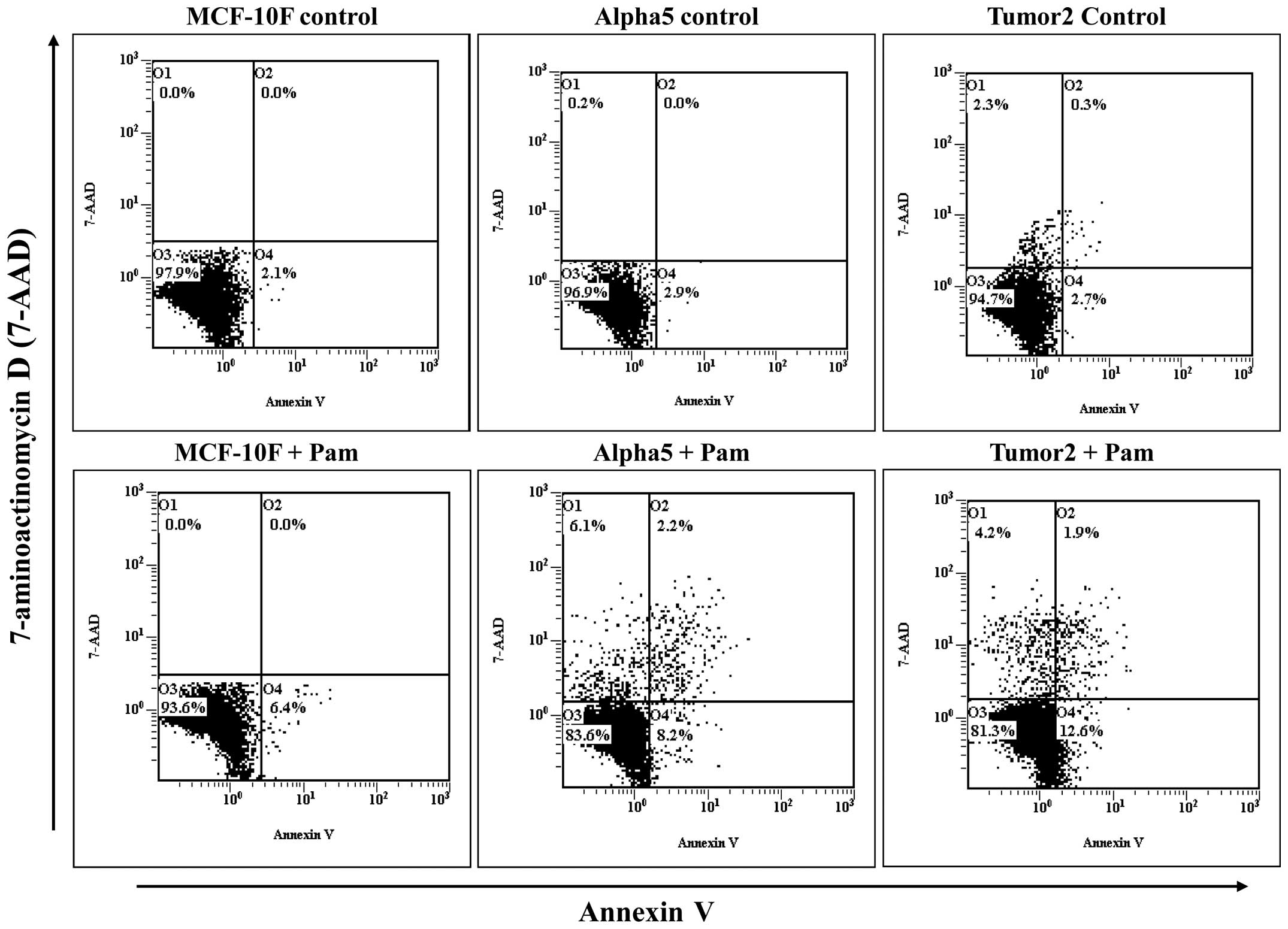
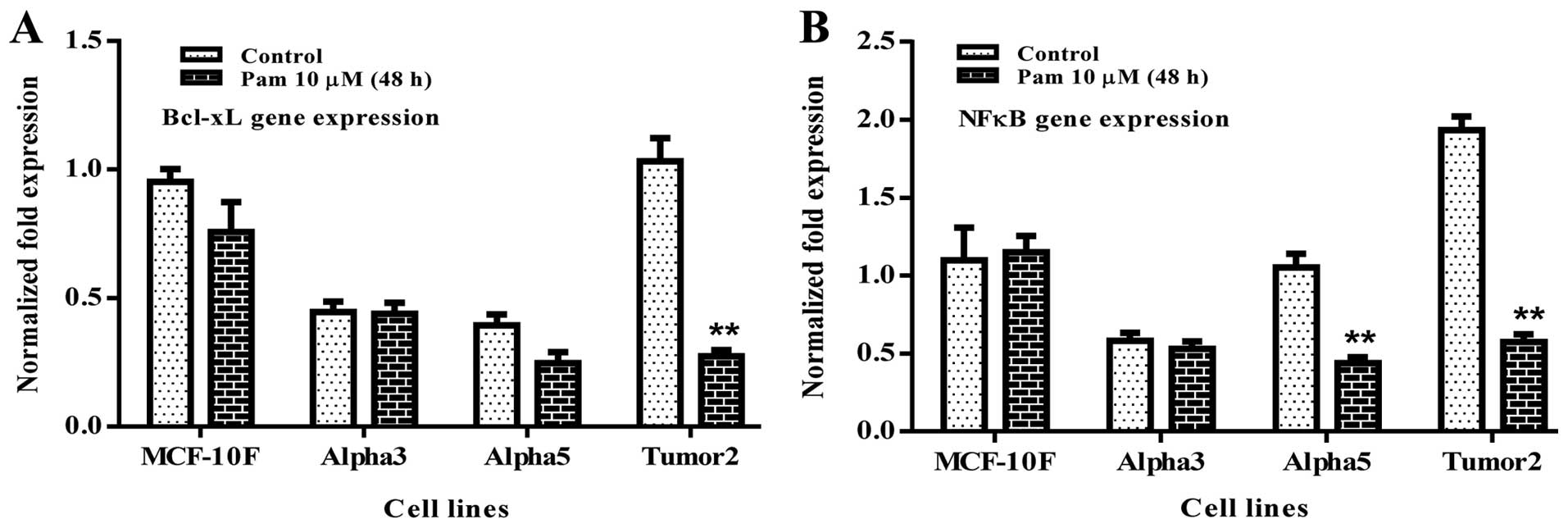
|
1
|
Hall A: The cellular functions of small
GTP-binding proteins. Science. 249:635–640. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ridley AJ and Hall A: The small
GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions
and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell.
70:389–399. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL,
Diekmann D and Hall A: The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates
growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 70:401–410. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lane DP: Cancer p53, guardian of the
genome. Nature. 358:15–16. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gatto M, Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A, Bassi
N, Pontisso P, Punzi L, Shoenfeld Y and Doria A: Serpins, immunity
and autoimmunity: Old molecules, new functions. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 45:267–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hnasko R and Lisanti MP: The biology of
caveolae: Lessons from caveolin knockout mice and implications for
human disease. Mol Interv. 3:445–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Witkiewicz AK, Dasgupta A, Sammons S, Er
O, Potoczek MB, Guiles F, Sotgia F, Brody JR, Mitchell EP and
Lisanti MP: Loss of stromal caveolin-1 expression predicts poor
clinical outcome in triple negative and basal-like breast cancers.
Cancer Biol Ther. 10:135–143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sotgia F, Schubert W, Pestell RG and
Lisanti MP: Genetic ablation of caveolin-1 in mammary epithelial
cells increases milk production and hyper-activates STAT5a
signaling. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:292–297. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Williams TM, Sotgia F, Lee H, Hassan G, Di
Vizio D, Bonuccelli G, Capozza F, Mercier I, Rui H, Pestell RG, et
al: Stromal and epithelial caveolin-1 both confer a protective
effect against mammary hyperplasia and tumorigenesis: Caveolin-1
antagonizes cyclin D1 function in mammary epithelial cells. Am J
Pathol. 169:1784–1801. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis mechanisms:
Implications for cancer drug discovery. Oncology (Williston Park).
18(Suppl 10): 11–20. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sethi G, Ahn KS and Aggarwal BB: Targeting
nuclear factor-kappa B activation pathway by thymoquinone: Role in
suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and enhancement of
apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1059–1070. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-κB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Arch. 446:475–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shipman R, Schraml P, Moch H, Colombi M,
Sauter G, Mihatsch M and Ludwig C: p53 protein accumulation and p53
gene alterations (RFLP, VNTR and p53 gene mutations) in
non-invasive versus invasive human transitional bladder cancer. Int
J Oncol. 10:801–806. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Donehower LA, Godley LA, Aldaz CM, Pyle R,
Shi YP, Pinkel D, Gray J, Bradley A, Medina D and Varmus HE: The
role of p53 loss in genomic instability and tumor progression in a
murine mammary cancer model. Prog Clin Biol Res. 395:1–11.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Calaf GM and Hei TK: Establishment of a
radiation- and estrogen-induced breast cancer model.
Carcinogenesis. 21:769–776. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wada A, Fukui K, Sawai Y, Imanaka K, Kiso
S, Tamura S, Shimomura I and Hayashi N: Pamidronate induced
anti-proliferative, apoptotic, and anti-migratory effects in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 44:142–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Clemons MJ, Dranitsaris G, Ooi WS,
Yogendran G, Sukovic T, Wong BY, Verma S, Pritchard KI, Trudeau M
and Cole DE: Phase II trial evaluating the palliative benefit of
second-line zoledronic acid in breast cancer patients with either a
skeletal-related event or progressive bone metastases despite
first-line bisphosphonate therapy. J Clin Oncol. 24:4895–4900.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Riebeling C, Forsea AM, Raisova M, Orfanos
CE and Geilen CC: The bisphosphonate pamidronate induces apoptosis
in human melanoma cells in vitro. Br J Cancer. 87:366–371. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang PL, Lun M, Siegelmann-Danieli N,
Blasick TM and Brown RE: Pamidronate resistance and associated low
ras levels in breast cancer cells: A role for combinatorial
therapy. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 34:263–270. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang PL, Quiery AT Jr, Blasick TM and
Brown RE: Morpho-proteomic expression of H-ras (p21ras) correlates
with serum monoclonal immunoglobulin reduction in multiple myeloma
patients following pamidronate treatment. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
37:34–38. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nguyen DH, Catling AD, Webb DJ, Sankovic
M, Walker LA, Somlyo AV, Weber MJ and Gonias SL: Myosin light chain
kinase functions downstream of Ras/ERK to promote migration of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator-stimulated cells in an
integrin-selective manner. J Cell Biol. 146:149–164. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oxford G and Theodorescu D: Ras
superfamily monomeric G proteins in carcinoma cell motility. Cancer
Lett. 189:117–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Caraglia M, D’Alessandro AM, Marra M,
Giuberti G, Vitale G, Viscomi C, Colao A, Prete SD, Tagliaferri P,
Tassone P, et al: The farnesyl transferase inhibitor R115777
(Zarnestra) synergistically enhances growth inhibition and
apoptosis induced on epidermoid cancer cells by Zoledronic acid
(Zometa) and Pamidronate. Oncogene. 23:6900–6913. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Congote LF and Temmel N: The C-terminal
26-residue peptide of serpin A1 stimulates proliferation of breast
and liver cancer cells: Role of protein kinase C and CD47. FEBS
Lett. 576:343–347. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aparicio A, Gardner A, Tu Y, Savage A,
Berenson J and Lichtenstein A: In vitro cytoreductive effects on
multiple myeloma cells induced by bisphosphonates. Leukemia.
12:220–229. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Senaratne SG, Pirianov G, Mansi JL, Arnett
TR and Colston KW: Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in human breast
cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 82:1459–1468. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|