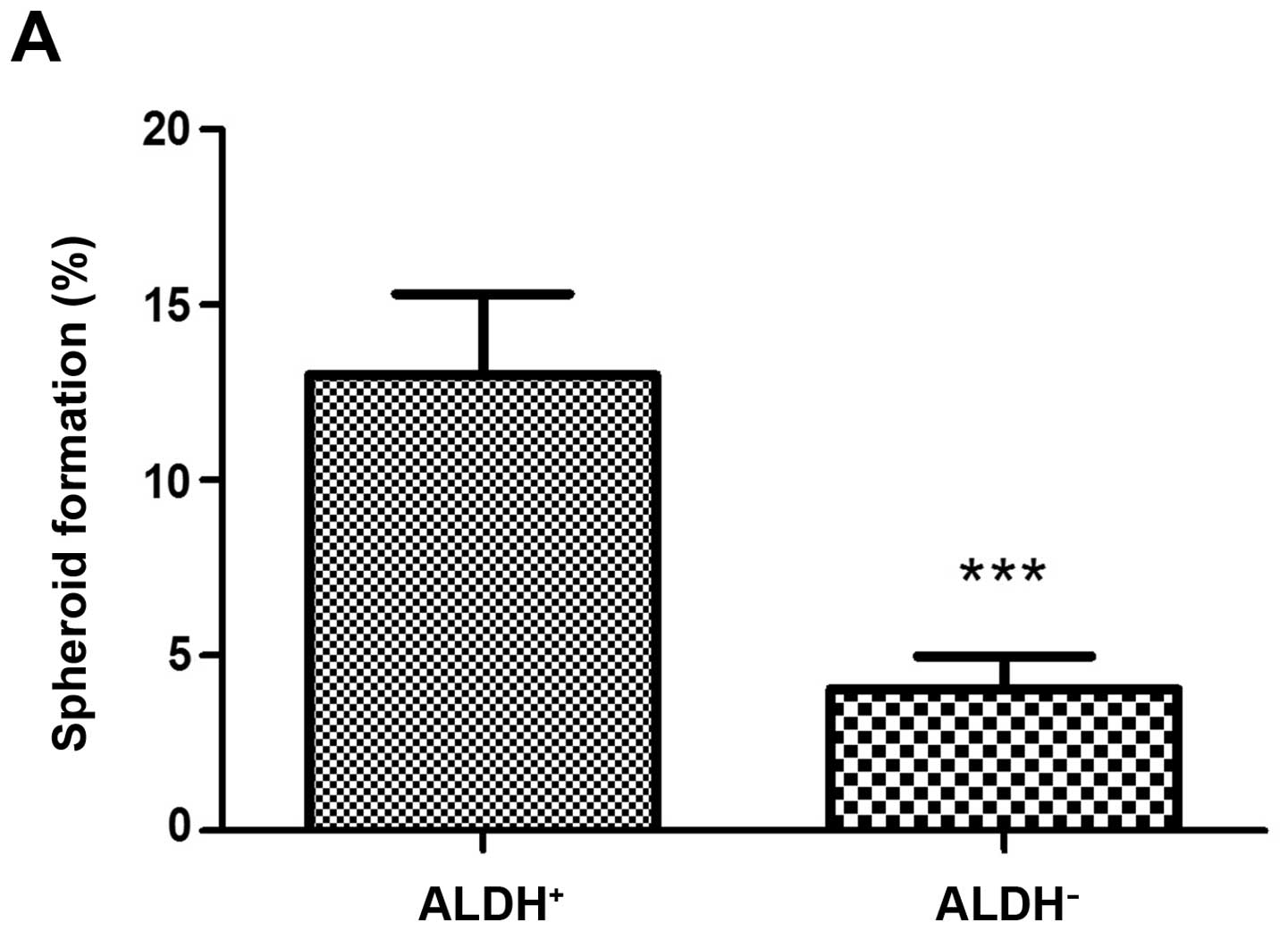
|
1
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pignon JP, Baujat B and Bourhis J:
Individual patient data meta-analyses in head and neck carcinoma:
what have we learnt? Cancer Radiother. 9:31–36. 2005.(In French).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan KS, Espinosa I, Chao M, Wong D,
Ailles L, Diehn M, Gill H, Presti J Jr, Chang HY, van de Rijn M, et
al: Identification, molecular characterization, clinical prognosis,
and therapeutic targeting of human bladder tumor-initiating cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:14016–14021. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dalerba P, Dylla SJ, Park IK, Liu R, Wang
X, Cho RW, Hoey T, Gurney A, Huang EH, Simeone DM, et al:
Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10158–10163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Prince ME, Sivanandan R, Kaczorowski A,
Wolf GT, Kaplan MJ, Dalerba P, Weissman IL, Clarke MF and Ailles
LE: Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem
cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:973–978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A,
Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ and Heeschen C: Distinct populations
of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity
in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 1:313–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Wang C, Chen Z, Jin Y, Wang Y,
Kolokythas A, Dai Y and Zhou X: MicroRNA-138 suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell
lines. Biochem J. 440:23–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nguyen LV, Vanner R, Dirks P and Eaves CJ:
Cancer stem cells: An evolving concept. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:133–143.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee HE, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Choi SY, Kim SW,
Kang E, Chung IY, Kim IA, Kim EJ, Choi Y, et al: An increase in
cancer stem cell population after primary systemic therapy is a
poor prognostic factor in breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
104:1730–1738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang W, Peng J, Zhang Y, Cho WC and Jin
K: The implications of cancer stem cells for cancer therapy. Int J
Mol Sci. 13:16636–16657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ghods AJ, Irvin D, Liu G, Yuan X,
Abdulkadir IR, Tunici P, Konda B, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Black KL and
Yu JS: Spheres isolated from 9L gliosarcoma rat cell line possess
chemoresistant and aggressive cancer stem-like cells. Stem Cells.
25:1645–1653. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Azari H, Rahman M, Sharififar S and
Reynolds BA: Isolation and expansion of the adult mouse neural stem
cells using the neurosphere assay. J Vis Exp.
45:23932010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Todaro M, Alea MP, Di Stefano AB,
Cammareri P, Vermeulen L, Iovino F, Tripodo C, Russo A, Gulotta G,
Medema JP, et al: Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and
resist cell death by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell.
1:389–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Schatton T, Murphy GF, Frank NY, Yamaura
K, Waaga-Gasser AM, Gasser M, Zhan Q, Jordan S, Duncan LM,
Weishaupt C, et al: Identification of cells initiating human
melanomas. Nature. 451:345–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Okamoto A, Chikamatsu K, Sakakura K,
Hatsushika K, Takahashi G and Masuyama K: Expansion and
characterization of cancer stem-like cells in squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 45:633–639. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chiou SH, Yu CC, Huang CY, Lin SC, Liu CJ,
Tsai TH, Chou SH, Chien CS, Ku HH and Lo JF: Positive correlations
of Oct-4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high-grade
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4085–4095. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu KJ and Yang MH: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cancer stemness: The Twist1-Bmi1 connection. Biosci
Rep. 31:449–455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Santisteban M, Reiman JM, Asiedu MK,
Behrens MD, Nassar A, Kalli KR, Haluska P, Ingle JN, Hartmann LC,
Manjili MH, et al: Immune-induced epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in vivo generates breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Res.
69:2887–2895. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen C, Zimmermann M, Tinhofer I, Kaufmann
AM and Albers AE: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer
stem(-like) cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 338:47–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hindriksen S and Bijlsma MF: Cancer stem
cells, EMT, and developmental pathway activation in pancreatic
tumors. Cancers (Basel). 4:989–1035. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reddy BY, Lim PK, Silverio K, Patel SA,
Won BW and Rameshwar P: The microenvironmental effect in the
progression, metastasis, and dormancy of breast cancer: A model
system within bone marrow. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012:7216592012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Phinney DG: Twist,
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and stem cells. Stem Cells.
29:3–4. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van der Pluijm G: Epithelial plasticity,
cancer stem cells and bone metastasis formation. Bone. 48:37–43.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Viñas-Castells R, Beltran M, Valls G,
Gómez I, García JM, Montserrat-Sentís B, Baulida J, Bonilla F, de
Herreros AG and Díaz VM: The hypoxia-controlled FBXL14 ubiquitin
ligase targets SNAIL1 for proteasome degradation. J Biol Chem.
285:3794–3805. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Martin A and Cano A: Tumorigenesis: Twist1
links EMT to self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 12:924–925. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang MH, Hsu DS, Wang HW, Wang HJ, Lan HY,
Yang WH, Huang CH, Kao SY, Tzeng CH, Tai SK, et al: Bmi1 is
essential in Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat
Cell Biol. 12:982–992. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qian X, Wagner S, Ma C, Coordes A, Gekeler
J, Klussmann JP, Hummel M, Kaufmann AM and Albers AE: Prognostic
significance of ALDH1A1-positive cancer stem cells in patients with
locally advanced, metastasized head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:1151–1158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li
L, Xiang D, Desano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D, et al: MicroRNA miR-34
inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One.
4:e68162009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kumar B, Yadav A, Lang J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor growth and tumor
angiogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e376012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Clay MR, Tabor M, Owen JH, Carey TE,
Bradford CR, Wolf GT, Wicha MS and Prince ME: Single-marker
identification of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem
cells with aldehyde dehydrogenase. Head Neck. 32:1195–1201. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qian X, Wagner S, Ma C, Klussmann JP,
Hummel M, Kaufmann AM and Albers AE: ALDH1-positive cancer
stem-like cells are enriched in nodal metastases of oropharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma independent of HPV status. Oncol Rep.
29:1777–1784. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Klinghammer K, Raguse JD, Plath T, Albers
AE, Joehrens K, Zakarneh A, Brzezicha B, Wulf-Goldenberg A,
Keilholz U, Hoffmann J, et al: A comprehensively characterized
large panel of head and neck cancer patient-derived xenografts
identifies the mTOR inhibitor everolimus as potential new treatment
option. Int J Cancer. 136:2940–2948. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ling GQ, Chen DB, Wang BQ and Zhang LS:
Expression of the pluripotency markers Oct3/4, Nanog and Sox2 in
human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Lett. 4:1264–1268.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Santini MT, Rainaldi G and Indovina PL:
Multicellular tumour spheroids in radiation biology. Int J Radiat
Biol. 75:787–799. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wicha MS, Liu S and Dontu G: Cancer stem
cells: an old idea - a paradigm shift. Cancer Res. 66:1883–1890;
discussion 1895–1886. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Fang D, Nguyen TK, Leishear K, Finko R,
Kulp AN, Hotz S, Van Belle PA, Xu X, Elder DE and Herlyn M: A
tumorigenic subpopulation with stem cell properties in melanomas.
Cancer Res. 65:9328–9337. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G,
Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA and Daidone MG:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kuch V, Schreiber C, Thiele W, Umansky V
and Sleeman JP: Tumor-initiating properties of breast cancer and
melanoma cells in vivo are not invariably reflected by spheroid
formation in vitro, but can be increased by long-term culturing as
adherent monolayers. Int J Cancer. 132:E94–E105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ma S, Chan KW, Lee TK, Tang KH, Wo JY,
Zheng BJ and Guan XY: Aldehyde dehydrogenase discriminates the
CD133 liver cancer stem cell populations. Mol Cancer Res.
6:1146–1153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen YC, Chen YW, Hsu HS, Tseng LM, Huang
PI, Lu KH, Chen DT, Tai LK, Yung MC, Chang SC, et al: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase 1 is a putative marker for cancer stem cells in head
and neck squamous cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 385:307–313.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chickarmane V and Peterson C: A
computational model for understanding stem cell, trophectoderm and
endoderm lineage determination. PLoS One. 3:e34782008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jensen JB and Parmar M: Strengths and
limitations of the neurosphere culture system. Mol Neurobiol.
34:153–161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Park EY, Chang E, Lee EJ, Lee HW, Kang HG,
Chun KH, Woo YM, Kong HK, Ko JY, Suzuki H, et al: Targeting of
miR34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and
chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 74:7573–7582. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kim NH, Kim HS, Li XY, Lee I, Choi HS,
Kang SE, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Yoon D, Fearon ER, et al: A p53/miRNA-34
axis regulates Snail1-dependent cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Biol. 195:417–433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Hünten S, Kaller
M, Menssen A, Götz U and Hermeking H: miR-34 and SNAIL form a
double-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions. Cell Cycle. 10:4256–4271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nalls D, Tang SN, Rodova M, Srivastava RK
and Shankar S: Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for
treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer
stem cells. PLoS One. 6:e240992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, Yang JY, Xiong
Y, Li CW, Yu WH, Rehman SK, Hsu JL, Lee HH, et al: p53 regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties through
modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 13:317–323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cannell IG and Bushell M: Regulation of
Myc by miR-34c: A mechanism to prevent genomic instability? Cell
Cycle. 9:2726–2730. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Christoffersen NR, Shalgi R, Frankel LB,
Leucci E, Lees M, Klausen M, Pilpel Y, Nielsen FC, Oren M and Lund
AH: p53-independent upregulation of miR-34a during oncogene-induced
senescence represses MYC. Cell Death Differ. 17:236–245. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Kong YW, Cannell IG, de Moor CH, Hill K,
Garside PG, Hamilton TL, Meijer HA, Dobbyn HC, Stoneley M, Spriggs
KA, et al: The mechanism of micro-RNA-mediated translation
repression is determined by the promoter of the target gene. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:8866–8871. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bader AG, Brown D and Winkler M: The
promise of microRNA replacement therapy. Cancer Res. 70:7027–7030.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Tsakmaki
V, Danielidis V and Sivridis E: Cancer stem cell phenotype relates
to radio-chemotherapy outcome in locally advanced squamous cell
head-neck cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:846–853. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xu J, Müller S, Nannapaneni S, Pan L, Wang
Y, Peng X, Wang D, Tighiouart M, Chen Z, Saba NF, et al: Comparison
of quantum dot technology with conventional immunohistochemistry in
examining aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 as a potential biomarker for
lymph node metastasis of head and neck cancer. Eur J Cancer.
48:1682–1691. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|