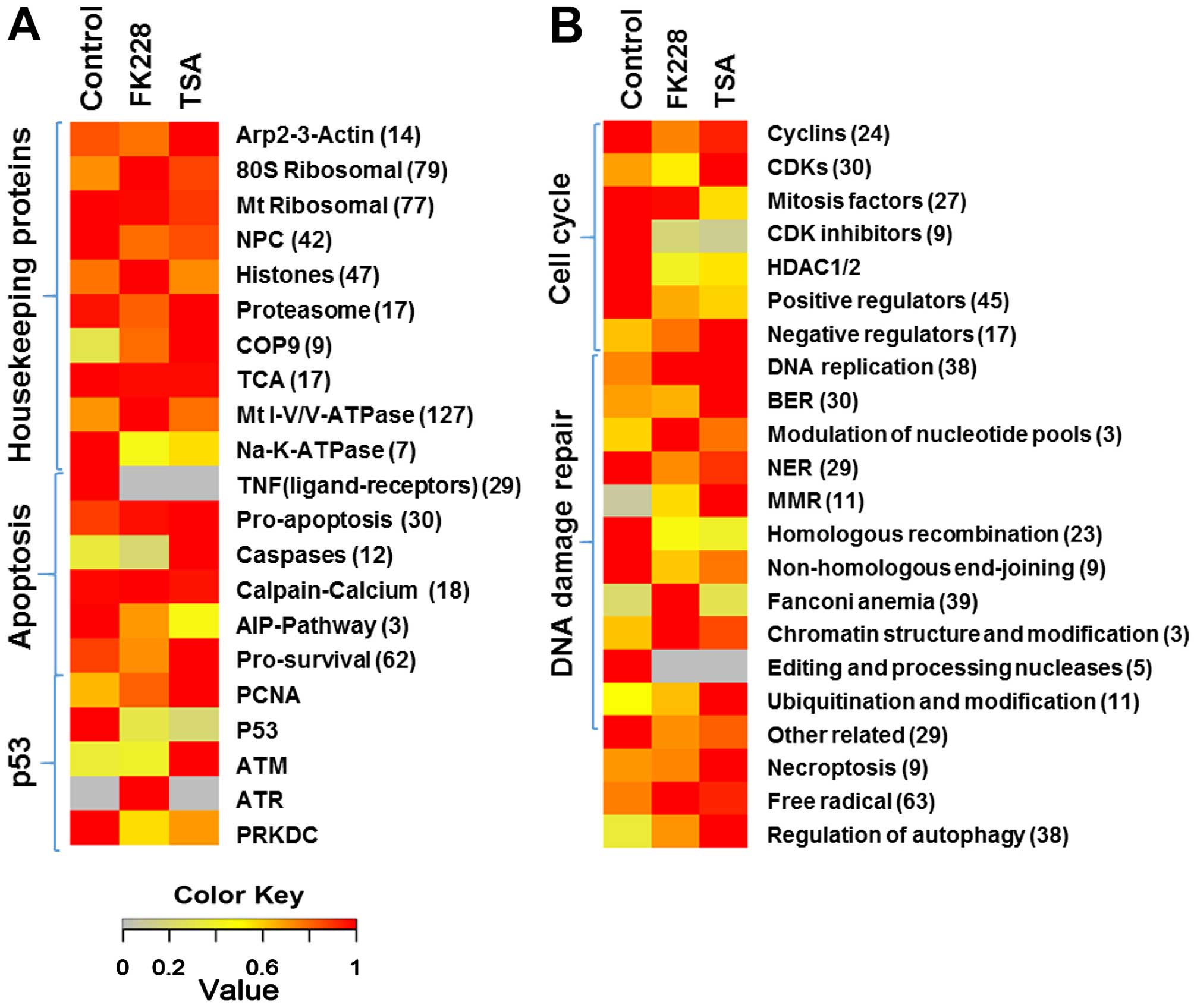
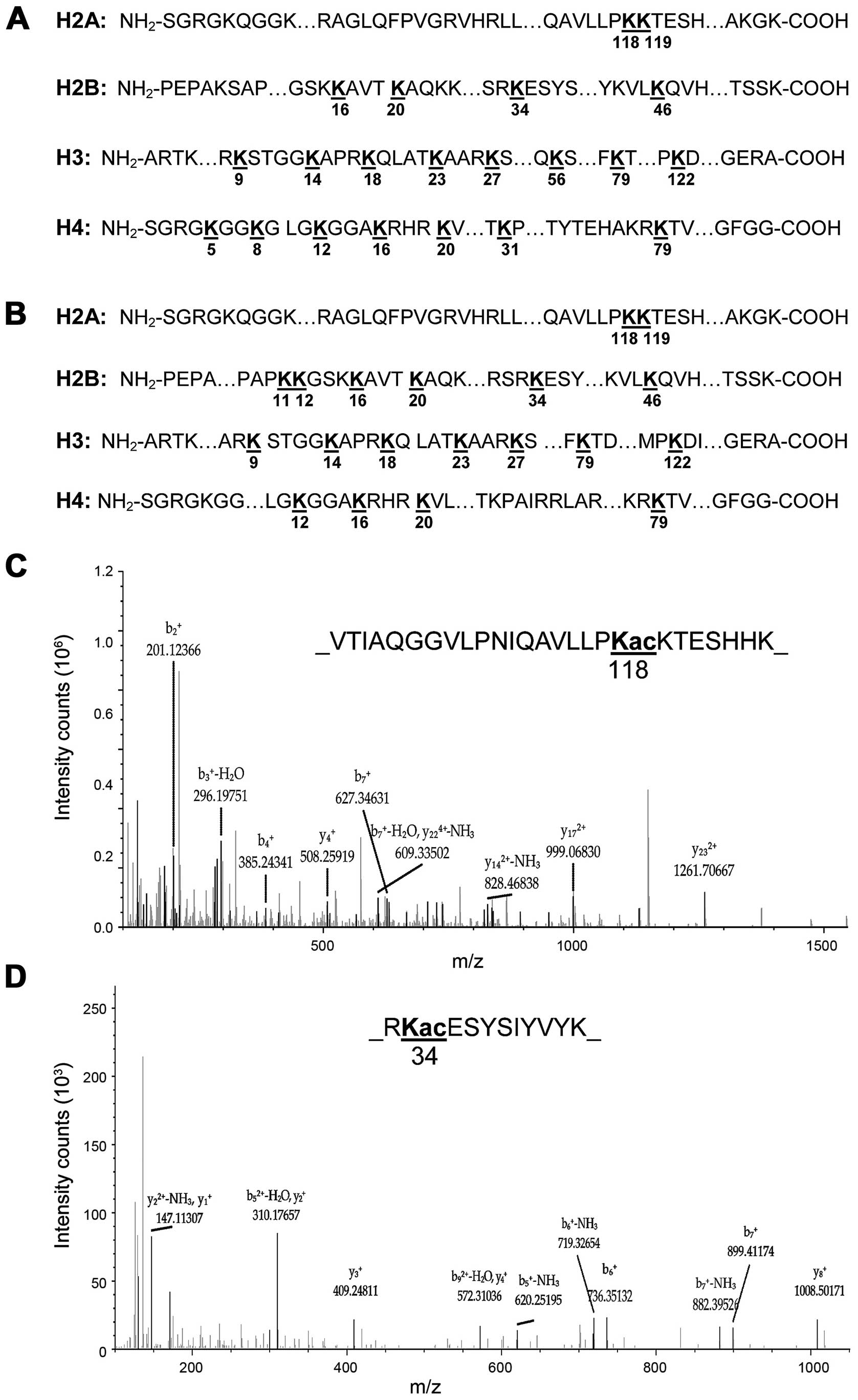
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weintraub MD, Li QQ and Agarwal PK:
Advances in intravesical therapy for the treatment of non-muscle
invasive bladder cancer (Review). Mol Clin Oncol. 2:656–660.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Kuczyk
MA, Merseburger AS, Ribal MJ, Sherif A and Witjes JA; European
Association of Urology (EAU). Treatment of muscle-invasive and
metastatic bladder cancer: Update of the EAU guidelines. Eur Urol.
59:1009–1018. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marks P, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, Breslow R,
Miller T and Kelly WK: Histone deacetylases and cancer: Causes and
therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:194–202. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB and Marks PA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene.
26:5541–5552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marks PA and Xu WS: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: Potential in cancer therapy. J Cell Biochem.
107:600–608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schrump DS: Cytotoxicity mediated by
histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer cells: Mechanisms and
potential clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3947–3957.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakagawa M, Oda Y, Eguchi T, Aishima S,
Yao T, Hosoi F, Basaki Y, Ono M, Kuwano M, Tanaka M, et al:
Expression profile of class I histone deacetylases in human cancer
tissues. Oncol Rep. 18:769–774. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Sugiura H,
Ando Y, Mita K, Hamaguchi M, Hara Y, Kobayashi S and Iwase H:
Quantitation of HDAC1 mRNA expression in invasive carcinoma of the
breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 94:11–16. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marquard L, Poulsen CB, Gjerdrum LM, de
Nully Brown P, Christensen IJ, Jensen PB, Sehested M, Johansen P
and Ralfkiaer E: Histone deacetylase 1, 2, 6 and acetylated histone
H4 in B- and T-cell lymphomas. Histopathology. 54:688–698. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T and Oehme I:
HDAC family: What are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett.
277:8–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ozawa A, Tanji N, Kikugawa T, Sasaki T,
Yanagihara Y, Miura N and Yokoyama M: Inhibition of bladder tumour
growth by histone deacetylase inhibitor. BJU Int. 105:1181–1186.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bolden JE, Peart MJ and Johnstone RW:
Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 5:769–784. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Minucci S and Pelicci PG: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more)
treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:38–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshida M, Kijima M, Akita M and Beppu T:
Potent and specific inhibition of mammalian histone deacetylase
both in vivo and in vitro by trichostatin A. J Biol Chem.
265:17174–17179. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tan J, Cang S, Ma Y, Petrillo RL and Liu
D: Novel histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical trials as
anti-cancer agents. J Hematol Oncol. 3:52010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGraw AL: Romidepsin for the treatment of
T-cell lymphomas. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 70:1115–1122. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li QQ, Wang G, Liang H, Li JM, Huang F,
Agarwal PK, Zhong Y and Reed E: β-Elemene promotes
cisplatin-induced cell death in human bladder cancer and other
carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 33:1421–1428. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Florens L, Carozza MJ, Swanson SK,
Fournier M, Coleman MK, Workman JL and Washburn MP: Analyzing
chromatin remodeling complexes using shotgun proteomics and
normalized spectral abundance factors. Methods. 40:303–311. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paoletti AC, Parmely TJ, Tomomori-Sato C,
Sato S, Zhu D, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Florens L and Washburn MP:
Quantitative proteomic analysis of distinct mammalian Mediator
complexes using normalized spectral abundance factors. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:18928–18933. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ou JN, Torrisani J, Unterberger A,
Provençal N, Shikimi K, Karimi M, Ekström TJ and Szyf M: Histone
deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A induces global and
gene-specific DNA demethylation in human cancer cell lines. Biochem
Pharmacol. 73:1297–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Swanton C: Cell-cycle targeted therapies.
Lancet Oncol. 5:27–36. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morgan DO: Principles of CDK regulation.
Nature. 374:131–134. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dynlacht BD: Regulation of transcription
by proteins that control the cell cycle. Nature. 389:149–152. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wesierska-Gadek J, Gueorguieva M and Horky
M: Dual action of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: Induction of
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. A comparison of the effects
exerted by roscovitine and cisplatin. Pol J Pharmacol. 55:895–902.
2003.
|
|
28
|
Parker LL, Sylvestre PJ, Byrnes MJ III,
Liu F and Piwnica-Worms H: Identification of a 95-kDa WEE1-like
tyrosine kinase in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
92:9638–9642. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mitra J and Enders GH: Cyclin A/Cdk2
complexes regulate activation of Cdk1 and Cdc25 phosphatases in
human cells. Oncogene. 23:3361–3367. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fisher DE: Apoptosis in cancer therapy:
Crossing the threshold. Cell. 78:539–542. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Haldar S, Chintapalli J and Croce CM:
Taxol induces bcl-2 phosphorylation and death of prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 56:1253–1255. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Blagosklonny MV, Schulte T, Nguyen P,
Trepel J and Neckers LM: Taxol-induced apoptosis and
phosphorylation of Bcl-2 protein involves c-Raf-1 and represents a
novel c-Raf-1 signal transduction pathway. Cancer Res.
56:1851–1854. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Blagosklonny MV, Giannakakou P, el-Deiry
WS, Kingston DG, Higgs PI, Neckers L and Fojo T: Raf-1/bcl-2
phosphorylation: A step from microtubule damage to cell death.
Cancer Res. 57:130–135. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Haldar S, Basu A and Croce CM: Bcl2 is the
guardian of microtubule integrity. Cancer Res. 57:229–233.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Haldar S, Basu A and Croce CM: Serine-70
is one of the critical sites for drug-induced Bcl2 phosphorylation
in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 58:1609–1615. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang BS, Minn AJ, Muchmore SW, Fesik SW
and Thompson CB: Identification of a novel regulatory domain in
Bcl-X(L) and Bcl-2. EMBO J. 16:968–977. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Roos WP, Thomas AD and Kaina B: DNA damage
and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat
Rev Cancer. 16:20–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W and
Schultz RA: DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. 2nd edition. ASM Press;
Washington, DC: 2006
|
|
39
|
Halliwell B: Free radicals, antioxidants,
and human disease: Curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet.
344:721–724. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brot N, Weissbach L, Werth J and Weissbach
H: Enzymatic reduction of protein-bound methionine sulfoxide. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:2155–2158. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Demple B and Linn S: 5,6-Saturated thymine
lesions in DNA: Production by ultraviolet light or hydrogen
peroxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 10:3781–3789. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M,
Sempf J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR and Nel AE:
Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured
nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative
stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 6:1794–1807. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Feng R, Oton A, Mapara MY, Anderson G,
Belani C and Lentzsch S: The histone deacetylase inhibitor, PXD101,
potentiates bortezomib-induced anti-multiple myeloma effect by
induction of oxidative stress and DNA damage. Br J Haematol.
139:385–397. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rosato RR, Maggio SC, Almenara JA, Payne
SG, Atadja P, Spiegel S, Dent P and Grant S: The histone
deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 induces human leukemia cell death
through a process involving XIAP down-regulation, oxidative injury,
and the acid sphingomyelinase-dependent generation of ceramide. Mol
Pharmacol. 69:216–225. 2006.
|
|
45
|
Feng R, Ma H, Hassig CA, Payne JE, Smith
ND, Mapara MY, Hager JH and Lentzsch S: KD5170, a novel
mercaptoketone-based histone deacetylase inhibitor, exerts
antimyeloma effects by DNA damage and mitochondrial signaling. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1494–1505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Maggio SC, Coe S,
Atadja P, Dent P and Grant S: Role of histone deacetylase
inhibitor-induced reactive oxygen species and DNA damage in
LAQ-824/fludarabine antileukemic interactions. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:3285–3297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V and Zhivotovsky B:
Mitochondrial oxidative stress: Implications for cell death. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:143–183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rao R, Nalluri S, Fiskus W, Savoie A,
Buckley KM, Ha K, Balusu R, Joshi A, Coothankandaswamy V, Tao J, et
al: Role of CAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein in
panobinostat-mediated potentiation of bortezomib-induced lethal
endoplasmic reticulum stress in mantle cell lymphoma cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:4742–4754. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rao R, Nalluri S, Kolhe R, Yang Y, Fiskus
W, Chen J, Ha K, Buckley KM, Balusu R, Coothankandaswamy V, et al:
Treatment with panobinostat induces glucose-regulated protein 78
acetylation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in breast cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:942–952. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kahali S, Sarcar B, Prabhu A, Seto E and
Chinnaiyan P: Class I histone deacetylases localize to the
endoplasmic reticulum and modulate the unfolded protein response.
FASEB J. 26:2437–2445. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yi C, Ma M, Ran L, Zheng J, Tong J, Zhu J,
Ma C, Sun Y, Zhang S, Feng W, et al: Function and molecular
mechanism of acetylation in autophagy regulation. Science.
336:474–477. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hassler MR and Egger G: Epigenomics of
cancer - emerging new concepts. Biochimie. 94:2219–2230. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jerónimo C and Henrique R: Epigenetic
biomarkers in urological tumors: A systematic review. Cancer Lett.
342:264–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bannister AJ and Kouzarides T: Regulation
of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 21:381–395. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Abbosh PH, McConkey DJ and Plimack ER:
Targeting signaling transduction pathways in bladder cancer. Curr
Oncol Rep. 17:582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
O'Rourke CJ, Knabben V, Bolton E, Moran D,
Lynch T, Hollywood D and Perry AS: Manipulating the epigenome for
the treatment of urological malignancies. Pharmacol Ther.
138:185–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|