|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kodama J, Seki N, Masahiro S, Kusumoto T,
Nakamura K, Hongo A and Hiramatsu Y: Prognostic factors in stage
IB-IIB cervical adenocarcinoma patients treated with radical
hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. J Surg Oncol. 101:413–417.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
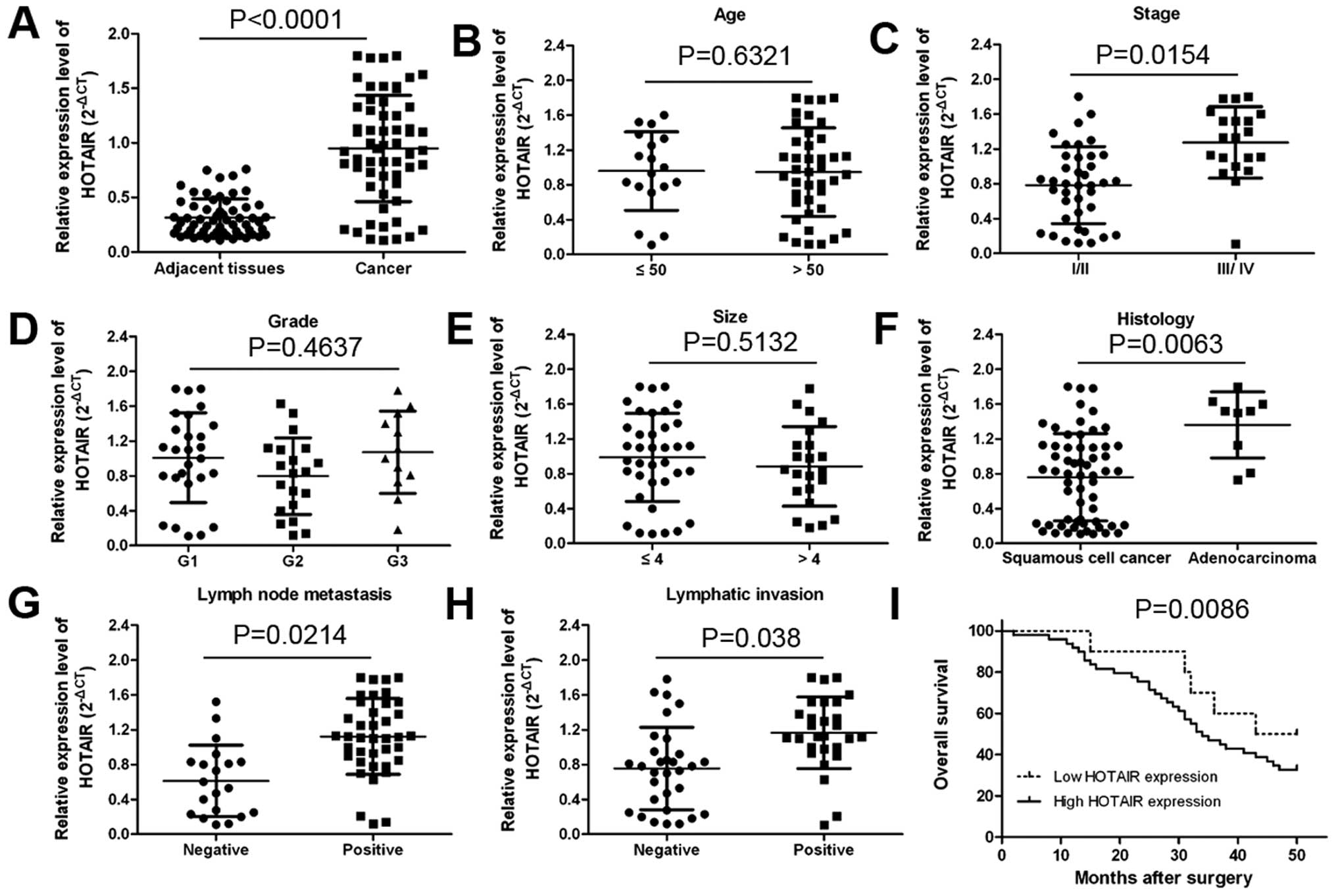
|
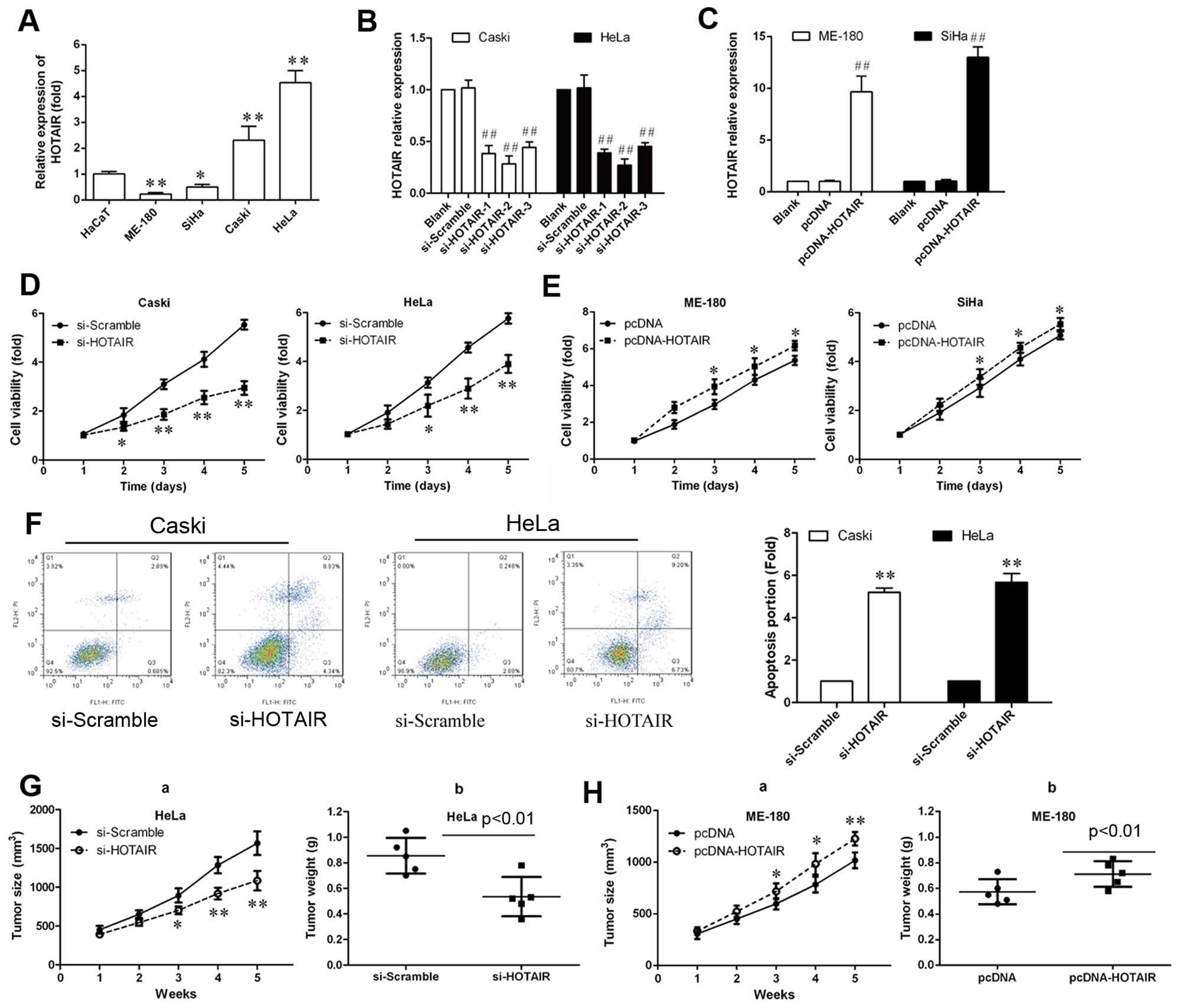
|
3
|
Noordhuis MG, Fehrmann RS, Wisman GB,
Nijhuis ER, van Zanden JJ, Moerland PD, Ver Loren van Themaat E,
Volders HH, Kok M, ten Hoor KA, et al: Involvement of the TGF-beta
and beta-catenin pathways in pelvic lymph node metastasis in
early-stage cervical cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1317–1330. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ and
Schreiber RD: Cancer immunoediting: From immunosurveillance to
tumor escape. Nat Immunol. 3:991–998. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Urosevic M, Willers J, Mueller B, Kempf W,
Burg G and Dummer R: HLA-G protein up-regulation in primary
cutaneous lymphomas is associated with interleukin-10 expression in
large cell T-cell lymphomas and indolent B-cell lymphomas. Blood.
99:609–617. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dunn GP, Old LJ and Schreiber RD: The
three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol. 22:329–360.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Urosevic M and Dummer R: Human leukocyte
antigen-G and cancer immunoediting. Cancer Res. 68:627–630. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sheu J and Shih Ie M: HLA-G and immune
evasion in cancer cells. J Formos Med Assoc. 109:248–257. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song B, Guan Z, Liu F, Sun D, Wang K and
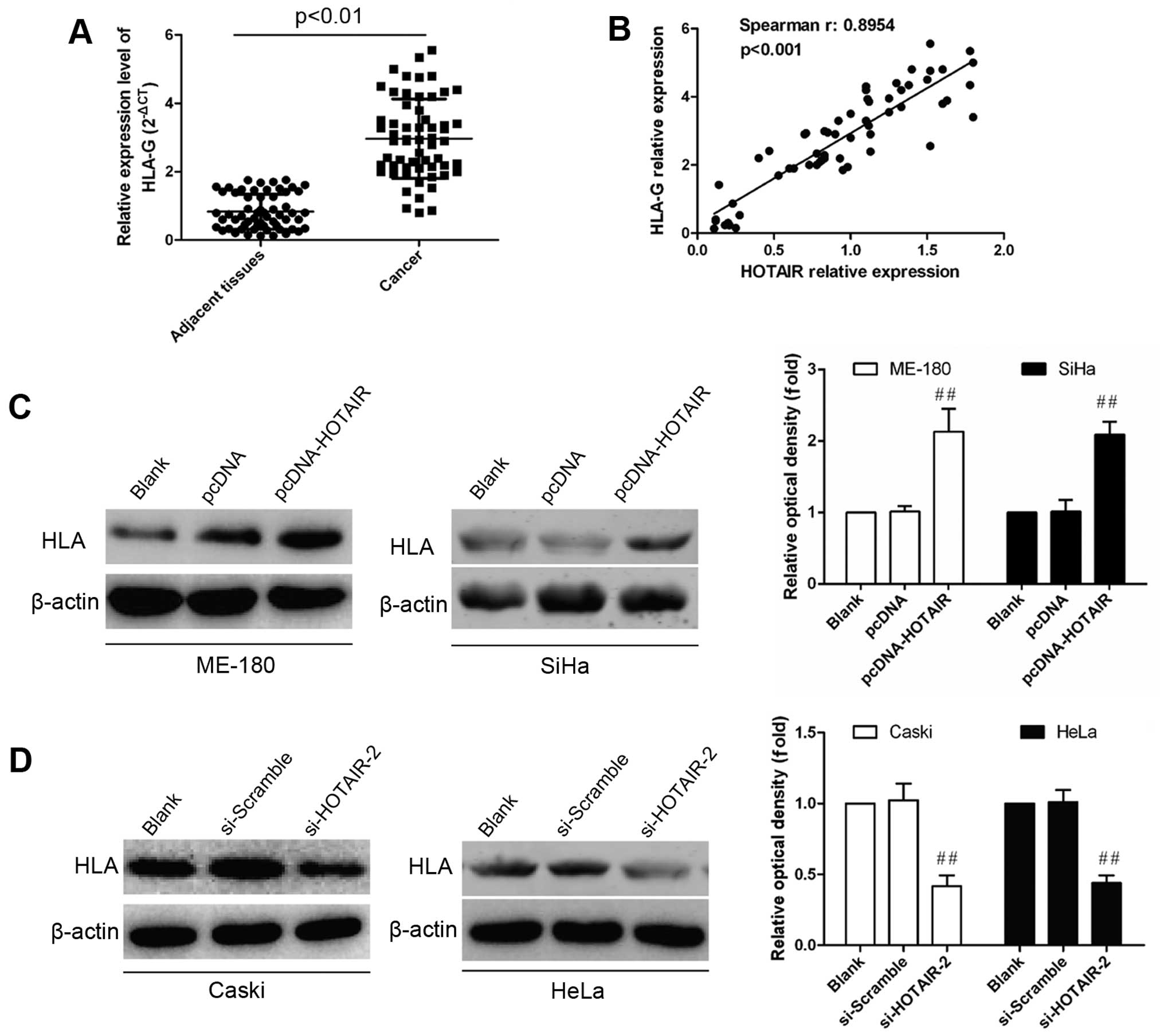
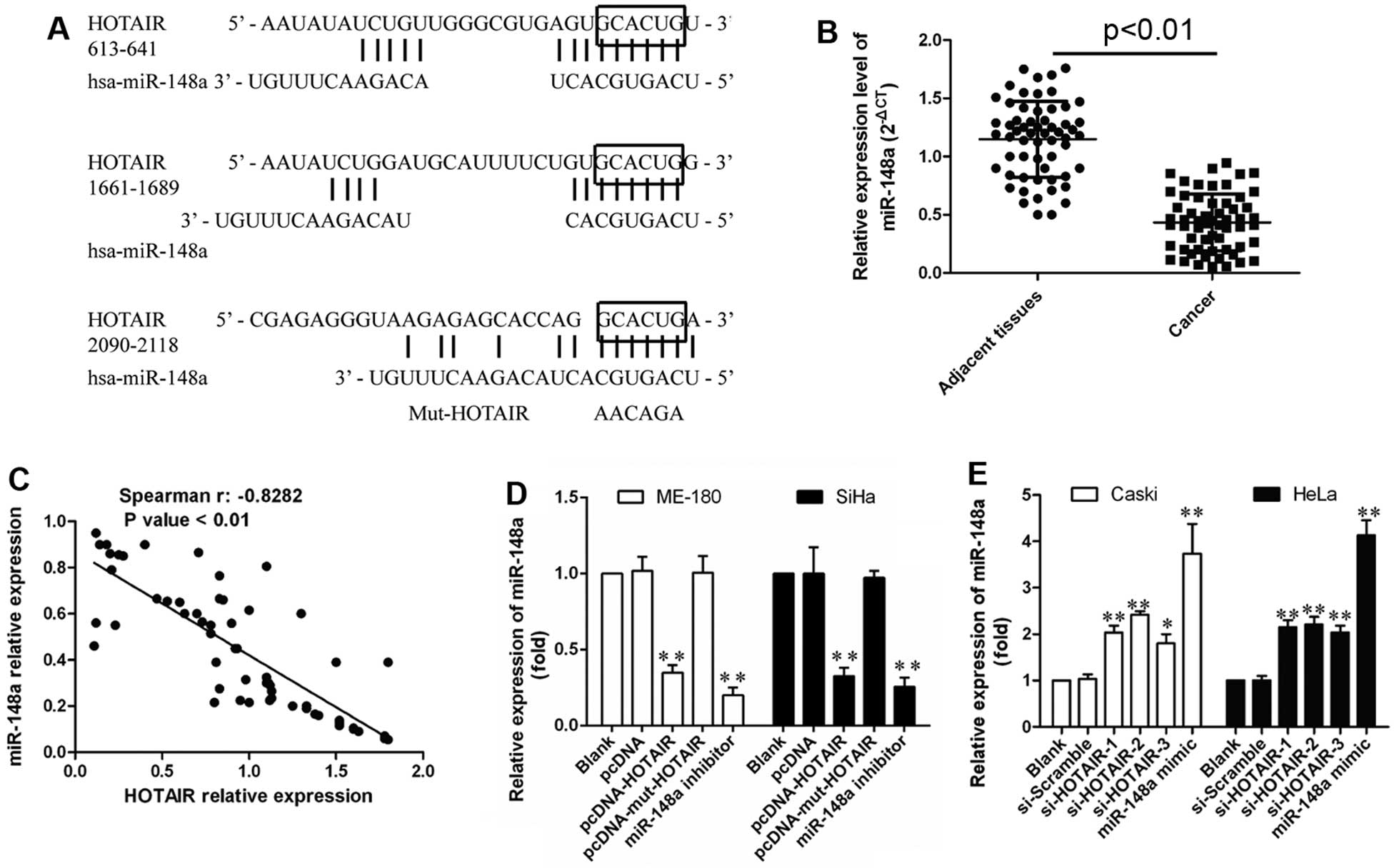
Qu H: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes HLA-G expression via
inhibiting miR-152 in gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:807–813. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Teixeira AC, Mendes-Junior CT, Souza FF,
Marano LA, Deghaide NH, Ferreira SC, Mente ED, Sankarankutty AK,
Elias-Junior J, Castro-e-Silva O, et al: The 14bp-deletion allele
in the HLA-G gene confers susceptibility to the development of
hepatocellular carcinoma in the Brazilian population. Tissue
Antigens. 81:408–413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakagawa T, Endo H, Yokoyama M, Abe J,
Tamai K, Tanaka N, Sato I, Takahashi S, Kondo T and Satoh K: Large
noncoding RNA HOTAIR enhances aggressive biological behavior and is
associated with short disease-free survival in human non-small cell
lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:319–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sørensen KP, Thomassen M, Tan Q, Bak M,
Cold S, Burton M, Larsen MJ and Kruse TA: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in
estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 142:529–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu ZH, Wang XL, Tang HM, Jiang T, Chen J,
Lu S, Qiu GQ, Peng ZH and Yan DW: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a
powerful predictor of metastasis and poor prognosis and is
associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer.
Oncol Rep. 32:395–402. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang JX, Han L, Bao ZS, Wang YY, Chen LY,
Yan W, Yu SZ, Pu PY, Liu N, You YP, et al; Chinese Glioma
Cooperative Group. HOTAIR, a cell cycle-associated long noncoding
RNA and a strong predictor of survival, is preferentially expressed
in classical and mesenchymal glioma. Neuro Oncol. 15:1595–1603.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Liu L and Zhu W: Up-regulation of
long non-coding RNA CCAT2 correlates with tumor metastasis and poor
prognosis in cervical squamous cell cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:13261–13266. 2015.
|
|
16
|
Kim HJ, Lee DW, Yim GW, Nam EJ, Kim S, Kim
SW and Kim YT: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with human
cervical cancer progression. Int J Oncol. 46:521–530. 2015.
|
|
17
|
Jing L, Yuan W, Ruofan D, Jinjin Y and
Haifeng Q: HOTAIR enhanced aggressive biological behaviors and
induced radio-resistance via inhibiting p21 in cervical cancer.
Tumour Biol. 36:3611–3619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rudstein-Svetlicky N, Loewenthal R,
Horejsi V and Gazit E: HLA-G levels in serum and plasma. Tissue
Antigens. 67:111–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G,
Kostoulas N, Reczko M, Maragkakis M, Dalamagas TM and Hatzigeorgiou
AG: DIANA-LncBase: Experimentally verified and computationally
predicted microRNA targets on long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:D239–D245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I,
Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A and Bozzoni I: A
long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kallen AN, Zhou XB, Xu J, Qiao C, Ma J,
Yan L, Lu L, Liu C, Yi JS, Zhang H, et al: The imprinted H19 lncRNA
antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell. 52:101–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan Z, Randall G, Fan J, Camoretti-Mercado
B, Brockman-Schneider R, Pan L, Solway J, Gern JE, Lemanske RF,
Nicolae D, et al: Allele-specific targeting of microRNAs to HLA-G
and risk of asthma. Am J Hum Genet. 81:829–834. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xing CY, Hu XQ, Xie FY, Yu ZJ, Li HY,
Bin-Zhou, Wu JB, Tang LY and Gao SM: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
modulates c-KIT expression through sponging miR-193a in acute
myeloid leukemia. FEBS Lett. 589:1981–1987. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E, et
al: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains
in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Kim J, Yang X,
Martindale JL, Tominaga-Yamanaka K, White EJ, Orjalo AV, Rinn JL,
Kreft SG, et al: Scaffold function of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in
protein ubiquitination. Nat Commun. 4:29392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu XH, Sun M, Nie FQ, Ge YB, Zhang EB,
Yin DD, Kong R, Xia R, Lu KH, Li JH, et al: Lnc RNA HOTAIR
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression
by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:922014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Paul P, Rouas-Freiss N, Khalil-Daher I,
Moreau P, Riteau B, Le Gal FA, Avril MF, Dausset J, Guillet JG and
Carosella ED: HLA-G expression in melanoma: A way for tumor cells
to escape from immunosurveillance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:4510–4515. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rouas-Freiss N, Moreau P, Ferrone S and
Carosella ED: HLA-G proteins in cancer: Do they provide tumor cells
with an escape mechanism? Cancer Res. 65:10139–10144. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tripathi P and Agrawal S: Non-classical
HLA-G antigen and its role in the cancer progression. Cancer
Invest. 24:178–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mallet V, Blaschitz A, Crisa L, Schmitt C,
Fournel S, King A, Loke YW, Dohr G and Le Bouteiller P: HLA-G in
the human thymus: A subpopulation of medullary epithelial but not
CD83+ dendritic cells expresses HLA-G as a
membrane-bound and soluble protein. Int Immunol. 11:889–898. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tuncel T, Karagoz B, Haholu A, Ozgun A,
Emirzeoglu L, Bilgi O and Kandemir EG: Immunoregulatory function of
HLA-G in gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7681–7684.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Amiot L, Vu N and Samson M: Biology of the
immunomodulatory molecule HLA-G in human liver diseases. J Hepatol.
62:1430–1437. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raisch J, Darfeuille-Michaud A and Nguyen
HT: Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 19:2985–2996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu G and Abraham E: MicroRNAs in immune
response and macrophage polarization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 33:170–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, Song YX and Wang ZN: The
microRNA-148/152 family: Multi-faceted players. Mol Cancer.
12:432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu X, Zhan Z, Xu L, Ma F, Li D, Guo Z, Li
N and Cao X: MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen
presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIα.
J Immunol. 185:7244–7251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Manaster I, Goldman-Wohl D, Greenfield C,
Nachmani D, Tsukerman P, Hamani Y, Yagel S and Mandelboim O:
MiRNA-mediated control of HLA-G expression and function. PLoS One.
7:e333952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|