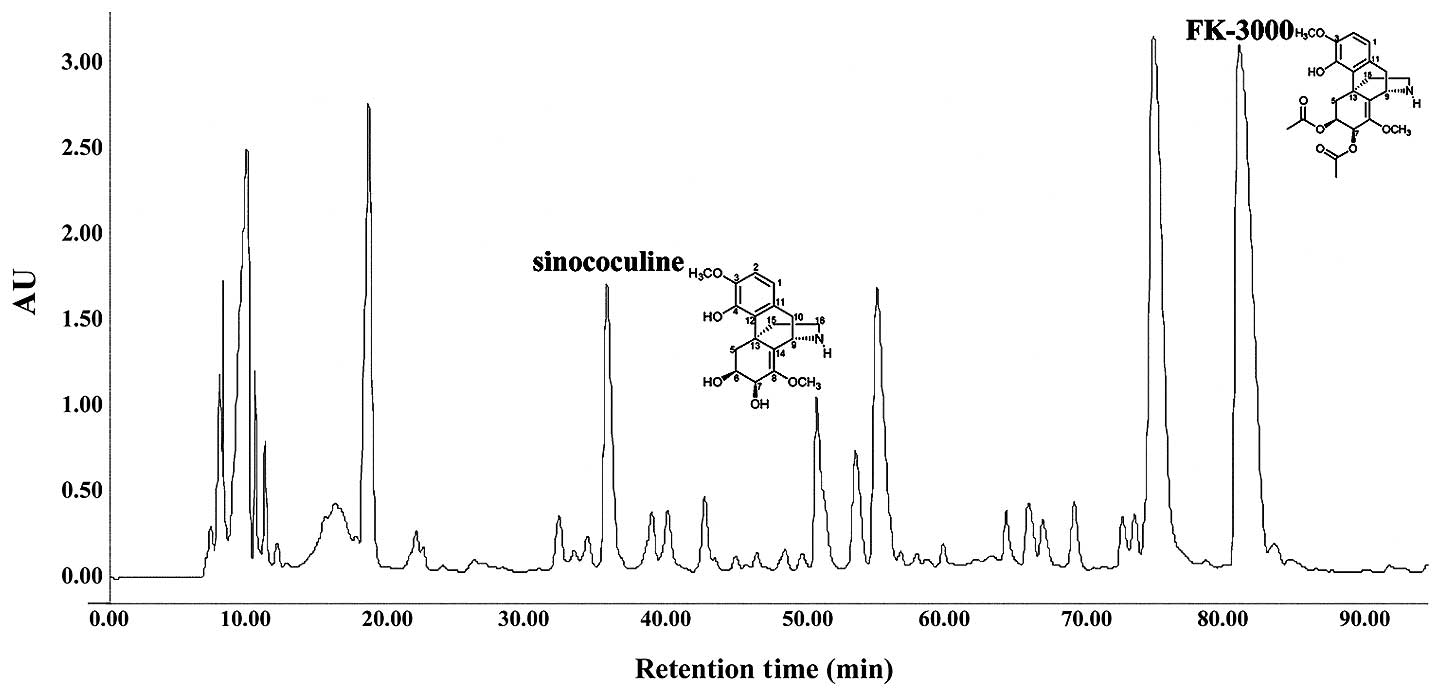
effects of sinococuline. Cancer Lett. 99:217–224. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carraz M, Jossang A, Rasoanaivo P, Mazier
D and Frappier F: Isolation and antimalarial activity of new
morphinan alkaloids on Plasmodium yoelii liver stage. Bioorg Med
Chem. 16:6186–6192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nawawi A, Ma C, Nakamura N, Hattori M,
Kurokawa M, Shiraki K, Kashiwaba N and Ono M: Anti-herpes simplex
virus activity of alkaloids isolated from Stephania cepharantha.
Biol Pharm Bull. 22:268–274. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Itokawa H, Tsuruoka S, Takeya K, Mori N,
Sonobe T, Kosemura S and Hamanaka T: An antitumor morphinane
alkaloid, sinococuline, from Cocculus trilobus. Chem Pharm Bull.
35:1660–1662. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chinembiri TN, du Plessis LH, Gerber M,
Hamman JH and du Plessis J: Review of natural compounds for
potential skin cancer treatment. Molecules. 19:11679–11721. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nesaretnam K and Meganathan P:
Tocotrienols: inflammation and cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1229:18–22.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ganguly A, Yang H and Cabral F:
Paclitaxel-dependent cell lines reveal a novel drug activity. Mol
Cancer Ther. 9:2914–2923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ghosh R, Garcia GE, Crosby K, Inoue H,
Thompson IM, Troyer DA and Kumar AP: Regulation of Cox-2 by cyclic
AMP response element binding protein in prostate cancer: potential
role for nexrutine. Neoplasia. 9:893–899. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kumar AP, Bhaskaran S, Ganapathy M, Crosby
K, Davis MD, Kochunov P, Schoolfield J, Yeh IT, Troyer DA and Ghosh
R: Akt/ cAMP-responsive element binding protein/cyclin D1 network:
a novel target for prostate cancer inhibition in transgenic
adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate model mediated by Nexrutine, a
Phellodendron amurense bark extract. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2784–2794.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
van Hogerlinden M, Rozell BL,
Ahrlund-Richter L and Toftgard R: Squamous cell carcinomas and
increased apoptosis in skin with inhibited Rel/nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer Res. 59:3299–3303. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miyamoto S, Maki M, Schmitt MJ, Hatanaka M
and Verma IM: Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation
of I kappa B alpha is a signal for its degradation but not
dissociation from NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:12740–12744. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang G, Yu F, Fu H, Lu F, Huang B, Bai L,
Zhao Z, Yao L and Lu Z: Identification of the distinct promoters
for the two transcripts of apoptosis related protein 3 and their
transcriptional regulation by NFAT and NFkappaB. Mol Cell Biochem.
302:187–194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Herrmann JL, Beham AW, Sarkiss M, Chiao
PJ, Rands MT, Bruckheimer EM, Brisbay S and McDonnell TJ: Bcl-2
suppresses apoptosis resulting from disruption of the NF-kappa B
survival pathway. Exp Cell Res. 237:101–109. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Notarbartolo M, Poma P, Perri D, Dusonchet
L, Cervello M and D’Alessandro N: Antitumor effects of curcumin,
alone or in combination with cisplatin or doxorubicin, on human
hepatic cancer cells. Analysis of their possible relationship to
changes in NF-κB activation levels and in IAP gene expression.
Cancer Lett. 224:53–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV
and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and
TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation.
Science. 281:1680–1683. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bian X, McAllister-Lucas LM, Shao F,
Schumacher KR, Feng Z, Porter AG, Castle VP and Opipari AW Jr:
NF-kappa B activation mediates doxorubicin-induced cell death in
N-type neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 276:48921–48929. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR and Vousden KH:
Role of NF-kappaB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature.
404:892–897. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chan FK, Hung LC, Suen BY, Wu JC, Lee KC,
Leung VK, Hui AJ, To KF, Leung WK, Wong VW, Chung SC and Sung JJ:
Celecoxib versus diclofenac and omeprazole in reducing the risk of
recurrent ulcer bleeding in patients with arthritis. N Engl J Med.
347:2104–2110. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|