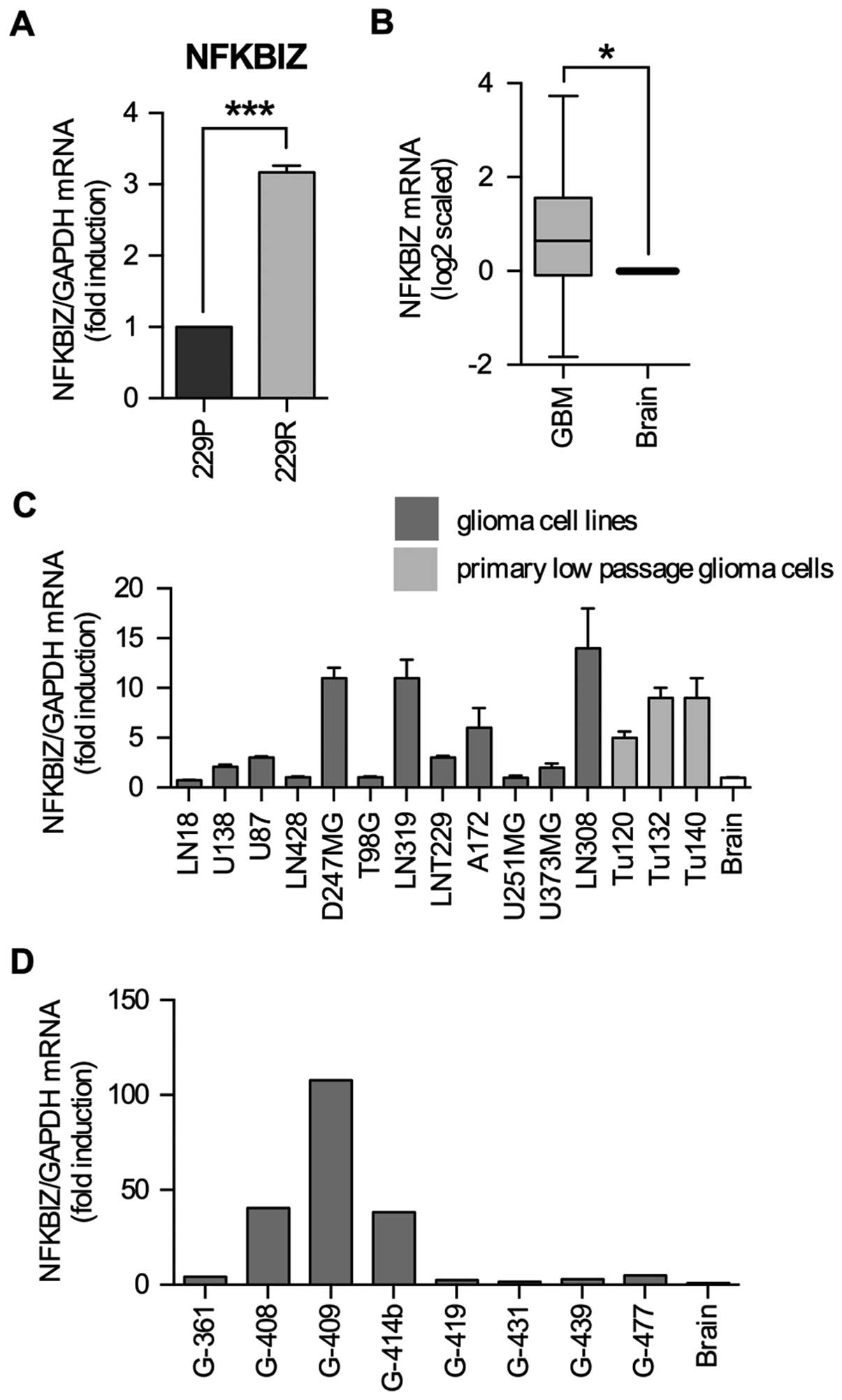
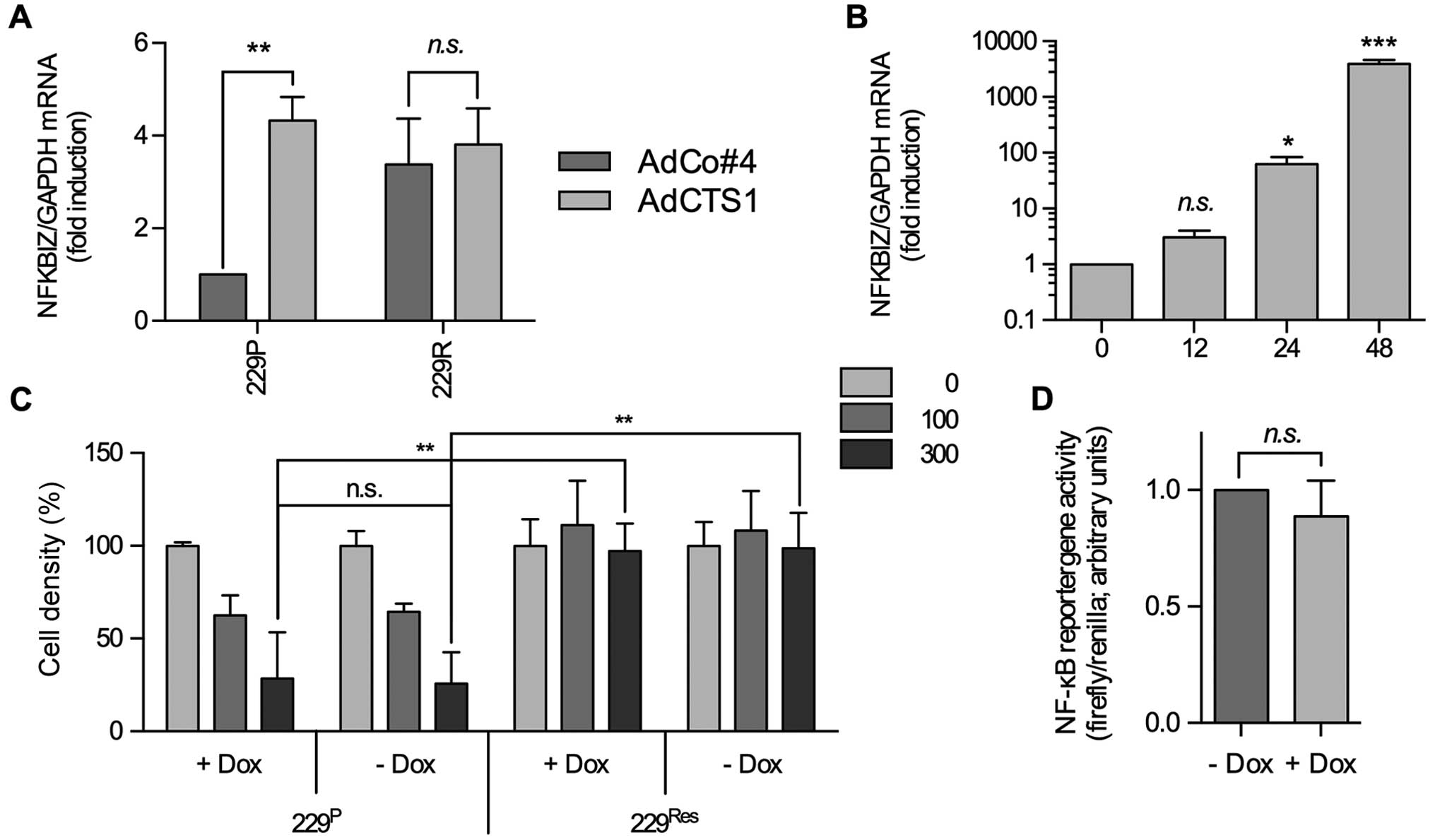
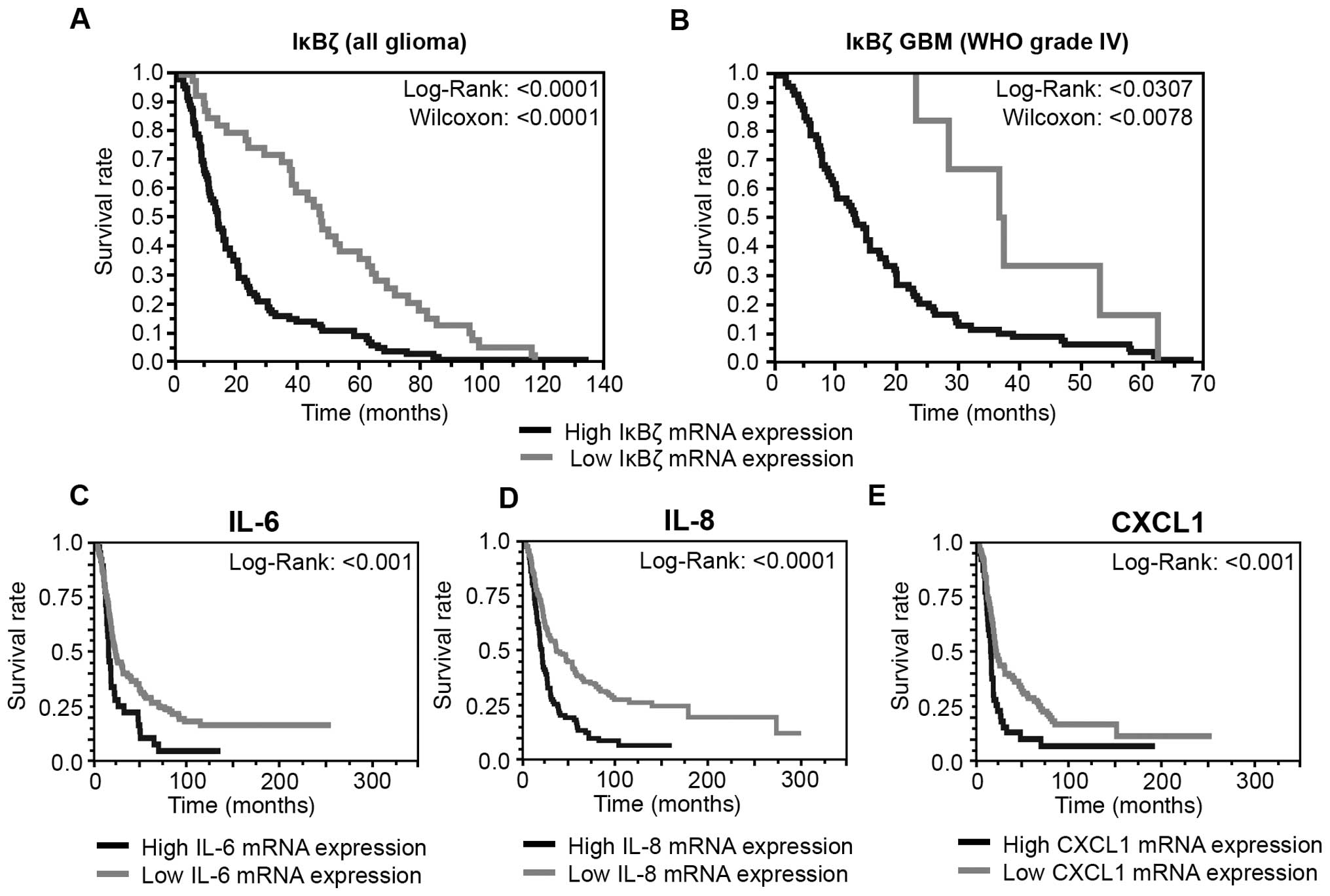
|
1
|
Bours V, Bentires-Alj M, Hellin AC,
Viatour P, Robe P, Delhalle S, Benoit V and Merville MP: Nuclear
factor-kappa B, cancer, and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol.
60:1085–1089. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perkins ND: The diverse and complex roles
of NF-κB subunits in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:121–132.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coupienne I, Bontems S, Dewaele M, Rubio
N, Habraken Y, Fulda S, Agostinis P and Piette J: NF-kappaB
inhibition improves the sensitivity of human glioblastoma cells to
5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 81:606–616. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ding GR, Honda N, Nakahara T, Tian F,
Yoshida M, Hirose H and Miyakoshi J: Radiosensitization by
inhibition of IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation in human glioma cells.
Radiat Res. 160:232–237. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zanotto-Filho A, Braganhol E, Schröder R,
de Souza LH, Dalmolin RJ, Pasquali MA, Gelain DP, Battastini AM and
Moreira JC: NFκB inhibitors induce cell death in glioblastomas.
Biochem Pharmacol. 81:412–424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Raychaudhuri B, Han Y, Lu T and Vogelbaum
MA: Aberrant constitutive activation of nuclear factor kappaB in
glioblastoma multiforme drives invasive phenotype. J Neurooncol.
85:39–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Chen T, Zhang J, Mao Q, Li S,
Xiong W, Qiu Y, Xie Q and Ge J: Notch1 promotes glioma cell
migration and invasion by stimulating β-catenin and NF-κB signaling
via AKT activation. Cancer Sci. 103:181–190. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xie TX, Xia Z, Zhang N, Gong W and Huang
S: Constitutive NF-kappaB activity regulates the expression of VEGF
and IL-8 and tumor angiogenesis of human glioblastoma. Oncol Rep.
23:725–732. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Griffin BD and Moynagh PN: Persistent
interleukin-1beta signaling causes long term activation of NFkappaB
in a promoter-specific manner in human glial cells. J Biol Chem.
281:10316–10326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Perkins ND and Gilmore TD: Good cop, bad
cop: The different faces of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ.
13:759–772. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR and Vousden KH:
Role of NF-kappaB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature.
404:892–897. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seznec J, Weit S and Naumann U: Gene
expression profile in a glioma cell line resistant to cell death
induced by the chimeric tumor suppressor-1 (CTS-1), a
dominant-positive variant of p53 - the role of NFkappaB.
Carcinogenesis. 31:411–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Perkins ND: Integrating cell-signalling
pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:49–62. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hildebrand DG, Alexander E, Hörber S,
Lehle S, Obermayer K, Münck NA, Rothfuss O, Frick JS, Morimatsu M,
Schmitz I, et al: IκBζ is a transcriptional key regulator of
CCL2/MCP-1. J Immunol. 190:4812–4820. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Totzke G, Essmann F, Pohlmann S,
Lindenblatt C, Jänicke RU and Schulze-Osthoff K: A novel member of
the IkappaB family, human IkappaB-zeta, inhibits transactivation of
p65 and its DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 281:12645–12654. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamazaki S, Muta T and Takeshige K: A
novel IkappaB protein, IkappaB-zeta, induced by proinflammatory
stimuli, negatively regulates nuclear factor-kappaB in the nuclei.
J Biol Chem. 276:27657–27662. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamazaki S, Matsuo S, Muta T, Yamamoto M,
Akira S and Takeshige K: Gene-specific requirement of a nuclear
protein, IkappaB-zeta, for promoter association of inflammatory
transcription regulators. J Biol Chem. 283:32404–32411. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naumann U, Kügler S, Wolburg H, Wick W,
Rascher G, Schulz JB, Conseiller E, Bähr M and Weller M: Chimeric
tumor suppressor 1, a p53-derived chimeric tumor suppressor gene,
kills p53 mutant and p53 wild-type glioma cells in synergy with
irradiation and CD95 ligand. Cancer Res. 61:5833–5842.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alexander E, Hildebrand DG, Kriebs A,
Obermayer K, Manz M, Rothfuss O, Schulze-Osthoff K and Essmann F:
IκBζ is a regulator of the senescence-associated secretory
phenotype in DNA damage- and oncogene-induced senescence. J Cell
Sci. 126:3738–3745. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Krtolica A, Parrinello S, Lockett S,
Desprez PY and Campisi J: Senescent fibroblasts promote epithelial
cell growth and tumorigenesis: A link between cancer and aging.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:12072–12077. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Conti A, Gulì C, La Torre D, Tomasello C,
Angileri FF and Aguennouz M: Role of inflammation and oxidative
stress mediators in gliomas. Cancers (Basel). 2:693–712. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Siu A, Wind JJ, Iorgulescu JB, Chan TA,
Yamada Y and Sherman JH: Radiation necrosis following treatment of
high grade glioma - a review of the literature and current
understanding. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 154:191–201; discussion 201.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler
KW and Vogelstein B: A simplified system for generating recombinant
adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:2509–2514. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grentzmann G, Ingram JA, Kelly PJ,
Gesteland RF and Atkins JF: A dual-luciferase reporter system for
studying recoding signals. RNA. 4:479–486. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsuboi Y, Kurimoto M, Nagai S, Hayakawa Y,
Kamiyama H, Hayashi N, Kitajima I and Endo S: Induction of
autophagic cell death and radiosensitization by the pharmacological
inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation in human glioma
cell lines. J Neurosurg. 110:594–604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pasi F, Facoetti A and Nano R: IL-8 and
IL-6 bystander signalling in human glioblastoma cells exposed to
gamma radiation. Anticancer Res. 30:2769–2772. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dubost JJ, Rolhion C, Tchirkov A, Bertrand
S, Chassagne J, Dosgilbert A and Verrelle P:
Interleukin-6-producing cells in a human glioblastoma cell line are
not affected by ionizing radiation. J Neurooncol. 56:29–34. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF,
de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani
L, et al: MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans
J and Wick W: Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and
invasiveness of glioma cells: Implications for radiotherapy of
human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 61:2744–2750. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Desmarais G, Fortin D, Bujold R, Wagner R,
Mathieu D and Paquette B: Infiltration of glioma cells in brain
parenchyma stimulated by radiation in the F98/Fischer rat model.
Int J Radiat Biol. 88:565–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kil WJ, Tofilon PJ and Camphausen K:
Post-radiation increase in VEGF enhances glioma cell motility in
vitro. Radiat Oncol. 7:252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Criswell T, Leskov K, Miyamoto S, Luo G
and Boothman DA: Transcription factors activated in mammalian cells
after clinically relevant doses of ionizing radiation. Oncogene.
22:5813–5827. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bhat KP, Balasubramaniyan V, Vaillant B,
Ezhilarasan R, Hummelink K, Hollingsworth F, Wani K, Heathcock L,
James JD, Goodman LD, et al: Mesenchymal differentiation mediated
by NF-κB promotes radiation resistance in glioblastoma. Cancer
Cell. 24:331–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nalla AK, Gogineni VR, Gupta R, Dinh DH
and Rao JS: Suppression of uPA and uPAR blocks radiation-induced
MCP-1 mediated recruitment of endothelial cells in meningioma. Cell
Signal. 23:1299–1310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Van Meir E, Sawamura Y, Diserens AC, Hamou
MF and de Tribolet N: Human glioblastoma cells release interleukin
6 in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 50:6683–6688. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Loeffler S, Fayard B, Weis J and
Weissenberger J: Interleukin-6 induces transcriptional activation
of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in astrocytes in vivo
and regulates VEGF promoter activity in glioblastoma cells via
direct interaction between STAT3 and Sp1. Int J Cancer.
115:202–213. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Weissenberger J, Loeffler S, Kappeler A,
Kopf M, Lukes A, Afanasieva TA, Aguzzi A and Weis J: IL-6 is
required for glioma development in a mouse model. Oncogene.
23:3308–3316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brat DJ, Bellail AC and Van Meir EG: The
role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and
tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro-oncol. 7:122–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsai HH, Frost E, To V, Robinson S,
Ffrench-Constant C, Geertman R, Ransohoff RM and Miller RH: The
chemokine receptor CXCR2 controls positioning of oligodendrocyte
precursors in developing spinal cord by arresting their migration.
Cell. 110:373–383. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Devalaraja RM, Nanney LB, Du J, Qian Q, Yu
Y, Devalaraja MN and Richmond A: Delayed wound healing in CXCR2
knockout mice. J Invest Dermatol. 115:234–244. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou Y, Zhang J, Liu Q, Bell R, Muruve DA,
Forsyth P, Arcellana-Panlilio M, Robbins S and Yong VW: The
chemokine GRO-alpha (CXCL1) confers increased tumorigenicity to
glioma cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:2058–2068. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Robinson S, Cohen M, Prayson R, Ransohoff
RM, Tabrizi N and Miller RH: Constitutive expression of
growth-related oncogene and its receptor in oligodendrogliomas.
Neurosurgery. 48:864–873; discussion 873–874. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Willems M, Kroonen J, Dubois N, Berendsen
S, Nguyen B, Bredel M, Artesi M, Kim H, Rados M, Chakravarti A, et
al: IkappaB zeta overexpression drives human glioma resistance to
necroptosis. Neuro-oncol. 16(Suppl 5): v58–v59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Platten M, Kretz A, Naumann U, Aulwurm S,
Egashira K, Isenmann S and Weller M: Monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 increases microglial infiltration and aggressiveness of
gliomas. Ann Neurol. 54:388–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Okamoto K, Iwai Y, Oh-Hora M, Yamamoto M,
Morio T, Aoki K, Ohya K, Jetten AM, Akira S, Muta T, et al:
IkappaBzeta regulates T(H)17 development by cooperating with ROR
nuclear receptors. Nature. 464:1381–1385. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Okada H and Khoury SJ: Type17 T-cells in
central nervous system autoimmunity and tumors. J Clin Immunol.
32:802–808. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|