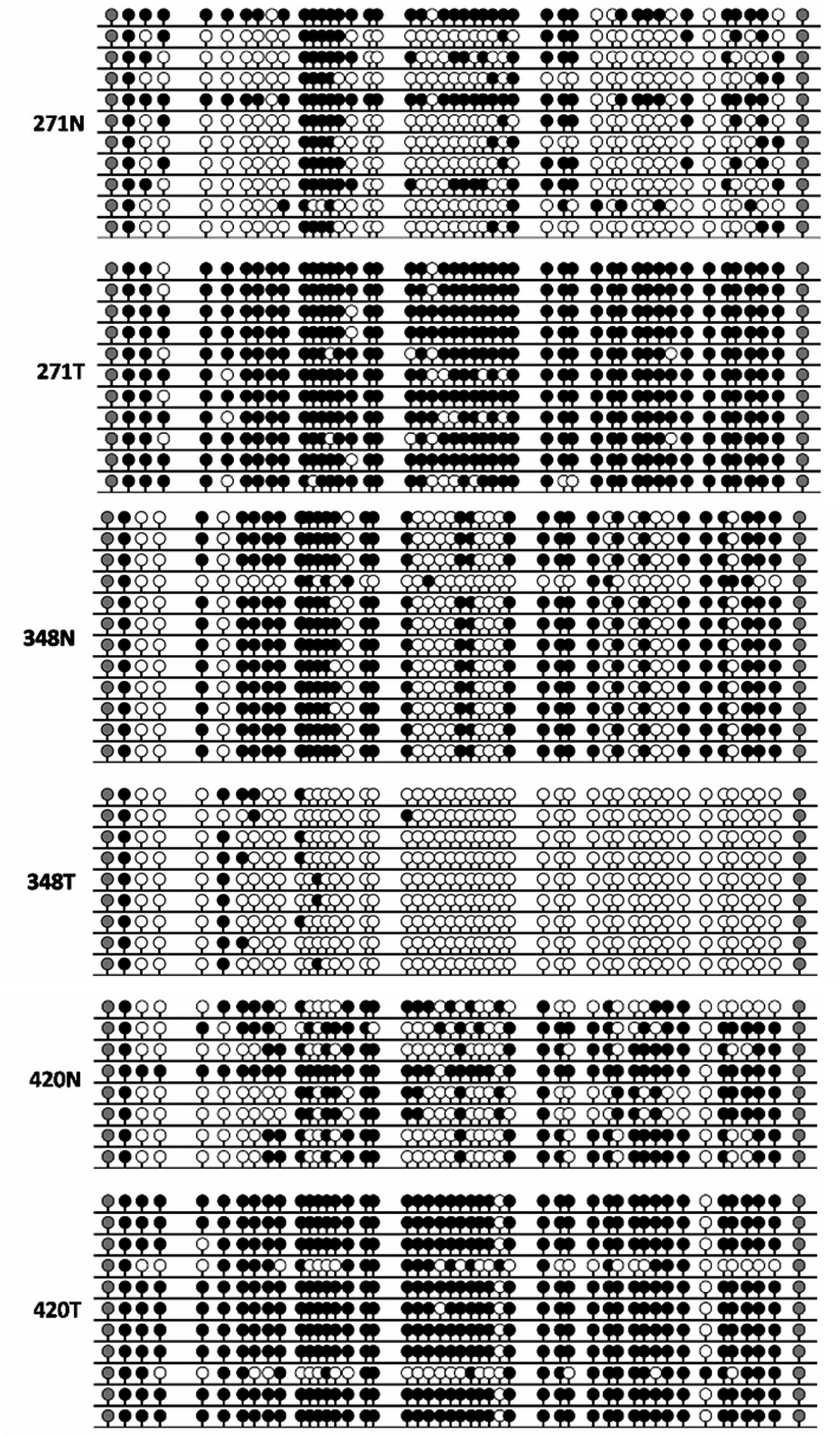
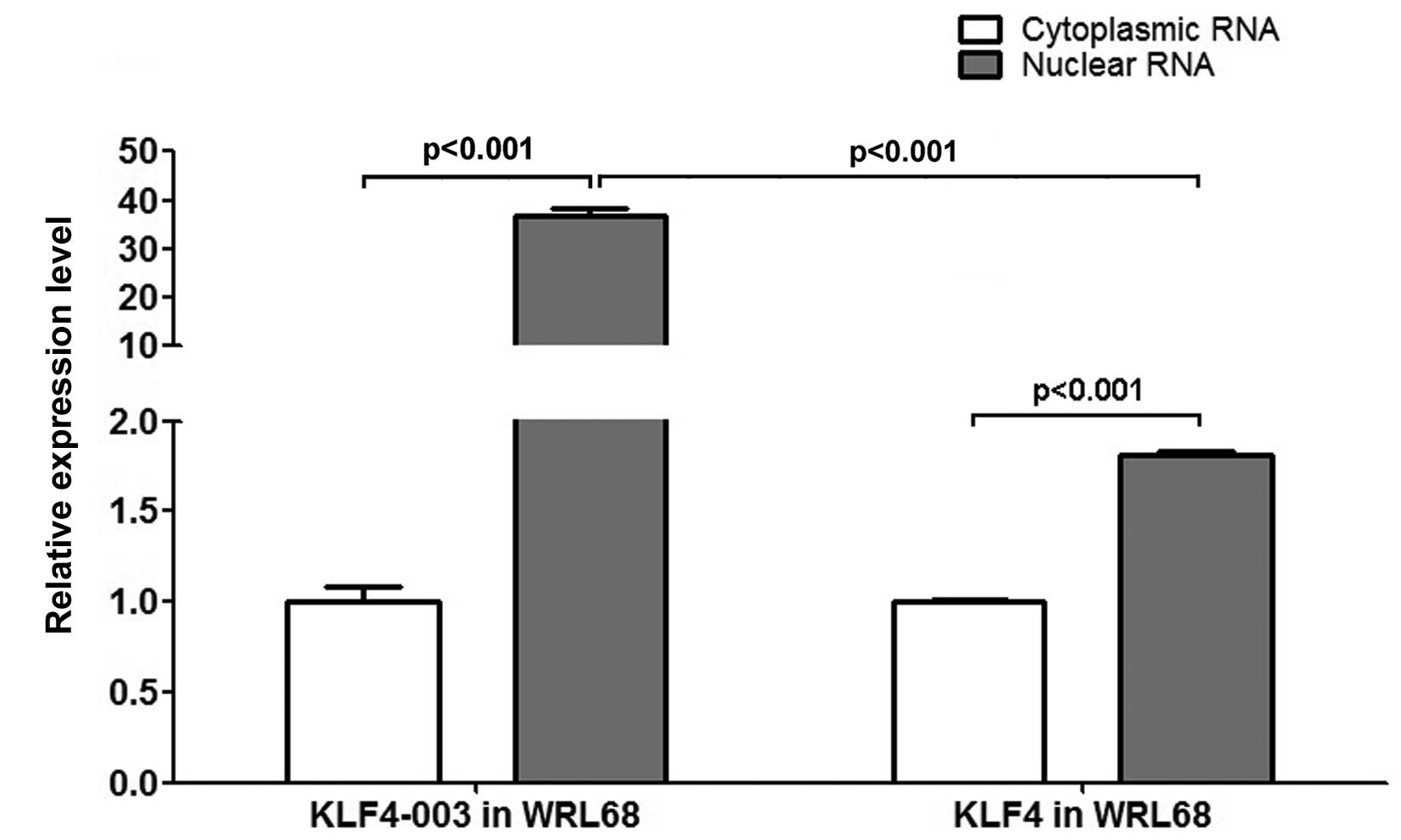
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blum HE: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapy
and prevention. World J Gastroenterol. 11:7391–7400. 2005.
|
|
3
|
Soini Y, Chia SC, Bennett WP, Groopman JD,
Wang JS, DeBenedetti VM, Cawley H, Welsh JA, Hansen C, Bergasa NV,
et al: An aflatoxin-associated mutational hotspot at codon 249 in
the p53 tumor suppressor gene occurs in hepatocellular carcinomas
from Mexico. Carcinogenesis. 17:1007–1012. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Donato F, Tagger A, Gelatti U, Parrinello
G, Boffetta P, Albertini A, Decarli A, Trevisi P, Ribero ML,
Martelli C, et al: Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma: The effect
of lifetime intake and hepatitis virus infections in men and women.
Am J Epidemiol. 155:323–331. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wei D, Wang L, Kanai M, Jia Z, Le X, Li Q,
Wang H and Xie K: KLF4α up-regulation promotes cell cycle
progression and reduces survival time of patients with pancreatic
cancer. Gastroenterology. 139:2135–2145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scherer SW, Cheung J, MacDonald JR,
Osborne LR, Nakabayashi K, Herbrick JA, Carson AR, Parker-Katiraee
L, Skaug J, Khaja R, et al: Human chromosome 7: DNA sequence and
biology. Science. 300:767–772. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, Otsuki T,
Sugiyama T, Irie R, Wakamatsu A, Hayashi K, Sato H, Nagai K, et al:
Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length
human cDNAs. Nat Genet. 36:40–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meltzer PS: Cancer genomics: Small RNAs
with big impacts. Nature. 435:745–746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Erdmann VA, Barciszewska MZ, Szymanski M,
Hochberg A, de Groot N and Barciszewski J: The non-coding RNAs as
riboregulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:189–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O'Neill MJ: The influence of non-coding
RNAs on allele-specific gene expression in mammals. Hum Mol Genet.
14(Suppl 1): R113–R120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steenman MJ, Rainier S, Dobry CJ, Grundy
P, Horon IL and Feinberg AP: Loss of imprinting of IGF2 is linked
to reduced expression and abnormal methylation of H19 in Wilms'
tumour. Nat Genet. 7:433–439. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lottin S, Adriaenssens E, Dupressoir T,
Berteaux N, Montpellier C, Coll J, Dugimont T and Curgy JJ:
Overexpression of an ectopic H19 gene enhances the tumorigenic
properties of breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 23:1885–1895.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Manoharan H, Babcock K, Willi J and Pitot
HC: Biallelic expression of the H19 gene during spontaneous
hepatocarcinogenesis in the albumin SV40 T antigen transgenic rat.
Mol Carcinog. 38:40–47. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hsu HT, Wu PR, Chen CJ, Hsu LS, Yeh CM,
Hsing MT, Chiang YS, Lai MT and Yeh KT: High cytoplasmic expression
of Krüppel-like factor 4 is an independent prognostic factor of
better survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
15:9894–9906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calin GA, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Hyslop T,
Spizzo R, Sevignani C, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Lee EJ, Wojcik SE, et
al: Ultraconserved regions encoding ncRNAs are altered in human
leukemias and carcinomas. Cancer Cell. 12:215–229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsai MC, Spitale RC and Chang HY: Long
intergenic noncoding RNAs: New links in cancer progression. Cancer
Res. 71:3–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, Wang Z, Ding G, Dong
Q, Qin L, Wu X, Zheng Y, Yang Y, et al: Identification of miRNomes
in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p
as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell.
19:232–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji J, Shi J, Budhu A, Yu Z, Forgues M,
Roessler S, Ambs S, Chen Y, Meltzer PS, Croce CM, et al: MicroRNA
expression, survival, and response to interferon in liver cancer. N
Engl J Med. 361:1437–1447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough
J, Frith MC, Maeda N, Oyama R, Ravasi T, Lenhard B, Wells C, et al:
RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group and Genome Science Group
(Genome Network Project Core Group): The transcriptional landscape
of the mammalian genome. Science. 309:1559–1563. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Boyes J and Bird A: DNA methylation
inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein.
Cell. 64:1123–1134. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Compere SJ and Palmiter RD: DNA
methylation controls the inducibility of the mouse
metallothionein-I gene lymphoid cells. Cell. 25:233–240. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kass SU, Landsberger N and Wolffe AP: DNA
methylation directs a time-dependent repression of transcription
initiation. Curr Biol. 7:157–165. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Siegfried Z, Eden S, Mendelsohn M, Feng X,
Tsuberi BZ and Cedar H: DNA methylation represses transcription in
vivo. Nat Genet. 22:203–206. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsieh CL: Stability of patch methylation
and its impact in regions of transcriptional initiation and
elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 17:5897–5904. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Watt F and Molloy PL: Cytosine methylation
prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor
required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late
promoter. Genes Dev. 2:1136–1143. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sarraf SA and Stancheva I: Methyl-CpG
binding protein MBD1 couples histone H3 methylation at lysine 9 by
SETDB1 to DNA replication and chromatin assembly. Mol Cell.
15:595–605. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klose RJ and Bird AP: Genomic DNA
methylation: The mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem Sci.
31:89–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Clark MB, Johnston RL, Inostroza-Ponta M,
Fox AH, Fortini E, Moscato P, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Genome-wide
analysis of long noncoding RNA stability. Genome Res. 22:885–898.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|