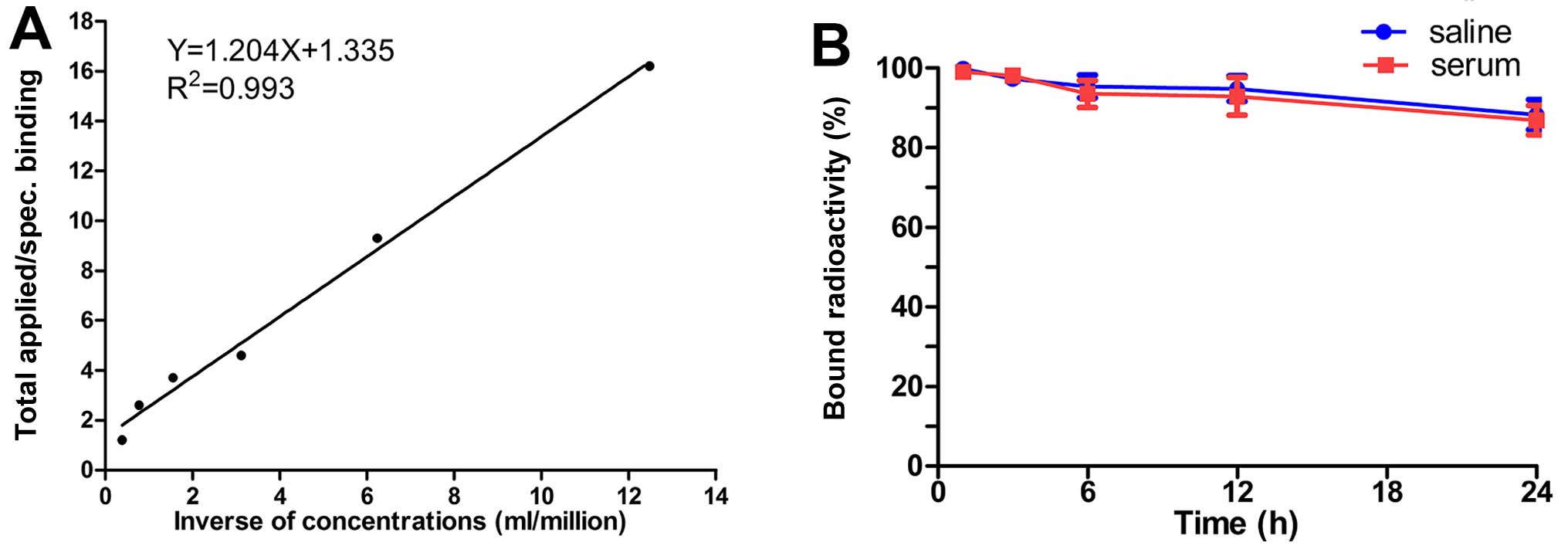
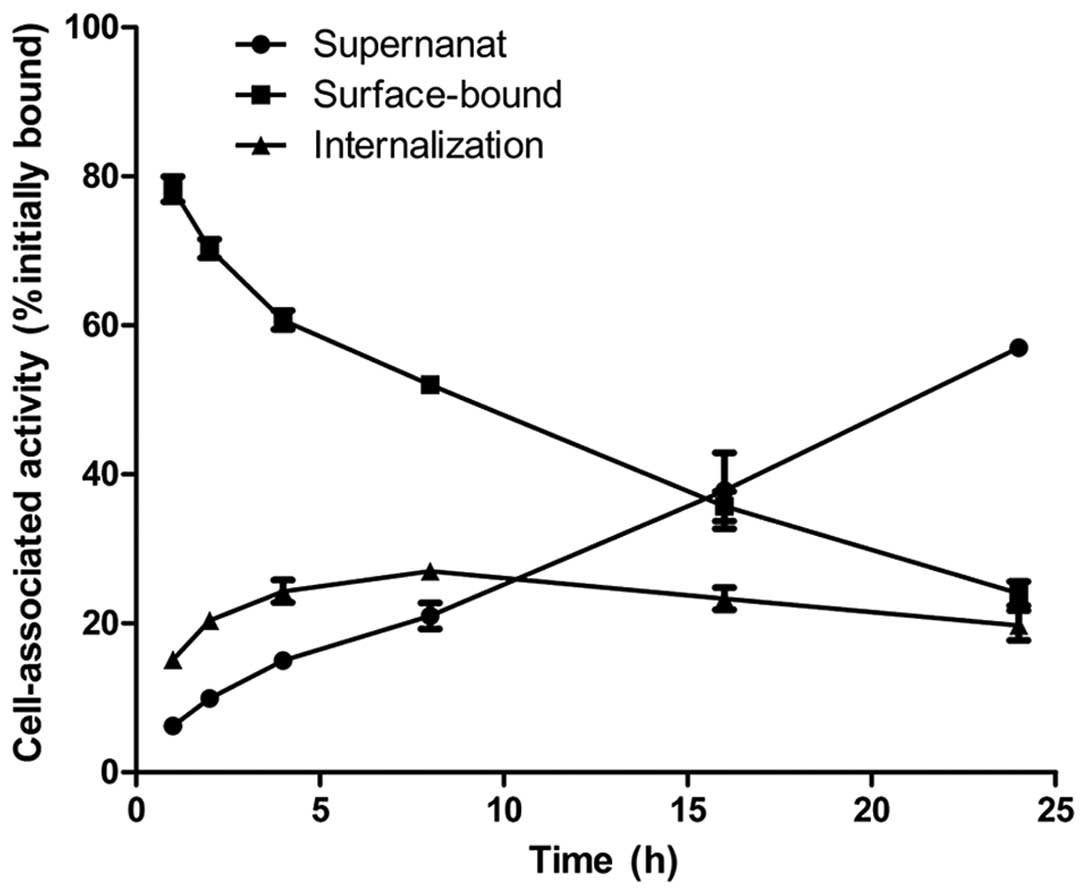
|
1
|
Gilbert MR: Renewing interest in targeting
angiogenesis in glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol. 15:907–908. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Spratlin JL, Mulder KE and Mackey JR:
Ramucirumab (IMC-1121B): A novel attack on angiogenesis. Future
Oncol. 6:1085–1094. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inoue M, Hager JH, Ferrara N, Gerber HP
and Hanahan D: VEGF-A has a critical, nonredundant role in
angiogenic switching and pancreatic beta cell carcinogenesis.
Cancer Cell. 1:193–202. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Otrock ZK, Makarem JA and Shamseddine AI:
Vascular endothelial growth factor family of ligands and receptors:
Review. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 38:258–268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cudmore MJ, Hewett PW, Ahmad S, Wang KQ,
Cai M, Al-Ani B, Fujisawa T, Ma B, Sissaoui S, Ramma W, et al: The
role of heterodimerization between VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in the
regulation of endothelial cell homeostasis. Nat Commun. 3:9722012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mac Gabhann F and Popel AS: Interactions
of VEGF isoforms with VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and neuropilin in vivo: A
computational model of human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 292:H459–H474. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gluzman-Poltorak Z, Cohen T, Herzog Y and
Neufeld G: Neuropilin-2 is a receptor for the vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) forms VEGF-145 and VEGF-165 [corrected]. J
Biol Chem. 275:18040–18045. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dhakal HP, Naume B, Synnestvedt M, Borgen
E, Kaaresen R, Schlichting E, Wiedswang G, Bassarova A, Holm R,
Giercksky KE, et al: Expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1 and 2 in
invasive breast carcinoma: Prognostic significance and relationship
with markers for aggressiveness. Histopathology. 61:350–364. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakayama T, Cho YC, Mine Y, Yoshizaki A,
Naito S, Wen CY and Sekine I: Expression of vascular endothelial
growth factor and its receptors VEGFR-1 and 2 in gastrointestinal
stromal tumors, leiomyomas and schwannomas. World J Gastroenterol.
12:6182–6187. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Staton CA, Kumar I, Reed MW and Brown NJ:
Neuropilins in physiological and pathological angiogenesis. J
Pathol. 212:237–248. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bagri A, Tessier-Lavigne M and Watts RJ:
Neuropilins in tumor biology. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1860–1864. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Jia H and
Zachary I: Neuropilins: Structure, function and role in disease.
Biochem J. 411:211–226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prud’homme GJ and Glinka Y: Neuropilins
are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation,
growth, metastasis and immunity. Oncotarget. 3:921–939. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chaudhary B, Khaled YS, Ammori BJ and
Elkord E: Neuropilin 1: Function and therapeutic potential in
cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:81–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Plein A, Fantin A and Ruhrberg C:
Neuropilin regulation of angiogenesis, arteriogenesis, and vascular
permeability. Microcirculation. 21:315–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sulpice E, Plouët J, Bergé M, Allanic D,
Tobelem G and Merkulova-Rainon T: Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 act
as coreceptors, potentiating proangiogenic activity. Blood.
111:2036–2045. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Geretti E, Shimizu A and Klagsbrun M:
Neuropilin structure governs VEGF and semaphorin binding and
regulates angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 11:31–39. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parker MW, Xu P, Li X and Vander Kooi CW:
Structural basis for selective vascular endothelial growth factor-A
(VEGF-A) binding to neuropilin-1. J Biol Chem. 287:11082–11089.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G
and Klagsbrun M: Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor
cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial
growth factor. Cell. 92:735–745. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fuh G, Garcia KC and de Vos AM: The
interaction of neuropilin-1 with vascular endothelial growth factor
and its receptor flt-1. J Biol Chem. 275:26690–26695.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kawasaki T, Kitsukawa T, Bekku Y, Matsuda
Y, Sanbo M, Yagi T and Fujisawa H: A requirement for neuropilin-1
in embryonic vessel formation. Development. 126:4895–4902.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kärpänen T, Heckman CA, Keskitalo S,
Jeltsch M, Ollila H, Neufeld G, Tamagnone L and Alitalo K:
Functional interaction of VEGF-C and VEGF-D with neuropilin
receptors. FASEB J. 20:1462–1472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Herzog Y, Kalcheim C, Kahane N, Reshef R
and Neufeld G: Differential expression of neuropilin-1 and
neuropilin-2 in arteries and veins. Mech Dev. 109:115–119. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim YJ, Bae J, Shin TH, Kang SH, Jeong M,
Han Y, Park JH, Kim SK and Kim YS: Immunoglobulin Fc-fused,
neuropilin-1-specific peptide shows efficient tumor tissue
penetration and inhibits tumor growth via anti-angiogenesis. J
Control Release. 216:56–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan Q, Chanthery Y, Liang WC, Stawicki S,
Mak J, Rathore N, Tong RK, Kowalski J, Yee SF, Pacheco G, et al:
Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with
anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 11:53–67. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caunt M1, Mak J, Liang WC, Stawicki S, Pan
Q, Tong RK, Kowalski J, Ho C, Reslan HB, Ross J, et al: Blocking
neuropilin-2 function inhibits tumor cell metastasis. Cancer Cell.
13:331–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Liu P, Jiang Y, Dou X, Yan J, Ma
C, Fan Q, Wang W, Su F, Tang H, et al: High expression of
neuropilin-1 associates with unfavorable clinicopathological
features in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 22:367–375.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xu Y, Li P, Zhang X, Wang J, Gu D and Wang
Y: Prognostic implication of neuropilllin-1 up-regulation in human
nasopharyngealc arcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 8:1552013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cheng W, Fu D, Wei ZF, Xu F, Xu XF, Liu
YH, Ge JP, Tian F, Han CH, Zhang ZY, et al: NRP-1 expression in
bladder cancer and its implications for tumor progression. Tumour
Biol. 35:6089–6094. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu H, Cai H, Tang M and Tang J:
Neuropilin-1 is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and contributes to
tumor progression and poor prognosis. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:732–738. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Weekes CD, Beeram M, Tolcher AW,
Papadopoulos KP, Gore L, Hegde P, Xin Y, Yu R, Shih LM, Xiang H, et
al: A phase I study of the human monoclonal anti-NRP1 antibody
MNRP1685A in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
32:653–660. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patnaik A, LoRusso PM, Messersmith WA,
Papadopoulos KP, Gore L, Beeram M, Ramakrishnan V, Kim AH, Beyer
JC, Mason Shih L, et al: A Phase Ib study evaluating MNRP1685A, a
fully human anti-NRP1 monoclonal antibody, in combination with
bevacizumab and paclitaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 73:951–960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tolmachev V, Stone-Elander S and Orlova A:
Current approaches to the use of radiolabeled tyrosine
kinase-targeting drugs for patient stratification and treatment
response monitoring: Prospects and pitfalls. Lancet Oncol.
11:992–1000. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Perret GY, Starzec A, Hauet N, Vergote J,
Le Pecheur M, Vassy R, Léger G, Verbeke KA, Bormans G, Nicolas P,
et al: In vitro evaluation and biodistribution of a
99mTc-labeled anti-VEGF peptide targeting neuropilin-1.
Nucl Med Biol. 31:575–581. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Feng GK, Liu RB, Zhang MQ, Ye XX, Zhong Q,
Xia YF, Li MZ, Wang J, Song EW, Zhang X, et al: SPECT and
near-infrared fluorescence imaging of breast cancer with a
neuropilin-1-targeting peptide. J Control Release. 192:236–242.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li X, Luo F, Wang S, Ni E, Tang X, Lv H,
Chen X, Chen L and Yan J: Monoclonal antibody against NRP-1 b1b2.
Hybridoma (Larchmt). 30:369–373. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen L, Miao W, Tang X, Zhang H, Wang S,
Luo F and Yan J: Inhibitory effect of neuropilin-1 monoclonal
antibody (NRP-1 MAb) on glioma tumor in mice. J Biomedical
Nanotechnol. 9:551–558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zeng F, Luo F, Lv S, Zhang H, Cao C, Chen
X, Wang S, Li Z, Wang X, Dou X, et al: A monoclonal antibody
targeting neuropilin-1 inhibits adhesion of MCF7 breast cancer
cells to fibronectin by suppressing the FAK/p130cas signaling
pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 25:663–672. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang C, Yun Q, Sun H, Yang G, Liang T,
Zhang C, Song J, Han J and Hou G: Non-invasive imaging of Toll-like
receptor 5 expression using 131I-labeled mAb in the mice
bearing H22 tumors. Oncol Lett. 7:1919–1924. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lindmo T, Boven E, Cuttitta F, Fedorko J
and Bunn PA Jr: Determination of the immunoreactive fraction of
radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies by linear extrapolation to
binding at infinite antigen excess. J Immunol Methods. 72:77–89.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Malviya G1, Anzola KL, Podestà E, Laganà
B, Del Mastro C, Dierckx RA, Scopinaro F and Signore A:
99mTc-labeled rituximab for imaging B lymphocyte
infiltration in inflammatory autoimmune disease patients. Mol
Imaging Biol. 14:637–646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Su X, Cheng K, Jeon J, Shen B, Venturin
GT, Hu X, Rao J, Chin FT, Wu H and Cheng Z: Comparison of two
site-specifically 18F-labeled affibodies for PET imaging
of EGFR positive tumors. Mol Pharm. 11:3947–3956. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao Q, Yan P, Wang RF, Zhang CL, Li L and
Yin L: A novel 99mTc-labeled molecular probe for tumor
angiogenesis imaging in hepatoma xenografts model: A pilot study.
PLoS One. 8:e610432013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Su X, Cheng K, Liu Y, Hu X, Meng S and
Cheng Z: PET imaging of insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor
expression with a 64Cu-labeled Affibody molecule. Amino
Acids. 47:1409–1419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kato Y, Vaidyanathan G, Kaneko MK, Mishima
K, Srivastava N, Chandramohan V, Pegram C, Keir ST, Kuan CT, Bigner
DD, et al: Evaluation of anti-podoplanin rat monoclonal antibody
NZ-1 for targeting malignant gliomas. Nucl Med Biol. 37:785–794.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Aldrich MB, Marshall MV and
Sevick-Muraca EM: Preclinical characterization and validation of a
dual-labeled trastuzumab-based imaging agent for diagnosing breast
cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 27:74–82. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bumbaca D, Xiang H, Boswell CA, Port RE,
Stainton SL, Mundo EE, Ulufatu S, Bagri A, Theil FP, Fielder PJ, et
al: Maximizing tumour exposure to anti-neuropilin-1 antibody
requires saturation of non-tumour tissue antigenic sinks in mice.
Br J Pharmacol. 166:368–377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
van Dongen GA, Visser GW, Lub-de Hooge MN,
de Vries EG and Perk LR: Immuno-PET: A navigator in monoclonal
antibody development and applications. Oncologist. 12:1379–1389.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Li X, Gong M, Xu W and Tang L: Market
dynamics of antibody drugs in both domestic and abroad. Drugs Clin.
27:185–191. 2012.
|
|
52
|
Bergé M, Allanic D, Bonnin P, de Montrion
C, Richard J, Suc M, Boivin JF, Contrerès JO, Lockhart BP, Pocard
M, et al: Neuropilin-1 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma
and contributes to tumour growth and vascular remodelling. J
Hepatol. 55:866–875. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Han Z, Jiang G, Zhang Y, Xu J, Chen C,
Zhang L, Xu Z and Du X: Effects of RNA interference-mediated NRP-1
silencing on the proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:513–519. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wey JS, Gray MJ, Fan F, Belcheva A,
McCarty MF, Stoeltzing O, Somcio R, Liu W, Evans DB, Klagsbrun M,
et al: Overexpression of neuropilin-1 promotes constitutive MAPK
signalling and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 93:233–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yue B, Ma JF, Yao G, Yang MD, Cheng H and
Liu GY: Knockdown of neuropilin-1 suppresses invasion,
angiogenesis, and increases the chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in
osteosarcoma cells: an in vitro study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:1735–1741. 2014.
|
|
56
|
Mehta S, Moon J, Hashmi M, Leblanc M,
Huang CH, Rinehart E, Wolf GT, Urba SG, Banerjee SK and Williamson
S: Predictive factors in patients with advanced and metastatic
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A study based on SWOG
protocol S0420. Oncol Rep. 29:2095–2100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|