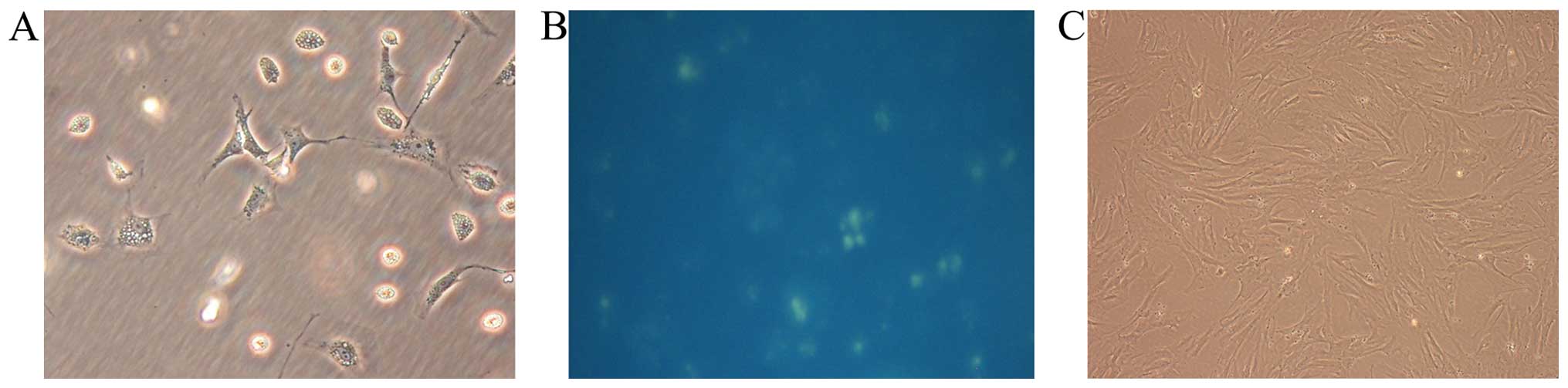
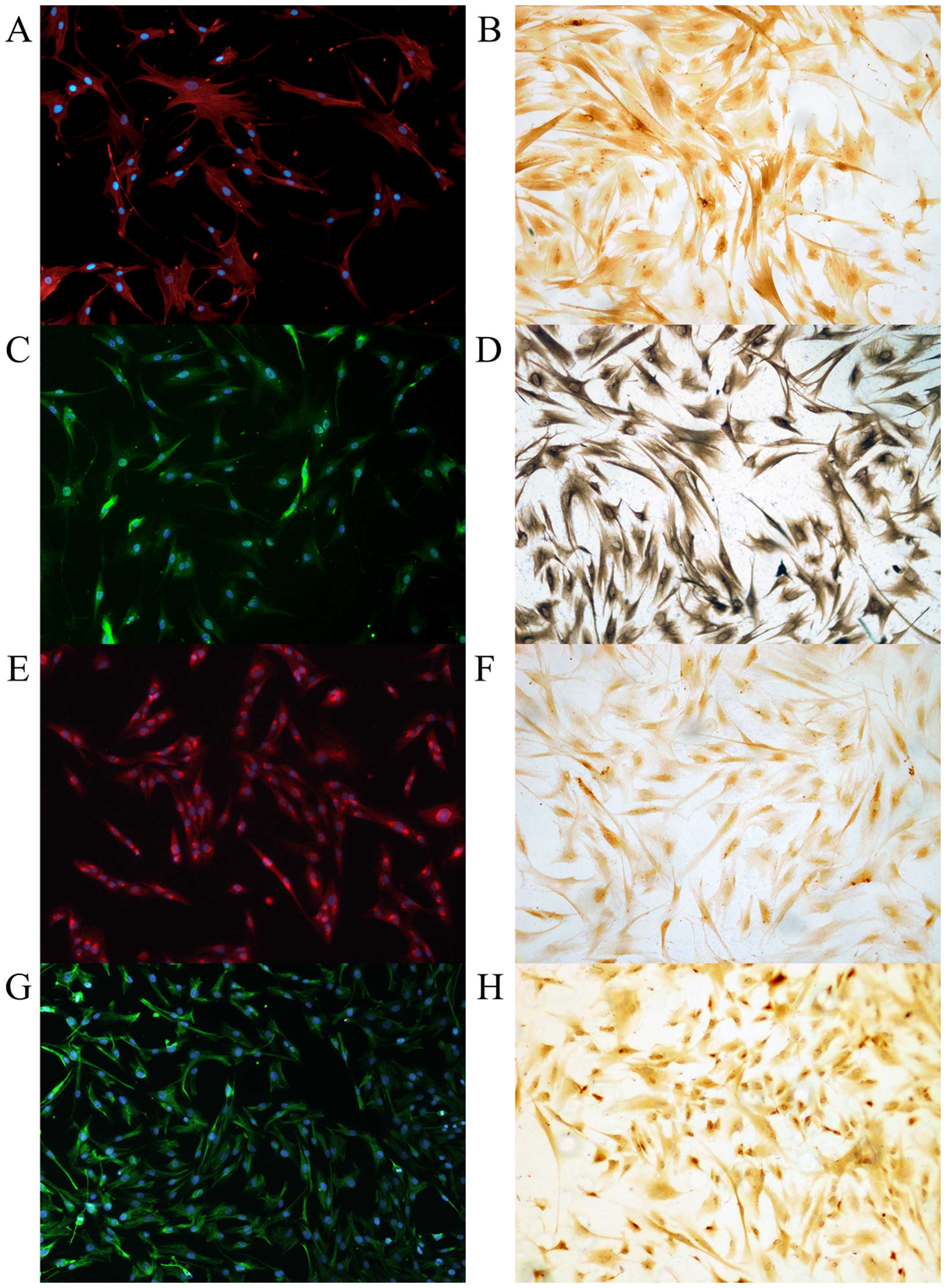
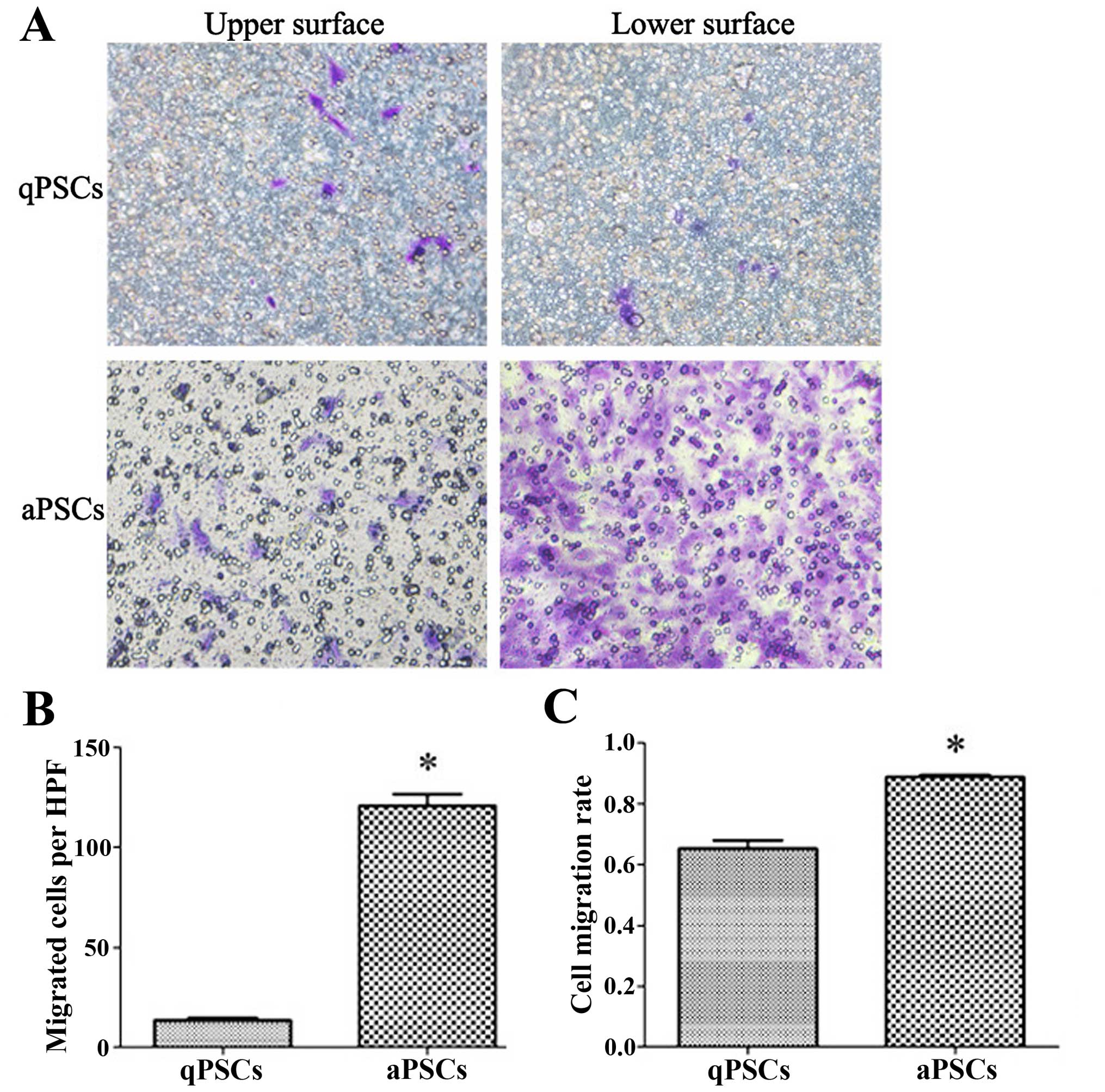
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pandol S, Gukovskaya A, Edderkaoui M,
Dawson D, Eibl G and Lugea A: Epidemiology, risk factors, and the
promotion of pancreatic cancer: Role of the stellate cell. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27(Suppl 2): 127–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chu GC, Kimmelman AC, Hezel AF and DePinho
RA: Stromal biology of pancreatic cancer. J Cell Biochem.
101:887–907. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Apte MV, Park S, Phillips PA, Santucci N,
Goldstein D, Kumar RK, Ramm GA, Buchler M, Friess H, McCarroll JA,
et al: Desmoplastic reaction in pancreatic cancer: Role of
pancreatic stellate cells. Pancreas. 29:179–187. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamaguchi K: How to define patients at
high risk for pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 11(Suppl 2): 3–6.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Liao Z, Li G, Li ZS, Chen J, Zhan
XB, Wang LW, Liu F, Hu LH, Guo Y, et al: Incidence of pancreatic
cancer in Chinese patients with chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatology. 11:16–23. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kudo Y, Kamisawa T, Anjiki H, Takuma K and
Egawa N: Incidence of and risk factors for developing pancreatic
cancer in patients with chronic pancreatitis.
Hepatogastroenterology. 58:609–611. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pezzilli R, Vecchiarelli S, Di Marco MC,
Serra C, Santini D, Calculli L, Fabbri D, Rojas Mena B and Imbrogno
A: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma associated with autoimmune
pancreatitis. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 5:378–385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liotta LA and Kohn EC: The
microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 411:375–379.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Wever O and Mareel M: Role of tissue
stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol. 200:429–447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guerra C, Schuhmacher AJ, Cañamero M,
Grippo PJ, Verdaguer L, Pérez-Gallego L, Dubus P, Sandgren EP and
Barbacid M: Chronic pancreatitis is essential for induction of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by K-Ras oncogenes in adult mice.
Cancer Cell. 11:291–302. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Erkan M, Adler G, Apte MV, Bachem MG,
Buchholz M, Detlefsen S, Esposito I, Friess H, Gress TM, Habisch
HJ, et al: StellaTUM: Current consensus and discussion on
pancreatic stellate cell research. Gut. 61:172–178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jaster R: Molecular regulation of
pancreatic stellate cell function. Mol Cancer. 3:262004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watari N, Hotta Y and Mabuchi Y:
Morphological studies on a vitamin A-storing cell and its complex
with macrophage observed in mouse pancreatic tissues following
excess vitamin A administration. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn.
58:837–858. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Apte MV, Haber PS, Applegate TL, Norton
ID, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC and Wilson JS: Periacinar
stellate shaped cells in rat pancreas: Identification, isolation,
and culture. Gut. 43:128–133. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bachem MG, Schneider E, Gross H,
Weidenbach H, Schmid RM, Menke A, Siech M, Beger H, Grünert A and
Adler G: Identification, culture, and characterization of
pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology.
115:421–432. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Apte M, Pirola R and Wilson J: The
fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis: new insights into the role of
pancreatic stellate cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:2711–2722.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Apte MV, Pirola RC and Wilson JS:
Pancreatic stellate cells: A starring role in normal and diseased
pancreas. Front Physiol. 3:3442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Apte MV, Wilson JS, Lugea A and Pandol SJ:
A starring role for stellate cells in the pancreatic cancer
microenvironment. Gastroenterology. 144:1210–1219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boyer B, Vallés AM and Edme N: Induction
and regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Biochem
Pharmacol. 60:1091–1099. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scheel C and Weinberg RA: Phenotypic
plasticity and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer and
normal stem cells? Int J Cancer. 129:2310–2314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Neilson EG: Plasticity, nuclear diapause,
and a requiem for the terminal differentiation of epithelia. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 18:1995–1998. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guarino M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and tumour invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:2153–2160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moustakas A: Integrins open the way to
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Cell Cycle. 9:16822010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Witek RP, Moylan CA,
Syn WK, Jung Y, Yang L, Sudan DL, Sicklick JK, Michelotti GA, et
al: Hedgehog pathway activation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transitions during myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic
cells in culture and cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 297:G1093–G1106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kikuta K, Masamune A, Watanabe T, Ariga H,
Itoh H, Hamada S, Satoh K, Egawa S, Unno M and Shimosegawa T:
Pancreatic stellate cells promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
403:380–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic proteins:
Multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes Dev.
10:1580–1594. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang MH, Kim JS, Seo JE, Oh SC and Yoo YA:
BMP2 accelerates the motility and invasiveness of gastric cancer
cells via activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
(PI3K)/Akt pathway. Exp Cell Res. 316:24–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Klahr S: The bone morphogenetic proteins
(BMPs). Their role in renal fibrosis and renal function. J Nephrol.
16:179–185. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ohta S, Schoenwolf GC and Yamada G: The
cessation of gastrulation: BMP signaling and EMT during and at the
end of gastrulation. Cell Adhes Migr. 4:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zeisberg M, Hanai J, Sugimoto H, Mammoto
T, Charytan D, Strutz F and Kalluri R: BMP-7 counteracts
TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses
chronic renal injury. Nat Med. 9:964–968. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zeisberg M, Shah AA and Kalluri R: Bone
morphogenic protein-7 induces mesenchymal to epithelial transition
in adult renal fibroblasts and facilitates regeneration of injured
kidney. J Biol Chem. 280:8094–8100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tarabykina S, Griffiths TR, Tulchinsky E,
Mellon JK, Bronstein IB and Kriajevska M: Metastasis-associated
protein S100A4: Spotlight on its role in cell migration. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 7:217–228. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mazzucchelli L: Protein S100A4: Too long
overlooked by pathologists? Am J Pathol. 160:7–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li ZH and Bresnick AR: The S100A4
metastasis factor regulates cellular motility via a direct
interaction with myosin-IIA. Cancer Res. 66:5173–5180. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta S, Xie L, Zeisberg M
and Kalluri R: Discovery of endothelial to mesenchymal transition
as a source for carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res.
67:10123–10128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone
RL, Tomaszewski JE and Neilson EG: Identification and
characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol.
130:393–405. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barrallo-Gimeno A and Nieto MA: The Snail
genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: Implications in
development and cancer. Development. 132:3151–3161. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nieto MA: The snail superfamily of
zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:155–166. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and García De Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Scarpa M, Grillo AR, Brun P, Macchi V,
Stefani A, Signori S, Buda A, Fabris P, Giordani MT, De Caro R, et
al: Snail1 transcription factor is a critical mediator of hepatic
stellate cell activation following hepatic injury. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 300:G316–G326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lipschutz JH: Molecular development of the
kidney: A review of the results of gene disruption studies. Am J
Kidney Dis. 31:383–397. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hogan BL and Kolodziej PA: Organogenesis:
Molecular mechanisms of tubulogenesis. Nat Rev Genet. 3:513–523.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rothenpieler UW and Dressler GR: Pax-2 is
required for mesenchyme-to-epithelium conversion during kidney
development. Development. 119:711–720. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mizuiri S, Hemmi H, Arita M, Tai R,
Hattori Y, Muto A, Suzuki Y, Ohashi Y, Sakai K and Aikawa A:
Effluent markers related to epithelial mesenchymal transition with
adjusted values for effluent cancer antigen 125 in peritoneal
dialysis patients. Int J Nephrol. 2011:2610402011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bailey JM, Singh PK and Hollingsworth MA:
Cancer metastasis facilitated by developmental pathways: Sonic
hedgehog, Notch, and bone morphogenic proteins. J Cell Biochem.
102:829–839. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Hedgehog signaling,
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and miRNA (review). Int J Mol
Med. 22:271–275. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Choi SS, Syn WK, Karaca GF, Omenetti A,
Moylan CA, Witek RP, Agboola KM, Jung Y, Michelotti GA and Diehl
AM: Leptin promotes the myofibroblastic phenotype in hepatic
stellate cells by activating the hedgehog pathway. J Biol Chem.
285:36551–36560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Omenetti A, Porrello A, Jung Y, Yang L,
Popov Y, Choi SS, Witek RP, Alpini G, Venter J, Vandongen HM, et
al: Hedgehog signaling regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition
during biliary fibrosis in rodents and humans. J Clin Invest.
118:3331–3342. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Syn WK, Jung Y, Omenetti A, Abdelmalek M,
Guy CD, Yang L, Wang J, Witek RP, Fearing CM, Pereira TA, et al:
Hedgehog-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
fibrogenic repair in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Gastroenterology. 137:1478–1488. e14782009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|