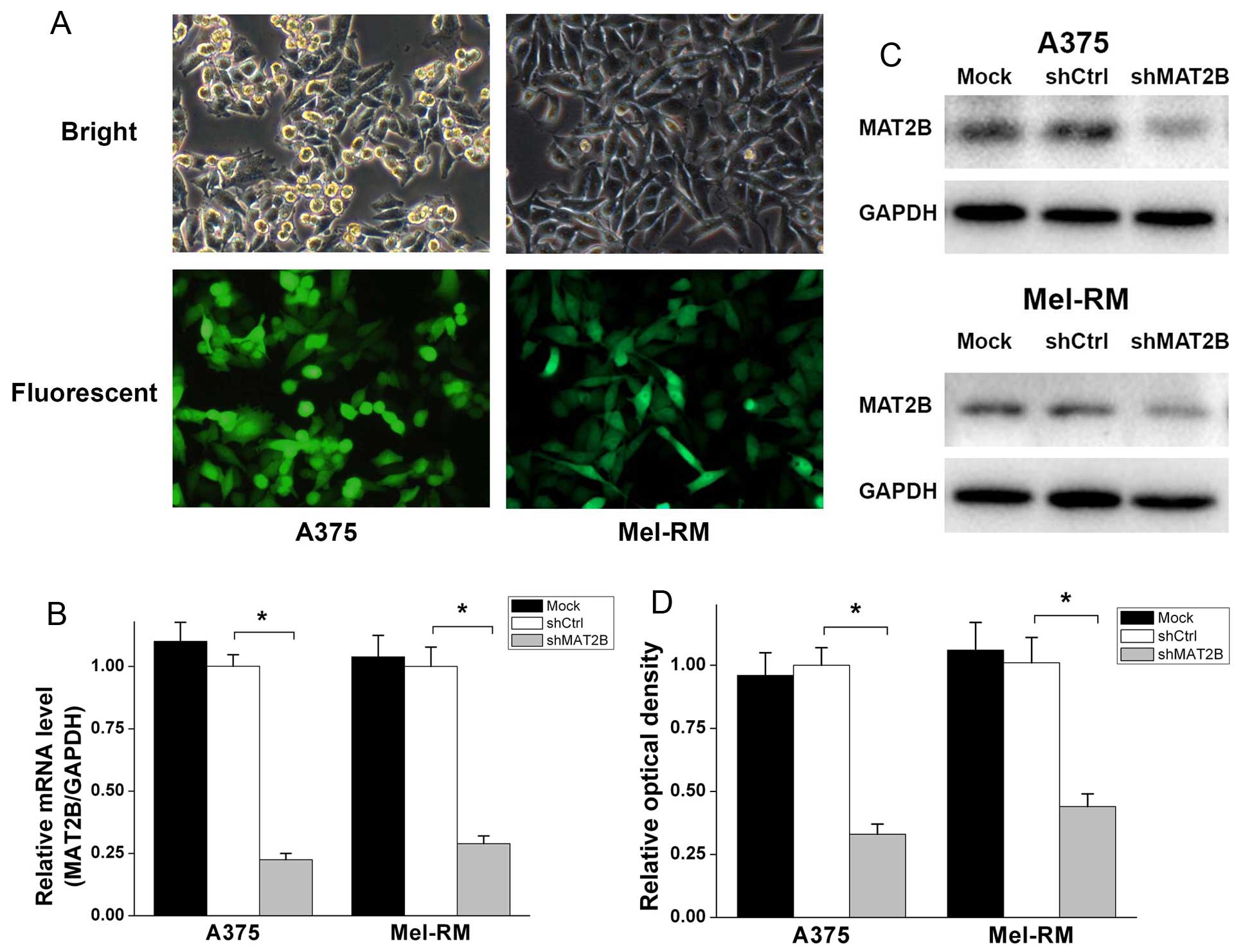
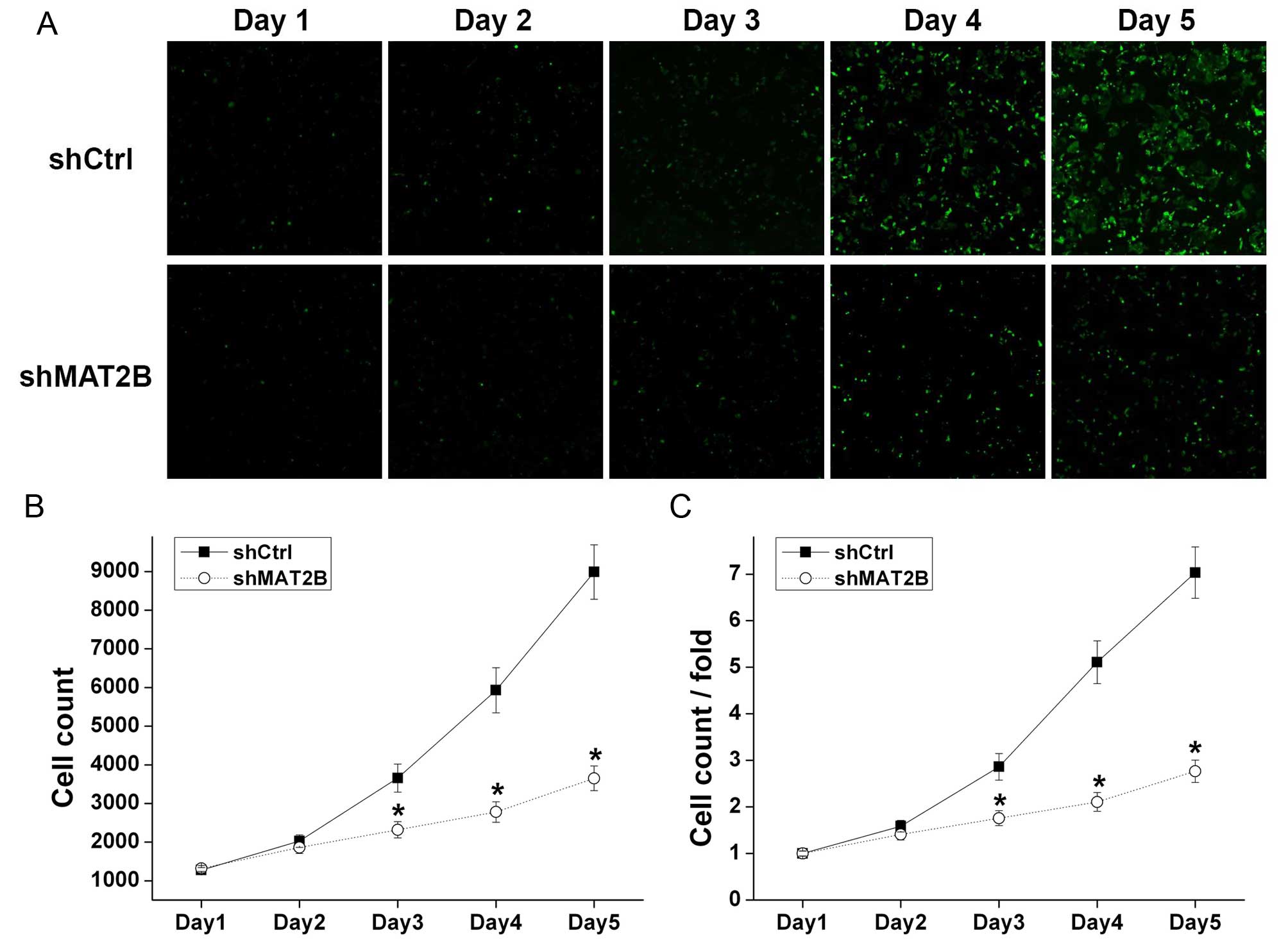
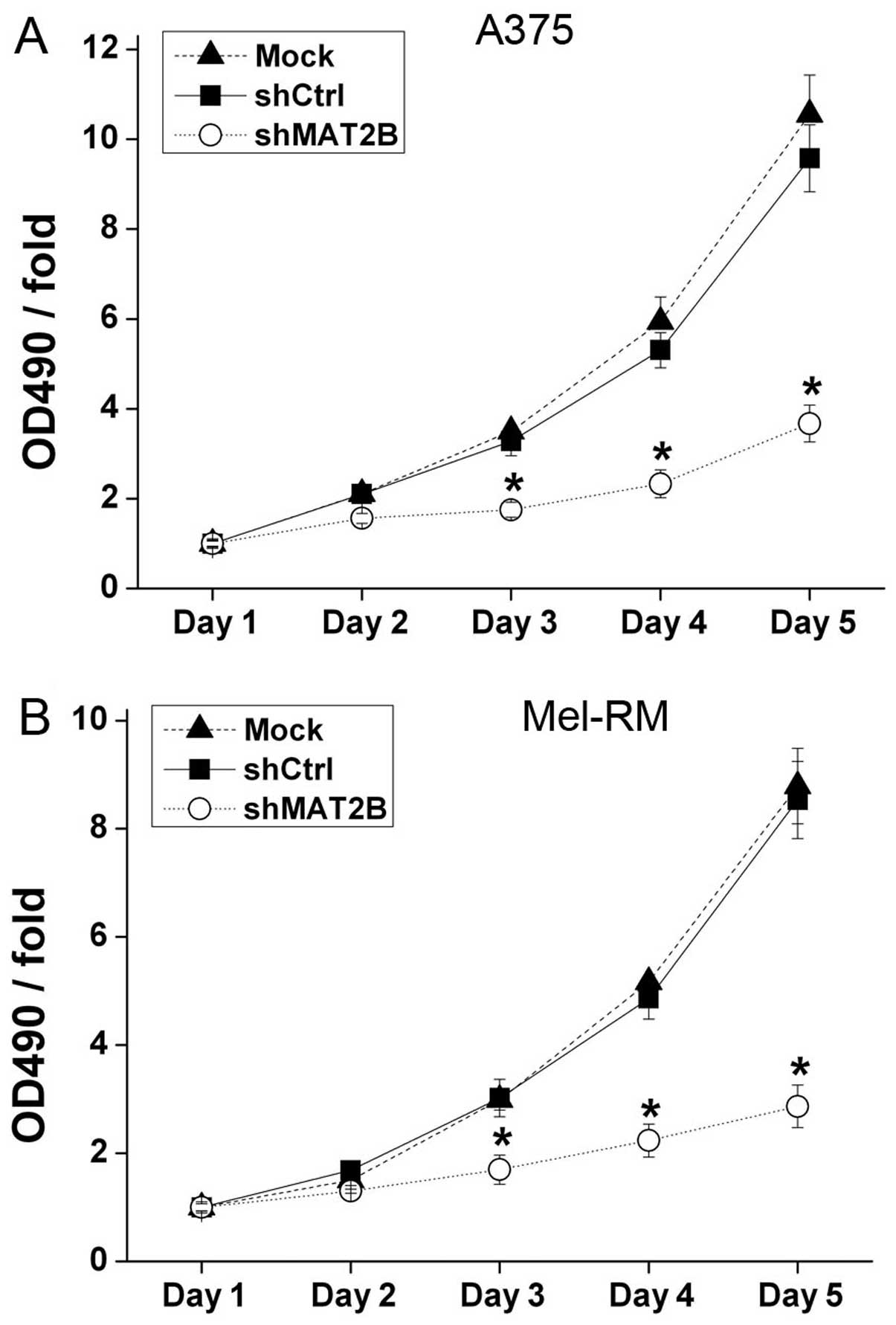
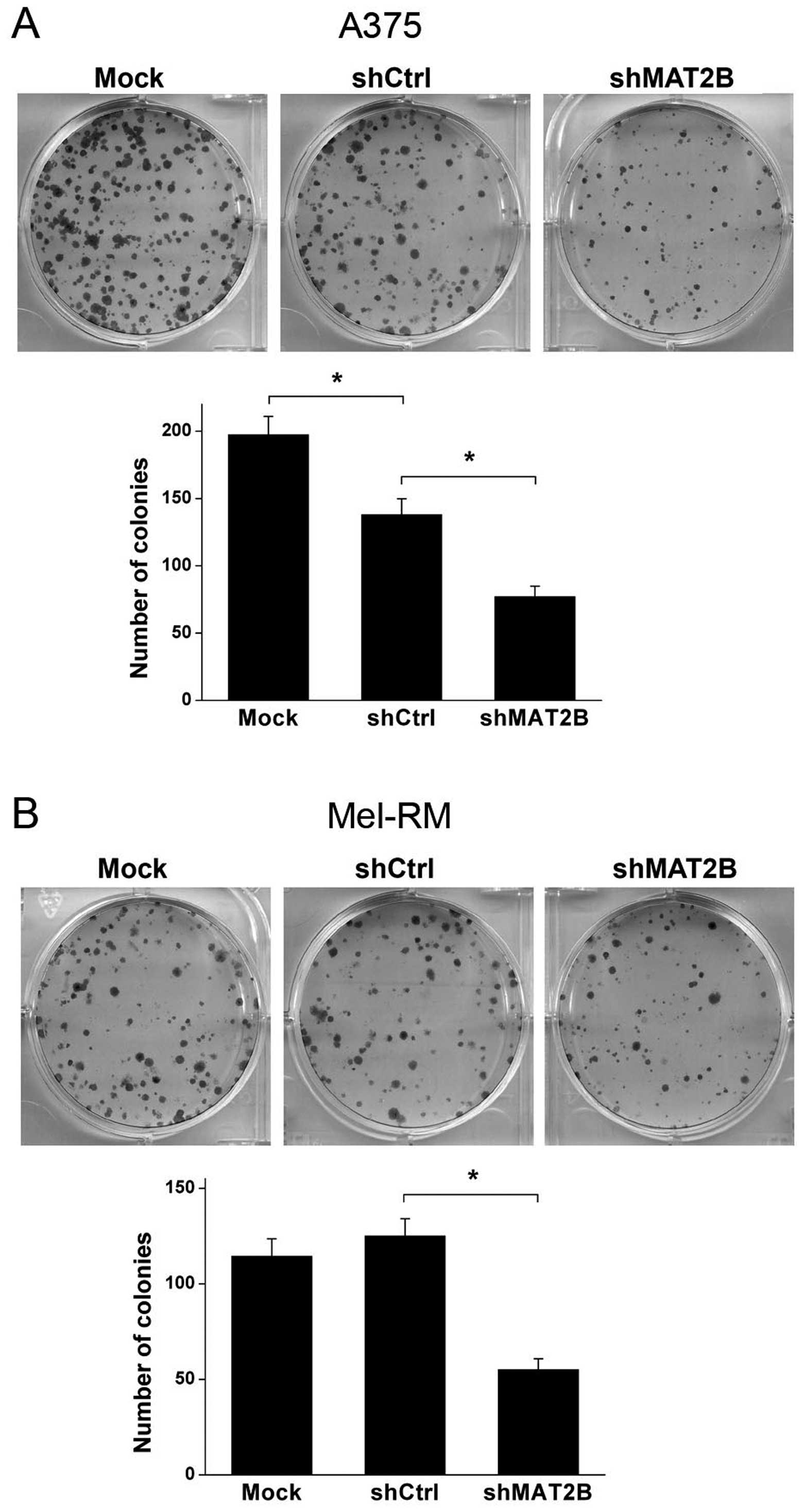
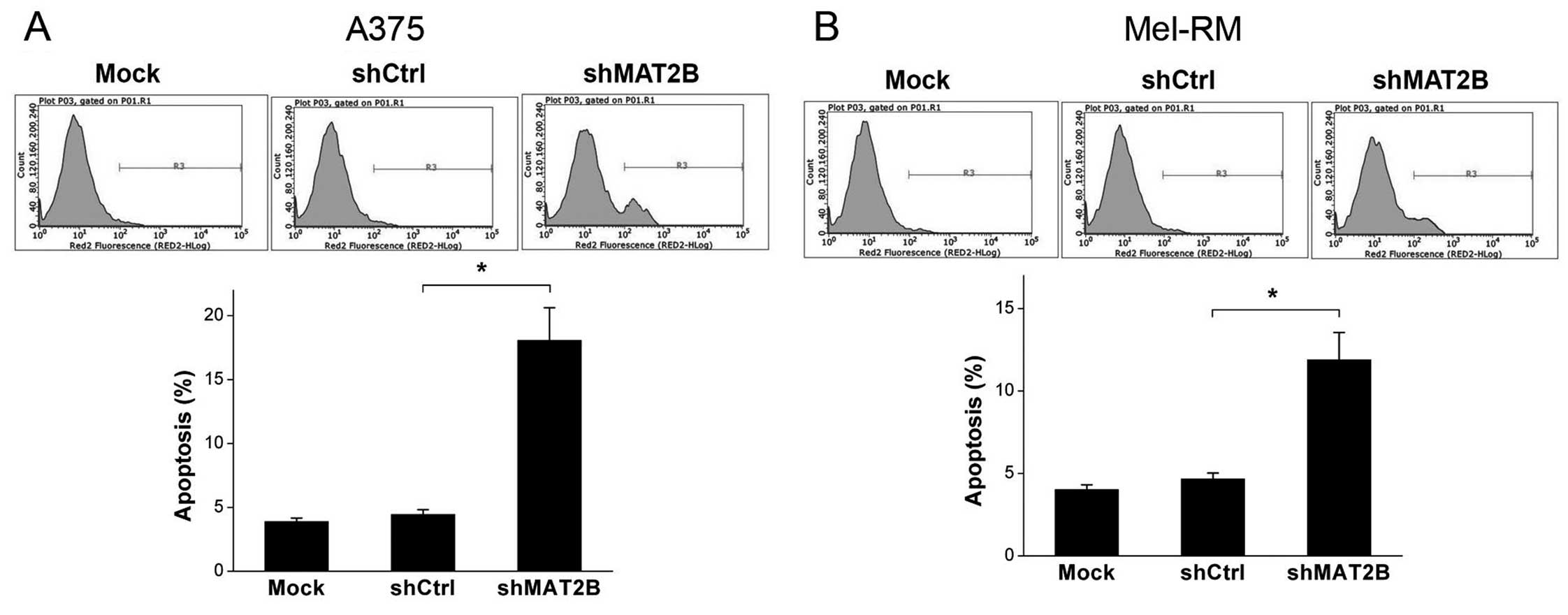
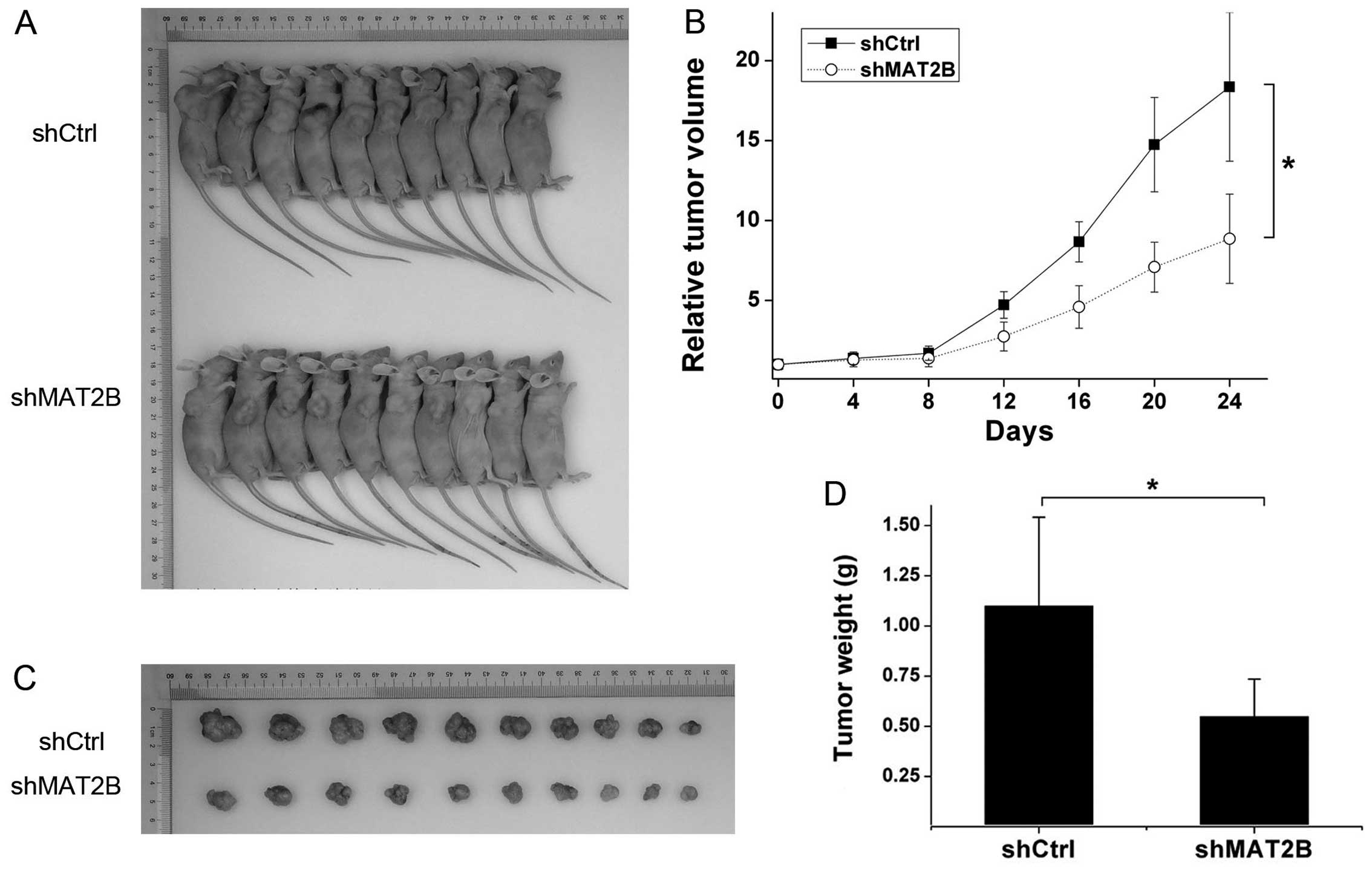
|
1
|
Lu SC and Mato JM: S-adenosylmethionine in
liver health, injury, and cancer. Physiol Rev. 92:1515–1542. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Halim AB, LeGros L, Geller A and Kotb M:
Expression and functional interaction of the catalytic and
regulatory subunits of human methionine adenosyltransferase in
mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 274:29720–29725. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
LeGros HL Jr, Halim AB, Geller AM and Kotb
M: Cloning, expression, and functional characterization of the β
regulatory subunit of human methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT
II). J Biol Chem. 275:2359–2366. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
LeGros L, Halim AB, Chamberlin ME, Geller
A and Kotb M: Regulation of the human MAT2B gene encoding the
regulatory beta subunit of methionine adenosyltransferase, MAT II.
J Biol Chem. 276:24918–24924. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang H, Ara AI, Magilnick N, Xia M, Ramani
K, Chen H, Lee TD, Mato JM and Lu SC: Expression pattern,
regulation, and functions of methionine adenosyltransferase 2beta
splicing variants in hepatoma cells. Gastroenterology. 134:281–291.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Q, Liu QY, Liu ZS, Qian Q, Sun Q and
Pan DY: Lentivirus mediated shRNA interference targeting MAT2B
induces growth-inhibition and apoptosis in hepatocelluar carcinoma.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:4633–4642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peng H, Dara L, Li TW, Zheng Y, Yang H,
Tomasi ML, Tomasi I, Giordano P, Mato JM and Lu SC: MAT2B-GIT1
interplay activates MEK1/ERK 1 and 2 to induce growth in human
liver and colon cancer. Hepatology. 57:2299–2313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng H, Li TW, Yang H, Moyer MP, Mato JM
and Lu SC: Methionine adenosyltransferase 2B-GIT1 complex serves as
a scaffold to regulate Ras/Raf/MEK1/2 activity in human liver and
colon cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 185:1135–1144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xia M, Chen Y, Wang LC, Zandi E, Yang H,
Bemanian S, Martínez-Chantar ML, Mato JM and Lu SC: Novel function
and intracellular localization of methionine adenosyltransferase
2beta splicing variants. J Biol Chem. 285:20015–20021. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Russo A, Ficili B, Candido S, Pezzino FM,
Guarneri C, Biondi A, Travali S, McCubrey JA, Spandidos DA and
Libra M: Emerging targeted therapies for melanoma treatment
(Review). Int J Oncol. 45:516–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilmott JS, Menzies AM, Haydu LE, Capper
D, Preusser M, Zhang YE, Thompson JF, Kefford RF, von Deimling A,
Scolyer RA, et al: BRAF(V600E) protein expression and outcome from
BRAF inhibitor treatment in BRAF(V600E) metastatic melanoma. Br J
Cancer. 108:924–931. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez
R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS, McArthur GA, Hutson TE, Moschos SJ,
Flaherty KT, et al: Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma
treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med. 366:707–714. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ascierto PA, Minor D, Ribas A, Lebbe C,
O’Hagan A, Arya N, Guckert M, Schadendorf D, Kefford RF, Grob JJ,
et al: Phase II trial (BREAK-2) of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib
(GSK2118436) in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol.
31:3205–3211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Budwit-Novotny DA, McCarty KS, Cox EB,
Soper JT, Mutch DG, Creasman WT, Flowers JL and McCarty KS Jr:
Immunohistochemical analyses of estrogen receptor in endometrial
adenocarcinoma using a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res.
46:5419–5425. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Specht E, Kaemmerer D, Sänger J, Wirtz RM,
Schulz S and Lupp A: Comparison of immunoreactive score, HER2/neu
score and H score for the immunohistochemical evaluation of
somatostatin receptors in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine
neoplasms. Histopathology. 67:368–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lei Y, Li HX, Jin WS, Peng WR, Zhang CJ,
Bu LJ, Du YY, Ma T and Sun GP: The radiosensitizing effect of
Paeonol on lung adenocarcinoma by augmentation of radiation-induced
apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Radiat
Biol. 89:1079–1086. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rygaard K and Spang-Thomsen M:
Quantitation and gompertzian analysis of tumor growth. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 46:303–312. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kocab AJ and Duckett CS: Inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins as intracellular signaling intermediates. FEBS
J. 283:221–231. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM and
Baradaran B: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer
development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2129–2144.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mohammad RM, Muqbil I, Lowe L, Yedjou C,
Hsu HY, Lin LT, Siegelin MD, Fimognari C, Kumar NB, Dou QP, et al:
Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35(Suppl): S78–S103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hartman ML and Czyz M: Anti-apoptotic
proteins on guard of melanoma cell survival. Cancer Lett.
331:24–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moldoveanu T, Follis AV, Kriwacki RW and
Green DR: Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem Sci.
39:101–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hata AN, Engelman JA and Faber AC: The
BCL2 family: Key mediators of the apoptotic response to targeted
anticancer therapeutics. Cancer Discov. 5:475–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Silke J and Vucic D: IAP family of cell
death and signaling regulators. Methods Enzymol. 545:35–65. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S,
Miyazaki T, Conte D, Tamai K, Craig CG, McBurney MW and Korneluk
RG: Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-Caspase
activity. Nat Cell Biol. 3:128–133. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao WJ, Deng BY, Wang XM, Miao Y and Wang
JN: XIAP associated factor 1 (XAF1) represses expression of
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) and regulates
invasion, cell cycle, apoptosis, and cisplatin sensitivity of
ovarian carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2453–2458.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu LM, Shi DM, Dai Q, Cheng XJ, Yao WY,
Sun PH, Y, Qiao MM, Wu YL, Jiang SH, et al: Tumor suppressor XAF1
induces apoptosis, inhibits angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:5403–5415. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ju WC, Huang GB, Luo XY, Ren WH, Zheng DQ,
Chen PJ, Lou YF and Li B: X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis-associated factor l (XAFl) enhances the sensitivity of
colorectal cancer cells to cisplatin. Med Oncol. 31:2732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang J, Yao WY, Zhu Q, Tu SP, Yuan F,
Wang HF, Zhang YP and Yuan YZ: XAF1 as a prognostic biomarker and
therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:559–567.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ng KC, Campos EI, Martinka M and Li G:
XAF1 expression is significantly reduced in human melanoma. J
Invest Dermatol. 123:1127–1134. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|