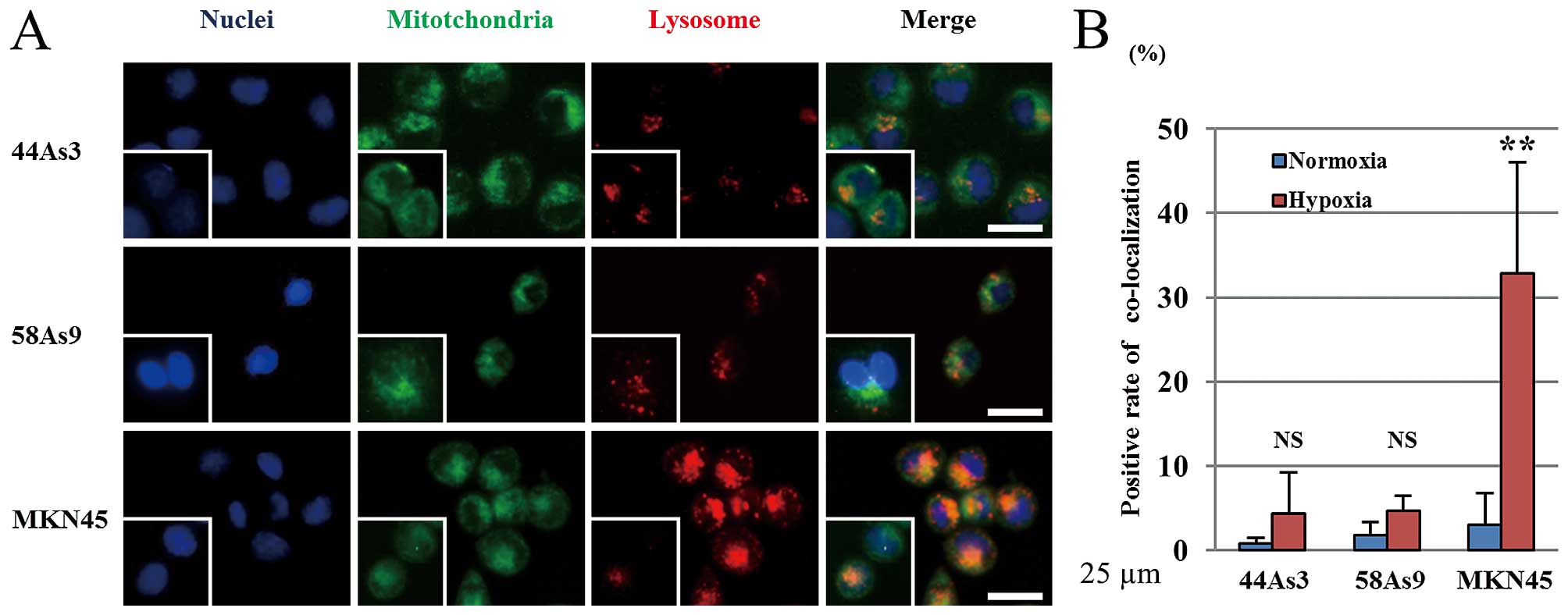
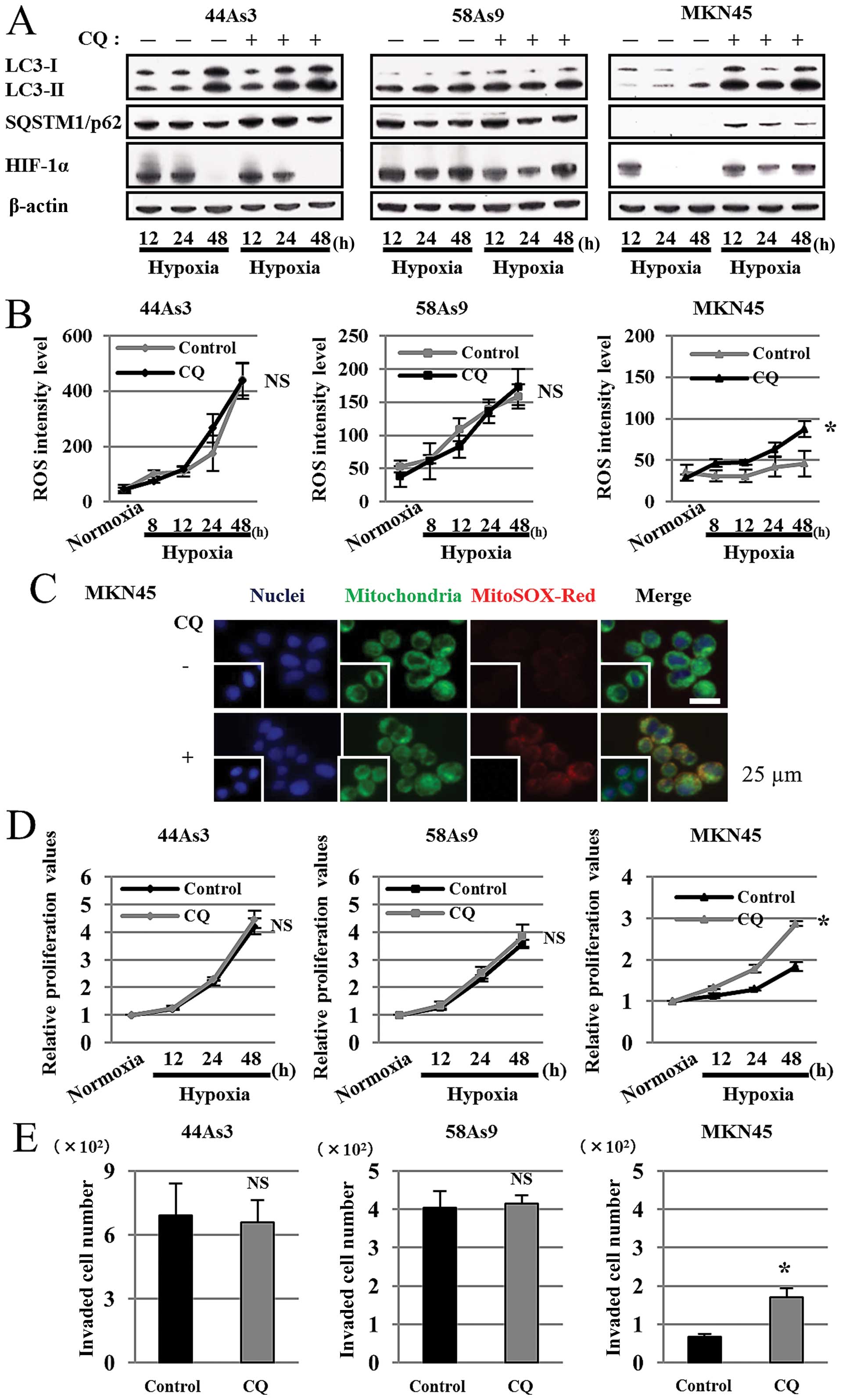
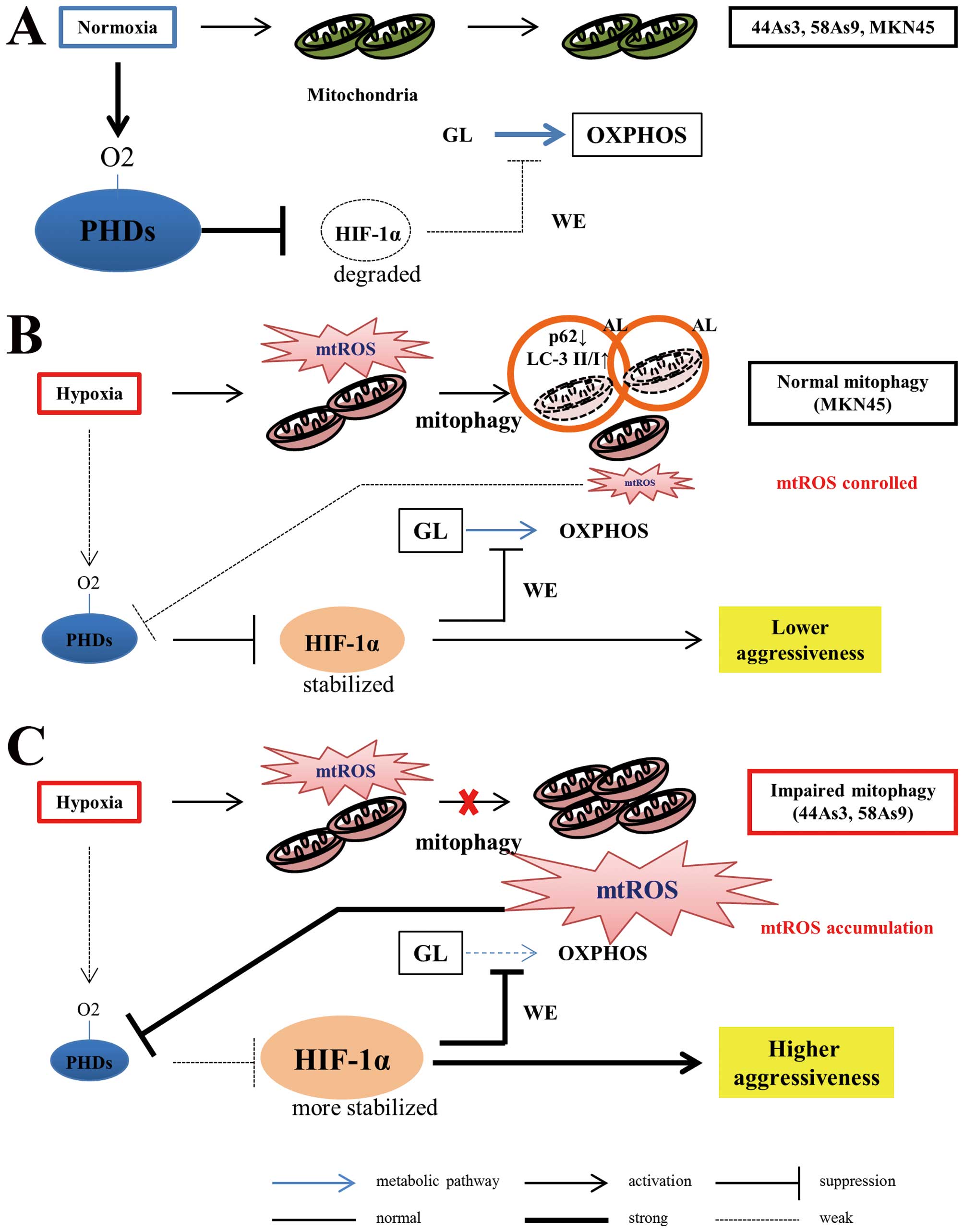
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shiraishi N, Inomata M, Osawa N, Yasuda K,
Adachi Y and Kitano S: Early and late recurrence after gastrectomy
for gastric carcinoma. Univariate and multivariate analyses.
Cancer. 89:255–261. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J,
Hundahl SA, Estes NC, Stemmermann GN, Haller DG, Ajani JA,
Gunderson LL, Jessup JM, et al: Chemoradiotherapy after surgery
compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or
gastro-esophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 345:725–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW,
Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Gearhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY,
et al: Cellular and developmental control of O2
homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev.
12:149–162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vaupel P, Mayer A and Höckel M: Tumor
hypoxia and malignant progression. Methods Enzymol. 381:335–354.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu X and Kang Y: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors: Master regulators of metastasis. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:5928–5935. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Höckel M and Vaupel P: Tumor hypoxia:
Definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:266–276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang BH, Semenza GL, Bauer C and Marti
HH: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 levels vary exponentially over a
physiologically relevant range of O2 tension. Am J
Physiol. 271:C1172–C1180. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 and tumor progression:
Pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 8(Suppl):
S62–S67. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Upstream and downstream
of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 20:51–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Kitajima Y and Miyazaki K: The critical
impact of HIF-1α on gastric cancer biology. Cancers (Basel).
5:15–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ide T, Kitajima Y, Miyoshi A, Ohtsuka T,
Mitsuno M, Ohtaka K, Koga Y and Miyazaki K: Tumor-stromal cell
interaction under hypoxia increases the invasiveness of pancreatic
cancer cells through the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met pathway.
Int J Cancer. 119:2750–2759. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sumiyoshi Y, Kakeji Y, Egashira A,
Mizokami K, Orita H and Maehara Y: Overexpression of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and p53 is a marker for an
unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
12:5112–5117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nam SY, Ko YS, Jung J, Yoon J, Kim YH,
Choi YJ, Park JW, Chang MS, Kim WH and Lee BL: A hypoxia-dependent
upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by nuclear factor-κB
promotes gastric tumour growth and angiogenesis. Br J Cancer.
104:166–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Stoeltzing O, McCarty MF, Wey JS, Fan F,
Liu W, Belcheva A, Bucana CD, Semenza GL and Ellis LM: Role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in gastric cancer cell growth,
angiogenesis, and vessel maturation. J Natl Cancer Inst.
96:946–956. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakamura J, Kitajima Y, Kai K, Hashiguchi
K, Hiraki M, Noshiro H and Miyazaki K: HIF-1alpha is an unfavorable
determinant of relapse in gastric cancer patients who underwent
curative surgery followed by adjuvant 5-FU chemotherapy. Int J
Cancer. 127:1158–1171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rohwer N and Cramer T: HIFs as central
regulators of gastric cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:383–385. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sena LA and Chandel NS: Physiological
roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
48:158–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zepeda AB, Pessoa A Jr, Castillo RL,
Figueroa CA, Pulgar VM and Farías JG: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms in the hypoxic tissue: Role of HIF-1 and ROS. Cell
Biochem Funct. 31:451–459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE,
Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM and Schumacker PT: Reactive
oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: A mechanism of
O2 sensing. J Biol Chem. 275:25130–25138. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gerald D, Berra E, Frapart YM, Chan DA,
Giaccia AJ, Mansuy D, Pouysségur J, Yaniv M and Mechta-Grigoriou F:
JunD reduces tumor angiogenesis by protecting cells from oxidative
stress. Cell. 118:781–794. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao T, Zhu Y, Morinibu A, Kobayashi M,
Shinomiya K, Itasaka S, Yoshimura M, Guo G, Hiraoka M and Harada H:
HIF-1-mediated metabolic reprogramming reduces ROS levels and
facilitates the metastatic colonization of cancers in lungs. Sci
Rep. 4:37932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaelin WG Jr: ROS: Really involved in
oxygen sensing. Cell Metab. 1:357–358. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1:
Regulator of mitochondrial metabolism and mediator of ischemic
preconditioning. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1263–1268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rogov V, Dötsch V, Johansen T and Kirkin
V: Interactions between autophagy receptors and ubiquitin-like
proteins form the molecular basis for selective autophagy. Mol
Cell. 53:167–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lemasters JJ: Selective mitochondrial
autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative
stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res.
8:3–5. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim I, Rodriguez-Enriquez S and Lemasters
JJ: Selective degradation of mitochondria by mitophagy. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 462:245–253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chourasia AH, Boland ML and Macleod KF:
Mitophagy and cancer. Cancer Metab. 3:42015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu L, Feng D, Chen G, Chen M, Zheng Q,
Song P, Ma Q, Zhu C, Wang R, Qi W, et al: Mitochondrial
outer-membrane protein FUNDC1 mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in
mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol. 14:177–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, Tan
YS, Baek JH, Wesley JB, Gonzalez FJ and Semenza GL: Mitochondrial
autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to
hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 283:10892–10903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cesari R, Martin ES, Calin GA, Pentimalli
F, Bichi R, McAdams H, Trapasso F, Drusco A, Shimizu M, Masciullo
V, et al: Parkin, a gene implicated in autosomal recessive juvenile
parkinsonism, is a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome
6q25-q27. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:5956–5961. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gong Y, Zack TI, Morris LG, Lin K,
Hukkelhoven E, Raheja R, Tan IL, Turcan S, Veeriah S, Meng S, et
al: Pan-cancer genetic analysis identifies PARK2 as a master
regulator of G1/S cyclins. Nat Genet. 46:588–594. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yanagihara K, Takigahira M, Tanaka H,
Komatsu T, Fukumoto H, Koizumi F, Nishio K, Ochiya T, Ino Y and
Hirohashi S: Development and biological analysis of peritoneal
metastasis mouse models for human scirrhous stomach cancer. Cancer
Sci. 96:323–332. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Miyake S, Kitajima Y, Nakamura J, Kai K,
Yanagihara K, Tanaka T, Hiraki M, Miyazaki K and Noshiro H: HIF-1α
is a crucial factor in the development of peritoneal dissemination
via natural metastatic routes in scirrhous gastric cancer. Int J
Oncol. 43:1431–1440. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanaka T, Kitajima Y, Miyake S, Yanagihara
K, Hara H, Nishijima-Matsunobu A, Baba K, Shida M, Wakiyama K,
Nakamura J, et al: The apoptotic effect of HIF-1α inhibition
combined with glucose plus insulin treatment on gastric cancer
under hypoxic conditions. PLoS One. 10:e01372572015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dolman NJ, Chambers KM, Mandavilli B,
Batchelor RH and Janes MS: Tools and techniques to measure
mitophagy using fluorescence microscopy. Autophagy. 9:1653–1662.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|