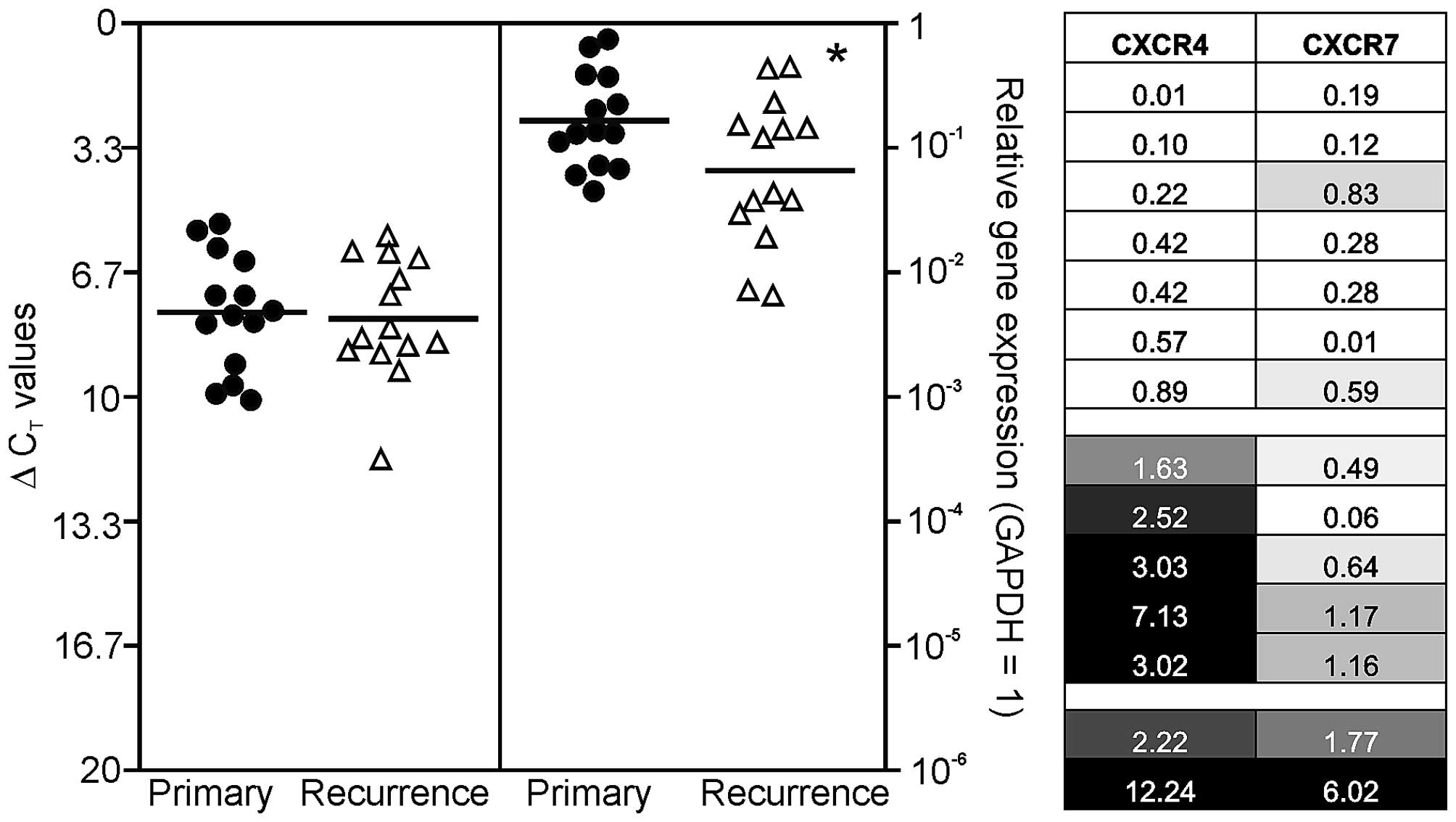
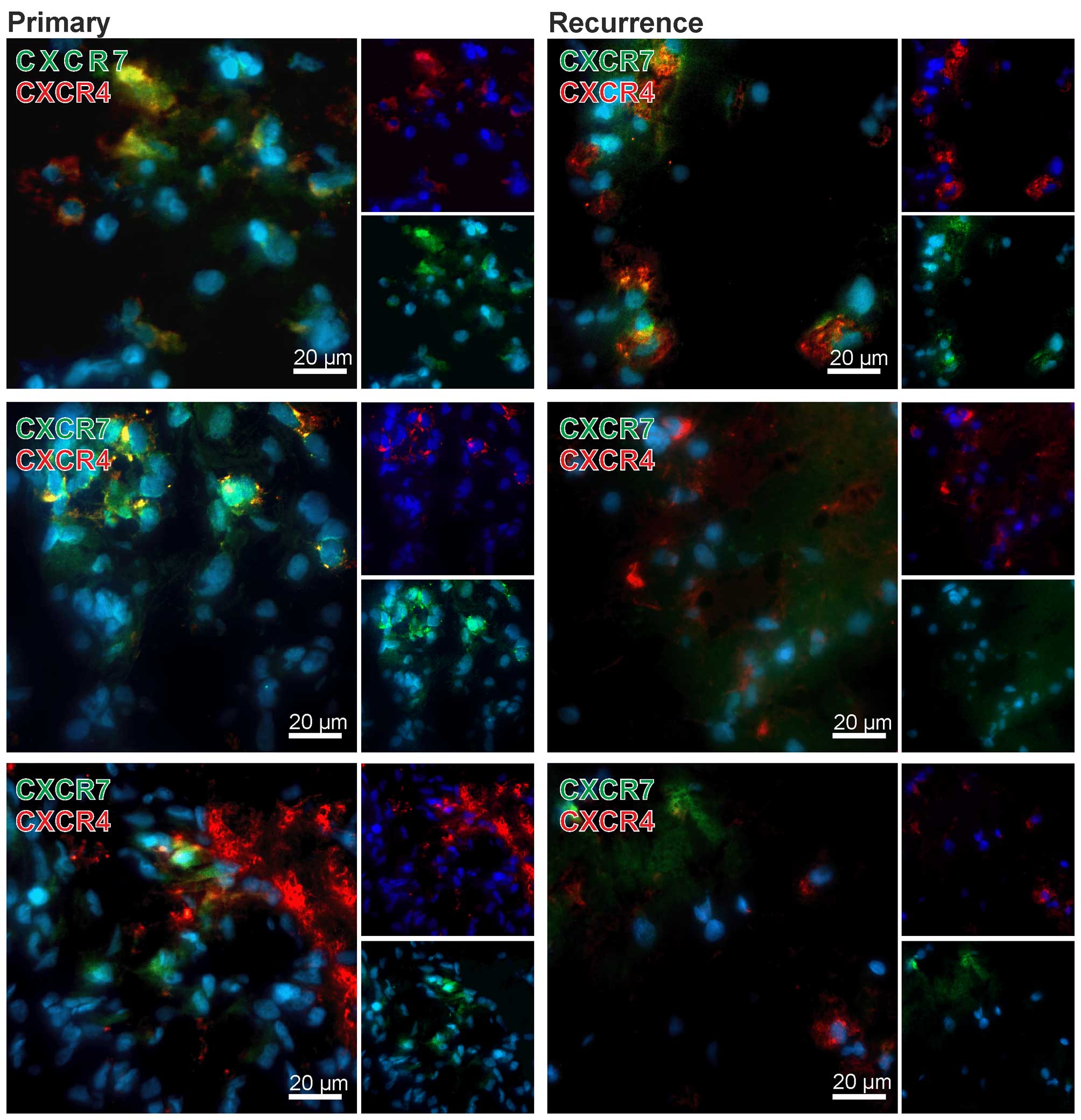
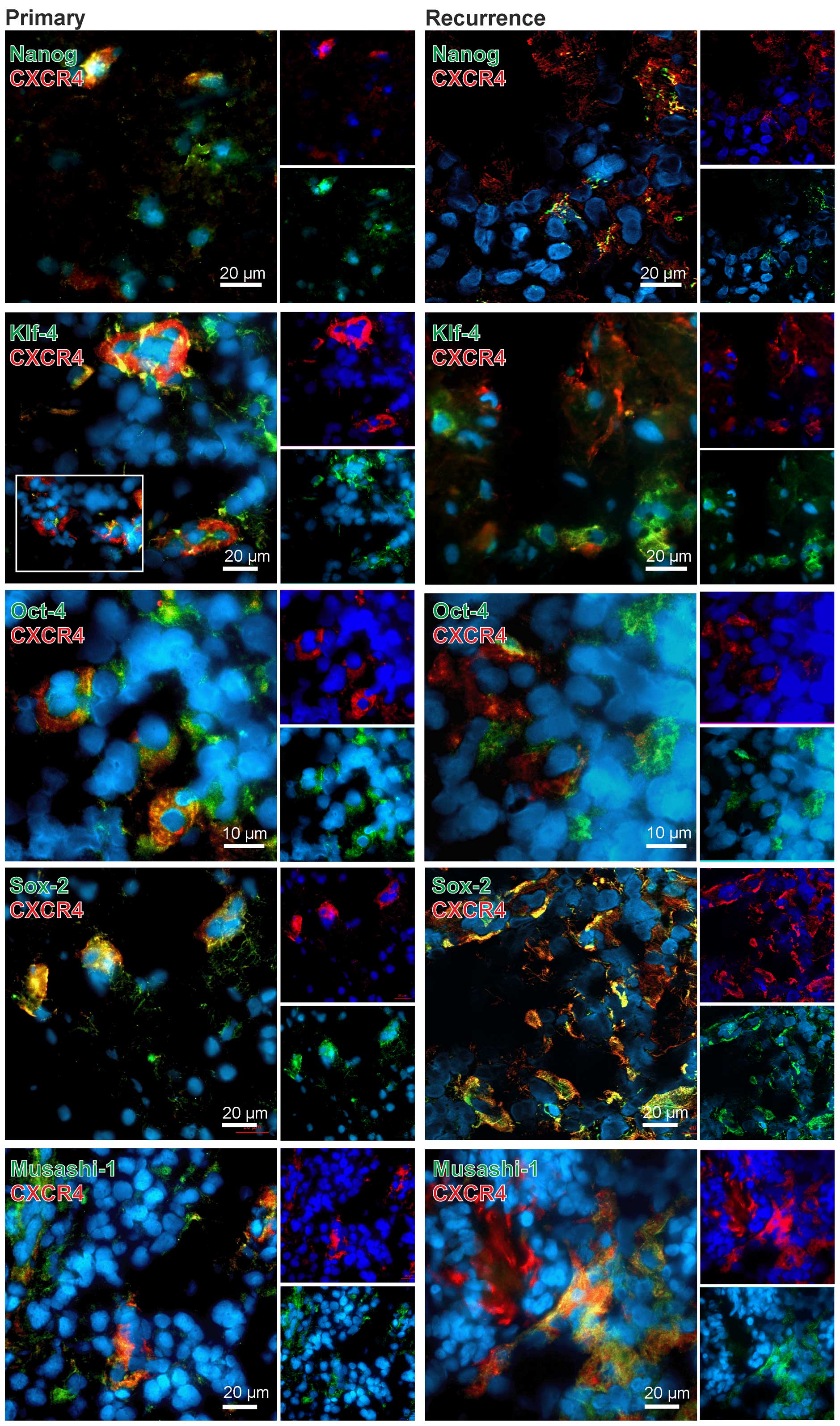
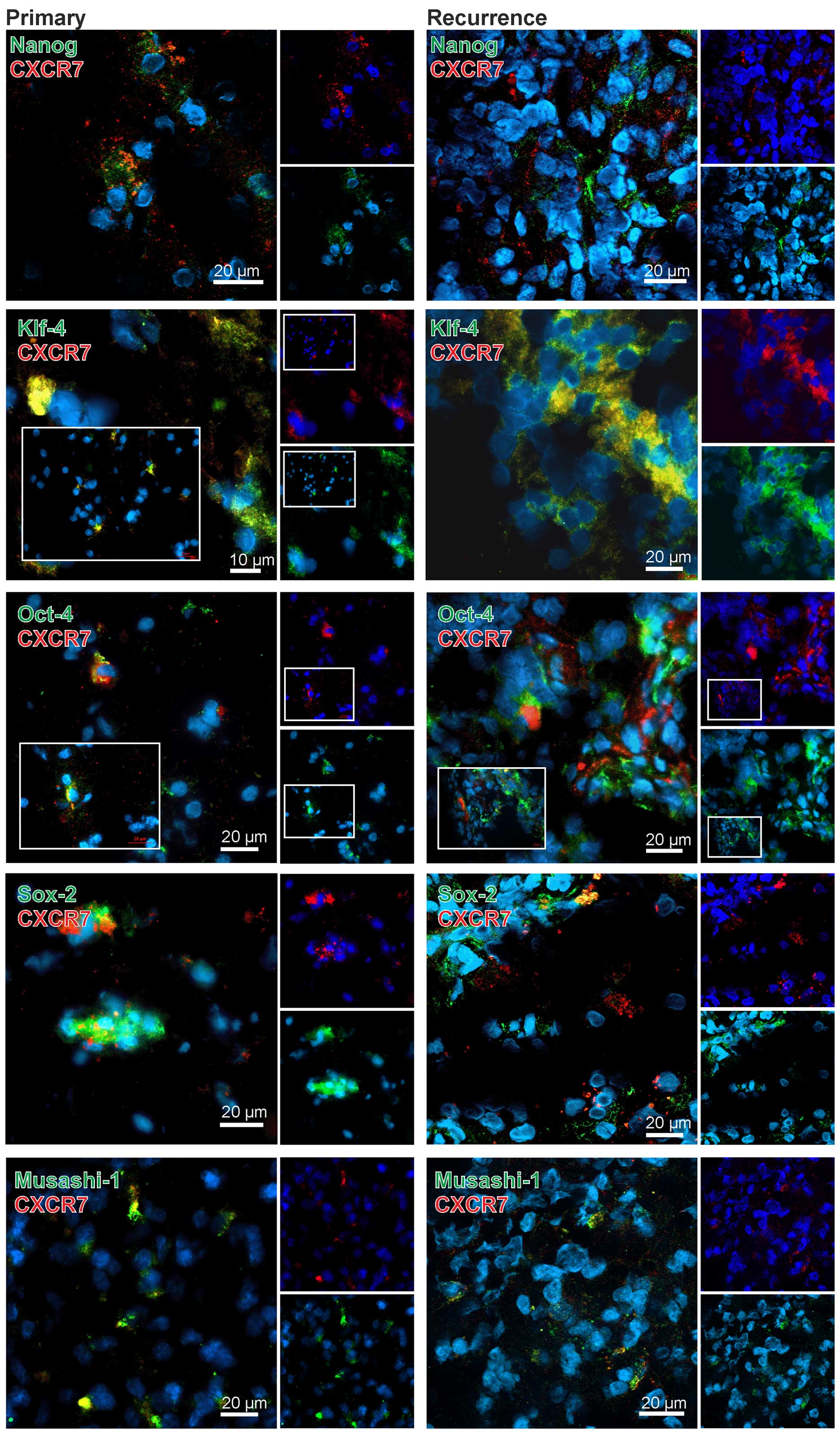
|
1
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Epidemiology and
etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 109:93–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of
Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Radiotherapy plus
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Strieter RM, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL,
Arenberg DA, Burdick MD, Kasper J, Dzuiba J, Van Damme J, Walz A,
Marriott D, et al: The functional role of the ELR motif in CXC
chemokine-mediated angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 270:27348–27357.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Broxmeyer HE and Kim CH: Regulation of
hematopoiesis in a sea of chemokine family members with a plethora
of redundant activities. Exp Hematol. 27:1113–1123. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dambly-Chaudière C, Cubedo N and Ghysen A:
Control of cell migration in the development of the posterior
lateral line: Antagonistic interactions between the chemokine
receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7/RDC1. BMC Dev Biol. 7:232007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hattermann K, Ludwig A, Gieselmann V,
Held-Feindt J and Mentlein R: The chemokine CXCL16 induces
migration and invasion of glial precursor cells via its receptor
CXCR6. Mol Cell Neurosci. 39:133–141. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J and Struyf
S: The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer
Lett. 267:226–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
O'Hayre M, Salanga CL, Handel TM and Allen
SJ: Chemokines and cancer: Migration, intracellular signalling and
intercellular communication in the microenvironment. Biochem J.
409:635–649. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D,
Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, et al:
Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 410:50–56. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hattermann K and Mentlein R: An infernal
trio: The chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 in
tumor biology. Ann Anat. 195:103–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM and Homey B:
Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:597–606. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bian XW, Yang SX, Chen JH, Ping YF, Zhou
XD, Wang QL, Jiang XF, Gong W, Xiao HL, Du LL, et al: Preferential
expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by highly malignant human
gliomas and its association with poor patient survival.
Neurosurgery. 61:570–579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Würth R, Bajetto A, Harrison JK, Barbieri
F and Florio T: CXCL12 modulation of CXCR4 and CXCR7 activity in
human glioblastoma stem-like cells and regulation of the tumor
microenvironment. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:144eCollection.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ehtesham M, Mapara KY, Stevenson CB and
Thompson RC: CXCR4 mediates the proliferation of glioblastoma
progenitor cells. Cancer Lett. 274:305–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Hattermann K, Held-Feindt J, Lucius R,
Müerköster SS, Penfold ME, Schall TJ and Mentlein R: The chemokine
receptor CXCR7 is highly expressed in human glioma cells and
mediates antiapoptotic effects. Cancer Res. 70:3299–3308. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Auffinger B, Spencer D, Pytel P, Ahmed AU
and Lesniak MS: The role of glioma stem cells in chemotherapy
resistance and glioblastoma multiforme recurrence. Expert Rev
Neurother. 15:741–752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hattermann K, Mentlein R and Held-Feindt
J: CXCL12 mediates apoptosis resistance in rat C6 glioma cells.
Oncol Rep. 27:1348–1352. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Carson-Walter EB, Cooper A, Winans
BN, Johnson MD and Walter KA: Vascular gene expression patterns are
conserved in primary and metastatic brain tumors. J Neurooncol.
99:13–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bianco AM, Uno M, Oba-Shinjo SM, Clara CA,
de Almeida Galatro TF, Rosemberg S, Teixeira MJ and Nagahashi Marie
SK: CXCR7 and CXCR4 expression in infiltrative astrocytomas and
their interactions with HIF1α expression and IDH1 mutation. Pathol
Oncol Res. 21:229–240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kubelt C, Hattermann K, Sebens S, Mehdorn
HM and Held-Feindt J: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
paired human primary and recurrent glioblastomas. Int J Oncol.
46:2515–2525. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rempel SA, Dudas S, Ge S and Gutiérrez JA:
Identification and localization of the cytokine SDF1 and its
receptor, CXC chemokine receptor 4, to regions of necrosis and
angiogenesis in human glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 6:102–111.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Naumann U, Cameroni E, Pruenster M,
Mahabaleshwar H, Raz E, Zerwes HG, Rot A and Thelen M:
CXCR/functions as a scavenger for CXCR12 and CXCL11. Plos One.
5:e91752010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gatti M, Pattarozzi A, Bajetto A, Würth R,
Daga A, Fiaschi P, Zona G, Florio T and Barbieri F: Inhibition of
CXCL12/CXCR4 autocrine/paracrine loop reduces viability of human
glioblastoma stem-like cells affecting self-renewal activity.
Toxicology. 314:209–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Walters MJ, Ebsworth K, Berahovich RD,
Penfold ME, Liu SC, Al Omran R, Kioi M, Chernikova SB, Tseng D,
Mulkearns-Hubert EE, et al: Inhibition of CXCR7 extends survival
following irradiation of brain tumours in mice and rats. Br J
Cancer. 110:1179–1188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu C, Pham K, Luo D, Reynolds BA, Hothi
P, Foltz G and Harrison JK: Expression and functional heterogeneity
of chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 in primary patient-derived
glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e597502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Razmkhah M, Arabpour F, Taghipour M,
Mehrafshan A, Chenari N and Ghaderi A: Expression of chemokines and
chemokine receptors in brain tumor tissue derived cells. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 15:7201–7205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ben-Porath I, Thomson MW, Carey VJ, Ge R,
Bell GW, Regev A and Weinberg RA: An embryonic stem cell-like gene
expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human
tumors. Nat Genet. 40:499–507. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Elsir T, Edqvist P-H, Carlson J, Ribom D,
Bergqvist M, Ekman S, Popova SN, Alafuzoff I, Ponten F, Nistér M,
et al: A study of embryonic stem cell-related proteins in human
astrocytomas: Identification of Nanog as a predictor of survival.
Int J Cancer. 134:1123–1131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Berezovsky AD, Poisson LM, Cherba D, Webb
CP, Transou AD, Lemke NW, Hong X, Hasselbach LA, Irtenkauf SM,
Mikkelsen T, et al: Sox2 promotes malignancy in glioblastoma by
regulating plasticity and astrocytic differentiation. Neoplasia.
16:193–206. 206.e19–206.e25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du Z, Jia D, Liu S, Wang F, Li G, Zhang Y,
Cao X, Ling EA and Hao A: Oct4 is expressed in human gliomas and
promotes colony formation in glioma cells. Glia. 57:724–733. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Galatro TF, Uno M, Oba-Shinjo SM, Almeida
AN, Teixeira MJ, Rosemberg S and Marie SK: Differential expression
of ID4 and its association with TP53 mutation, SOX2, SOX4 and OCT-4
expression levels. PLoS One. 8:e616052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo Y, Liu S, Wang P, Zhao S, Wang F, Bing
L, Zhang Y, Ling EA, Gao J and Hao A: Expression profile of
embryonic stem cell-associated genes Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog in human
gliomas. Histopathology. 59:763–775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Holmberg J, He X, Peredo I, Orrego A,
Hesselager G, Ericsson C, Hovatta O, Oba-Shinjo SM, Marie SK,
Nistér M, et al: Activation of neural and pluripotent stem cell
signatures correlates with increased malignancy in human glioma.
PLoS One. 6:e184542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ikushima H, Todo T, Ino Y, Takahashi M,
Saito N, Miyazawa K and Miyazono K: Glioma-initiating cells retain
their tumorigenicity through integration of the Sox axis and Oct4
protein. J Biol Chem. 286:41434–41441. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Muto J, Imai T, Ogawa D, Nishimoto Y,
Okada Y, Mabuchi Y, Kawase T, Iwanami A, Mischel PS, Saya H, et al:
RNA-binding protein Musashi1 modulates glioma cell growth through
the post-transcriptional regulation of Notch and PI3 kinase/Akt
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 7:e334312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mühlethaler-Mottet A, Liberman J, Ascenção
K, Flahaut M, Balmas Bourloud K, Yan P, Jauquier N, Gross N and
Joseph JM: The CXCR4/CXCR7/CXCL12 axis is involved in a secondary
but complex control of neuroblastoma metastatic cell homing. PLoS
One. 10:e01256162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee CC, Lai JH, Hueng DY, Ma HI, Chung Y,
Sun YY, Tsai YJ, Wu WB and Chen CL: Disrupting the CXCL12/CXCR4
axis disturbs the characteristics of glioblastoma stem-like cells
of rat RG2 glioblastoma. Cancer Cell Int. 13:852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK,
Cazacu S, Finniss S, Xiang C, Poisson L, deCarvalho AC, Slavin S,
et al: MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits
the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget.
4:665–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fareh M, Turchi L, Virolle V, Debruyne D,
Almairac F, de-la- Forest Divonne S, Paquis P, Preynat-Seauve O,
Krause K-H, Chneiweiss H, et al: The miR 302–367 cluster
drastically affects self-renewal and infiltration properties of
glioma-initiating cells through CXCR4 repression and consequent
disruption of the SHH-GLI-NANOG network. Cell Death Differ.
19:232–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Chen Q, Zhang M, Li Y, Xu D, Wang Y, Song
A, Zhu B, Huang Y and Zheng JC: CXCR7 mediates neural progenitor
cells migration to CXCL12 independent of CXCR4. Stem Cells.
33:2574–2585. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ma J, Yao Y, Wang P, Liu Y, Zhao L, Li Z,
Li Z and Xue Y: MiR-152 functions as a tumor suppressor in
glioblastoma stem cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4. Cancer
Lett. 355:85–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu XY, Wang L, Luan SH, Zhang HS, Huang
WT and Wang NH: The PGI-KLF4 pathway regulates self-renewal of
glioma stem cells residing in the mesenchymal niches in human
gliomas. Neoplasma. 61:401–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|