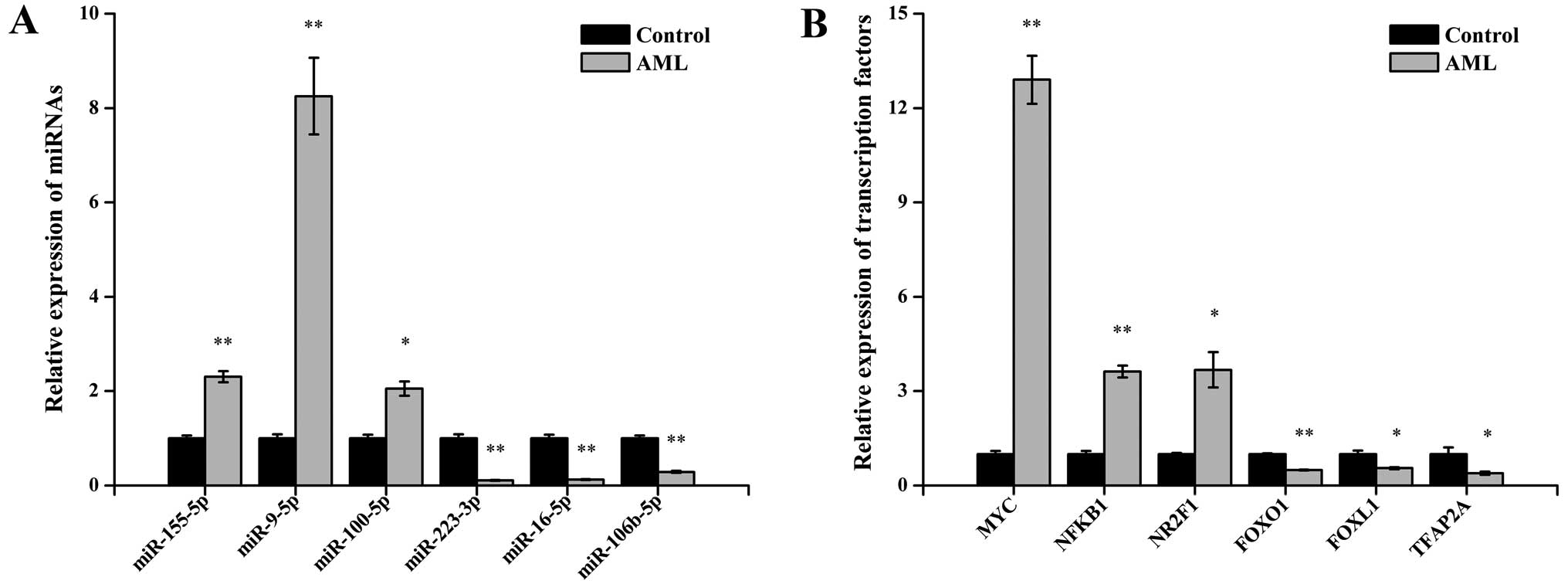
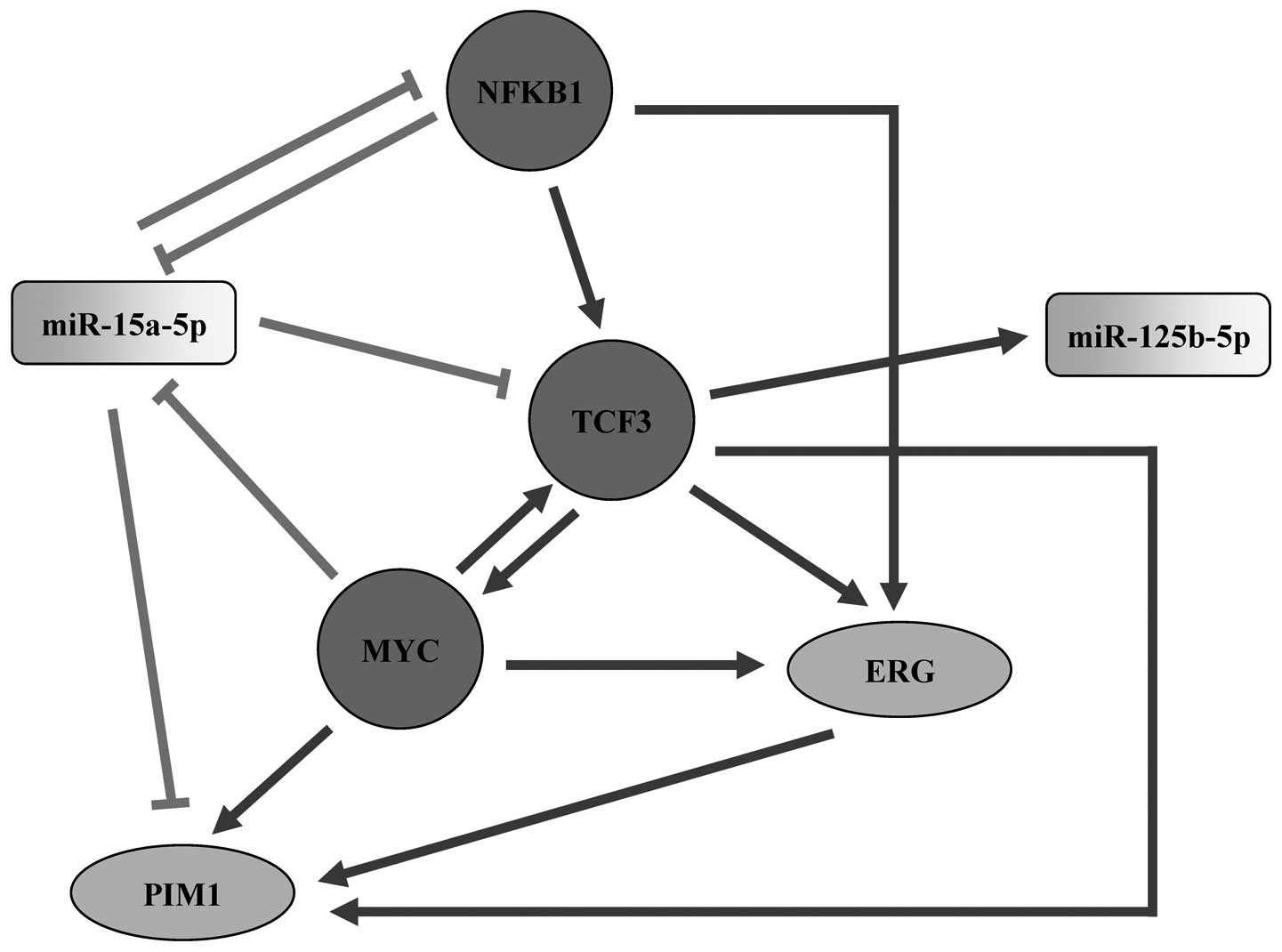
|
1
|
Conway O'Brien E, Prideaux S and Chevassut
T: The epigenetic landscape of acute myeloid leukemia. Adv Hematol.
2014:1031752014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee HJ, Daver N, Kantarjian HM, Verstovsek
S and Ravandi F: The role of JAK pathway dysregulation in the
pathogenesis and treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:327–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zaidi SK, Trombly DJ, Dowdy CR, Lian JB,
Stein JL, van Wijnen AJ and Stein GS: Epigenetic mechanisms in
leukemia. Adv Biol Regul. 52:369–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jamieson K and Odenike O: Late-phase
investigational approaches for the treatment of relapsed/refractory
acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 13:2171–2187.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sabnis H, Bradley HL, Bunting ST, Cooper
TM and Bunting KD: Capillary nano-immunoassay for Akt 1/2/3 and
4EBP1 phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia. J Transl Med.
12:1662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Naoe T and Kiyoi H: Gene mutations of
acute myeloid leukemia in the genome era. Int J Hematol.
97:165–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Larsson CA, Cote G and Quintás-Cardama A:
The changing mutational landscape of acute myeloid leukemia and
myelodysplastic syndrome. Mol Cancer Res. 11:815–827. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abdel-Wahab O and Levine RL: Mutations in
epigenetic modifiers in the pathogenesis and therapy of acute
myeloid leukemia. Blood. 121:3563–3572. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan S, Yim LY, Lu L, Lau CS and Chan VS:
MicroRNA regulation in systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis.
Immune Netw. 14:138–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Rooij E and Kauppinen S: Development
of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol Med. 6:851–864.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, Tavirani MR,
Farivar S and Soleimani M: Aberrant microRNA expression and its
implications in the pathogenesis of leukemias. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
35:317–334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Marcucci G, Mrózek K, Radmacher MD, Garzon
R and Bloomfield CD: The prognostic and functional role of
microRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 117:1121–1129. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Han YC, Park CY, Bhagat G, Zhang J, Wang
Y, Fan JB, Liu M, Zou Y, Weissman IL and Gu H: microRNA-29a induces
aberrant self-renewal capacity in hematopoietic progenitors, biased
myeloid development, and acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med.
207:475–489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bai J, Guo A, Hong Z and Kuai W:
Upregulation of microRNA-100 predicts poor prognosis in patients
with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Onco Targets Ther.
5:213–219. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Hong Z, Gao F and Feng W:
Upregulation of microRNA-375 is associated with poor prognosis in
pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cell Biochem. 383:59–65.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Gao L, Luo X, Wang L, Gao X, Wang W,
Sun J, Dou L, Li J, Xu C, et al: Epigenetic silencing of
microRNA-193a contributes to leukemogenesis in t(8;21) acute
myeloid leukemia by activating the PTEN/PI3K signal pathway. Blood.
121:499–509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hickey CJ, Schwind S, Radomska HS,
Dorrance AM, Santhanam R, Mishra A, Wu YZ, Alachkar H, Maharry K,
Nicolet D, et al: Lenalidomide-mediated enhanced translation of
C/EBPα-p30 protein up-regulates expression of the antileukemic
microRNA-181a in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 121:159–169. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Zhang HM, Kuang S, Xiong X, Gao T, Liu C
and Guo AY: Transcription factor and microRNA co-regulatory loops:
Important regulatory motifs in biological processes and diseases.
Brief Bioinform. 16:45–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cheng C, Yan KK, Hwang W, Qian J, Bhardwaj
N, Rozowsky J, Lu ZJ, Niu W, Alves P, Kato M, et al: Construction
and analysis of an integrated regulatory network derived from
high-throughput sequencing data. PLoS Comput Biol. 7:e10021902011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pulikkan JA, Dengler V, Peramangalam PS,
Peer Zada AA, Müller-Tidow C, Bohlander SK, Tenen DG and Behre G:
Cell-cycle regulator E2F1 and microRNA-223 comprise an
auto-regulatory negative feedback loop in acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood. 115:1768–1778. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Katzerke C, Madan V, Gerloff D,
Bräuer-Hartmann D, Hartmann JU, Wurm AA, Müller-Tidow C, Schnittger
S, Tenen DG, Niederwieser D, et al: Transcription factor
C/EBPα-induced microRNA-30c inactivates Notch1 during
granulopoiesis and is downregulated in acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood. 122:2433–2442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Padró T, Ruiz S, Bieker R, Bürger H,
Steins M, Kienast J, Büchner T, Berdel WE and Mesters RM: Increased
angiogenesis in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid
leukemia. Blood. 95:2637–2644. 2000.
|
|
23
|
Aurelius J, Martner A, Brune M, Palmqvist
L, Hansson M, Hellstrand K and Thoren FB: Remission maintenance in
acute myeloid leukemia: Impact of functional histamine H2 receptors
expressed by leukemic cells. Haematologica. 97:1904–1908. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sui W, Lin H, Peng W, Huang Y, Chen J,
Zhang Y and Dai Y: Molecular dysfunctions in acute rejection after
renal transplantation revealed by integrated analysis of
transcription factor, microRNA and long noncoding RNA. Genomics.
102:310–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin Y, Wu J, Chen H, Mao Y, Liu Y, Mao Q,
Yang K, Zheng X and Xie L: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 is a novel
target in micoRNA-195-mediated cell cycle arrest in bladder cancer
cells. FEBS Lett. 586:442–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rappaport N, Twik M, Nativ N, Stelzer G,
Bahir I, Stein TI, Safran M and Lancet D: MalaCards: A
comprehensive automatically-mined database of human diseases. Curr
Protoc Bioinformatics. 47:1.24.1–1.24.19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Felice B, Cattoglio C, Cittaro D, Testa A,
Miccio A, Ferrari G, Luzi L, Recchia A and Mavilio F: Transcription
factor binding sites are genetic determinants of retroviral
integration in the human genome. PLoS One. 4:e45712009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC, et al: DAVID
Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded annotation database and novel
algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic
Acids Res. 35(Web Server): W169–W175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, Mi S, Zhang H, Luo RT,
Chen P, Wang Y, Yan M, Qian Z, et al: Distinct microRNA expression
profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocations. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15535–15540. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fischer J, Rossetti S, Datta A, Eng K,
Beghini A and Sacchi N: miR-17 deregulates a core RUNX1-miRNA
mechanism of CBF acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer. 14:72015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Grosjean-Raillard J, Adès L, Boehrer S,
Tailler M, Fabre C, Braun T, De Botton S, Israel A, Fenaux P and
Kroemer G: Flt3 receptor inhibition reduces constitutive NFkappaB
activation in high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid
leukemia. Apoptosis. 13:1148–1161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brondfield S, Umesh S, Corella A, Zuber J,
Rappaport AR, Gaillard C, Lowe SW, Goga A and Kogan SC: Direct and
indirect targeting of MYC to treat acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 76:35–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mott JL, Kurita S, Cazanave SC, Bronk SF,
Werneburg NW and Fernandez-Zapico ME: Transcriptional suppression
of mir-29b-1/mir-29a promoter by c-Myc, hedgehog, and NF-kappaB. J
Cell Biochem. 110:1155–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tao J, Zhao X and Tao J: c-MYC-miRNA
circuitry: A central regulator of aggressive B-cell malignancies.
Cell Cycle. 13:191–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Steffen B, Müller-Tidow C, Schwäble J,
Berdel WE and Serve H: The molecular pathogenesis of acute myeloid
leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 56:195–221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schimmer AD: Novel therapies targeting the
apoptosis pathway for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Curr
Treat Options Oncol. 8:277–286. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim HS, Lim GY, Hwang J, Ryoo ZY, Huh TL
and Lee S: Induction of apoptosis by obovatol as a novel
therapeutic strategy for acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Mol Med.
34:1675–1680. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mikesch JH, Steffen B, Berdel WE, Serve H
and Müller-Tidow C: The emerging role of Wnt signaling in the
pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 21:1638–1647.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Tan Y, Chen X, Xu Z, Yang S, Ren F,
Guo H, Wang X, Chen Y, Li G, et al: MDM4 overexpressed in acute
myeloid leukemia patients with complex karyotype and wild-type
TP53. PLoS One. 9:e1130882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chim CS, Wong AS and Kwong YL: Epigenetic
inactivation of INK4/CDK/RB cell cycle pathway in acute leukemias.
Ann Hematol. 82:738–742. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fukuda Y, Lian S and Schuetz JD: Leukemia
and ABC transporters. Adv Cancer Res. 125:171–196. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li YJ, Higgins RR, Pak BJ, Shivdasani RA,
Ney PA, Archer M and Ben-David Y: p45NFE2 is a negative
regulator of erythroid proliferation which contributes to the
progression of friend virus-induced erythroleukemias. Mol Cell
Biol. 21:73–80. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Somasundaram R, Prasad MA, Ungerbäck J and
Sigvardsson M: Transcription factor networks in B-cell
differentiation link development to acute lymphoid leukemia. Blood.
126:144–152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zada AA, Pulikkan JA, Bararia D, Geletu M,
Trivedi AK, Balkhi MY, Hiddemann WD, Tenen DG, Behre HM and Behre
G: Proteomic discovery of Max as a novel interacting partner of
C/EBPalpha: A Myc/Max/Mad link. Leukemia. 20:2137–2146. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pellicano F, Scott MT, Helgason GV,
Hopcroft LE, Allan EK, Aspinall-O'Dea M, Copland M, Pierce A,
Huntly BJ, Whetton AD, et al: The antiproliferative activity of
kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells is mediated by
FOXO transcription factors. Stem Cells. 32:2324–2337. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gao SM, Xing CY, Chen CQ, Lin SS, Dong PH
and Yu FJ: miR-15a and miR-16-1 inhibit the proliferation of
leukemic cells by down-regulating WT1 protein level. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 30:1102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cho JH, Gelinas R, Wang K, Etheridge A,
Piper MG, Batte K, Dakhallah D, Price J, Bornman D, Zhang S, et al:
Systems biology of interstitial lung diseases: Integration of mRNA
and microRNA expression changes. BMC Med Genomics. 4:82011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ye H, Liu X, Lv M, Wu Y, Kuang S, Gong J,
Yuan P, Zhong Z, Li Q, Jia H, et al: MicroRNA and transcription
factor co-regulatory network analysis reveals miR-19 inhibits CYLD
in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:5201–5214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yan Z, Shah PK, Amin SB, Samur MK, Huang
N, Wang X, Misra V, Ji H, Gabuzda D and Li C: Integrative analysis
of gene and miRNA expression profiles with transcription
factor-miRNA feed-forward loops identifies regulators in human
cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:e1352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gao SM, Xing CY, Chen CQ, Lin SS, Dong PH
and Yu FJ: miR-15a and miR-16-1 inhibit the proliferation of
leukemic cells by down-regulating WT1 protein level. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 30:1102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA and Croce CM: miR-15a
and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future
perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 17:215–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chaudhuri AA, So AY, Mehta A, Minisandram
A, Sinha N, Jonsson VD, Rao DS, O'Connell RM and Baltimore D:
Oncomir miR-125b regulates hematopoiesis by targeting the gene
Lin28A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:4233–4238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo H, Li Q, O'Neal J, Kreisel F, Le Beau
MM and Tomasson MH: c-Myc rapidly induces acute myeloid leukemia in
mice without evidence of lymphoma-associated antiapoptotic
mutations. Blood. 106:2452–2461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, Grimes
B, Howard DS, Rizzieri DA, Luger SM and Jordan CT: Nuclear
factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute
myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 98:2301–2307. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Howard JM, Nuguid JM, Ngole D and Nguyen
H: Tcf3 expression marks both stem and progenitor cells in multiple
epithelia. Development. 141:3143–3152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Slyper M, Shahar A, Bar-Ziv A, Granit RZ,
Hamburger T, Maly B, Peretz T and Ben-Porath I: Control of breast
cancer growth and initiation by the stem cell-associated
transcription factor TCF3. Cancer Res. 72:5613–5624. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li C, Cai S, Wang X and Jiang Z:
Hypomethylation-associated up-regulation of TCF3 expression and
recurrence in stage II and III colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
9:e1120052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Patel D and Chaudhary J: Increased
expression of bHLH transcription factor E2A (TCF3) in prostate
cancer promotes proliferation and confers resistance to doxorubicin
induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 422:146–151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Salek-Ardakani S, Smooha G, de Boer J,
Sebire NJ, Morrow M, Rainis L, Lee S, Williams O, Izraeli S and
Brady HJ: ERG is a megakaryocytic oncogene. Cancer Res.
69:4665–4673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Marcucci G, Maharry K, Whitman SP,
Vukosavljevic T, Paschka P, Langer C, Mrózek K, Baldus CD, Carroll
AJ, Powell BL, et al; Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. High
expression levels of the ETS-related gene, ERG, predict adverse
outcome and improve molecular risk-based classification of
cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: A Cancer and
Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol. 25:3337–3343. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Goldberg L, Tijssen MR, Birger Y, Hannah
RL, Kinston SJ, Schütte J, Beck D, Knezevic K, Schiby G,
Jacob-Hirsch J, et al: Genome-scale expression and transcription
factor binding profiles reveal therapeutic targets in transgenic
ERG myeloid leukemia. Blood. 122:2694–2703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Burger MT, Han W, Lan J, Nishiguchi G,
Bellamacina C, Lindval M, Atallah G, Ding Y, Mathur M, McBride C,
et al: Structure guided optimization, in vitro activity, and in
vivo activity of Pan-PIM kinase inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett.
4:1193–1197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Shah N, Pang B, Yeoh KG, Thorn S, Chen CS,
Lilly MB and Salto-Tellez M: Potential roles for the PIM1 kinase in
human cancer - a molecular and therapeutic appraisal. Eur J Cancer.
44:2144–2151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|