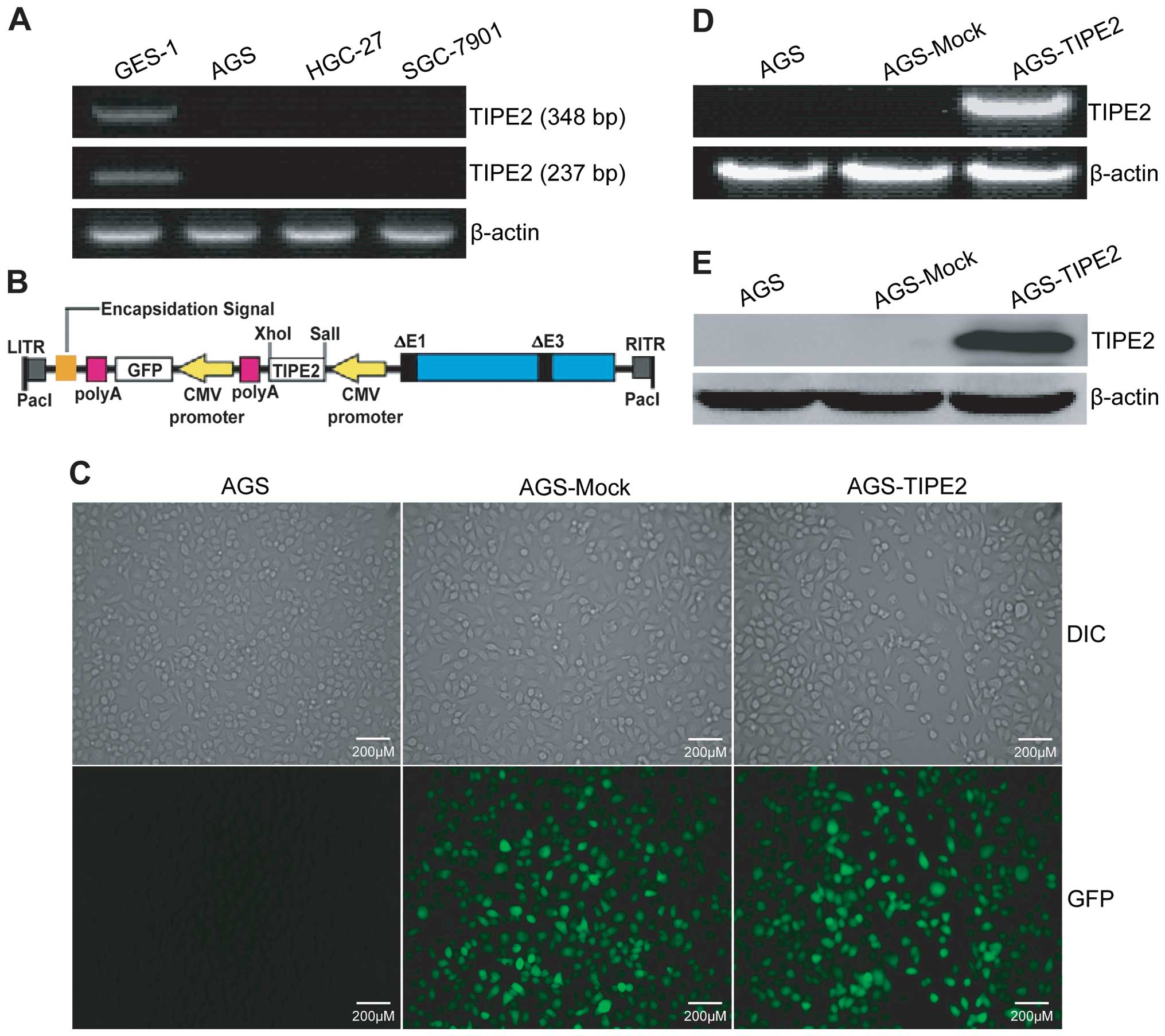
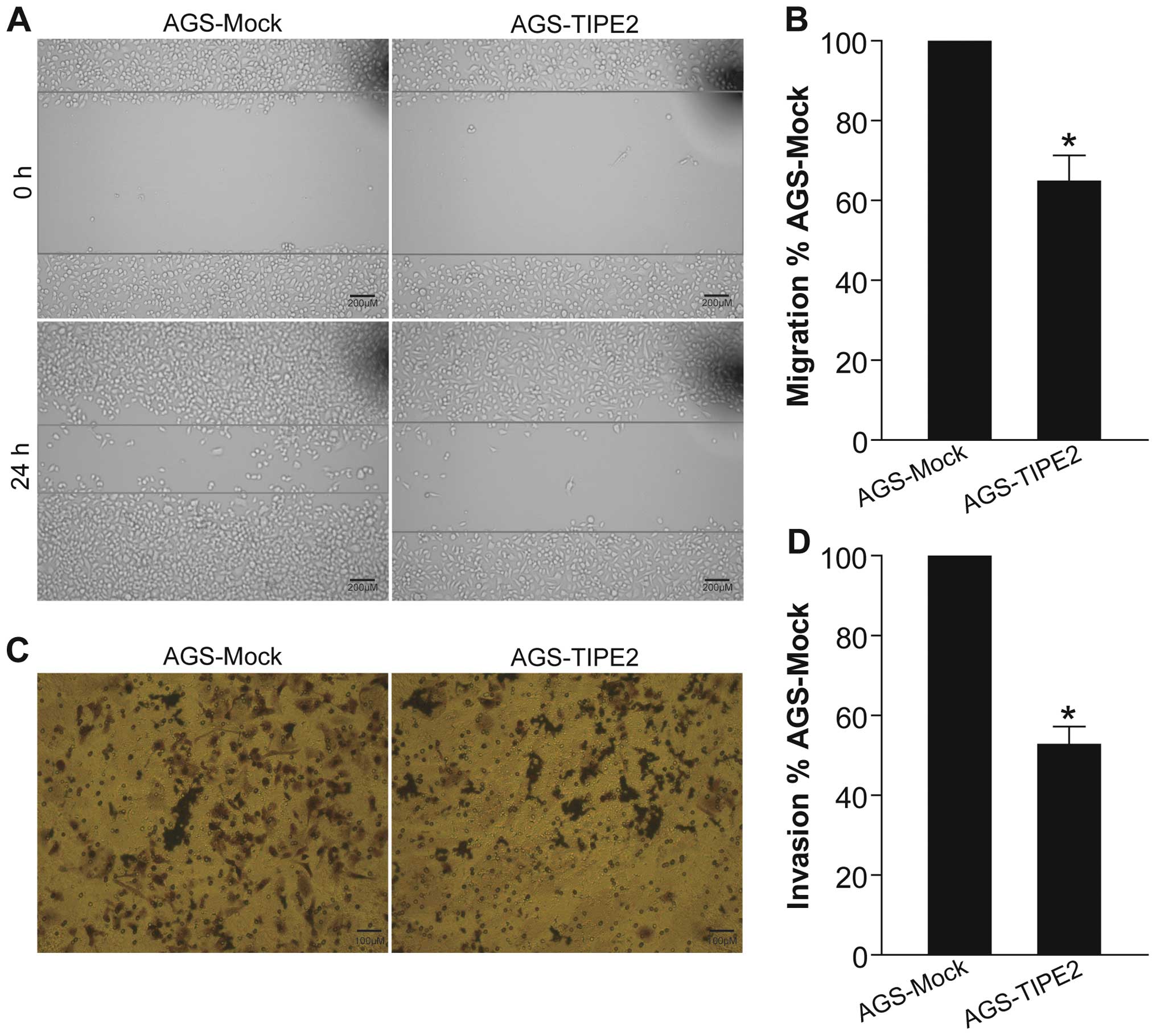
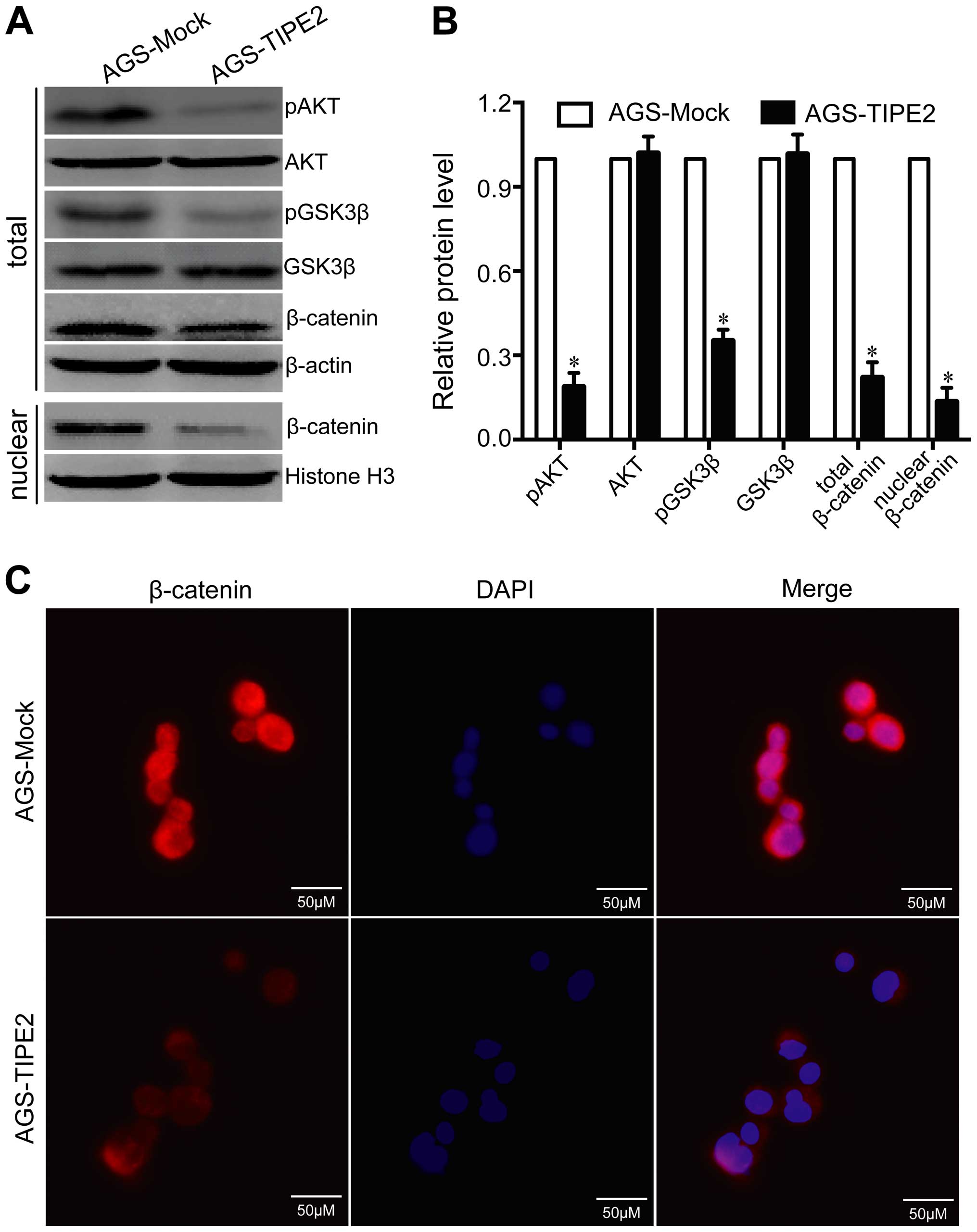
|
1
|
Sun H, Gong S, Carmody RJ, Hilliard A, Li
L, Sun J, Kong L, Xu L, Hilliard B, Hu S, et al: TIPE2, a negative
regulator of innate and adaptive immunity that maintains immune
homeostasis. Cell. 133:415–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lou Y and Liu S: The TIPE (TNFAIP8) family
in inflammation, immunity, and cancer. Mol Immunol. 49:4–7. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Freundt EC, Bidere N and Lenardo MJ: A
different TIPE of immune homeostasis. Cell. 133:401–402. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Fayngerts S, Wang P, Sun H,
Johnson DS, Ruan Q, Guo W and Chen YH: TIPE2 protein serves as a
negative regulator of phagocytosis and oxidative burst during
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15413–15418. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun H, Zhuang G, Chai L, Wang Z, Johnson
D, Ma Y and Chen YH: TIPE2 controls innate immunity to RNA by
targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Rac pathway. J Immunol.
189:2768–2773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lou Y, Zhang G, Geng M, Zhang W, Cui J and
Liu S: TIPE2 negatively regulates inflammation by switching
arginine metabolism from nitric oxide synthase to arginase. PLoS
One. 9:e965082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luan YY, Yao YM, Zhang L, Dong N, Zhang
QH, Yu Y and Sheng ZY: Expression of tumor necrosis factor-α
induced protein 8 like-2 contributes to the immunosuppressive
property of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells in mice. Mol Immunol.
49:219–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gus-Brautbar Y, Johnson D, Zhang L, Sun H,
Wang P, Zhang S, Zhang L and Chen YH: The anti-inflammatory TIPE2
is an inhibitor of the oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell. 45:610–618. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao X, Zhang L, Shi Y, Sun Y, Dai S, Guo
C, Zhu F, Wang Q, Wang J, Wang X, et al: Human tumor necrosis
factor (TNF)-alpha-induced protein 8-like 2 suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through inhibiting Rac1. Mol
Cancer. 12:1492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao Q, Zhao M, Dong T, Zhou C, Peng Y,
Zhou X, Fan B, Ma W, Han M and Liu S: Tumor necrosis
factor-α-induced protein-8 like-2 (TIPE2) upregulates p27 to
decrease gastic cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biochem.
116:1121–1129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu QQ, Zhang FF, Wang F, Qiu JH, Luo CH,
Zhu GY and Liu YF: TIPE2 inhibits lung cancer growth attributing to
promotion of apoptosis by regulating some apoptotic molecules
expression. PLoS One. 10:e01261762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Li X, Liu G, Sun R, Wang L, Wang J
and Wang H: Downregulated TIPE2 is associated with poor prognosis
and promotes cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:43–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler
KW and Vogelstein B: A simplified system for generating recombinant
adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:2509–2514. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Ye T, Sun D, Maynard J and
Deisseroth A: Conditionally replication-competent adenoviral
vectors with enhanced infectivity for use in gene therapy of
melanoma. Hum Gene Ther. 15:637–647. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie Y, Sheng W, Xiang J, Ye Z and Yang J:
Interleukin-17F suppresses hepatocarcinoma cell growth via
inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Invest. 28:598–607. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang G, Hao C, Lou Y, Xi W, Wang X, Wang
Y, Qu Z, Guo C, Chen Y and Zhang Y: Tissue-specific expression of
TIPE2 provides insights into its function. Mol Immunol.
47:2435–2442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Conacci-Sorrell M, Zhurinsky J and
Ben-Ze'ev A: The cadherin-catenin adhesion system in signaling and
cancer. J Clin Invest. 109:987–991. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chiurillo MA: Role of the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer: An in-depth literature review. World J
Exp Med. 5:84–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Porta C, Paglino C and Mosca A: Targeting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Cancer. Front Oncol. 4:642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang T, Wei Y, Honaker Y, Yamaguchi H,
Appella E, Hung MC and Piwnica-Worms H: GSK-3 beta targets Cdc25A
for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, and GSK-3 beta inactivation
correlates with Cdc25A overproduction in human cancers. Cancer
Cell. 13:36–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fang D, Hawke D, Zheng Y, Xia Y,
Meisenhelder J, Nika H, Mills GB, Kobayashi R, Hunter T and Lu Z:
Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by AKT promotes beta-catenin
transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 282:11221–11229. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cohen P and Frame S: The renaissance of
GSK3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:769–776. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|