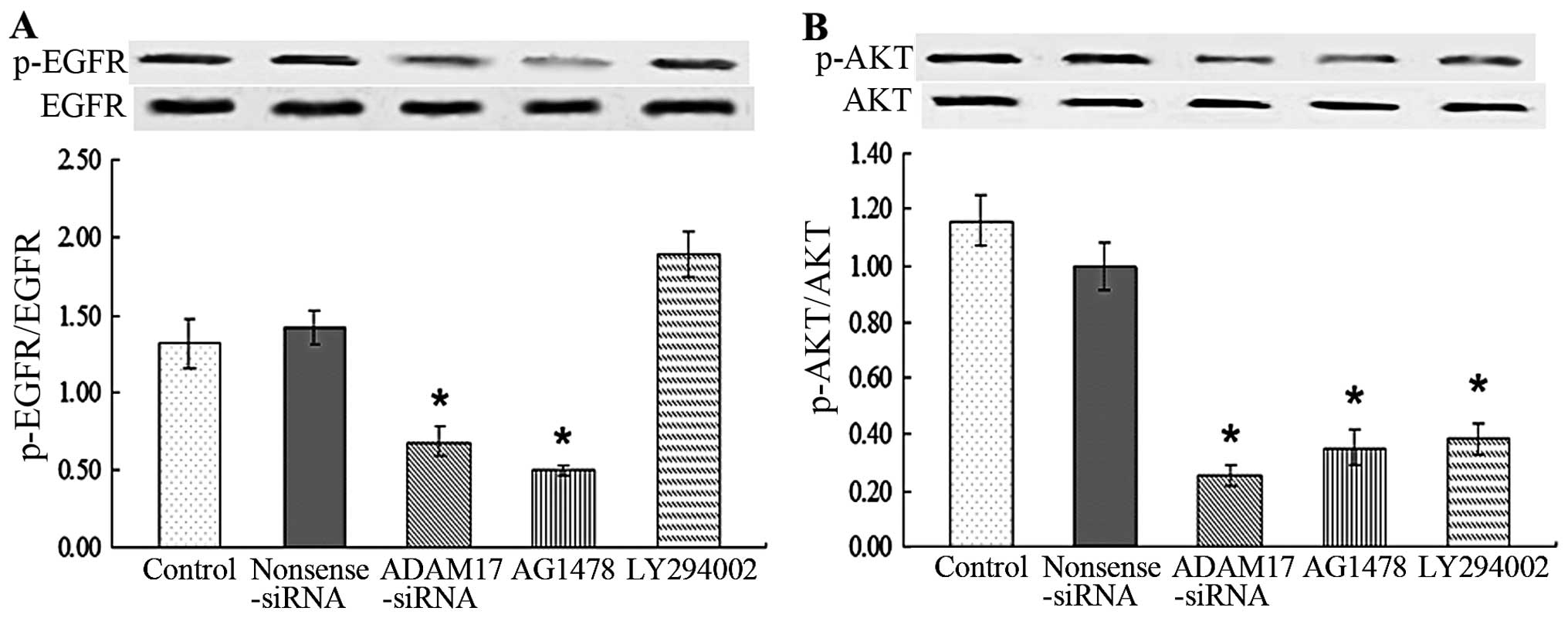
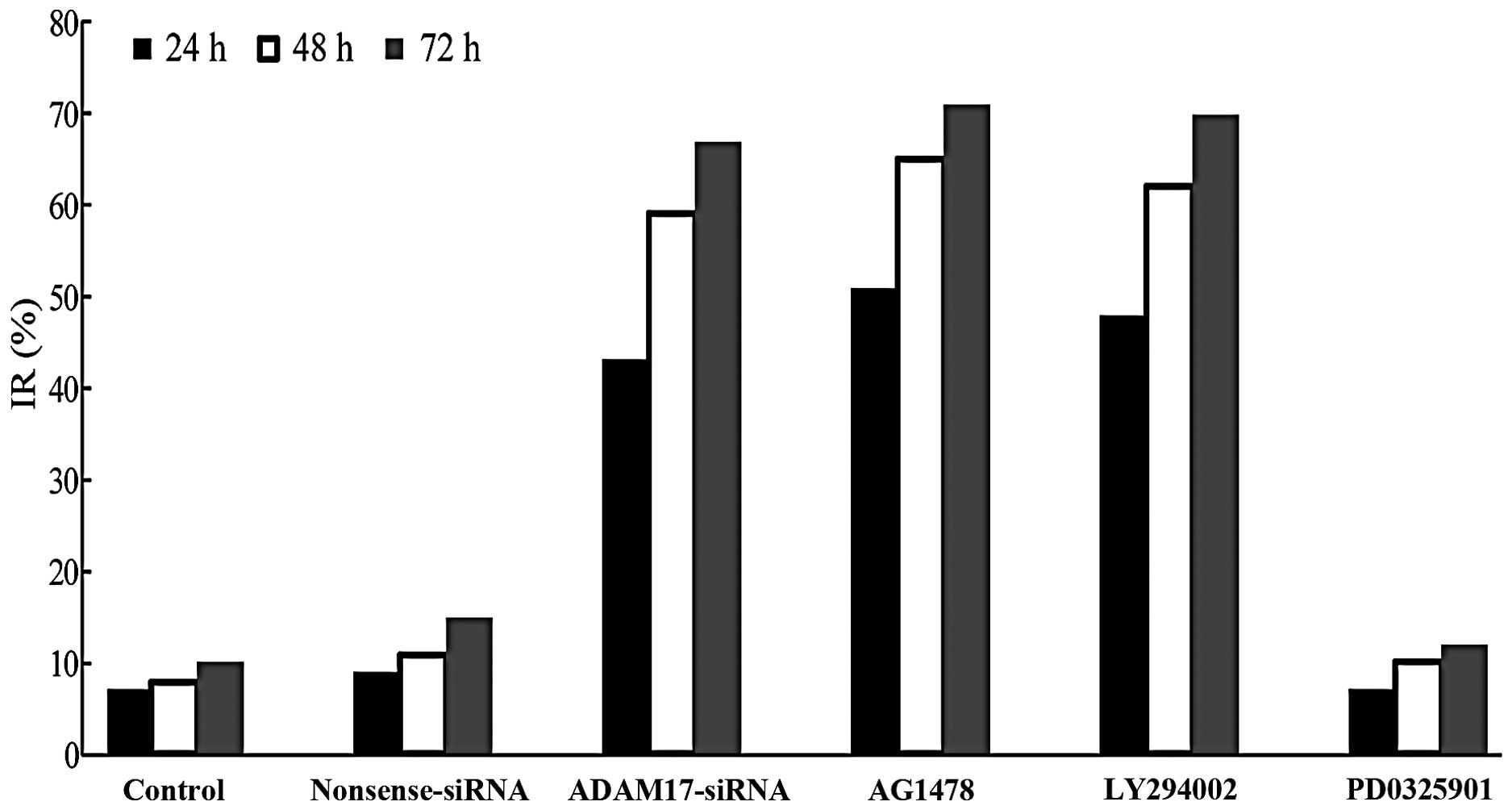
|
1
|
Krieger N, Bassett MT and Gomez SL: Breast
and cervical cancer in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010. Lancet.
379:1391–1392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Caiazza F, McGowan PM, Mullooly M, Murray
A, Synnott N, O'Donovan N, Flanagan L, Tape CJ, Murphy G, Crown J,
et al: Targeting ADAM-17 with an inhibitory monoclonal antibody has
antitumour effects in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 112:1895–1903. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ocaña A, Amir E, Seruga B, Martin M and
Pandiella A: The evolving landscape of protein kinases in breast
cancer: Clinical implications. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:68–76. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang P, Shen M, Fernandez-Patron C and
Kassiri Z: ADAMs family and relatives in cardiovascular physiology
and pathology. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 93:186–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bolger JC and Young LS: ADAM22 as a
prognostic and therapeutic drug target in the treatment of
endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Vitam Horm. 93:307–321. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rose-John S: ADAM17, shedding, TACE as
therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Res. 71:19–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu Y, Jiang F, Zheng X, Katakowski M,
Buller B, To SS and Chopp M: TGF-β1 promotes motility and
invasiveness of glioma cells through activation of ADAM17. Oncol
Rep. 25:1329–1335. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Santiago-Josefat B, Esselens C, Bech-Serra
JJ and Arribas J: Post-transcriptional up-regulation of ADAM17 upon
epidermal growth factor receptor activation and in breast tumors. J
Biol Chem. 282:8325–8331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murphy G: The ADAMs: Signalling scissors
in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:929–941. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rego SL, Helms RS and Dréau D: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme activities and
tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer. Immunol Res.
58:87–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Maretzky T, Zhou W, Huang XY and Blobel
CP: A transforming Src mutant increases the bioavailability of EGFR
ligands via stimulation of the cell-surface metalloproteinase
ADAM17. Oncogene. 30:611–618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zheng X, Jiang F, Katakowski M, Lu Y and
Chopp M: ADAM17 promotes glioma cell malignant phenotype. Mol
Carcinog. 51:150–164. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xiao LJ, Lin P, Lin F, Liu X, Qin W, Zou
HF, Guo L, Liu W, Wang SJ and Yu XG: ADAM17 targets MMP-2 and MMP-9
via EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway activation to promote prostate cancer cell
invasion. Int J Oncol. 40:1714–1724. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Zheng X, Jiang F, Katakowski M, Zhang ZG,
Lu QE and Chopp M: ADAM17 promotes breast cancer cell malignant
phenotype through EGFR-PI3K-AKT activation. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1045–1054. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McGowan PM, McKiernan E, Bolster F, Ryan
BM, Hill AD, McDermott EW, Evoy D, O'Higgins N, Crown J and Duffy
MJ: ADAM-17 predicts adverse outcome in patients with breast
cancer. Ann Oncol. 19:1075–1081. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han X, Yang XF, Zhang XP, Sun Y, Zhao JH
and Zhao GM: Expression of ADAM17 in tissue of breast cancer and
its clinical significance. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional
Chinese and Western Medicine. 19:2486–2488. 2010.
|
|
17
|
Yang XF, Zhang XP, Zhao GM, Sun Y and Han
X: Clinical significance of ADAM-17 protein expression in invasive
breast cancer. Shandong Med J. 51:84–85. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Yang WJ, Zhang XP, Jiao JM, Zhao GM, Lu YQ
and Hu BS: Inhibitory effects of ADAM17-siRNA on the invasion of
human MCF-7 breast cancer. Tianjin Med J. 39:1045–1407. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Lu YQ, Zhao GM and Zhang XP: Effects of
ADAM17-siRNA on the proliferation of human MCF-7 breast cancer.
Modern J Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Med.
20:3003–3005. 2011.
|
|
20
|
Brand TM, Iida M, Luthar N, Starr MM,
Huppert EJ and Wheeler DL: Nuclear EGFR as a molecular target in
cancer. Radiother Oncol. 108:370–377. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dienstmann R, Braña I, Rodon J and
Tabernero J: Toxicity as a biomarker of efficacy of molecular
targeted therapies: Focus on EGFR and VEGF inhibiting anticancer
drugs. Oncologist. 16:1729–1740. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Azuaje F, Tiemann K and Niclou SP:
Therapeutic control and resistance of the EGFR-driven signaling
network in glioblastoma. Cell Commun Signal. 13:232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee CC, Shiao HY, Wang WC and Hsieh HP:
Small-molecule EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of
cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 23:1333–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lorusso V, Forcignano R, Cinieri S,
Tinelli A, Porcelli L, Quatrale AE and Chiuri VE: Which role for
EGFR therapy in breast cancer? Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 4:31–42.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lluch A, Eroles P and Perez-Fidalgo JA:
Emerging EGFR antagonists for breast cancer. Expert Opin Emerg
Drugs. 19:165–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Howe LR and Brown PH: Targeting the
HER/EGFR/ErbB family to prevent breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 4:1149–1157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Davis NM, Sokolosky M, Stadelman K, Abrams
SL, Libra M, Candido S, Nicoletti F, Polesel J, Maestro R, D'Assoro
A, et al: Deregulation of the EGFR/PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTORC1 pathway in
breast cancer: Possibilities for therapeutic intervention.
Oncotarget. 5:4603–4650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li P, Torossian A, Zhang Q, Xu WC and Fu
S: Inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhances the
cytotoxicity of AG1478, an epidermal growth factor receptor
inhibitor, in breast cancer cells. Med Oncol. 29:3258–3264. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Caja L, Sancho P, Bertran E, Ortiz C,
Campbell JS, Fausto N and Fabregat I: The tyrphostin AG1478
inhibits proliferation and induces death of liver tumor cells
through EGF receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms. Biochem
Pharmacol. 82:1583–1592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang YG, Du Q, Fang WG, Jin ML and Tian
XX: Tyrphostin AG1478 suppresses proliferation and invasion of
human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 33:595–602. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ke XY, Wang Y, Xie ZQ, Liu ZQ, Zhang CF,
Zhao Q and Yang DL: LY294002 enhances inhibitory effect of
gemcitabine on proliferation of human pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1
cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 33:57–62. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tian S, Chang W, Du H, Bai J, Sun Z, Zhang
Q, Wang H, Zhu G, Tao K and Long Y: The interplay between GRP78
expression and Akt activation in human colon cancer cells under
celecoxib treatment. Anticancer Drugs. 26:964–973. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Ding Y, Li Q, Wang R,
Liu T, Sun Q, Yang H, Peng S, Wang W, et al: MiR-20a induces cell
radioresistance by activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
92:1132–1140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen P, Wu J, Yuan Q, Jiang X and Huang H:
The synergistic killing of AML cells co-cultured with HS-5 bone
marrow stromal cells by As2O3 and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
inhibitor LY294002. Pharmazie. 70:322–327. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y and Lazo JS: Metastasis-associated
phosphatase PRL-2 regulates tumor cell migration and invasion.
Oncogene. 31:818–827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Whitsett TG, Cheng E, Inge L, Asrani K,
Jameson NM, Hostetter G, Weiss GJ, Kingsley CB, Loftus JC, Bremner
R, et al: Elevated expression of Fn14 in non-small cell lung cancer
correlates with activated EGFR and promotes tumor cell migration
and invasion. Am J Pathol. 181:111–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han J, Xie Y, Lan F, Yu Y, Liu W, Chen J,
Zheng F, Ouyang X, Lin X, Lin Y, et al: Additive effects of EGF and
IL-1β regulate tumor cell migration and invasion in gastric
adenocarcinoma via activation of ERK1/2. Int J Oncol. 45:291–301.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kenny PA and Bissell MJ: Targeting
TACE-dependent EGFR ligand shedding in breast cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:337–345. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tanei T, Shimomura A, Shimazu K, Nakayama
T, Kim SJ, Iwamoto T, Tamaki Y and Noguchi S: Prognostic
significance of Ki67 index after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast
cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 37:155–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yoshioka T, Hosoda M, Yamamoto M, Taguchi
K, Hatanaka KC, Takakuwa E, Hatanaka Y, Matsuno Y and Yamashita H:
Prognostic significance of pathologic complete response and Ki67
expression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer. 22:185–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|