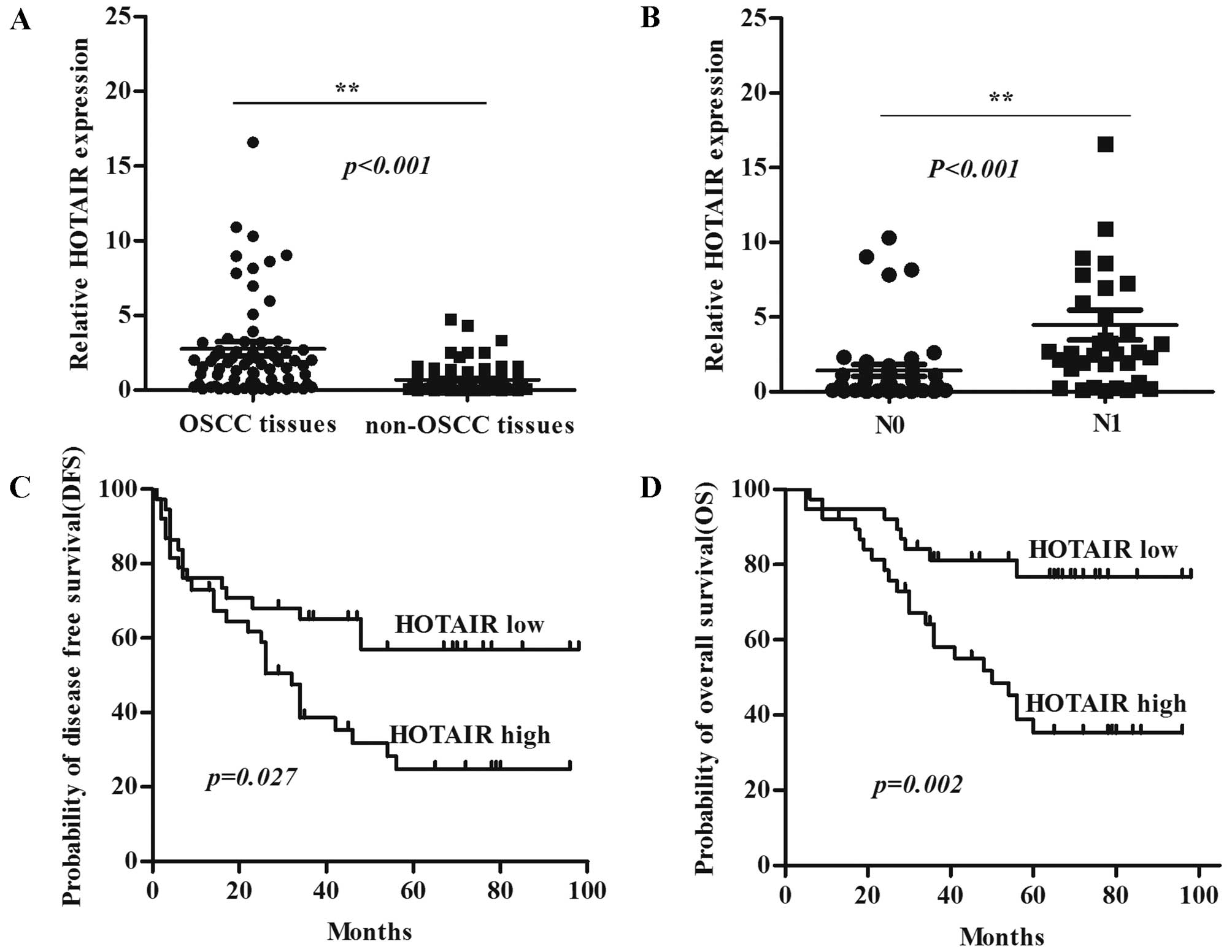
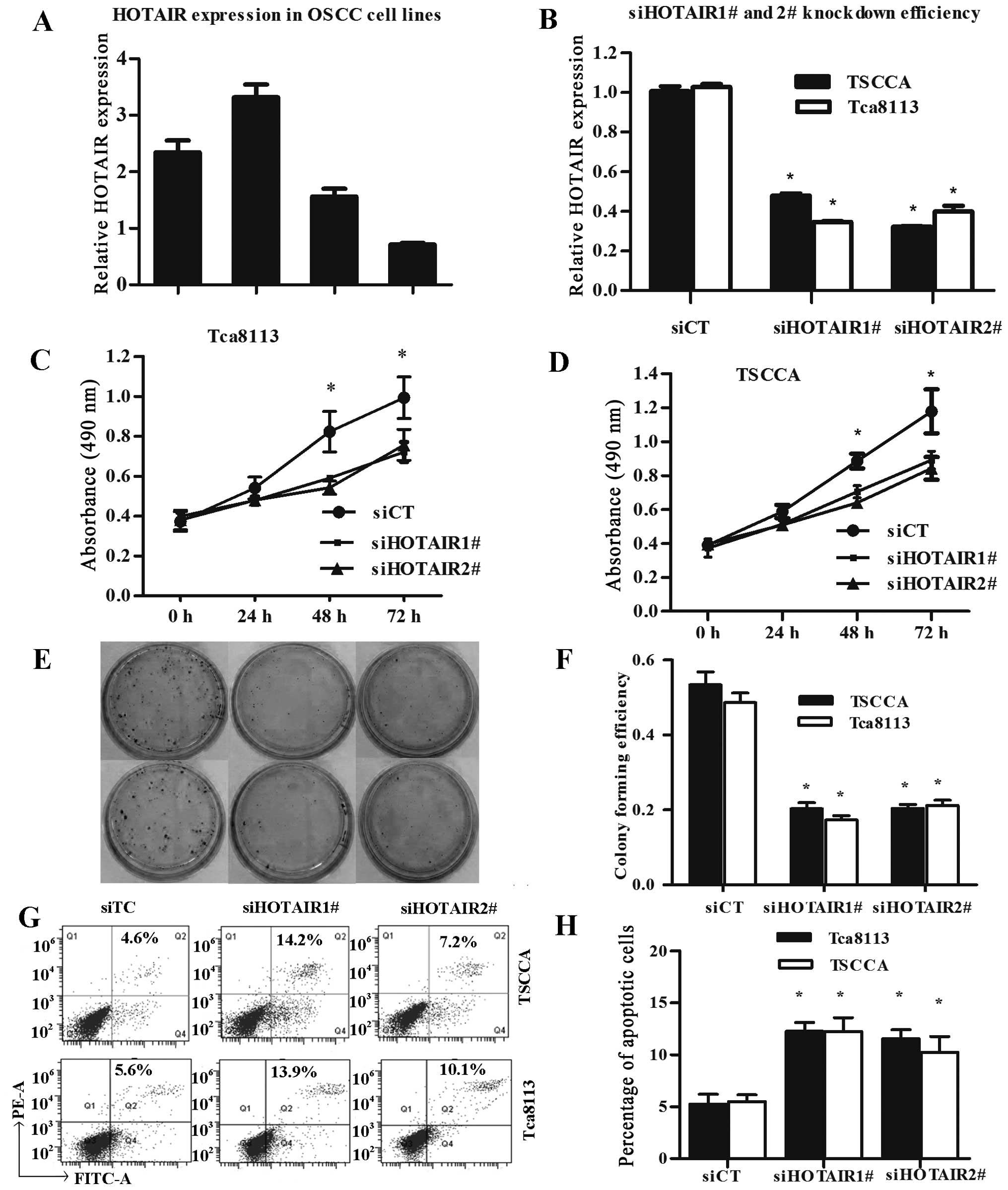
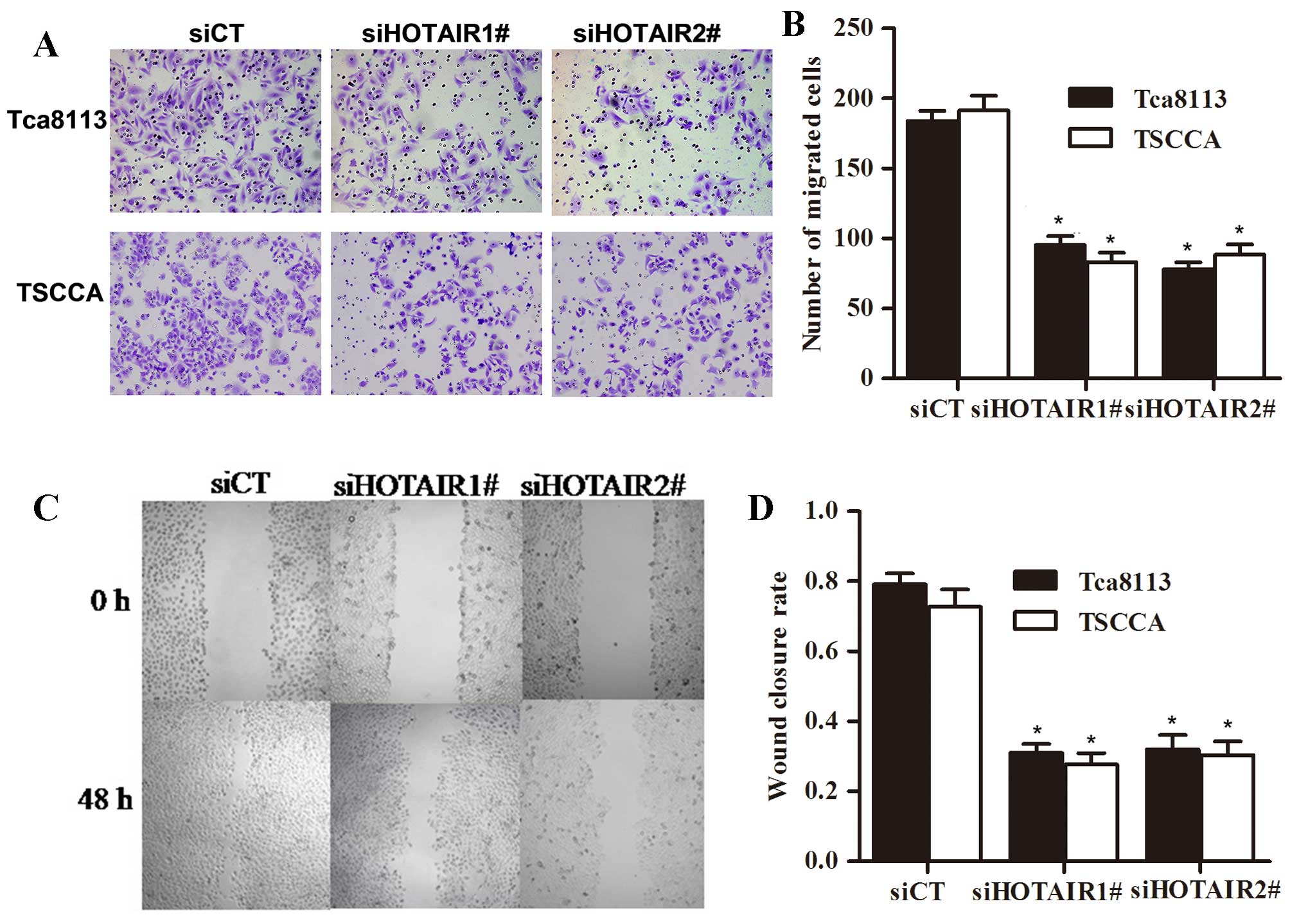
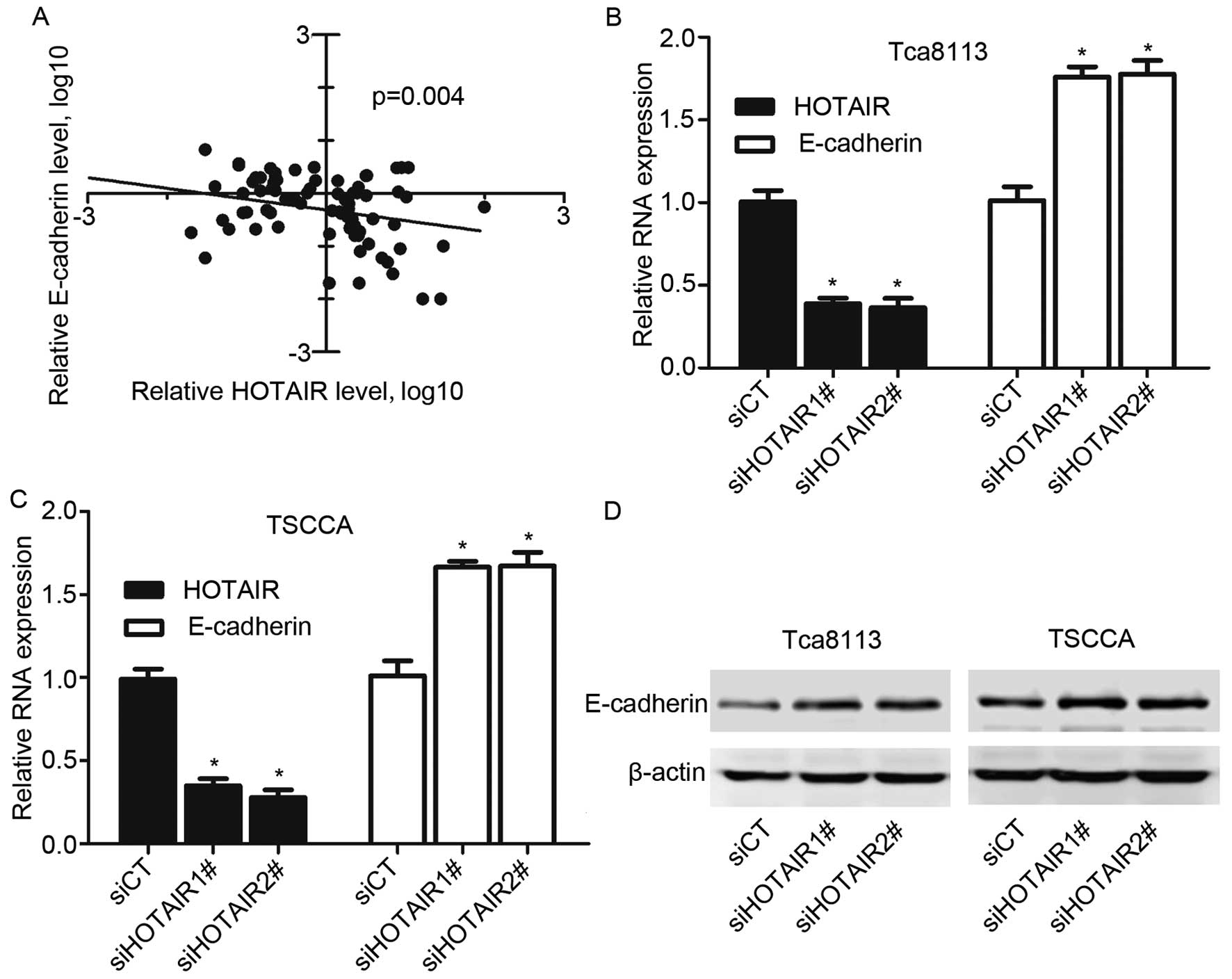
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Molinolo AA, Amornphimoltham P, Squarize
CH, Castilho RM, Patel V and Gutkind JS: Dysregulated molecular
networks in head and neck carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol. 45:324–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Sabour S and Moezizadeh M: Prediction of
OSCC using biomarkers: Methodological mistake. Oral Oncol.
48:e512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Raj LSM, Boaz K and Natarajan S:
Prognostic significance of lymph node pattern in oral squamous cell
carcinoma (OSCC). J Clin Diagn Res. 8:232–235. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Grimm M: Prognostic value of
clinicopathological parameters and outcome in 484 patients with
oral squamous cell carcinoma: Microvascular invasion (V+) is an
independent prognostic factor for OSCC. Clin Transl Oncol.
14:870–880. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JT: Epigenetic regulation by long
noncoding RNAs. Science. 338:1435–1439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kung JT, Colognori D and Lee JT: Long
noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics. 193:651–669.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N,
Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E and Chang HY: Long noncoding RNA as
modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science.
329:689–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E, et
al: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains
in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Woo CJ and Kingston RE: HOTAIR lifts
noncoding RNAs to new levels. Cell. 129:1257–1259. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun L and Fang J: Writer meets eraser in
HOTAIR. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:1–3. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson
G, Frank J, Burghardt R, Kim S and Safe S: HOTAIR is a negative
prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic
cancer. Oncogene. 32:1616–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tang L, Zhang W, Su B and Yu B: Long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR is associated with motility, invasion, and
metastatic potential of metastatic melanoma. BioMed Res Int.
2013:2510982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu XH, Liu ZL, Sun M, Liu J, Wang ZX and
De W: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
13:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ono H, Motoi N, Nagano H, Miyauchi E,
Ushijima M, Matsuura M, Okumura S, Nishio M, Hirose T, Inase N, et
al: Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is relevant to cellular
proliferation, invasiveness, and clinical relapse in small-cell
lung cancer. Cancer Med. 3:632–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Wu Z, Mei Q, Li X, Guo M, Fu X and
Han W: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a driver of malignancy, predicts
negative prognosis and exhibits oncogenic activity in oesophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 109:2266–2278. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qiu JJ, Lin YY, Ye LC, Ding JX, Feng WW,
Jin HY, Zhang Y, Li Q and Hua KQ: Overexpression of long non-coding
RNA HOTAIR predicts poor patient prognosis and promotes tumor
metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
134:121–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen FJ, Sun M, Li SQ, Wu QQ, Ji L, Liu
ZL, Zhou GZ, Cao G, Jin L, Xie HW, et al: Upregulation of the long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
metastasis and poor prognosis. Mol Carcinog. 52:908–915. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bello IO, Soini Y and Salo T: Prognostic
evaluation of oral tongue cancer: Means, markers and perspectives
(I). Oral Oncol. 46:630–635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bhan A, Hussain I, Ansari KI, Bobzean SA,
Perrotti LI and Mandal SS: Bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol
exposure induces the expression of breast cancer associated long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR in vitro and in vivo. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 141:160–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He X, Bao W, Li X, Chen Z, Che Q, Wang H
and Wan XP: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is upregulated in
endometrial carcinoma and correlates with poor prognosis. Int J Mol
Med. 33:325–332. 2014.
|
|
25
|
Zhuang Y, Wang X, Nguyen HT, Zhuo Y, Cui
X, Fewell C, Flemington EK and Shan B: Induction of long intergenic
non-coding RNA HOTAIR in lung cancer cells by type I collagen. J
Hematol Oncol. 6:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nakagawa T, Endo H, Yokoyama M, Abe J,
Tamai K, Tanaka N, Sato I, Takahashi S, Kondo T and Satoh K: Large
noncoding RNA HOTAIR enhances aggressive biological behavior and is
associated with short disease-free survival in human non-small cell
lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:319–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Endo H, Shiroki T, Nakagawa T, Yokoyama M,
Tamai K, Yamanami H, Fujiya T, Sato I, Yamaguchi K, Tanaka N, et
al: Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated
with the development of gastric cancer. PLoS One. 8:e770702013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu ZY, Yu QM, Du YA, Yang LT, Dong RZ,
Huang L, Yu PF and Cheng XD: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR suppresses tumor invasion and reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Int J Biol
Sci. 9:587–597. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hajjari M, Behmanesh M, Sadeghizadeh M and
Zeinoddini M: Up-regulation of HOTAIR long non-coding RNA in human
gastric adenocarcinoma tissues. Med Oncol. 30:6702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ge XS, Ma HJ, Zheng XH, Ruan HL, Liao XY,
Xue WQ, Chen YB, Zhang Y and Jia WH: HOTAIR, a prognostic factor in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, inhibits WIF-1 expression and
activates Wnt pathway. Cancer Sci. 104:1675–1682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li D, Feng J, Wu T, Wang Y, Sun Y, Ren J
and Liu M: Long intergenic noncoding RNA HOTAIR is overexpressed
and regulates PTEN methylation in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 182:64–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Niinuma T, Suzuki H, Nojima M, Nosho K,
Yamamoto H, Takamaru H, Yamamoto E, Maruyama R, Nobuoka T, Miyazaki
Y, et al: Upregulation of miR-196a and HOTAIR drive malignant
character in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Res.
72:1126–1136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu L, Murat P, Matak-Vinkovic D, Murrell A
and Balasubramanian S: Binding interactions between long noncoding
RNA HOTAIR and PRC2 proteins. Biochemistry. 52:9519–9527. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang H, Cai K, Wang J, Wang X, Cheng K,
Shi F, Jiang L, Zhang Y and Dou J: MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by
lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of
breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem
Cells. 32:2858–2868. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pádua Alves C, Fonseca AS, Muys BR, de
Barros E, Lima Bueno R, Bürger MC, de Souza JE, Valente V, Zago MA
and Silva WA Jr: Brief report: The lincRNA Hotair is required for
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of
cancer cell lines. Stem Cells. 31:2827–2832. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang C, Liu X, Chen Z, Huang H, Jin Y,
Kolokythas A, Wang A, Dai Y, Wong DT and Zhou X: Polycomb group
protein EZH2-mediated E-cadherin repression promotes metastasis of
oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 52:229–236.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liu L, Xu Z, Zhong L, Wang H, Jiang S,
Long Q, Xu J and Guo J: EZH2 promotes tumor cell migration and
invasion via epigenetic repression of E-cadherin in renal cell
carcinoma. BJU Int. Feb 25–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sun NX, Ye C, Zhao Q, Zhang Q, Xu C, Wang
SB, Jin ZJ, Sun SH, Wang F and Li W: Long noncoding RNA-EBIC
promotes tumor cell invasion by binding to EZH2 and repressing
E-cadherin in cervical cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1003402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|