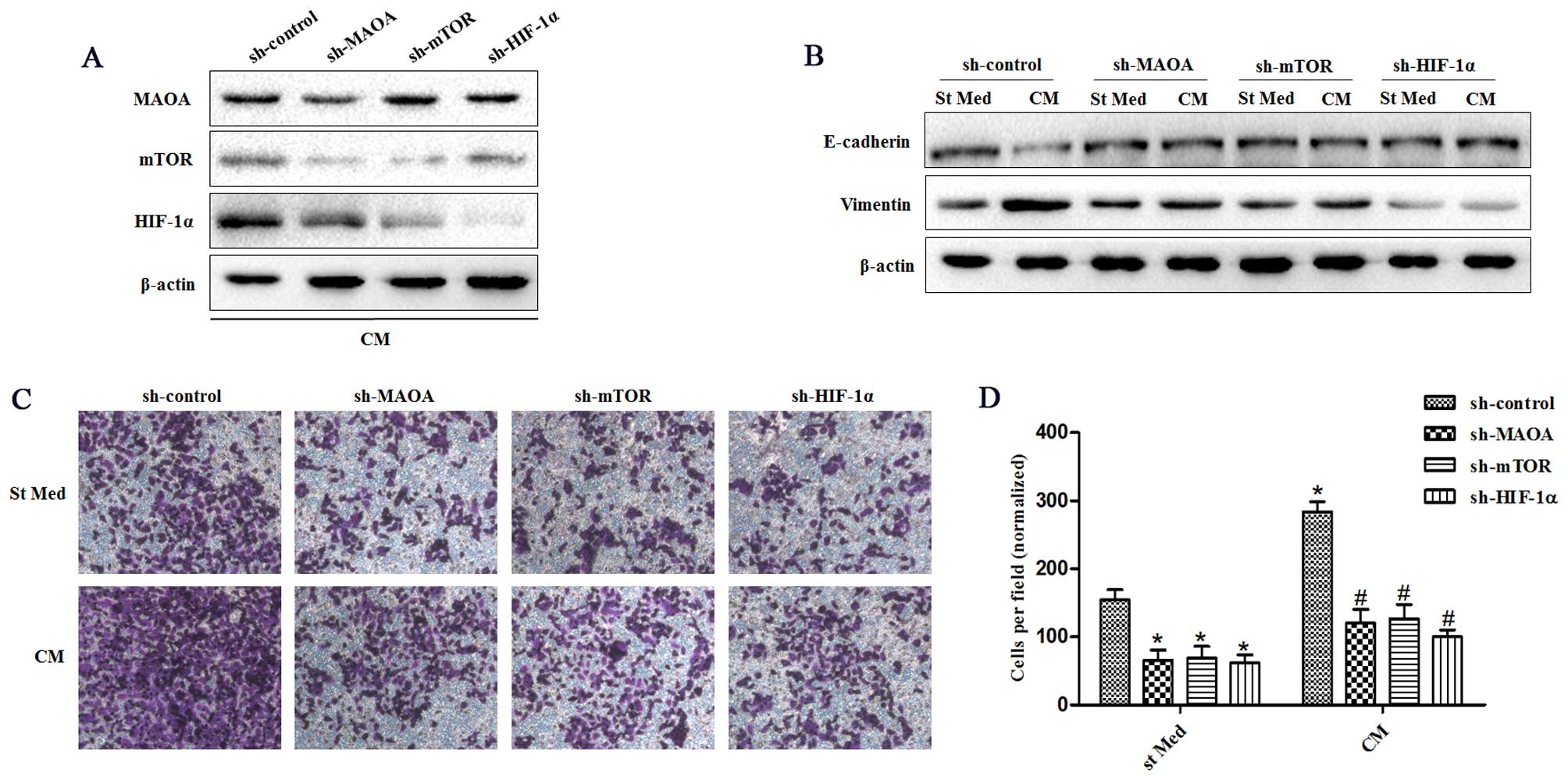
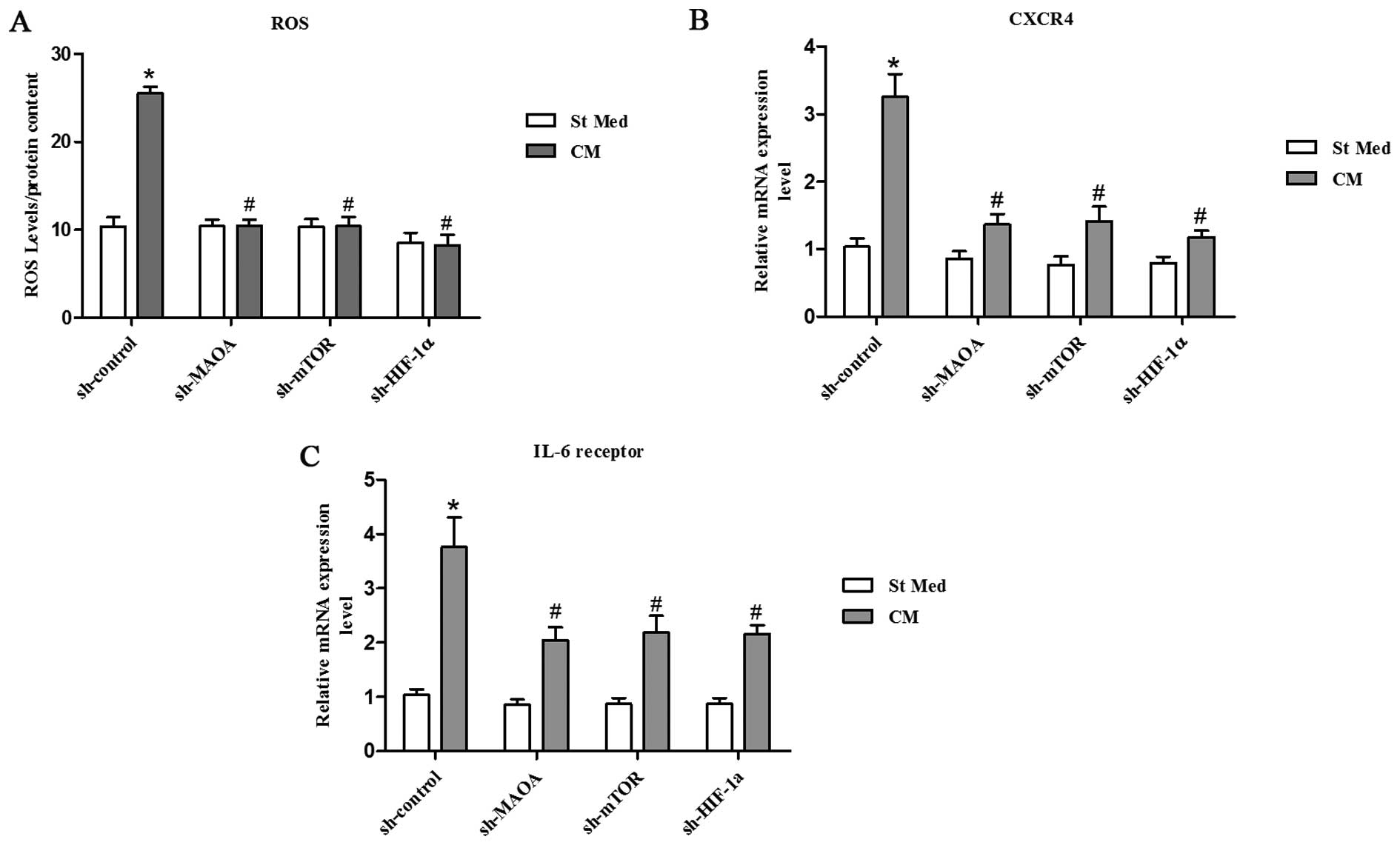
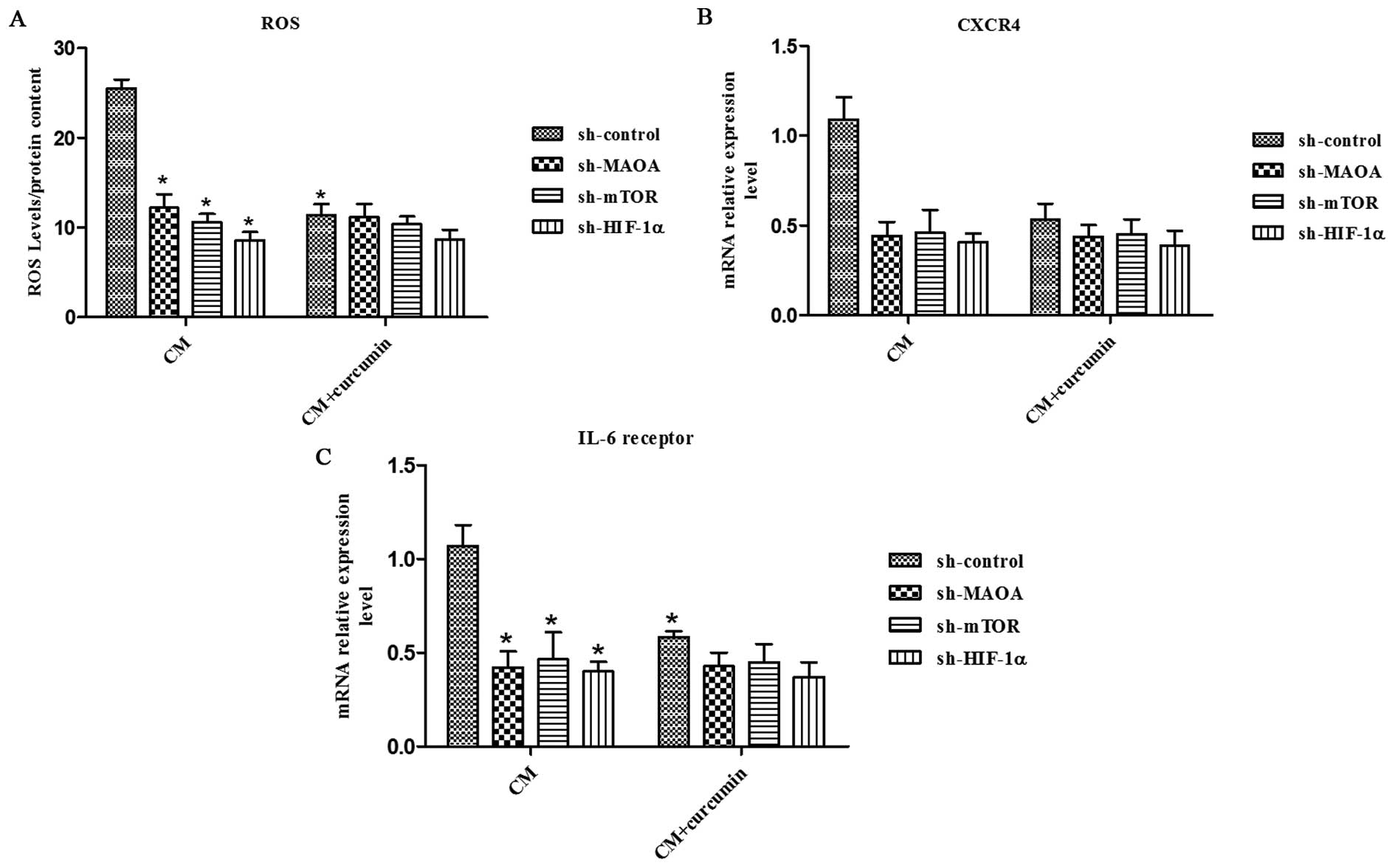
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Partin AW, Kattan MW, Subong EN, Walsh PC,
Wojno KJ, Oesterling JE, Scardino PT and Pearson JD: Combination of
prostate-specific antigen, clinical stage, and Gleason score to
predict pathological stage of localized prostate cancer. A
multi-institutional update. JAMA. 277:1445–1451. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bissell MJ and Radisky D: Putting tumours
in context. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:46–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kalluri R and Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:392–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Desmoulière A, Guyot C and Gabbiani G: The
stroma reaction myofibroblast: A key player in the control of tumor
cell behavior. Int J Dev Biol. 48:509–517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giannoni E, Bianchini F, Masieri L, Serni
S, Torre E, Calorini L and Chiarugi P: Reciprocal activation of
prostate cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts stimulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness. Cancer Res.
70:6945–6956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Micke P and Ostman A: Tumour-stroma
interaction: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as novel targets in
anti-cancer therapy? Lung Cancer. 45(Suppl 2): S163–S175. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sugimoto H, Mundel TM, Kieran MW and
Kalluri R: Identification of fibroblast heterogeneity in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1640–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Begley LA, Kasina S, MacDonald J and
Macoska JA: The inflammatory microenvironment of the aging prostate
facilitates cellular proliferation and hypertrophy. Cytokine.
43:194–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bhowmick NA, Neilson EG and Moses HL:
Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature.
432:332–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Trimboli AJ, Cantemir-Stone CZ, Li F,
Wallace JA, Merchant A, Creasap N, Thompson JC, Caserta E, Wang H,
Chong JL, et al: Pten in stromal fibroblasts suppresses mammary
epithelial tumours. Nature. 461:1084–1091. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, Brennan C,
Lahti-Domenici J, Huang H, Porter D, Hu M, Chin L, Richardson A, et
al: Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in
breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 6:17–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Olumi AF, Grossfeld GD, Hayward SW,
Carroll PR, Tlsty TD and Cunha GR: Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
direct tumor progression of initiated human prostatic epithelium.
Cancer Res. 59:5002–5011. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL
and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human
breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through
elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Crawford Y and Ferrara N: Tumor and
stromal pathways mediating refractoriness/resistance to
anti-angiogenic therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:624–630. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pietras K, Pahler J, Bergers G and Hanahan
D: Functions of paracrine PDGF signaling in the proangiogenic tumor
stroma revealed by pharmacological targeting. PLoS Med. 5:e192008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Friedl P: Prespecification and plasticity:
Shifting mechanisms of cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:14–23. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Christofori G: New signals from the
invasive front. Nature. 441:444–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cowin P, Rowlands TM and Hatsell SJ:
Cadherins and catenins in breast cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
17:499–508. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Francí C, Takkunen M, Dave N, Alameda F,
Gómez S, Rodríguez R, Escrivà M, Montserrat-Sentís B, Baró T,
Garrido M, et al: Expression of Snail protein in tumor-stroma
interface. Oncogene. 25:5134–5144. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu JB, Shao C, Li X, Li Q, Hu P, Shi C, Li
Y, Chen YT, Yin F, Liao CP, et al: Monoamine oxidase A mediates
prostate tumorigenesis and cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:2891–2908. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng SC, Quintin J, Cramer RA, Shepardson
KM, Saeed S, Kumar V, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Martens JH, Rao
NA, Aghajanirefah A, et al: mTOR- and HIF-1α-mediated aerobic
glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science.
345:12506842014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N and
Ichikawa H: Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. Adv Exp Med Biol.
595:1–75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ammon HP and Wahl MA: Pharmacology of
Curcuma longa. Planta Med. 57:1–7. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wilken R, Veena MS, Wang MB and Srivatsan
ES: Curcumin: A review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic
activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
10:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beevers CS, Zhou H and Huang S: Hitting
the golden TORget: Curcumin's effects on mTOR signaling. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 13:988–994. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Beevers CS, Chen L, Liu L, Luo Y, Webster
NJ and Huang S: Curcumin disrupts the mammalian target of
rapamycin-raptor complex. Cancer Res. 69:1000–1008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu S, Shen G, Khor TO, Kim JH and Kong AN:
Curcumin inhibits Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling
through protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:2609–2620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schnaitman C, Erwin VG and Greenawalt JW:
The submitochondrial localization of monoamine oxidase. An
enzymatic marker for the outer membrane of rat liver mitochondria.
J Cell Biol. 32:719–735. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chiarugi P, Pani G, Giannoni E, Taddei L,
Colavitti R, Raugei G, Symons M, Borrello S, Galeotti T and Ramponi
G: Reactive oxygen species as essential mediators of cell adhesion:
The oxidative inhibition of a FAK tyrosine phosphatase is required
for cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 161:933–944. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mantovani A: Role of inflammatory cells
and mediators in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 29:2412010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pani G, Galeotti T and Chiarugi P:
Metastasis: Cancer cell's escape from oxidative stress. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 29:351–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Ramponi G and
Chiarugi P: Redox regulation of anoikis resistance of metastatic
prostate cancer cells: Key role for Src and EGFR-mediated
pro-survival signals. Oncogene. 28:2074–2086. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Khandrika L, Kumar B, Koul S, Maroni P and
Koul HK: Oxidative stress in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett.
282:125–136. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim HI, Huang H, Cheepala S, Huang S and
Chung J: Curcumin inhibition of integrin (alpha6beta4)-dependent
breast cancer cell motility and invasion. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
1:385–391. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A, Busch F, Aldinger
C, Stahlmann R, Montaseri A and Shakibaei M: Curcumin modulates
nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated inflammation in human
tenocytes in vitro: Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt
pathway. J Biol Chem. 286:28556–28566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shehzad A, Lee J and Lee YS: Curcumin in
various cancers. Biofactors. 39:56–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cheng TS, Chen WC, Lin YY, Tsai CH, Liao
CI, Shyu HY, Ko CJ, Tzeng SF, Huang CY, Yang PC, et al:
Curcumin-targeting peri-cellular serine protease matriptase role in
suppression of prostate cancer cell invasion, tumor growth, and
metastasis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 6:495–505. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhao H, Nolley R, Chen Z, Reese SW and
Peehl DM: Inhibition of monoamine oxidase A promotes secretory
differentiation in basal prostatic epithelial cells.
Differentiation. 76:820–830. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen X, Cheng H, Pan T, et al: mTOR
regulate EMT through RhoA and Rac1 pathway in prostate cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 54:1086–1095. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu L, Li F, Cardelli JA, Martin KA,
Blenis J and Huang S: Rapamycin inhibits cell motility by
suppression of mTOR-mediated S6K1 and 4E-BP1 pathways. Oncogene.
25:7029–7040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gulhati P, Bowen KA, Liu J, Stevens PD,
Rychahou PG, Chen M, Lee EY, Weiss HL, O'Connor KL, Gao T, et al:
mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate EMT, motility, and metastasis of
colorectal cancer via RhoA and Rac1 signaling pathways. Cancer Res.
71:3246–3256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cannito S, Novo E, Compagnone A, Valfrè di
Bonzo L, Busletta C, Zamara E, Paternostro C, Povero D, Bandino A,
Bozzo F, et al: Redox mechanisms switch on hypoxia-dependent
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
29:2267–2278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang MH and Wu KJ: TWIST activation by
hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): Implications in metastasis and
development. Cell Cycle. 7:2090–2096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Calvani M, Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B,
Shoemaker RH and Melillo G: Hypoxic induction of an HIF-1
alpha-dependent bFGF autocrine loop drives angiogenesis in human
endothelial cells. Blood. 107:2705–2712. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Stasinopoulos I, O'Brien DR and Bhujwalla
ZM: Inflammation, but not hypoxia, mediated HIF-1alpha activation
depends on COX-2. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:31–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mori K, Shibanuma M and Nose K: Invasive
potential induced under long-term oxidative stress in mammary
epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 64:7464–7472. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lei J, Huo X, Duan W, Xu Q, Li R, Ma J, Li
X, Han L, Li W, Sun H, et al: α-Mangostin inhibits hypoxia-driven
ROS-induced PSC activation and pancreatic cancer cell invasion.
Cancer Lett. 347:129–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE,
Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM and Schumacker PT: Reactive
oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha during hypoxia: A mechanism of
O2 sensing. J Biol Chem. 275:25130–25138. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chandel NS, Maltepe E, Goldwasser E,
Mathieu CE, Simon MC and Schumacker PT: Mitochondrial reactive
oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:11715–11720. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Semenza GL: Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2:336–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Youn SW, Lee SW, Lee J, Jeong HK, Suh JW,
Yoon CH, Kang HJ, Kim HZ, Koh GY, Oh BH, et al: COMP-Ang1
stimulates HIF-1α-mediated SDF-1 overexpression and recovers
ischemic injury through BM-derived progenitor cell recruitment.
Blood. 117:4376–4386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li X, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Lei J, Duan W,
Bhat K, Wang F, Wu E and Wang Z: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling induces
pancreatic cancer cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in vitro through non-canonical activation of Hedgehog
pathway. Cancer Lett. 322:169–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R,
Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, et
al: IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:1853–1867. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou DY, Ding N, Du ZY, Cui XX, Wang H,
Wei XC, Conney AH, Zhang K and Zheng X: Curcumin analogues with
high activity for inhibiting human prostate cancer cell growth and
androgen receptor activation. Mol Med Rep. 10:1315–1322.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dorai T, Diouri J, O'Shea O and Doty SB:
Curcumin inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis by up-regulating
bone morphogenic protein-7 in vivo. J Cancer Ther. 5:369–386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Eom DW, Lee JH, Kim YJ, et al: Synergistic
effect of curcumin on epigallocatechin gallate-induced anticancer
action in PC3 prostate cancer cells. BMB Rep. 48:461–466. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Wang P, Wang B, Chung S, Wu Y, Henning SM
and Vadgama JV: Increased chemopreventive effect by combining
arctigenin, green tea polyphenol and curcumin in prostate and
breast cancer cells. RSC Advances. 4:35242–35250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mohandas KM and Desai DC: Epidemiology of
digestive tract cancers in India. V. Large and small bowel. Indian
J Gastroenterol. 18:118–121. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|