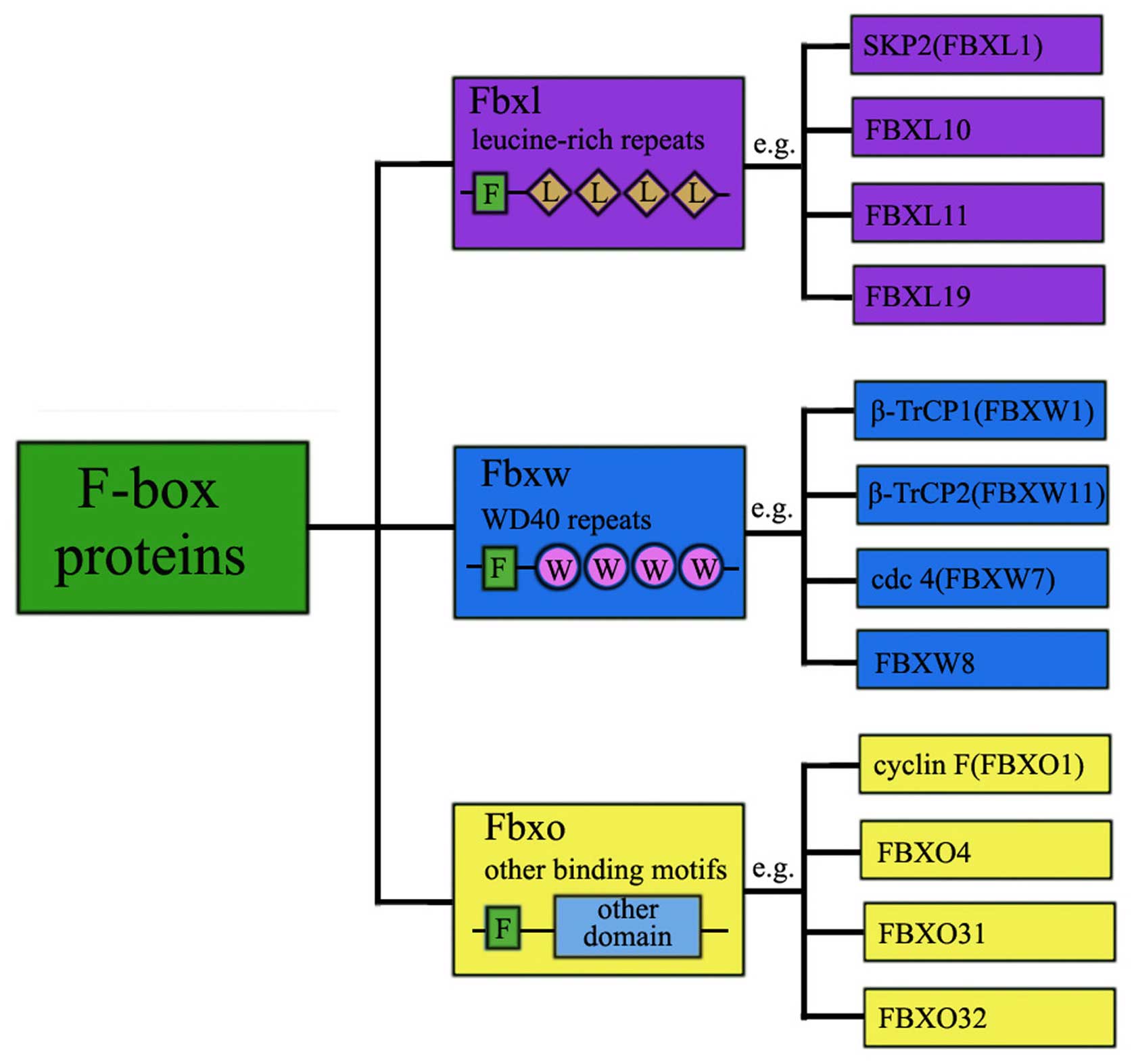
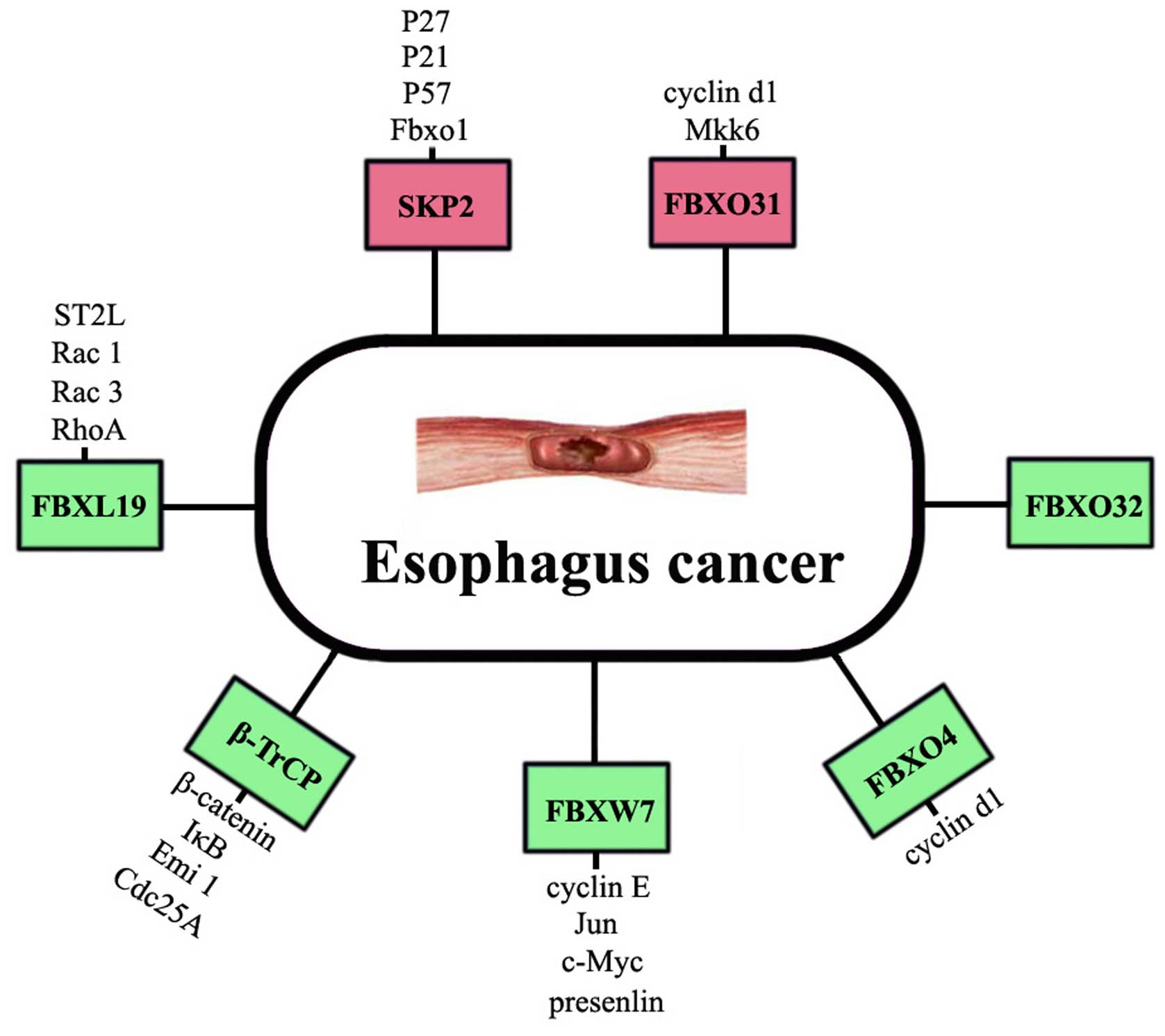
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gammon MD, Schoenberg JB, Ahsan H, Risch
HA, Vaughan TL, Chow WH, Rotterdam H, West AB, Dubrow R, Stanford
JL, et al: Tobacco, alcohol, and socioeconomic status and
adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastric cardia. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 89:1277–1284. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang WR, Fang JY, Wu KS, Shi XJ, Luo JY
and Lin K: Epidemiological characteristics and prediction of
esophageal cancer mortality in China from 1991 to 2012. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:6929–6934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hershko DD: Oncogenic properties and
prognostic implications of the ubiquitin ligase Skp2 in cancer.
Cancer. 112:1415–1424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao M and Karin M: Regulating the
regulators: Control of protein ubiquitination and ubiquitin-like
modifications by extra-cellular stimuli. Mol Cell. 19:581–593.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thrower JS, Hoffman L, Rechsteiner M and
Pickart CM: Recognition of the polyubiquitin proteolytic signal.
EMBO J. 19:94–102. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kitagawa K, Kotake Y and Kitagawa M:
Ubiquitin-mediated control of oncogene and tumor suppressor gene
products. Cancer Sci. 100:1374–1381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y and Sun Y: Cullin-RING Ligases as
attractive anti-cancer targets. Curr Pharm Des. 19:3215–3225. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Reed SI: Ratchets and clocks: The cell
cycle, ubiquitylation and protein turnover. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
4:855–864. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peters J-M: The anaphase promoting
complex/cyclosome: A machine designed to destroy. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:644–656. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Z, Liu P, Inuzuka H and Wei W: Roles
of F-box proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:233–247. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lockwood WW, Chandel SK, Stewart GL,
Erdjument-Bromage H and Beverly LJ: The novel ubiquitin ligase
complex, SCF(Fbxw4), interacts with the COP9 signalosome in an
F-box dependent manner, is mutated, lost and under-expressed in
human cancers. PLoS One. 8:e636102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huber C, Dias-Santagata D, Glaser A,
O'Sullivan J, Brauner R, Wu K, Xu X, Pearce K, Wang R, Uzielli ML,
et al: Identification of mutations in CUL7 in 3-M syndrome. Nat
Genet. 37:1119–1124. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tzatsos A, Paskaleva P, Ferrari F,
Deshpande V, Stoykova S, Contino G, Wong KK, Lan F, Trojer P, Park
PJ, et al: KDM2B promotes pancreatic cancer via Polycomb-dependent
and -independent transcriptional programs. J Clin Invest.
123:727–739. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu W, Ding H, Cao J and Zhang W: FBXL5
inhibits metastasis of gastric cancer through suppressing Snail1.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1764–1772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cardozo T and Pagano M: The SCF ubiquitin
ligase: Insights into a molecular machine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:739–751. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Y, Tang Q, Ni R, Huang X, Wang Y, Lu
C, Shen A, Wang Y, Li C, Yuan Q, et al: Early mitotic inhibitor-1,
an anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome inhibitor, can control
tumor cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation
with Skp2 stability and degradation of p27(Kip1). Hum Pathol.
44:365–373. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Duan S, Cermak L, Pagan JK, Rossi M,
Martinengo C, di Celle PF, Chapuy B, Shipp M, Chiarle R and Pagano
M: FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in
diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Nature. 481:90–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Demetrick DJ, Zhang H and Beach DH:
Chromosomal mapping of the genes for the human CDK2/cyclin
A-associated proteins p19 (SKP1A and SKP1B) and p45 (SKP2).
Cytogenet Cell Genet. 73:104–107. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hershko D, Bornstein G, Ben-Izhak O,
Carrano A, Pagano M, Krausz MM and Hershko A: Inverse relation
between levels of p27(Kip1) and of its ubiquitin ligase subunit
Skp2 in colorectal carcinomas. Cancer. 91:1745–1751. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fukuchi M, Masuda N, Nakajima M, Fukai Y,
Miyazaki T, Kato H and Kuwano H: Inverse correlation between
expression levels of p27 and the ubiquitin ligase subunit Skp2 in
early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 24(2B):
777–783. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang G, Ayala G, De Marzo A, Tian W,
Frolov A, Wheeler TM, Thompson TC and Harper JW: Elevated Skp2
protein expression in human prostate cancer: Association with loss
of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and PTEN and with
reduced recurrence-free survival. Clin Cancer Res. 8:3419–3426.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Traub F, Mengel M, Lück HJ, Kreipe HH and
von Wasielewski R: Prognostic impact of Skp2 and p27 in human
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 99:185–191. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Masuda TA, Inoue H, Sonoda H, Mine S,
Yoshikawa Y, Nakayama K, Nakayama K and Mori M: Clinical and
biological significance of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2
(Skp2) gene expression in gastric carcinoma: Modulation of
malignant phenotype by Skp2 overexpression, possibly via p27
proteolysis. Cancer Res. 62:3819–3825. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Frescas D and Pagano M: Deregulated
proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and beta-TrCP: Tipping the
scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:438–449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rose AE, Wang G, Hanniford D, Monni S, Tu
T, Shapiro RL, Berman RS, Pavlick AC, Pagano M, Darvishian F, et
al: Clinical relevance of SKP2 alterations in metastatic melanoma.
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 24:197–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xu HM, Liang Y, Chen Q, Wu QN, Guo YM,
Shen GP, Zhang RH, He ZW, Zeng YX, Xie FY, et al: Correlation of
Skp2 overexpression to prognosis of patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma from South China. Chin J Cancer. 30:204–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schüler S, Diersch S, Hamacher R, Schmid
RM, Saur D and Schneider G: SKP2 confers resistance of pancreatic
cancer cells towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
38:219–225. 2011.
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Fukushima H, Inuzuka H, Wan L, Liu
P, Gao D, Sarkar FH and Wei W: Skp2 is a promising therapeutic
target in breast cancer. Front Oncol. 1:187022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shapira M, Ben-Izhak O, Linn S, Futerman
B, Minkov I and Hershko DD: The prognostic impact of the ubiquitin
ligase subunits Skp2 and Cks1 in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer.
103:1336–1346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang XC, Wu YP, Ye B, Lin DC, Feng YB,
Zhang ZQ, Xu X, Han YL, Cai Y, Dong JT, et al: Suppression of
anoikis by SKP2 amplification and overexpression promotes
metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res.
7:12–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yokoi S, Yasui K, Saito-Ohara F, Koshikawa
K, Iizasa T, Fujisawa T, Terasaki T, Horii A, Takahashi T,
Hirohashi S, et al: A novel target gene, SKP2, within the 5p13
amplicon that is frequently detected in small cell lung cancers. Am
J Pathol. 161:207–216. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang XC, Tian LL, Tian J and Jiang XY:
Overexpression of SKP2 promotes the radiation resistance of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Radiat Res. 177:52–58. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bai P, Xiao X, Zou J, Cui L, Bui Nguyen
TM, Liu J, Xiao J, Chang B, Wu J and Wang H: Expression of
p14(ARF), p15(INK4b), p16(INK4a) and skp2 increases during
esophageal squamous cell cancer progression. Exp Ther Med.
3:1026–1032. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liang Y, Hou X, Cui Q, Kang T-B, Fu J-H,
Zhang L-J, Luo R-Z, He J-H, Zeng Y-X and Yang H-X: Skp2 expression
unfavorably impacts survival in resectable esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10:732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y and
Mills GB: Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug
discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:988–1004. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gao D, Inuzuka H, Tseng A, Chin RY, Toker
A and Wei W: Phosphorylation by Akt1 promotes cytoplasmic
localization of Skp2 and impairs APCCdh1-mediated Skp2 destruction.
Nat Cell Biol. 11:397–408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
van Duijn PW and Trapman J: PI3K/Akt
signaling regulates p27(kip1) expression via Skp2 in PC3 and DU145
prostate cancer cells, but is not a major factor in p27(kip1)
regulation in LNCaP and PC346 cells. Prostate. 66:749–760. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Reichert M, Saur D, Hamacher R, Schmid RM
and Schneider G: Phosphoinositide-3-kinase signaling controls
S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 transcription via E2F1 in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:4149–4156.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nakayama KI and Nakayama K: Ubiquitin
ligases: Cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:369–381.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Andreu EJ, Lledó E, Poch E, Ivorra C,
Albero MP, Martínez-Climent JA, Montiel-Duarte C, Rifón J,
Pérez-Calvo J, Arbona C, et al: BCR-ABL induces the expression of
Skp2 through the PI3K pathway to promote p27Kip1 degradation and
proliferation of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Res.
65:3264–3272. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hartwell LH, Mortimer RK, Culotti J and
Culotti M: Genetic Control of the Cell Division Cycle in Yeast: V.
Genetic Analysis of cdc Mutants. Genetics. 74:267–286.
1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sionov RV, Netzer E and Shaulian E:
Differential regulation of FBXW7 isoforms by various stress
stimuli. Cell Cycle. 12:3547–3554. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Davis RJ, Welcker M and Clurman BE: Tumor
suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: Mechanisms and
opportunities. Cancer Cell. 26:455–464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Minella AC, Welcker M and Clurman BE: Ras
activity regulates cyclin E degradation by the Fbw7 pathway. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:9649–9654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yada M: Hat ediated by the F-box protein
Fbw7. EMBO J. 23:2116–2125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hoeck JD, Jandke A, Blake SM, Nye E,
Spencer-Dene B, Brandner S and Behrens A: Fbw7 controls neural stem
cell differentiation and progenitor apoptosis via Notch and c-Jun.
Nat Neurosci. 13:1365–1372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Enkhbold C, Utsunomiya T, Morine Y, Imura
S, Ikemoto T, Arakawa Y, Kanamoto M, Iwahashi S, Saito Y, Ishikawa
D, et al: Loss of FBXW7 expression is associated with poor
prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatol Res.
44:E346–E352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ibusuki M, Yamamoto Y, Shinriki S, Ando Y
and Iwase H: Reduced expression of ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 mRNA is
associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Cancer
Sci. 102:439–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Ishii H, Yokobori T,
Takatsuno Y, Sato T, Toh H, Onoyama I, Nakayama KI, Baba H, et al:
Loss of FBXW7, a cell cycle regulating gene, in colorectal cancer:
Clinical significance. Int J Cancer. 126:1828–1837. 2010.
|
|
54
|
Kurashige J, Watanabe M, Iwatsuki M,
Kinoshita K, Saito S, Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Baba Y, Mimori K and
Baba H: Overexpression of microRNA-223 regulates the ubiquitin
ligase FBXW7 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
106:182–188. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Yokobori T, Mimori K, Iwatsuki M, Ishii H,
Onoyama I, Fukagawa T, Kuwano H, Nakayama KI and Mori M:
p53-altered FBXW7 expression determines poor prognosis in gastric
cancer cases. Cancer Res. 69:3788–3794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kimura T, Gotoh M, Nakamura Y and Arakawa
H: hCDC4b, a regulator of cyclin E, as a direct transcriptional
target of p53. Cancer Sci. 94:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, Gao D,
Tseng A, Maser RS, Zhai B, Wan L, Gutierrez A, Lau AW, et al:
SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for
ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature. 471:104–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T,
Sandoval W, Anderson DJ, Helgason E, Ernst JA, Eby M, Liu J, et al:
Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1
and FBW7. Nature. 471:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen J, Shin JH, Zhao R, Phan L, Wang H,
Xue Y, Post SM, Ho Choi H, Chen JS, Wang E, et al: CSN6 drives
carcinogenesis by positively regulating Myc stability. Nat Commun.
5:53842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ji S, Qin Y, Shi S, Liu X, Hu H, Zhou H,
Gao J, Zhang B, Xu W, Liu J, et al: ERK kinase phosphorylates and
destabilizes the tumor suppressor FBW7 in pancreatic cancer. Cell
Res. 25:561–573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sterian A, Kan T, Berki AT, Mori Y, Olaru
A, Schulmann K, Sato F, Wang S, Paun B, Cai K, et al: Mutational
and LOH analyses of the chromosome 4q region in esophageal
adenocarcinoma. Oncology. 70:168–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Balamurugan K, Sharan S, Klarmann KD,
Zhang Y, Coppola V, Summers GH, Roger T, Morrison DK, Keller JR and
Sterneck E: FBXW7α attenuates inflammatory signalling by
downregulating C/EBPδ and its target gene Tlr4. Nat Commun.
4:16622013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Yokobori T, Mimori K, Iwatsuki M, Ishii H,
Tanaka F, Sato T, Toh H, Sudo T, Iwaya T, Tanaka Y, et al: Copy
number loss of FBXW7 is related to gene expression and poor
prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
41:253–259. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xu Y, Sengupta T, Kukreja L and Minella
AC: MicroRNA-223 regulates cyclin E activity by modulating
expression of F-box and WD-40 domain protein 7. J Biol Chem.
285:34439–34446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gomes MD, Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Navon A and
Goldberg AL: Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly
expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:14440–14445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hanai J, Cao P, Tanksale P, Imamura S,
Koshimizu E, Zhao J, Kishi S, Yamashita M, Phillips PS, Sukhatme
VP, et al: The muscle-specific ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1/MAFbx
mediates statin-induced muscle toxicity. J Clin Invest.
117:3940–3951. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Guo W, Zhang M, Shen S, Guo Y, Kuang G,
Yang Z and Dong Z: Aberrant methylation and decreased expression of
the TGF-β/Smad target gene FBXO32 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer. 120:2412–2423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Guo W, Zhang M, Guo Y, Shen S, Guo X and
Dong Z: FBXO32, a new TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway target gene, is
epigenetically inactivated in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma.
Neoplasma. 62:646–657. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Chou JL, Su HY, Chen LY, Liao YP,
Hartman-Frey C, Lai YH, Yang HW, Deatherage DE, Kuo CT, Huang YW,
et al: Promoter hypermethylation of FBXO32, a novel TGF-beta/SMAD4
target gene and tumor suppressor, is associated with poor prognosis
in human ovarian cancer. Lab Invest. 90:414–425. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM
and Zhou BP: Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for
inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell.
15:416–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Shirane M, Hatakeyama S, Hattori K and
Nakayama K and Nakayama K: Common pathway for the ubiquitination of
IkappaBalpha, IkappaBbeta, and IkappaBepsilon mediated by the F-box
protein FWD1. J Biol Chem. 274:28169–28174. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Spiegelman VS, Slaga TJ, Pagano M,
Minamoto T, Ronai Z and Fuchs SY: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
induces the expression and activity of betaTrCP ubiquitin ligase
receptor. Mol Cell. 5:877–882. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT,
Colman H, Huang H, Xue J, Liu M, Wang Y, et al: FoxM1 promotes
β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene
expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 20:427–442. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Mokkapati S, Niopek K, Huang L, Cunniff
KJ, Ruteshouser EC, deCaestecker M, Finegold MJ and Huff V:
β-catenin activation in a novel liver progenitor cell type is
sufficient to cause hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatoblastoma.
Cancer Res. 74:4515–4525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li AF, Hsu PK, Tzao C, Wang YC, Hung IC,
Huang MH and Hsu HS: Reduced axin protein expression is associated
with a poor prognosis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of
esophagus. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2486–2493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Identification and
characterization of FBXL19 gene in silico. Int J Mol Med.
14:1109–1114. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
O'Rielly DD and Rahman P: Genetics of
psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 28:673–685.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Chandran V: The genetics of psoriasis and
psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 44:149–156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Cabaleiro T, Prieto-Pérez R, Navarro R,
Solano G, Román M, Ochoa D, Abad-Santos F and Daudén E: Paradoxical
psoria-siform reactions to anti-TNFα drugs are associated with
genetic polymorphisms in patients with psoriasis. Pharmacogenomics
J. Jul 21–2015, (Epub ahead of print) http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2015.53.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Hueber A, Stolarski
B and McInnes IB: Interleukin-33: A novel mediator with a role in
distinct disease pathologies. J Intern Med. 269:29–35. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Zhao J, Wei J, Mialki RK, Mallampalli DF,
Chen BB, Coon T, Zou C, Mallampalli RK and Zhao Y: F-box protein
FBXL19-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of the receptor for
IL-33 limits pulmonary inflammation. Nat Immunol. 13:651–658. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhao J, Mialki RK, Wei J, Coon TA, Zou C,
Chen BB, Mallampalli RK and Zhao Y: SCF E3 ligase F-box protein
complex SCF (FBXL19) regulates cell migration by mediating Rac1
ubiquitination and degradation. FASEB J. 27:2611–2619. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
ten Klooster JP, Leeuwen I, Scheres N,
Anthony EC and Hordijk PL: Rac1-induced cell migration requires
membrane recruitment of the nuclear oncogene SET. EMBO J.
26:336–345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Su J and Li H: RAC1 overexpression
promotes the proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of lens epithelial cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10760–11767. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Filippi MD, Szczur K, Harris CE and
Berclaz PY: Rho GTPase Rac1 is critical for neutrophil migration
into the lung. Blood. 109:1257–1264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Lao-Sirieix P and Fitzgerald RC: Role of
the micro-environment in Barrett's carcinogenesis. Biochem Soc
Trans. 38:327–330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Dong S, Zhao J, Wei J, Bowser RK, Khoo A,
Liu Z, Luketich JD, Pennathur A, Ma H and Zhao Y: F-box protein
complex FBXL19 regulates TGFβ1-induced E-cadherin down-regulation
by mediating Rac3 ubiquitination and degradation. Mol Cancer.
13:762014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Wei J, Mialki RK, Dong S, Khoo A,
Mallampalli RK, Zhao Y and Zhao J: A new mechanism of RhoA
ubiquitination and degradation: roles of SCF(FBXL19) E3 ligase and
Erk2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:2757–2764. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sheppard KE and McArthur GA: The
cell-cycle regulator CDK4: An emerging therapeutic target in
melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5320–5328. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lian Z, Lee EK, Bass AJ, Wong KK,
Klein-Szanto AJ, Rustgi AK and Diehl JA: FBXO4 loss facilitates
carcinogen induced papilloma development in mice. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:750–755. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lee TH, Perrem K, Harper JW, Lu KP and
Zhou XZ: The F-box protein FBX4 targets PIN2/TRF1 for
ubiquitin-mediated degradation and regulates telomere maintenance.
J Biol Chem. 281:759–768. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Barbash O, Zamfirova P, Lin DI, Chen X,
Yang K, Nakagawa H, Lu F, Rustgi AK and Diehl JA: Mutations in Fbx4
inhibit dimerization of the SCF(Fbx4) ligase and contribute to
cyclin D1 overexpression in human cancer. Cancer Cell. 14:68–78.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Santra MK, Wajapeyee N and Green MR: F-box
protein FBXO31 mediates cyclin D1 degradation to induce G1 arrest
after DNA damage. Nature. 459:722–725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jia L and Sun Y: F-box proteins FBXO31 and
FBX4 in regulation of cyclin D1 degradation upon DNA damage.
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 22:518–519. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kumar R, Neilsen PM, Crawford J, McKirdy
R, Lee J, Powell JA, Saif Z, Martin JM, Lombaerts M, Cornelisse CJ,
et al: FBXO31 is the chromosome 16q24.3 senescence gene, a
candidate breast tumor suppressor, and a component of an SCF
complex. Cancer Res. 65:11304–11313. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Huang HL, Zheng WL, Zhao R, Zhang B and Ma
WL: FBXO31 is down-regulated and may function as a tumor suppressor
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 24:715–720. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhang X, Kong Y, Xu X, Xing H, Zhang Y,
Han F, Li W, Yang Q, Zeng J, Jia J, et al: F-box protein FBXO31 is
down-regulated in gastric cancer and negatively regulated by miR-17
and miR-20a. Oncotarget. 5:6178–6190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Malonia SK, Dutta P, Santra MK and Green
MR: F-box protein FBXO31 directs degradation of MDM2 to facilitate
p53-mediated growth arrest following genotoxic stress. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:8632–8637. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Huang HL, Jiang Y, Wang YH, Chen T, He HJ,
Liu T, Yang T, Yang LW, Chen J, Song ZQ, et al: FBXO31 promotes
cell proliferation, metastasis and invasion in lung cancer. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:1814–1822. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S and
Mori M: FBXO31 determines poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 39:155–159. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu J, Han L, Li B, Yang J, Huen MS, Pan
X, Tsao SW and Cheung AL: F-box only protein 31 (FBXO31) negatively
regulates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling by
mediating lysine 48-linked ubiquitination and degradation of
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MKK6). J Biol Chem.
289:21508–21518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Balamurugan K, Wang JM, Tsai HH, Sharan S,
Anver M, Leighty R and Sterneck E: The tumour suppressor C/EBPδ
inhibits FBXW7 expression and promotes mammary tumour metastasis.
EMBO J. 29:4106–4117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Sancho R, Blake SM, Tendeng C, Clurman BE,
Lewis J and Behrens A: Fbw7 repression by hes5 creates a feedback
loop that modulates Notch-mediated intestinal and neural stem cell
fate decisions. PLoS Biol. 11:e10015862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kane RC, Bross PF, Farrell AT and Pazdur
R: Velcade: U.S. FDA approval for the treatment of multiple myeloma
progressing on prior therapy. Oncologist. 8:508–513. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Skaar JR, Pagan JK and Pagano M: SCF
ubiquitin ligase-targeted therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
13:889–903. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|