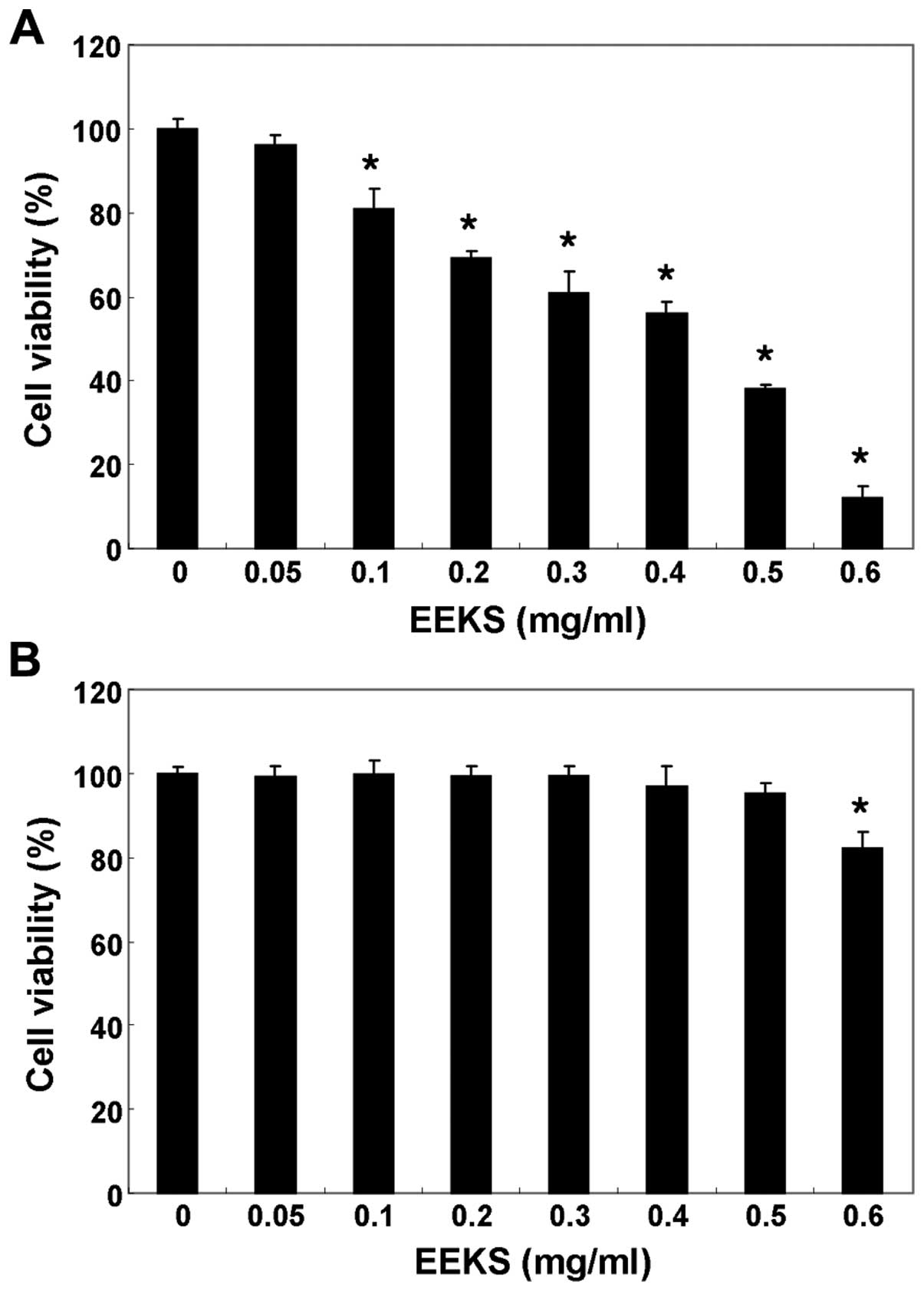
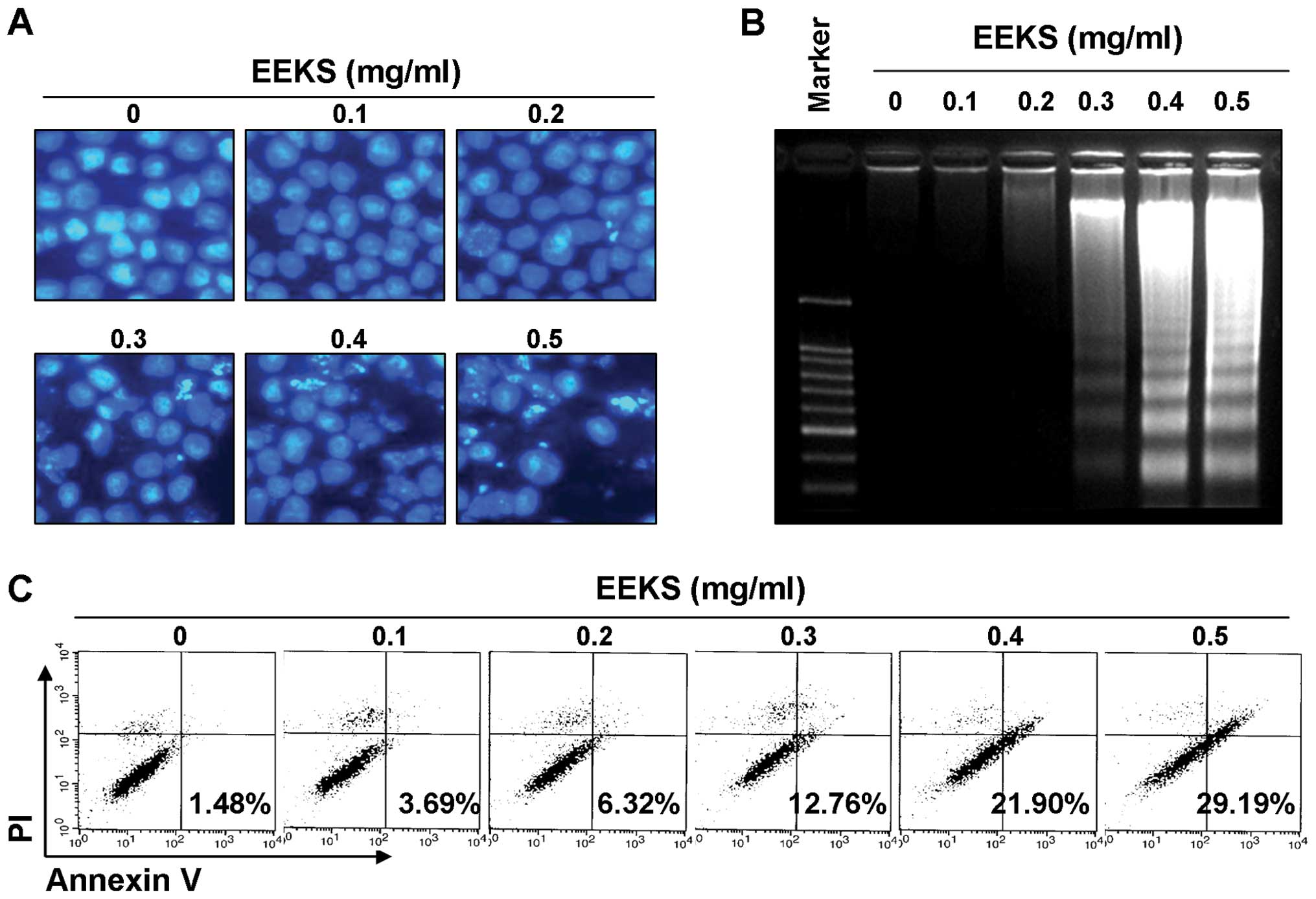
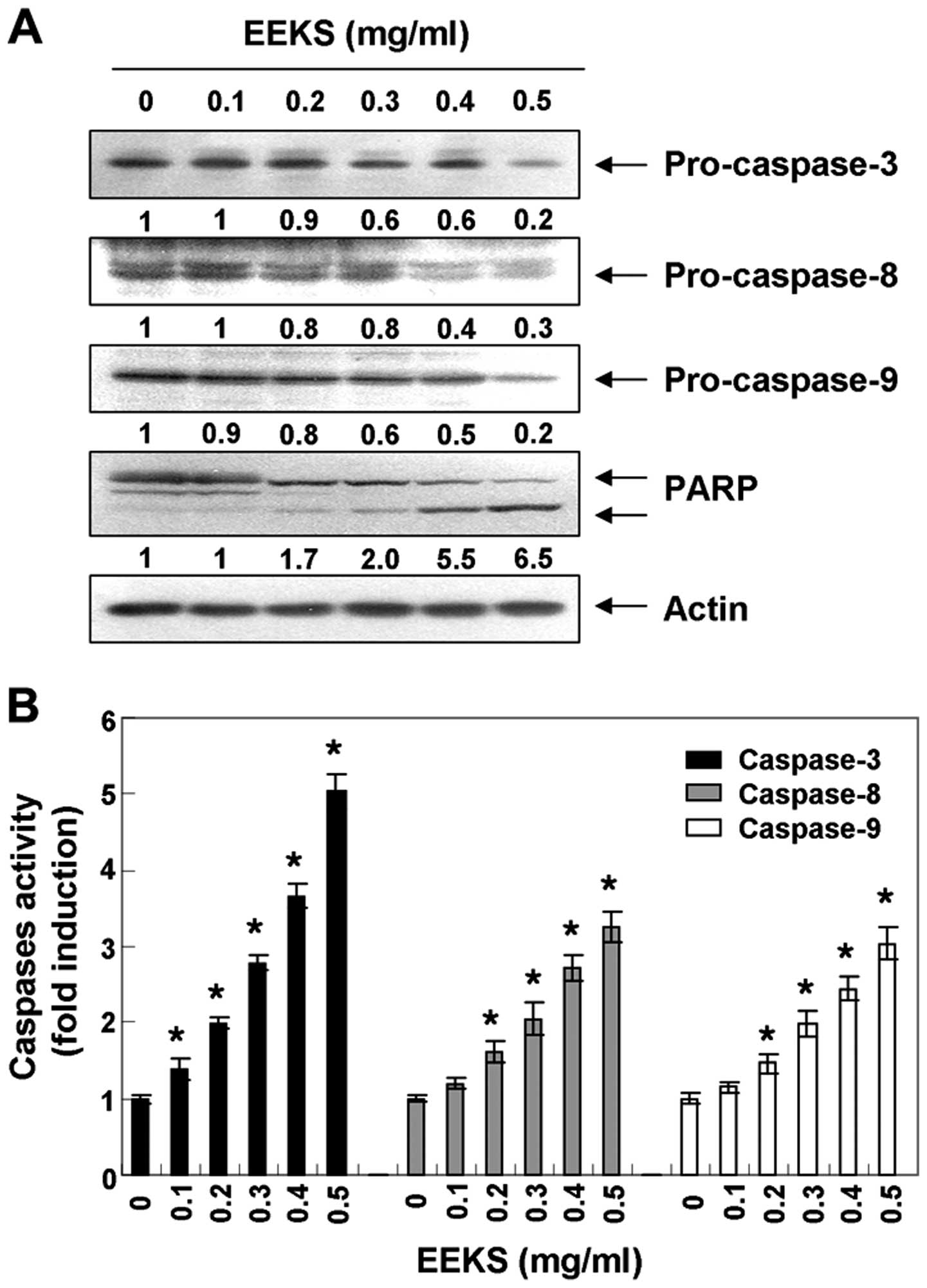
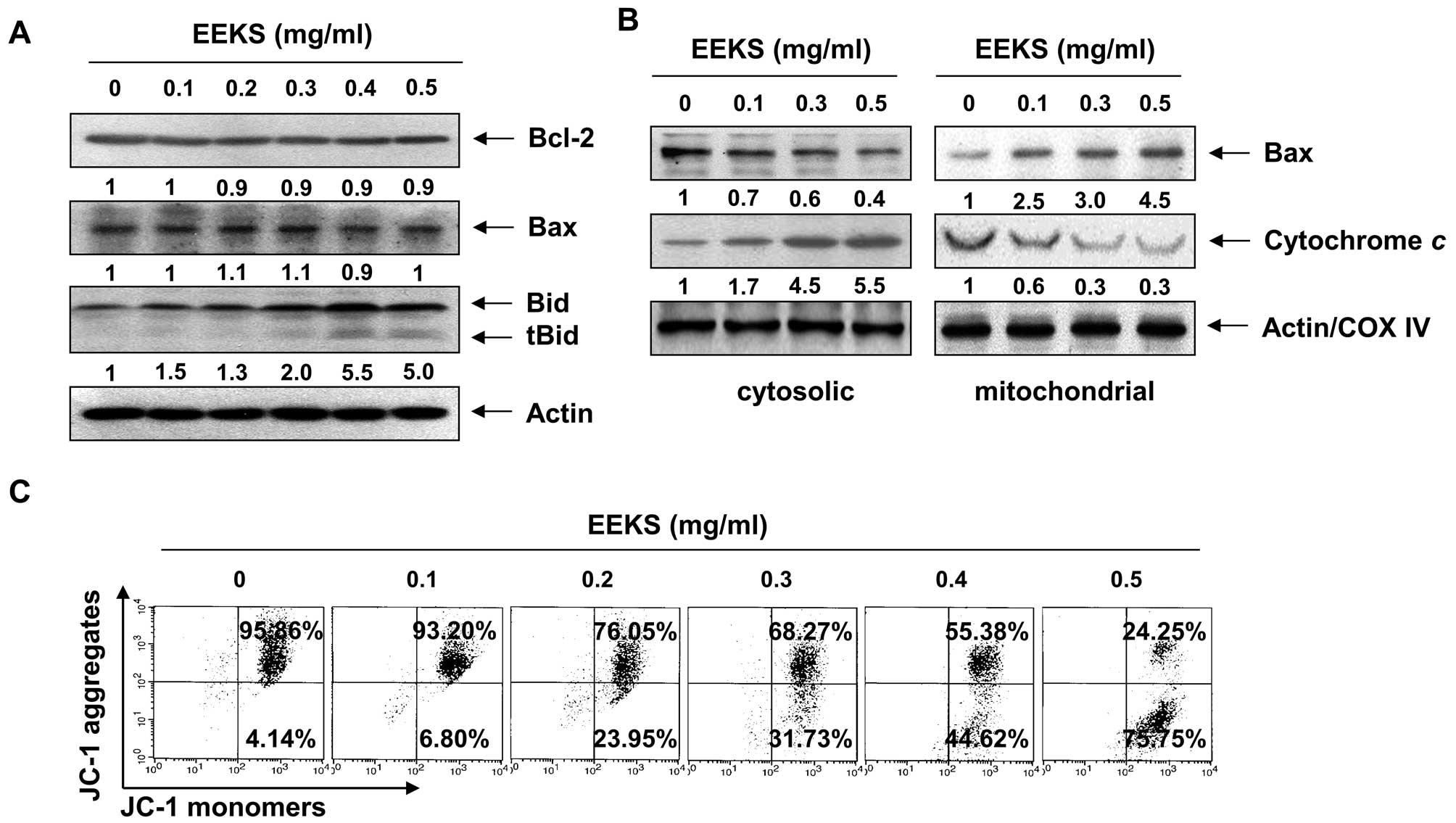
|
1
|
Kao JH and Chen DS: Changing disease
burden of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Far East and Southeast
Asia. Liver Int. 25:696–703. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J and de
Guevara LL: The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 15(Suppl
4): 5–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen CJ, Wang LY, Lu SN, Wu MH, You SL,
Zhang YJ, Wang LW and Santella RM: Elevated aflatoxin exposure and
increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 24:38–42.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feitelson MA, Sun B, Satiroglu Tufan NL,
Liu J, Pan J and Lian Z: Genetic mechanisms of
hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2593–2604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thorgeirsson SS and Grisham JW: Molecular
pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet.
31:339–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ben Ari Z, Weitzman E and Safran M:
Oncogenic viruses and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis.
19:341–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Avila MA, Berasain C, Sangro B and Prieto
J: New therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
25:3866–3884. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng GL, Zeng S and Shen H: Chemotherapy
and target therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: New advances and
challenges. World J Hepatol. 7:787–798. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fadeel B and Orrenius S: Apoptosis: A
basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human
disease. J Intern Med. 258:479–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lavrik IN: Systems biology of apoptosis
signaling networks. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 21:551–555. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walczak H and Krammer PH: The CD95
(APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems. Exp Cell Res.
256:58–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hensley P, Mishra M and Kyprianou N:
Targeting caspases in cancer therapeutics. Biol Chem. 394:831–843.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mantovani J and Roy R: Re-evaluating the
general(ized) roles of AMPK in cellular metabolism. FEBS Lett.
585:967–972. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li W, Saud SM, Young MR, Chen G and Hua B:
Targeting AMPK for cancer prevention and treatment. Oncotarget.
6:7365–7378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Marley AE, Sullivan JE, Carling D, Abbott
WM, Smith GJ, Taylor IW, Carey F and Beri RK: Biochemical
characterization and deletion analysis of recombinant human protein
phosphatase 2C alpha. Biochem J. 320:801–806. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oakhill JS, Scott JW and Kemp BE: AMPK
functions as an adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 23:125–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hardie DG: AMPK: A key regulator of energy
balance in the single cell and the whole organism. Int J Obes.
32(Suppl 4): S7–S12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee CW, Wong LL, Tse EY, Liu HF, Leong VY,
Lee JM, Hardie DG, Ng IO and Ching YP: AMPK promotes p53
acetylation via phosphorylation and inactivation of SIRT1 in liver
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 72:4394–4404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han JY, Park SH, Yang JH, Kim MG, Cho SS,
Yoon G, Cheon SH and Ki SH: Licochalcone suppresses LXRα-induced
hepatic lipogenic gene expression through AMPK/Sirt1 pathway
activation. Toxicol Res. 30:19–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hwang WC, Kim MK, Song JH, Choi KY and Min
S: Inhibition of phospholipase D2 induces autophagy in colorectal
cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Min B, Lee H, Song JH, Han MJ and Chung J:
Arctiin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and decreases
adiposity and body weight in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutr Res
Pract. 8:655–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rehman G, Shehzad A, Khan AL and Hamayun
M: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in cancer therapy. Arch
Pharm (Weinheim). 347:457–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Martelli AM, Chiarini F, Evangelisti C,
Ognibene A, Bressanin D, Billi AM, Manzoli L, Cappellini A and
McCubrey JA: Targeting the liver kinase B1/AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway as a therapeutic strategy for hematological
malignancies. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:729–742. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng L, Yang W, Wu F, Wang C, Yu L, Tang
L, Qiu B, Li Y, Guo L, Wu M, et al: Prognostic significance of AMPK
activation and therapeutic effects of metformin in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5372–5380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lv Q, Zhen Q, Liu L, Gao R, Yang S, Zhou
H, Goswami R and Li Q: AMP-kinase pathway is involved in tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced lipid accumulation in human hepatoma
cells. Life Sci. 131:23–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu R, Zhang ZQ, Wang B, Jiang HX, Cheng L
and Shen LM: Berberine-induced apoptotic and autophagic death of
HepG2 cells requires AMPK activation. Cancer Cell Int. 14:492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ishijima N, Kanki K, Shimizu H and Shiota
G: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by retinoic acid
sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by
sorafenib. Cancer Sci. 106:567–575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu JJ, Omar HA, Lee YR, Teng YN, Chen PS,
Chen YC, Huang HS, Lee KH and Hung JH: 6-Shogaol induces cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma cells through pleiotropic
mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 762:449–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Singh AK and Singh I:
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside inhibits
cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via AMP-activated
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:39582–39593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao H, Zhu H, Lin Z, Lin G and Lv G:
Compound 13, an α1-selective small molecule activator of AMPK,
inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced oxidative stresses and gastric
epithelial cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:510–517.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qu Z, Zhang Y, Liao M, Chen Y, Zhao J and
Pan Y: In vitro and in vivo antitumoral action of metformin on
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saito T, Chiba T, Yuki K, Zen Y, Oshima M,
Koide S, Motoyama T, Ogasawara S, Suzuki E, Ooka Y, et al:
Metformin, a diabetes drug, eliminates tumor-initiating
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e700102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang X, Sun D, Tian Y, Ling S and Wang L:
Metformin sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis by downregulating Bcl2 expression.
Tumour Biol. 36:2957–2964. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chou CW, Cheng YW and Tsai CH:
Phyllostachys edulis extract induces apoptosis signaling in
osteosarcoma cells, associated with AMPK activation. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 8:1577–1584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee HW, Jang KS, Choi HJ, Jo A, Cheong JH
and Chun KH: Celastrol inhibits gastric cancer growth by induction
of apoptosis and autophagy. BMB Rep. 47:697–702. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shin JA, Kwon KH and Cho SD:
AMPK-activated protein kinase activation by Impatiens balsamina L.
is related to apoptosis in HSC-2 human oral cancer cells.
Pharmacogn Mag. 11:136–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang TP, Lee HJ, Ou TT, Chang YJ and Wang
CJ: Mulberry leaf polyphenol extract induced apoptosis involving
regulation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein
kinase/fatty acid synthase in a p53-negative hepatocellular
carcinoma cell. J Agric Food Chem. 60:6891–6898. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang G, Li X, Li X, Wang L, Li J, Song X,
Chen J, Guo Y, Sun X, Wang S, et al: Traditional Chinese medicine
in cancer care: A review of case series published in the chinese
literature. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:7510462012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang X, Feng Y, Wang N, Cheung F, Tan HY,
Zhong S, Li C and Kobayashi S: Chinese medicines induce cell death:
The molecular and cellular mechanisms for cancer therapy. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:5303422014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shin JS, Kim YM, Hong SS, Kang HS, Yang
YJ, Lee DK, Hwang BY, Ro JS and Lee MK: Induction of neurite
outgrowth by (-)-(7R, 8S)-dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol from
PC12 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 28:1337–1340. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jun DH, Lee JT, Cheon SJ, Lee CE, Kim TH,
Lee DH, Han J and Kim SH: Polyphenol and anti-oxidant effects of
Kalopanax septemlobus Koidz. leaf extracts Korean. J Plant Res.
22:343–348. 2009.
|
|
45
|
Wang LS, Zhao DQ, Xu TH, Zhou XF, Yang XW
and Liu YH: A new triterpene hexaglycoside from the bark of
Kalopanax septemlobus (Thunb.) Koidz. Molecules. 14:4497–4504.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim HJ, Kim MJ, Oh SI, Hwangbo MH, Jang
SJ, Kim HI and Lee IS: Antioxidant activity of Kalopanax pictus
leaf extract and its effects on the quality characteristics of
fried pork skin. Korean J Food Sci Technol. 44:185–190. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Duriez PJ and Shah GM: Cleavage of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: A sensitive parameter to study cell
death. Biochem Cell Biol. 75:337–349. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
de Graaf AO, de Witte T and Jansen JH:
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: New therapeutic targets in
hematological cancer? Leukemia. 18:1751–1759. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Danson S, Dean E, Dive C and Ranson M:
IAPs as a target for anticancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
7:785–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ: Mechanisms of
cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:437–444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jourdain A and Martinou JC: Mitochondrial
outer-membrane permeabilization and remodelling in apoptosis. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1884–1889. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Scott JW, Norman DG, Hawley SA,
Kontogiannis L and Hardie DG: Protein kinase substrate recognition
studied using the recombinant catalytic domain of AMP-activated
protein kinase and a model substrate. J Mol Biol. 317:309–323.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. BioMed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kantari C and Walczak H: Caspase-8 and
bid: Caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:558–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|