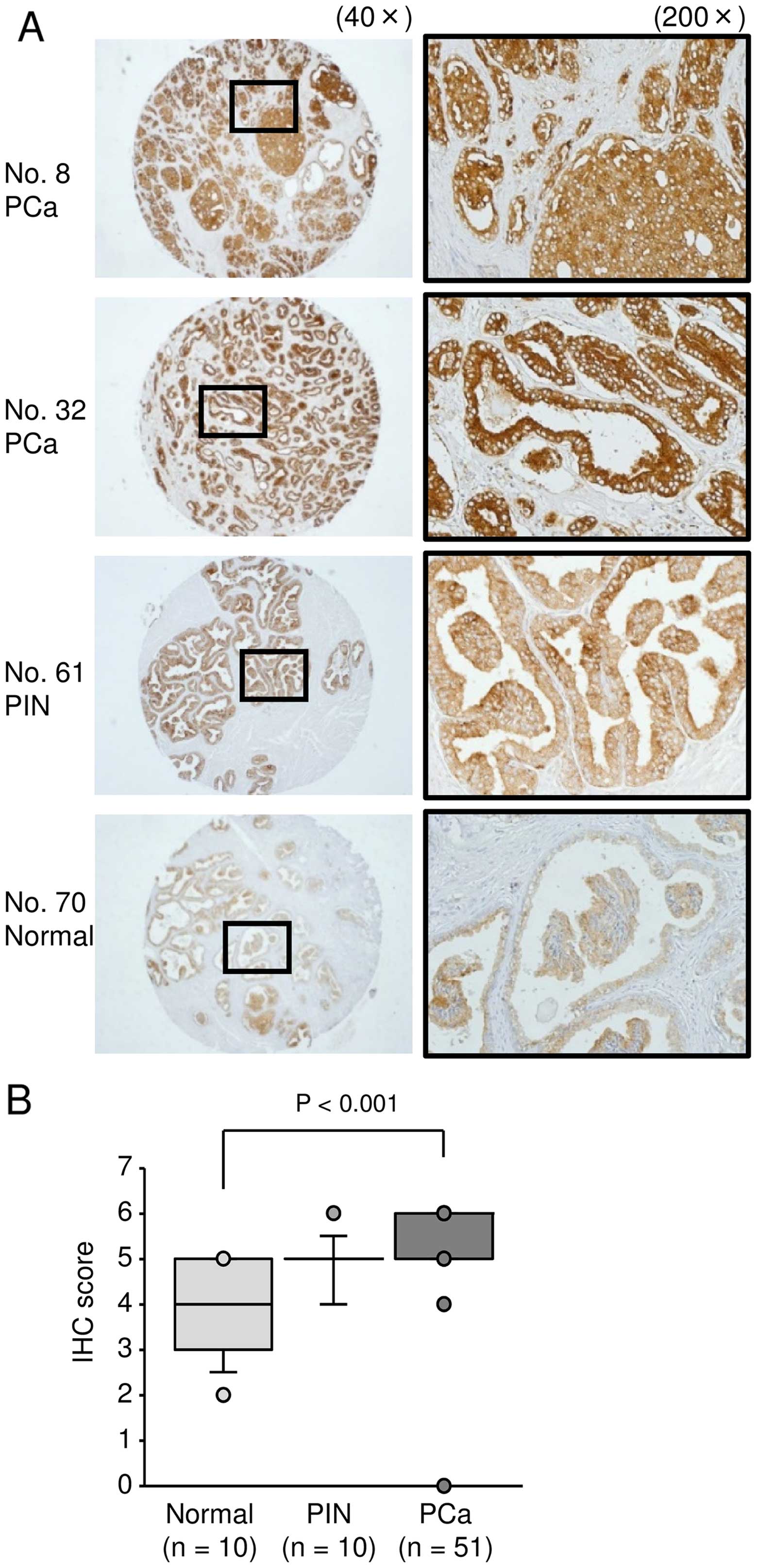
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sridhar SS, Freedland SJ, Gleave ME,
Higano C, Mulders P, Parker C, Sartor O and Saad F:
Castration-resistant prostate cancer: From new pathophysiology to
new treatment. Eur Urol. 65:289–299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hobert O: Gene regulation by transcription
factors and microRNAs. Science. 319:1785–1786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Fuse M, Kojima S, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T,
Yoshino H, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Sakamoto S, Naya Y, Nakagawa M,
et al: Tumor suppressive microRNAs (miR-222 and miR-31) regulate
molecular pathways based on microRNA expression signature in
prostate cancer. J Hum Genet. 57:691–699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goto Y, Kurozumi A, Enokida H, Ichikawa T
and Seki N: Functional significance of aberrantly expressed
microRNAs in prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 22:242–252. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goto Y, Kojima S, Nishikawa R, Enokida H,
Chiyomaru T, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M, Naya Y, Ichikawa T and Seki
N: The microRNA-23b/27b/24-1 cluster is a disease progression
marker and tumor suppressor in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
5:7748–7759. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Kojima S, Enokida H,
Chiyomaru T, Kinoshita T, Sakamoto S, Fuse M, Nakagawa M, Naya Y,
et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-29s inhibit cancer cell migration
and invasion via targeting LAMC1 in prostate cancer. Int J Oncol.
45:401–410. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Sakamoto S, Chiyomaru
T, Enokida H, Kojima S, Kinoshita T, Yamamoto N, Nakagawa M, Naya
Y, et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell
migration and invasion via targeting of LASP1 in prostate cancer.
Cancer Sci. 105:802–811. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kato M, Goto Y, Matsushita R, Kurozumi A,
Fukumoto I, Nishikawa R, Sakamoto S, Enokida H, Nakagawa M,
Ichikawa T, et al: MicroRNA-26a/b directly regulate La-related
protein 1 and inhibit cancer cell invasion in prostate cancer. Int
J Oncol. 47:710–718. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kojima S, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K, Yoshino
H, Enokida H, Nohata N, Fuse M, Ichikawa T, Naya Y, Nakagawa M, et
al: Tumour suppressors miR-1 and miR-133a target the oncogenic
function of purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) in prostate
cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:405–413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Kurozumi A,
Matsushita R, Enokida H, Kojima S, Naya Y, Nakagawa M, Ichikawa T
and Seki N: MicroRNA-205 inhibits cancer cell migration and
invasion via modulation of centromere protein F regulating pathways
in prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 22:867–877. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Goto Y, Kojima S, Nishikawa R, Kurozumi A,
Kato M, Enokida H, Matsushita R, Yamazaki K, Ishida Y, Nakagawa M,
et al: MicroRNA expression signature of castration-resistant
prostate cancer: The microRNA-221/222 cluster functions as a tumour
suppressor and disease progression marker. Br J Cancer.
113:1055–1065. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kurozumi A, Goto Y, Matsushita R, Fukumoto
I, Kato M, Nishikawa R, Sakamoto S, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Ichikawa
T, et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-223 inhibits cancer cell
migration and invasion by targeting ITGA3/ITGB1 signaling in
prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 107:84–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sturge J, Caley MP and Waxman J: Bone
metastasis in prostate cancer: Emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 8:357–368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Kojima S, Chiyomaru
T, Enokida H, Inoguchi S, Kinoshita T, Fuse M, Sakamoto S, Nakagawa
M, et al: Tumour-suppressive microRNA-224 inhibits cancer cell
migration and invasion via targeting oncogenic TPD52 in prostate
cancer. FEBS Lett. 588:1973–1982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsieh IS, Chang KC, Tsai YT, Ke JY, Lu PJ,
Lee KH, Yeh SD, Hong TM and Chen YL: MicroRNA-320 suppresses the
stem cell-like characteristics of prostate cancer cells by
downregulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 34:530–538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun JY, Huang Y, Li JP, Zhang X, Wang L,
Meng YL, Yan B, Bian YQ, Zhao J, Wang WZ, et al: MicroRNA-320a
suppresses human colon cancer cell proliferation by directly
targeting β-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 420:787–792. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lü M, Ding K, Zhang G, Yin M, Yao G, Tian
H, Lian J, Liu L, Liang M, Zhu T, et al: MicroRNA-320a sensitizes
tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells to tamoxifen by targeting
ARPP-19 and ERRγ. Sci Rep. 5:87352015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hoffmans R, Städeli R and Basler K:
Pygopus and legless provide essential transcriptional coactivator
functions to armadillo/beta-catenin. Curr Biol. 15:1207–1211. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yokoyama NN, Shao S, Hoang BH, Mercola D
and Zi X: Wnt signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer:
Implications for therapy. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2:27–44.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun L, Liu B, Lin Z, Yao Y, Chen Y, Li Y,
Chen J, Yu D, Tang Z, Wang B, et al: MiR-320a acts as a prognostic
factor and Inhibits metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma
by targeting ITGB3. Mol Cancer. 14:962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xishan Z, Ziying L, Jing D and Gang L:
MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL
oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. 5:124602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jensen SS, Aaberg-Jessen C, Christensen KG
and Kristensen B: Expression of the lysosomal-associated membrane
protein-1 (LAMP-1) in astrocytomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
6:1294–1305. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parkinson-Lawrence EJ, Dean CJ, Chang M,
Hopwood JJ, Meikle PJ and Brooks DA: Immunochemical analysis of
CD107a (LAMP-1). Cell Immunol. 236:161–166. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Furuta K, Ikeda M, Nakayama Y, Nakamura K,
Tanaka M, Hamasaki N, Himeno M, Hamilton SR and August JT:
Expression of lysosome-associated membrane proteins in human
colorectal neoplasms and inflammatory diseases. Am J Pathol.
159:449–455. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Agarwal AK, Gude RP and Kalraiya RD:
Regulation of melanoma metastasis to lungs by cell surface lysosome
associated membrane protein-1 (LAMP1) via galectin-3. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 449:332–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarafian V, Jadot M, Foidart JM, Letesson
JJ, Vanden Brûle F, Castronovo V, Wattiaux R and Coninck SW:
Expression of Lamp-1 and Lamp-2 and their interactions with
galectin-3 in human tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 75:105–111. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mane SM, Marzella L, Bainton DF, Holt VK,
Cha Y, Hildreth JE and August JT: Purification and characterization
of human lysosomal membrane glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys.
268:360–378. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krishnan V, Bane SM, Kawle PD, Naresh KN
and Kalraiya RD: Altered melanoma cell surface glycosylation
mediates organ specific adhesion and metastasis via lectin
receptors on the lung vascular endothelium. Clin Exp Metastasis.
22:11–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fortuna-Costa A, Gomes AM, Kozlowski EO,
Stelling MP and Pavão MS: Extracellular galectin-3 in tumor
progression and metastasis. Front Oncol. 4:1382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ahmed H and AlSadek DM: Galectin-3 as a
potential target to prevent cancer metastasis. Clin Med Insights
Oncol. 9:113–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Nangia-Makker P, Tait L, Balan V,
Hogan V, Pienta KJ and Raz A: Regulation of prostate cancer
progression by galectin-3. Am J Pathol. 174:1515–1523. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dachineni R, Ai G, Kumar DR, Sadhu SS,
Tummala H and Bhat GJ: Cyclin A2 and CDK2 as novel targets of
aspirin and salicylic acid: A potential role in cancer prevention.
Mol Cancer Res. 14:241–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Scaltriti M, Elkabets M and Baselga J:
Molecular pathways: AXL, a membrane receptor mediator of resistance
to therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 22:1313–1317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou W, Wang Z, Shen N, Pi W, Jiang W,
Huang J, Hu Y, Li X and Sun L: Knockdown of ANLN by lentivirus
inhibits cell growth and migration in human breast cancer. Mol Cell
Biochem. 398:11–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|